Relationship of Methylation Status and mRNA Expression of PTEN, RASSF1A in Peripheral Blood with Thyroid Nodule Disease
-
摘要:目的
探讨PTEN、RASSF1A基因启动子甲基化及其mRNA表达与结节性甲状腺疾病之间的关系。
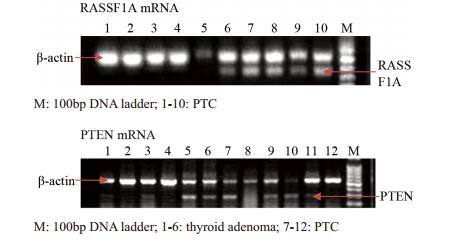
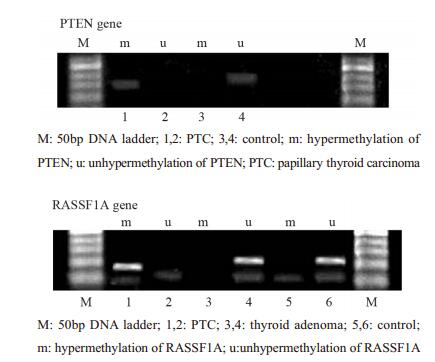
方法选取46例结节性甲状腺肿、34例甲状腺腺瘤、24例甲状腺乳头状癌患者(甲癌)和30例健康体检者,利用甲基化特异性PCR检测外周血中PTEN、RASSF1A基因启动子区甲基化状态及利用反转录—多聚酶链反应法(RT-PCR)检测mRNA表达情况。
结果(1)腺瘤组和甲癌组中PTEN、RASSF1A甲基化率分别与对照组比较, 差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。(2)腺瘤组和甲癌组中PTEN、RASSF1A基因mRNA表达阳性率分别与对照组比较, 差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。(3)甲癌组中PTEN和RASSF1A基因甲基化率、mRNA表达与淋巴结转移有关(均P < 0.05),与年龄、性别、结节大小无关。
结论甲状腺肿瘤外周血中存在抑癌基因PTEN、RASSF1A高甲基化改变进而导致其功能失活,从而在甲状腺肿瘤的发生发展过程中发挥重要作用。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo observe the methylation status and mRNA expression of PTEN, RASSF1A in the peripheral blood of thyroid nodule patients and to explore the relationship between these genes and the clinical characteristics.
MethodsMethylation-specific PCR(MSP) was used to detect the hypermethylation status of PTEN, RASSF1A promoter in the peripheral blood from 46 cases of nodular goiter, 34 cases of thyroid adenoma, 24 cases of papillary thyroid carcinoma(PTC) and 30 healthy controls. The mRNA expression of PTEN and RASSF1A was tested by reverse-transcription polymerse chain reaction.
Results(1) The methylation rates of PTEN, RASSF1A between thyroid adenoma, PTC and normal controls had significant difference (P < 0.05). (2) The positive mRNA expression rates of PTEN and RASSF1A between thyroid adenoma, PTC and normal control had significant difference (P < 0.05). (3)The methylation status, mRNA expression of PTEN and RASSF1A in PTC were correlated with lymph node metastasis (P < 0.05), and were not correlated with age, gender, size of nodule.
ConclusionThe hypermethylation, and hence functional inactivation of tumor suppressor genes PTEN, RASSF1A are common in peripheral blood of thyroid tumors, which play an important role during the occurrence and development of thyroid tumors.
-
Key words:
- PTEN /
- RASSF1A /
- Thyroid nodule /
- Methylation specific PCR /
- RT-PCR /
- Peripheral blood
-
-
表 1 本研究PCR所用引物序列、片段大小
Table 1 Primer sequence, fragment size in PCR

表 2 PTEN、RASSF1A基因启动子区甲基化与mRNA表达关系
Table 2 Relationship between PTEN, RASSF1A gene promoter methylation and mRNA expression

表 3 甲状腺癌患者外周血中PTEN与RASSF1A基因启动子甲基化与临床指标的关系
Table 3 Relationship between PTEN, RASSF1A gene promoter methylation in peripheral blood of thyroid cancer and clinical indicators

表 4 甲状腺癌患者外周血PTEN、RASSF1A基因mRNA的表达及与临床指标关系
Table 4 Relationship between mRNA expression of PTEN, RASSF1A in peripheral blood of thyroid cancer and clinical indicators

-
[1] Stsrk LA. Epigentics online: multimedia teaching resources[J]. CBE Life Sci Educ, 2010, 9(1): 6-9.
[1] Stsrk LA. Epigentics online: multimedia teaching resources[J]. CBE Life Sci Educ, 2010, 9(1): 6-9. [2] Sharma S, Kelly TK, Jones PA. Epigenetics in cancer[J].Carcinogenesis, 2010, 31(1): 27-36.
[2] Sharma S, Kelly TK, Jones PA. Epigenetics in cancer[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2010, 31(1): 27-36. [3] Song XY, Shang XL, Zhang YT. DNA Methylation in Thyroid Carcinoma[J]. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2015, 29(6): 573-6. [宋现运, 尚小领, 张玉妥. DNA甲基化 在甲状腺肿瘤中的研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 20 15, 29(6): 573-6.] [3] 宋现运, 尚小领, 张玉妥. DNA甲基化在甲状腺肿瘤中的研究进展[J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015, 29(6): 573-6. Song XY, Shang XL, Zhang YT. DNA Methylation in Thyroid Carcinoma[J]. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2015, 29(6): 573-6.
[4] Goel A, Arnold CN, Niedzwiecki D, et al. Frequent inactivation of PTEN by promoter hypermethylation in microsatellite instability- High Sporadic Colorectal Cancers[J]. Cancer Res, 2004, 64(9): 30 14-21. [4] Goel A, Arnold CN, Niedzwiecki D, et al. Frequent inactivation of PTEN by promoter hypermethylation in microsatellite instability-High Sporadic Colorectal Cancers[J]. Cancer Res, 2004, 64(9): 3014-21.
[5] Schagdarsurengin U, Gimm O, Hoang-Vu C, et al. Frequent epigenetic silencing of the CpG island promoter of RASSF1A in thyroid carcinoma[J]. Cancer Res, 2002, 62(13): 3698-701.
[5] Schagdarsurengin U, Gimm O, Hoang-Vu C, et al. Frequent epigenetic silencing of the CpG island promoter of RASSF1A in thyroid carcinoma[J]. Cancer Res, 2002, 62(13): 3698-701. [6] Tell G, Pines A, Arturi F, et al. Control of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) gene expression in normal and thyroid cells[J]. Endocrinology, 2004, 145(10): 4660-6.
[6] Tell G, Pines A, Arturi F, et al. Control of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) gene expression in normal and thyroid cells[J]. Endocrinology, 2004, 145(10): 4660-6. [7] Ho DH, Burggren WW. Epigenetics and transgenerational transfer: a physiological perspective[J]. J Exp Biol, 2010, 213(1): 3-16.
[7] Ho DH, Burggren WW. Epigenetics and transgenerational transfer: a physiological perspective[J]. J Exp Biol, 2010, 213(1): 3-16. [8] Aleqria-Toms JA, Baccarelli A, Bollati V. Epigenetics and lifestyle[J]. Epigenetics, 2011, 3(3): 267-77.
[8] Aleqria-Toms JA, Baccarelli A, Bollati V. Epigenetics and lifestyle[J]. Epigenetics, 2011, 3(3): 267-77. [9] 廖萍, 刘茶珍, 罗全勇, 等.甲状腺癌患者血DNA甲基化分子标志物[J].环境与职业医学, 2012, 29(2): 77-82. Liao P, Liu CZ, Luo QY, et al. Blood DNA Methylation Markers for Thyroid Cancer[J]. Huan Jing Yu Zhi Ye Yi Xue, 2012, 29(2): 77-82.
[9] Liao P, Liu CZ, Luo QY, et al. Blood DNA Methylation Markers for Thyroid Cancer[J]. Huan Jing Yu Zhi Ye Yi Xue, 2012, 29(2): 77 -82. [廖萍, 刘茶珍, 罗全勇, 等. 甲状腺癌患者血DNA甲基化 分子标志物[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2012, 29(2): 77-82.] [10] Zeng ZP. Carry out Epigenetic research in endocrine and metabolic disease and adrenal tumors[J]. Zhonghua Nei Fen Mi Dai Xie Za Zhi, 2010, 26(8): 629-32. [曾正陪. 开展内分泌代谢疾病及肾 上腺肿瘤的表观遗传学研究[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2010, 26 (8): 629-32.] [10] 曾正陪.开展内分泌代谢疾病及肾上腺肿瘤的表观遗传学研究[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2010, 26(8): 629-32. Zeng ZP. Carry out Epigenetic research in endocrine and metabolic disease and adrenal tumors[J]. Zhonghua Nei Fen Mi Dai Xie Za Zhi, 2010, 26(8): 629-32.
[11] Alvarez-Nuñez F, Bussaglia E, Mauricio D, et al. PTEN promoter methylation in sporadic thyroid carcinomas[J]. Thyroid, 2006, 16 (1): 17-23. [11] Alvarez-Nuñez F, Bussaglia E, Mauricio D, et al. PTEN promoter methylation in sporadic thyroid carcinomas[J]. Thyroid, 2006, 16(1): 17-23.
[12] Yin DT, Yin FY, Zheng LY, et al. Promoter rmethylation and Protein Expression of the PTEN Gene in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and their correlation[J]. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2010, 45(4): 330-3. [殷德涛, 尹峰燕, 郑立运, 等. 甲状腺乳头状癌中PTEN基因启动子甲基化及其蛋白表达 的相关性[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2010, 45(4): 330-3.] [12] 殷德涛, 尹峰燕, 郑立运, 等.甲状腺乳头状癌中PTEN基因启动子甲基化及其蛋白表达的相关性[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2010, 45(4): 330-3. Yin DT, Yin FY, Zheng LY, et al. Promoter rmethylation and Protein Expression of the PTEN Gene in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and their correlation[J]. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2010, 45(4): 330-3.
[13] Xing M. Gene Methylation in thyroid tumorigenesis[J]. Endocrinology, 2007, 148(3): 948-53. [13] Xing M. Gene Methylation in thyroid tumorigenesis[J]. Endocrinology, 2007, 148(3): 948-53.
[14] Hou P, Ji M, Xing M. Association of PTEN Gene Methylation With Genetic Alterations in the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/ AKT Signaling Pathway in Thyroid Tumors[J]. Cancer, 2008, 11 3(9): 2440-7. [14] Hou P, Ji M, Xing M. Association of PTEN Gene Methylation With Genetic Alterations in the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/AKT Signaling Pathway in Thyroid Tumors[J]. Cancer, 2008, 113(9): 2440-7.
[15] 钱光煜, 梁勇, 杨林军, 等. PTEN异常表达及甲基化与PTC的关系[J].医学研究杂志, 2011, 40(3): 39-43. Qian GY, Liang Y, Yang LJ, et al. Protein Expression and Promoter Methylation of the PTEN Gene in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma[J]. Yi Xue Yan Jiu Za Zhi, 2011, 40(3): 39-43.
[15] Qian GY, Liang Y, Yang LJ, et al. Protein Expression and Promoter Methylation of the PTEN Gene in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma[J]. Yi Xue Yan Jiu Za Zhi, 2011, 40(3): 39-43. [钱光煜, 梁勇, 杨林军, 等. PTEN 异常表达及甲基化与PTC的关系[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2011, 40(3): 39-43.] [16] Wang YL, Wang JC, Wu Y, et al. Incidentally simultaneous occurrence of RET/ PTC, H4-PT EN and BRAF mutation in papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. Cancer Lett, 2008, 263(1): 44-52 . [16] Wang YL, Wang JC, Wu Y, et al. Incidentally simultaneous occurrence of RET/ PTC, H4-PT EN and BRAF mutation in papillary thyroid carcinoma[J]. Cancer Lett, 2008, 263(1): 44-52.
[17] Bruni P, Boccia A, Baldassarre G, et al. PTEN expressionis reduced in a subset of sporadic thyroid carcinomas:evidence that PTEN growth suppressing activity in thyroid cancer cells mediated by p27kip1[J]. Oncogene, 2000, 19(28): 3146-55. [17] Bruni P, Boccia A, Baldassarre G, et al. PTEN expressionis reduced in a subset of sporadic thyroid carcinomas:evidence that PTEN growth suppressing activity in thyroid cancer cells mediated by p27kip1[J]. Oncogene, 2000, 19(28): 3146-55.
[18] Bi J, Gao MY, Wang YF. Promoter rmethylation of the Ras association domain family in carcinoma[J/CD]. Zhonghua Lin Chuang Yi Shi Za Zhi(Dian Zi Ban), 2012, 6(16): 4835-8. [毕婧, 高明阳, 王衍富. Ras相关区域家族基因启动子甲基化改变与肿 瘤发生相关性的研究进展[J/CD]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 20 12, 6(16): 4835-8. [18] 毕婧, 高明阳, 王衍富. Ras相关区域家族基因启动子甲基化改变与肿瘤发生相关性的研究进展[J/CD].中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2012, 6(16): 4835-8. Bi J, Gao MY, Wang YF. Promoter rmethylation of the Ras association domain family in carcinoma[J/CD]. Zhonghua Lin Chuang Yi Shi Za Zhi(Dian Zi Ban), 2012, 6(16): 4835-8.
[19] Xing M, Cohen Y, Mambo E, et al. Early occurrence of RASSF1A hypermethylation and its mutual exclusion with BRAF mutation in thyroid tumorigenesis[J]. Cancer Res, 2004, 64 (5): l664-8.
[19] Xing M, Cohen Y, Mambo E, et al. Early occurrence of RASSF1A hypermethylation and its mutual exclusion with BRAF mutation in thyroid tumorigenesis[J]. Cancer Res, 2004, 64 (5): l664-8. [20] Stutterneim J, Ichou FA, den Ouden E, et al. Methylated RASSF1A is the first specific DNA marker for minimal residual disease testing in neuroblastoma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2012, 18(3): 80 8-14. [20] Stutterneim J, Ichou FA, den Ouden E, et al. Methylated RASSF1A is the first specific DNA marker for minimal residual disease testing in neuroblastoma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2012, 18(3): 808-14.
[21] Sun JW, Xu XJ, Cai QM, et al. Epidemiological Study on Thyroid Cancer in China[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Liu, 2013, 22(9): 690-3. [孙 嘉伟, 许晓君, 蔡秋茂, 等. 中国甲状腺癌发病趋势分析[J]. 中国 肿瘤, 2013, 22(9): 690-3.] [21] 孙嘉伟, 许晓君, 蔡秋茂, 等.中国甲状腺癌发病趋势分析[J].中国肿瘤, 2013, 22(9): 690-3. Sun JW, Xu XJ, Cai QM, et al. Epidemiological Study on Thyroid Cancer in China[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Liu, 2013, 22(9): 690-3.
[22] Xing M, Haugen BR, Schlumberger M. Progress in molecular-based management of differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Lancet, 2013, 381(9871): 1058-69.
[22] Xing M, Haugen BR, Schlumberger M. Progress in molecularbased management of differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Lancet, 20 13, 381(9871): 1058-69.



 下载:
下载: