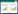文章信息
- 桂安萍,姚和瑞,凌飞海.
- GUI Anping, YAO Herui, LING Feihai.
- 三阴性乳腺癌细胞中上皮间质转化与EGFR单抗治疗效果的相关性
- Correlation Between Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition and Sensitivity to EGFR Targeted Monoclonal Antibody in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2016, 43(4): 249-252
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2016, 43(4): 249-252
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2016.04.002
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2015-10-30
- 修回日期: 2016-01-10
2. 528400 中山,中山市人民医院乳腺外科;
3.510120 广州,中山大学孙逸仙纪念医院肿瘤科
2. Department of Breast Surgery, People’s Hospital of Zhongshan City, Zhongshan 528400, China;
3. Department of Oncology, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510120, China Corresponding Author: YAO Herui, E-mail: yaoherui@163.com
表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)是表皮生长因子受体(ErbB)家族之一,通过与配体如EGF、TGFα等结合激活下游PI3K-Akt-mTOR及Ras-Raf-Mek-Erk信号通路,从而刺激细胞增殖、转移、黏附、侵袭,抑制肿瘤细胞凋亡以及促进间质血管生成。EGFR的靶向药物有作用于受体胞内区的小分子酪氨酸激酶抑制剂,例如吉非替尼、厄洛替尼;也有作用于受体胞外区的单克隆抗体,例如西妥昔单抗、帕尼单抗。目前,西妥昔单抗已成为转移性结直肠癌的一线治疗方案[1]。
三阴性乳腺癌是指缺乏ER、PR、HER2表达的乳腺癌亚群。ER、PR、HER2阴性,CK5/6及EGFR阳性的乳腺癌亚群代表基底细胞样癌[2]。三阴性乳腺癌因缺少特异性分子靶点,临床上治疗方案主要是全身系统性化疗。三阴性乳腺癌中EGFR过表达率为33%~50%,提示临床预后不良[3, 4]。然而,临床试验TBCTC 001指出西妥昔单抗单药治疗晚期TNBC的反应率仅为6%,西妥昔单抗作用下,肿瘤内EGFR信号通路活化的抑制率仅为27.8%[5]。西妥昔单抗单药耐药可能与EGFR持续循环至细胞表面而非受降解[6]以及PI3K-Akt等旁路信号通路异常活化有关[7]。
波形蛋白(vimentin),Sip1及zeb1等EMT标志物在TNBC中的发现率较高,基底细胞样乳腺癌中的发现率明显高于其他类型TNBC[8]。目前尚不明确EMT与西妥昔单抗耐药是否相关。本研究通过体外细胞学实验表明,高表达E钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)的上皮型TNBC细胞株MDA-MB468对西妥昔单抗的敏感度明显高于高表达vimentin的间质型TNBC细胞株MDA-MB231及MDA-MB436。另外,通过Ⅰ型组蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制剂ENT逆转MDA-MB231的间质化水平后,细胞对西妥昔单抗的敏感度明显增强。TNBC的EMT可能影响EGFR单克隆抗体西妥昔单抗的药敏性。
1 材料与方言 1.1 实验抗体及试剂小鼠抗EGFR单克隆抗体IgG2(528)购自Santa Cruz生物科技公司(Santa Cruz,CA)。小鼠抗β-actin单克隆抗体购自Sigma Aldrich公司(St. Louis,MO)。兔抗E-cadherin单克隆抗体购自CST公司(Danvers,MA),小鼠抗vimentin单克隆抗体购自Abcam公司(Cambridge,MA)。西妥昔单抗购于MERCK公司(德国)。CCK8购于同仁化学研究所(日本)。Ⅰ型组蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制剂ENT购自Sigma-Aldrich公司(St. Louis,MO)。
1.2 细胞培养与处理TNBC细胞株MDA-MB468、MDA-MB436、MDA-MB231及激素受体阳性乳腺癌细胞株MCF-7均来自于中国科学院上海生命科学院细胞资源中心。除MCF-7细胞株需要在含10 μg/ml胰岛素、10% FBS及1%青、链霉素的DMEM培养液中培养之外,TNBC细胞株均在含有10% FBS及1%青、链霉素的DMEM培养液(Invitrogen,日本)中培养并于覆盖率约80%时按1:4比例传代。
1.3 免疫印迹法细胞在1 ml含有0.5% Triton X-100,50 mmol/L三羟甲基氨基甲烷,pH7.5,150 mmol/L氯化钠,1 mmol/L EDTA的冰温裂解液中裂解。将10 μg蛋白样品进行SDS-PAGE,电泳结束后转至PVDF膜。胶片由Canoscan 8400F扫描仪摄影。
1.4 细胞活性检测标准96孔板中按500个细胞每孔接种于100 μl培养液中,贴壁培养24 h后,测量细胞OD值,加入50 μmol/L西妥昔单抗和(或)1 μmol/L ENT至实验组,加入相同体积PBS至对照组,分别于24、48、72 h后测量各组OD值。100 μl培养液中加入10 μl CCK-8溶液,将培养板在培养箱中孵育2 h,用酶标仪测定在450 nm处吸光度值。
1.5 统计学方法Excel软件整理数据,采用SPSS13.0统计软件进行统计学处理,数据均表示为平均值±标准差。Mann-Whitney检验用于比较实验组与对照组组间差异,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 不同细胞株上皮细胞标志物、间皮细胞标志物及EGFR表达量对比MDA-MB468的EGFR表达量略高于MDA-MB436及MDA-MB231,而EGFR在激素受体阳性的MCF-7中几乎不表达;MDA-MB468的上皮细胞标志物E-cadherin表达水平明显高于MDA-MB436及MDA-MB231,与MCF-7相当;MDA-MB468的间皮细胞标志物vimentin表达量明显低于MDA-MB436及MDA-MB231,见图 1。
|
| 图 1 TNBC细胞株中E-cadherin、vimenti及EGFR的表达 Fig. 1 Expression of E-cadherin, vimentin andepidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in triple negativebreast cancer(TNBC) cell lines |
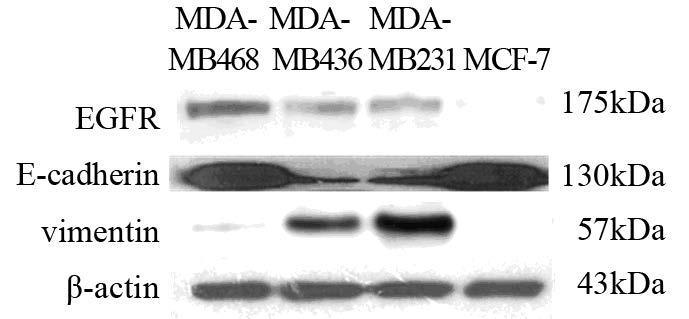
在MDA-MB468中,西妥昔单抗组细胞生长24 h后,细胞活性较对照组细胞差异有统计学意义[(1.42±0.06)vs.(1.05±0.08),P=0.002];48 h后,细胞活性差异更显著[(2.36±0.06)vs.(1.10±0.01),P<0.001];72 h后,细胞活性较对照组细胞差异亦具有统计学意义[(3.19±0.16)vs.(1.8±0.10),P=0.001],见图 2A。MDA-MB231中加入西妥昔单抗24、48、72 h后,与对照组比较,细胞活性差异无统计学意义,见图 2B。MDA-MB436对西妥昔单抗也不敏感,西妥昔单抗组与对照组比较细胞活性差异无统计学意义(结果未显示)。
|
| 图 2 西妥昔单抗对MDA-MB468和MDA-MB231细胞活性的影响 Fig. 2 Effect of cetuximab on viability of MDA-MB468and MDA-MB231 cells |
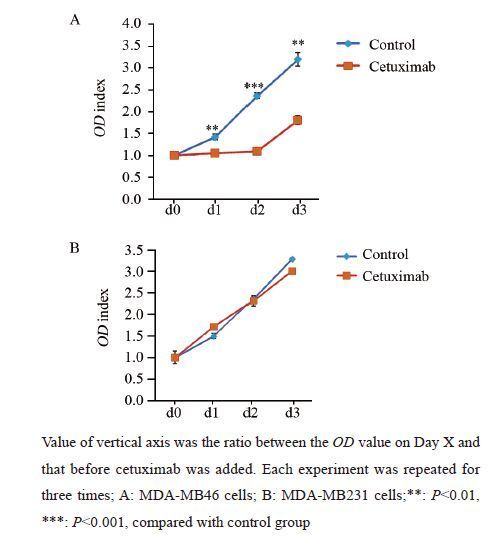
MDA-MB231细胞株经ENT(1 μmol/L)处理72 h后,vimentin的表达明显降低,Ⅰ型组蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制剂ENT能够逆转MDA-MB231细胞株的EMT,见图 3。
|
| 图 3 Ⅰ型组蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制剂ENT(MS275)逆转MDA-MB231EMT化 Fig. 3 TypeⅠhistone deacetylase inhibitor Entinostat(ENT) reversed epithelial-mesenchymal transition(EMT) ofMDA-MB231 cells |
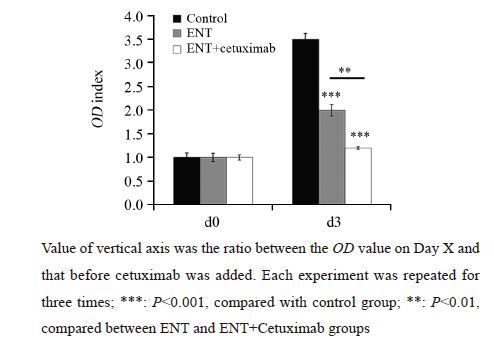
MDA-MB231中加入ENT培养72 h后,细胞活性较对照组细胞显著降低[(2.01±0.12)vs. (3.48±0.10),P<0.001],联用ENT+西妥昔单抗培养72 h后,细胞活性较对照组细胞活性显著降低[(1.20±0.03)vs.(3.48±0.10),P<0.001];ENT联合西妥昔单抗组较单用ENT组的细胞活性差异亦有统计学意义[(1.20±0.03)vs.(2.01±0.12),P=0.002],见图 4。
|
| 图 4 ENT联合西妥昔单抗治疗对MDA-MB231细胞活性的抑制作用 Fig. 4 Suppression effect of ENT and cetuximab onviability of MDA-MB231 cells |
既往研究提示EGFR靶向治疗耐药的分子机制可能有:EGFR下游信号分子突变;P53突变使得EGFR不断循环至细胞表面;受体型酪氨酸激酶如MET、AXL等的活化;EGFR转至细胞核内并成为细胞增殖及血管形成相关基因的协同转录因子等[9, 10, 11, 12]。在一些癌症如非小细胞肺癌中,EGFR靶向药物敏感度可能与EMT有关。小分子酪氨酸激酶抑制剂厄洛替尼只能延长部分高表达E-cadherin的非小细胞肺癌患者的无病生存时间[13]。本研究结果显示,间质型TNBC细胞MDA-MB436及MDA-MB231对西妥昔单抗耐药,而上皮型TNBC细胞MDA-MB468对西妥昔单抗敏感。通过ENT逆转MDA-MB231间质化水平后,细胞对西妥昔单抗的敏感度增加。本研究结果提示三阴性乳腺癌细胞株的EMT可能影响细胞对西妥昔单抗的敏感度。
正如Shah等[14]报道,Ⅰ型组蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制剂恩替诺特(ENT)能逆转TNBC细胞的EMT水平。ENT在乳腺癌中的应用正受到研究者关注。恩替诺特能够增强HER2阳性乳腺癌对拉帕替尼的敏感度[15],并能通过调节Her2逆转耐药性乳腺癌细胞对来曲唑的耐药性[16]。本实验中,ENT单药显著抑制TNBC细胞的细胞活性,ENT联合西妥昔单抗较ENT单药对细胞生长的抑制作用更加显著。EMT可能是ENT协同西妥昔单抗作用的分子机制。
EMT导致EGFR靶向药物耐药的机制可能是PI3K-Akt-mTOR及Ras-Raf-Me-Erk下游信号通路受IGF-R、PDGFR等受体激酶旁路活化。未来的研究需要进一步探讨在MDA-MB231中EMT影响西妥昔单抗药敏性的分子机制。
本研究未能在促进MDA-MB468的EMT后观察细胞株的药敏性变化。目前最常见促EMT的方法是使用TGFβ。然而,除Smad信号通路外,TGFβ亦能激活Erk、JNK、p38MAPK以及PI3K等下游信号因子。这些信号通路与EGFR下游信号通路具有交叉性[17],极有可能会干扰EGFR靶向药物疗效的观察。未来研究也需要采用可靠且不影响EGFR信号通路的方法观察促进MDA-MB468 EMT后对西妥昔单抗的敏感度变化。
| [1] | Sotelo MJ, García-Paredes B, Aguado C, et al. Role of cetuximab in first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(15): 4208-19. |
| [2] | Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, et al. Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2004, 10(16): 5367-74. |
| [3] | Zhang M, Zhang X, Zhao S, et al. Prognostic value of survivin and EGFR protein expression in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients[J]. Target Oncol, 2014, 9(4): 349-57. |
| [4] | Liu D, He J, Yuan Z, et al. EGFR expression correlates with decreased disease-free survival in triple-negative breast cancer: a retrospective analysis based on a tissue microarray[J]. Med Oncol, 2012, 29(2): 401-5. |
| [5] | Carey LA, Rugo HS, Marcom PK, et al. TBCRC 001: randomized phase Ⅱ study of cetuximab in combination with carboplatin in stage Ⅳ triple-negative breast cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2012, 30(21): 2615-23. |
| [6] | Ferraro DA, Gaborit N, Maron R, et al. Inhibition of triple-negative breast cancer models by combinations of antibodies to EGFR[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2013, 110(5): 1815-20. |
| [7] | Tao JJ, Castel P, Radosevic-Robin N, et al. Antagonism of EGFR and HER3 Enhances the Response to Inhibitors of the PI3K-Akt Pathway in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer[J]. Sci Signal, 2014, 7(318): ra29. |
| [8] | Karihtala P, Auvinen P, Kauppila S, et al. Vimentin, zeb1 and Sip1 are up-regulated in triple-negative and basal-like breast cancers: association with anaggressive tumour phenotype[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2013, 138(1): 81-90. |
| [9] | Shapira I, Lee A, Vora R, et al. P53 mutations in triple negative breast cancer upregulate endosomal recycling of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) increasing its oncogenic potency[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2013, 88(2): 284-92. |
| [10] | Meyer AS, Miller MA, Gertler FB, et al. The receptor AXL diversifies EGFR signaling and limits the response to EGFR-targeted inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer cells[J]. Sci Signal, 2013, 6(287): ra66. |
| [11] | Mueller KL, Madden JM, Zoratti GL, et al. Fibroblast-secreted hepatocyte growth factor mediates epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in triple-negative breast cancers through paracrine activation of Met[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2012, 14(4): R104. |
| [12] | Brand TM, Iida M, Luthar N, et al. Nuclear EGFR as a molecular target in cancer[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2013, 108(3): 370-7. |
| [13] | Yauch RL, Januario T, Eberhard DA, et al. Epithelial versus mesenchymal phenotype determines in vitro sensitivity and predicts clinical activity of erlotinib in lung cancer patients[J].Clin Cancer Res, 2005, 11(24 Pt 1): 8686-98. |
| [14] | Shah P, Gau Y, Sabnis G. Histone deacetylase inhibitor entinostat reverses epithelial to mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells by reversing the repression of E-cadherin[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2014, 143(1): 99-111. |
| [15] | Lee J, Bartholomeusz C, Mansour O, et al. A class I histone deacetylase inhibitor, entinostat, enhances lapatinib efficacy in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells through FOXO3-mediated Bim1 expression[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2014, 146(2): 259-72. |
| [16] | Sabnis GJ, Goloubeva OG, Kazi AA, et al. HDAC inhibitor entinostat restores responsiveness of letrozole-resistant MCF-7Ca xenografts to aromatase inhibitors through modulation of Her-2[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2013, 12(12): 2804-16. |
| [17] | Miyazono K. Transforming growth factor-β signaling in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and progression of cancer[J]. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci, 2009, 85(8): 314-23. |
 2016, Vol. 43 No.4
2016, Vol. 43 No.4