Expression and Clinical Significance of miRNA-181d in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-
摘要:目的
探讨miR-181d在食管鳞状细胞癌组织中的表达,并分析其临床意义。
方法应用反转录实时荧光定量PCR(reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR, RT-qPCR)技术检测37例食管鳞状细胞癌癌组织及癌旁组织中miR-181d的表达,分析miR-181d表达与肿瘤临床病理特征的相关性。
结果miR-181d在89.2%(33/37)的食管鳞状细胞癌组织中表达水平显著高于对应癌旁组织(P < 0.01);miR-181d表达水平与性别、年龄、浸润深度、淋巴结转移、组织学分级、肿瘤部位均无明显相关性(P > 0.05),但与TNM分期显著相关(P < 0.05)。Kaplan-Meier生存分析显示,miR-181d高表达组总生存率和无病生存率明显低于低表达组(P < 0.05)。
结论miR-181d在食管鳞状细胞癌组织中的表达与肿瘤的TNM分期及预后相关,miR-181d可能作为潜在预测指标评估食管鳞状细胞癌患者的预后。
-
关键词:
- 食管鳞状细胞癌 /
- 微小RNA-181d /
- 预后
Abstract:ObjectiveTo observe the expression of microRNA(miRNA, miR)-181d in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) tissues and to explore its clinical significance.
MethodsReverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR(RT-qPCR) was used to detect the miR-181d expression in 37 cases of ESCC tissues and matched adjacent tissues. The correlations of miR-181d expression with clinicpathological features and clinical prognosis were analyzed.
ResultsmiR-181d expression was up-regulated in 89.2%(33/37) of ESCC tissues, compared with the matched adjacent tissues (P < 0.01). The expression level of miR-181d was not significantly correlated with gender, age, depth of invasion, lymph node metastasis, histological grade or tumor location(P > 0.05), but significantly related to TNM staging (P < 0.05). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that the overall survival rate and the disease-free survival rate of the high miR-181d expression group was significantly lower than that of the low miR-181d expression group (P < 0.05).
ConclusionmiR-181d expression is related to TNM and prognosis of ESCC patients. miR-181d may be used as a potential predictor to evaluate the prognosis of ESCC patients.
-
Key words:
- Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma /
- miR-181d /
- Prognosis
-
0 引言
我国是全球食管癌高发地区,据估计,2013年全国食管癌新发病例数为27.7万例,死亡病例数约20.6万例[1]。食管癌分为鳞癌和腺癌两种亚型,亚洲90%的食管癌为食管鳞状细胞癌(esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, ESCC)。食管癌的病因和发生机制目前尚不完全清楚,虽然近年来在食管癌的诊治方面取得了一定的进展,但5年生存率仅有25%~30%[2]。深入研究ESCC发生、发展机制对食管癌的早期诊治和提高患者生存期具有重要的意义。微小RNA最早发现于1993年[3],是一类长度为21~22个核苷酸内源性的非编码小分子RNA,通过与靶基因mRNA的3’端非编码区互补结合来调节其转录或降解,从而影响细胞增殖、凋亡、侵袭等生物学行为[4]。越来越多的研究表明miRNAs在多种肿瘤的发生、发展及预后中发挥重要作用[5~6]。miR-181d位于19号染色体,是一个重要的基因表达调控因子[7]。近年来研究表明,miR-181d的异常表达与多种肿瘤的发生、发展及预后密切相关[8-10]。但是miR-181d在ESCC中的表达与预后的关系目前报道甚少。因此本研究通过检测miR-181d在ESCC及其相应癌旁组织中的表达,并进一步分析其与临床病理特征和预后的相关性,为寻找ESCC早期诊断和预后的生物标志物提供依据。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
收集2011年8月—2013年4月在河南省肿瘤医院行手术切除并经病理确诊为ESCC组织及相应癌旁组织标本37例,组织标本离体后立即放入液氮保存。患者的临床、预后资料主要通过病历回顾和电话随访获得。末次随访时间为2016年8月。术后分期采用国际抗癌联盟(Union for International Cancer Control, UICC)第7版食管癌分期标准[11-12];组织学分级采用WHO病理分级标准[13],1级为高度分化,2级为中度分化,3级为低度分化。本研究通过郑州大学附属郑州中心医院医学研究伦理委员会的批准,所有研究对象均签署知情同意书。
1.2 试剂与仪器
TRIzol试剂购自美国Invitrogen公司,RNA反转录试剂盒、U6snRNA,实时荧光定量试剂盒均购自上海吉玛生物科技有限公司。无酶枪头、PCR管和EP管购自美国Axygen公司;其余试剂均为国产分析纯。NanoDrop微量核酸蛋白分析仪购自美国Thermo Fisher公司,7500fast实时荧光定量PCR仪购自美国Applied Biosystems公司。
1.3 实验方法
根据说明书应用TRIzol试剂(Invitrogen, 美国)提取癌组织及癌旁组织总RNA,NanoDrop微量核酸蛋白分析仪(Thermo Scientific)检测RNA浓度及纯度。根据“Hairpin-itTM microRNA和U6 snRNA Normalization RT-PCR Quantitation Kit(Gene Pharma)”试剂盒说明书分别配制20 μl反应体系进行反转录实时荧光定量PCR反应。PCR扩增反应程序:预变性95℃ 3 min,PCR反应95℃ 12 s,62℃ 40 s,40个循环,设定统一的阈值,以PCR反应管内荧光信号到达设定阈值时经历的循环数(cycle threshold, Ct)分析结果,并取3次结果的平均值。以U6 snRNA管家基因作为内参,采用1号样本癌旁组织的平均Ct值作为标准对照,应用2-ΔΔCt方法计算样本中miR-181d的相对表达水平。以ESCC组织中miR-181d表达量的中位数为分界点将其分为低表达组和高表达组[14]。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS19.0软件进行统计学分析,miR-181d在癌组织和癌旁组织中的表达水平差异分析采用Wilcoxon检验;Fisher精确检验分析肿瘤组织中miR-181d的表达水平与临床病理特征的关系;利用Kaplan-Meier生存曲线法及Log rank检验分析无病生存时间(disease-free survival, DFS)和总生存时间(overall survival, OS)。P值为双向性检验,检验水准α=0.05, P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 miR-181d在ESCC组织中的表达水平
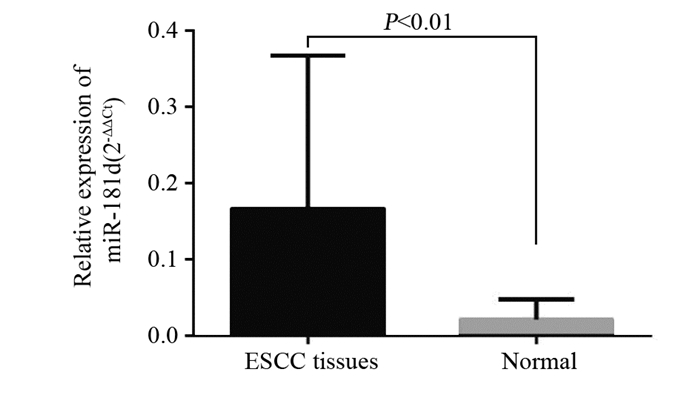
RT-qPCR检测结果显示,与相应癌旁组织相比,miR-181d在89.2%(33/37)癌组织中相对高表达,且miR-181d在癌组织中的表达水平显著高于癌旁组织中的表达水平,差异有统计学意义(P=0.000),见图 1。
2.2 miR-181d的表达与ESCC临床病理特征的关系
以ESCC组织中miR-181d表达量的中位数为分界点将其分为低表达组和高表达组,分析两组与临床病理特征间的关系。结果表明,miR-181d表达水平与性别、年龄、病理分级、淋巴结转移,组织学分级,肿瘤部位均无明显相关性(P > 0.05),但与TNM分期相关(P < 0.05),见表 1。
表 1 食管癌组织中miR-181d的表达与临床病理特征的关系Table 1 Correlation between miR-181d expression and clinicopathological features of ESCC patients
2.3 miR-181d的表达与预后的关系
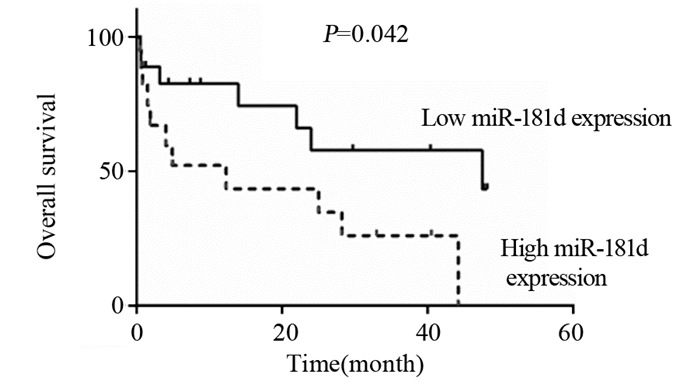
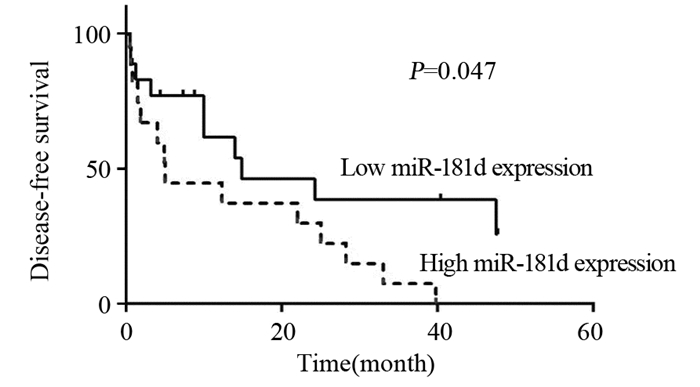
利用Kaplan-Meier法绘制生存曲线以及Log rank检验比较miR-181d高表达和低表达两组之间生存率的差异。结果显示:与miR-181d低表达组比较,miR-181d高表达组患者的中位OS和中位DFS均显著缩短(χ2=4.15, P=0.042; χ2 =3.94, P=0.047),见图 2~3。
3 讨论
miRNAs是一类进化保守、长约22个核苷酸的内源性非编码小RNA。它既可以作为癌基因,又可以作为抑癌基因,参与肿瘤的形成与演进,是肿瘤潜在的诊断和预后标志物及治疗靶点。食管癌是一种多因素作用,多基因参与,多阶段发展的复杂性疾病,其发生发展的分子机制仍未阐明。研究表明,miRNAs与ESCC的发生发展密切相关,如miR-375在ESCC中表达下调,且与远处转移和较低的总体生存率密切相关[15]。miR-508在ESCC中表达显著上调,是ESCC患者独立的预后因素[16]。
miR-181d是miR-181家族成员,在肿瘤发生发展中发挥重要的调控作用[17]。miR-181d在不同的肿瘤中表达情况不尽相同,在一些肿瘤中高表达发挥致癌作用,而在另一些肿瘤中却低表达发挥抑癌作用。这可能与肿瘤形成过程中一种miRNA可以调控多个靶基因,一个靶基因又可以被多种miRNA所调控,多条信号通路交错形成复杂的信息网络有关[18]。Guo等[19]发现miR-181d在结直肠癌组织中表达上调,敲低miR-181d通过影响糖酵解抑制结直肠癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭;miR-181d通过直接靶向CRY2和FBXL3发挥癌基因的作用。与之相反,Huang等[8]发现181d在结直肠癌中低表达,且与患者较短的生存期相关;过表达miR-181d抑制结直肠癌细胞的生长和迁移;miR-181d通过靶向PEAK1发挥抑癌作用。Wang等[9]发现miR-181d在胶质瘤表达下调,可能通过靶向K-ras和Bcl-2发挥抑癌基因的作用且miR-181d的抑制肿瘤活性与K-ras相关的PI3K/AKT和MAPK/ERK途径有关。Zhang等[10]发现miR-181d在胰腺癌细胞系及组织中均高表达;下调miR-181d的表达抑制胰腺癌细胞增殖、迁移和氟尿嘧啶抗性,并且抑制裸鼠移植瘤的生长;miR-181d通过靶向调节NKAIN2抑制胰腺癌的进展。Zhang[20]和Khalil[21]等发现miR-181d的表达水平与胶质瘤患者总生存期呈负相关,且通过靶向MGMT发挥作用。Li等[22]检测了16例ESCC患者癌组织及对应癌旁组织中miR-181d的表达,显示其在ESCC组织中的表达水平均显著低于癌旁组织(P < 0.05),且在ESCC进展中,miR-181d的分子机制可能是通过对癌基因DERL1的反向调控而起作用的。以上研究表明miR-181d在肿瘤发生发展中发挥重要的作用,且在不同肿瘤中的表达模式可能与其作用机制有关。
miR-181d在ESCC组织中的表达及临床意义报道甚少,为了明确miR-181d在ESCC中的作用,我们检测了miR-181d在37对ESCC组织及癌旁组织中的表达情况。结果显示miR-181d在89.2%(33/37)癌组织中相对高表达(P < 0.01);这与Li等[22]报道的并不一致,分析原因可能如下:(1)两项研究中人群分布地域不一样,遗传背景有差异;(2)Li等检测的16对组织未显示临床病理资料,可能和本研究中的标本临床分期和术前治疗情况不同从而导致miR-181d在ESCC中的表达存在差异;(3)Li等发现在ESCC进展中,miR-181d通过靶向DERL1发挥作用,这可能和本研究中的作用机制不一致,从而导致其表达模式也不一样。
我们进一步分析ESCC患者miR-181d的相对表达水平与临床病理特征之间的关系,发现miR-181d的表达水平与性别、年龄、肿瘤浸润深度、淋巴结转移、组织学分级、肿瘤部位均无明显相关性(P > 0.05),但与TNM分期相关(P < 0.05),即TNM分期为Ⅲ期的ESCC组织中miR-181d的表达量相对于TNM分期为Ⅰ~Ⅱ期显著升高,说明miR-181d的表达上调可能促进了ESCC的进展;miR-181d的表达与组织学分级不相关,推测miR-181d的表达可能并不影响ESCC的分化;本研究并未证实miR-181d的表达与浸润深度、淋巴结转移等因素之间的关系,分析可能与样本量小及miR-181d不同表达水平的患者其临床病理因素分布不均衡有关。Kaplan-Meier生存分析结果显示,与miR-181d低表达组相比,miR-181d高表达组患者的总生存期和无病生存期显著缩短(P < 0.05)。
综上所述,miR-181d在ESCC组织中表达上调,且其表达与肿瘤临床分期及预后相关,这些结果表明miR-181d可能在食管癌的发展过程中起重要作用,可能成为食管癌早期诊断和预后的生物标志物。
-
表 1 食管癌组织中miR-181d的表达与临床病理特征的关系
Table 1 Correlation between miR-181d expression and clinicopathological features of ESCC patients

-
[1] 贺宇彤, 李道娟, 梁迪, 等. 2013年中国食管癌发病和死亡估计[J].中华肿瘤杂志, 2017, 39(4): 315-20. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2017.04.016 He YT, Li DJ, Liang D, et al. Estimated of esophageal cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2013[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2017, 39(4): 315-20. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2017.04.016
[2] Takeshita N, Hoshino I, Mori M, et al. Serum microRNA expression profile: miR-1246 as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Br J Cancer, 2013, 108(3): 644-52. http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC3593570/
[3] Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C.elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14[J]. Cell, 1993, 75(5): 843-54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90529-Y
[4] Shen J, Stass SA, Jiang F. MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers in human solid tumors[J]. Cancer Lett, 2013, 329(2): 125-36. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.11.001
[5] 王玉霞, 王芳, 崔华胜, 等. miR-205对胃癌细胞侵袭迁移的调控作用及其潜在机制[J].肿瘤防治研究, 2018, 45(5): 280-4. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2018.17.1217 Wang YX, Wang F, Cui HS, et al. Regulatory Effects of miR-205 on Invasion and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells and Potential Mechanism[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2018, 45(5): 280-4. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2018.17.1217
[6] 张伟, 赵学辉, 阮腊林, 等. miRNA-130b在骨肉瘤组织中的表达及其对骨肉瘤细胞增殖与凋亡的影响[J].肿瘤防治研究, 2017, 44(5): 334-9. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2017.05.005 Zhang W, Zhao XH, Ruan LL, et al. Expression of miRNA-130b in osteosarcoma tissues and its impact on proliferation and apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2017, 44(5): 334-9. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2017.05.005
[7] Song MK, Park YK, Ryu JC. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-mediated upregulation of hepatic microRNA-181 family promotes cancer cell migration by targeting MAPK phosphatase-5, regulating the activation of p38 MAPK[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2013, 273(1): 130-9. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.08.016
[8] Huang L, Wen C, Yang X, et al. PEAK1, acting as a tumor promoter in colorectal cancer, is regulated by the EGFR/KRas signaling axis and miR-181d[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(3): 271. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0320-8
[9] Wang XF, Shi ZM, Wang XR, et al. MiR-181d acts as a tumor suppressor in glioma by targeting K-ras and Bcl-2[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2012, 138(4): 573-84. doi: 10.1007/s00432-011-1114-x
[10] Zhang G, Liu D, Long G, et al. Downregulation of microRNA-181d had suppressive effect on pancreatic cancer development through inverse regulation of KNAIN2[J]. Tumour Biol, 2017, 39(4): 010428317698364. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28381166
[11] 陈龙奇.食管癌国际TNM分期第7版解读与评价[J].中华肿瘤杂志, 2010, 32(3): 237-40. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhzl201003018 Chen LQ. Understanding and appraisal of the new TNM classification for esophageal cancer in the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual (7th edition)[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2010, 32(3): 237-40. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhzl201003018
[12] Edge S, Byrd DR, Compton CC, et al. AJCC cancer staging manual[M]. NewYork: Springer-verlag, 2009: 103-15.
[13] Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, et al. World Health Organization classification of tumours of the digestive system[M]. Lyon: IARC Press, 2010: 16-24.
[14] Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F, et al. MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis[J]. JAMA, 2007, 297(17): 1901-8. doi: 10.1001/jama.297.17.1901
[15] Kong KL, Kwong DL, Chan TH, et al. MicroRNA-375 inhibits tumour growth and metastasis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma through repressing insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor[J]. Gut, 2012, 61(1): 33-42. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300178
[16] Lin C, Liu A, Zhu J, et al. miR-508 sustains phosphoinositide signalling and promotes aggressive phenotype of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Nat Commun, 2014, 5: 4620. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5620
[17] Li R, Li X, Ning S, et al. Identification of a core miRNA-pathway regulatory network in glioma by therapeutically targeting miR-181d, miR-21, miR-23b, β-Catenin, CBP, and STAT3[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(7): e101903. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101903
[18] Gyugos M, Lendvai G, Kenessey I, et al. MicroRNA expression might predict prognosis of epithelial hepatoblastoma[J]. Virchows Arch, 2014, 464(4): 419-27. doi: 10.1007/s00428-014-1549-y
[19] Guo X, Zhu Y, Hong X, et al. miR-181d and c-myc-mediated inhibition of CRY2 and FBXL3 reprograms metabolism in colorectal cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2017, 8(7): e2958. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.300
[20] Zhang W, Zhang J, Hoadley K, et al. miR-181d: a predictive glioblastoma biomarker that downregulates MGMT expression[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2012, 14(6): 712-9. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nos089
[21] Khalil S, Fabbri E, Santangelo A, et al. miRNA array screening reveals cooperative MGMT-regulation between miR-181d-5p and miR-409-3p in glioblastoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(19): 28195-206. http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC5053720/
[22] Li D, Shi M, Ji H, et al. MicroRNA-181d is a tumor suppressor in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma inversely regulating Derlin-1[J]. Oncol Rep, 2016, 36(4): 2041-8. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5028



 下载:
下载: