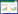文章信息
- 崔凯,王焕,冯衍生
- CUI Kai, WANG Huan, FENG Yansheng
- 人mcl1不同亚型在结肠癌组织中表达变化的临床意义
- Clinical Significance of Different Human mcl1 Subtypes Expression in Colorectal Cancer Tissues
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2016, 43(02): 141-145
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2016, 43(02): 141-145
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2016.02.010
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2014-12-31
- 修回日期: 2015-08-01
2. 453000 新乡,新乡医学院附属中心医院肾内科;
3. 453003 新乡,新乡医学院基础医学院病理生理教研室
2. Department of Nephrology, Central Affiliated Hospital, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang 453000, China;
3. Department of Pathophysiology, School of Basic Medicine, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang 453003, China
根据最新综述表明,结肠癌(colorectal cancer,CRC)已成为世界上男性中仅次于肺癌、前列腺癌,女性中仅次于乳腺癌的具有高致死率的肿瘤[1]。鉴于对肿瘤发生、转移机制缺乏系统认识,目前虽然有大量中文文献证明了许多基因与结肠癌发生转移具有一定相关性,其中包括报道较多的mcl1[2]等基因,但由于所检测的这些分子大多数均存在多种类型转录本以及蛋白亚型,而目前又没有这方面详细准确的研究,因此对结肠癌的临床分子诊断造成一定局限性。
本研究以mcl1为例,对其不同亚型在结肠癌中的表达及功能进行检测,并结合结肠癌临床病理特征进行分析,从而证明mcl1的特定亚型可以作为结肠癌临床检测指标,并为广大同仁在相关领域的后续研究中提供一些思路和参考。
1 资料与方法 1.1 资料 1.1.1 一般资料收集2008年3月—2011年6月间新乡医学院附属中心医院普瘤外科手术切除的结肠腺瘤124例、结肠腺癌89例以及相应的癌旁组织。其中男101例,女112例,年龄36~65岁,平均年龄55.7岁。89例结肠腺癌依据AJCC癌症分期手册第六版进行分期,其中Ⅰ期患者30例,Ⅱ期患者32例,Ⅲ期患者18例,Ⅳ期患者9例。另取正常结肠组织51例,作为正常对照。
1.1.2 试剂反转录试剂盒购自大连Takara公司。人Mcl1抗体购自美国Santa Cruz公司,其中抗全蛋白的sc-12756、抗111-149长度(位于1号外显子内部458 bp编码的氨基酸中)蛋白序列的sc-377487、抗C端(代表 2号外显子编码的氨基酸)的sc-958,人β-actin一抗、二抗购自中国碧云天生物技术研究所,ECL化学发光试剂盒购自上海BestBIO公司。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 RT-PCR检测mRNA的表达水平
样本按正常结肠组织、结肠腺瘤、结肠腺瘤旁组织、结肠腺癌及腺癌旁组织分为5组,每组随机抽取20个样本,进行TRIzol法抽提全RNA。反转录合成cDNA。mcl1上下游引物序列分别为:F:5’-CGCCCGGGAGGGCGACTTTTG-3’,R:5’-TGGAAGAACTCCACAAACCCATC-3’,见图 1;β-actin上下游引物序列分别为:F:5’-ACACTGTGCCCATCTACTAGG-3’,R:5’-AGGGGCCGGACGCGTCATACT-3。反应条件:95℃ 5 min,95℃ 10 s,60℃ 15 s,72℃ 1 min (30个循环);72℃ 5 min。
|
| 图 1 mcl1基因的三种亚型 Fig. 1 Three subtypes of mcl1 gene |
4%SDS-PAGE浓缩胶电泳80 V,30 min,10%SDS-PAGE分离胶,电泳120 V,100 min。PVDF膜半干转100 V,30 min。5%脱脂奶粉封闭2 h。一抗(1:1 000)孵育2 h或4℃过夜,二抗(1:5 000)孵育1 h。随后进行化学发光,操作见ECL化学发光试剂盒说明书。
1.3 统计学方法所有数据均采用SPSS20.0统计软件进行分析。mRNA与蛋白表达水平均采用灰度分析并对所得数据进行方差分析,样本信息比较用χ2检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
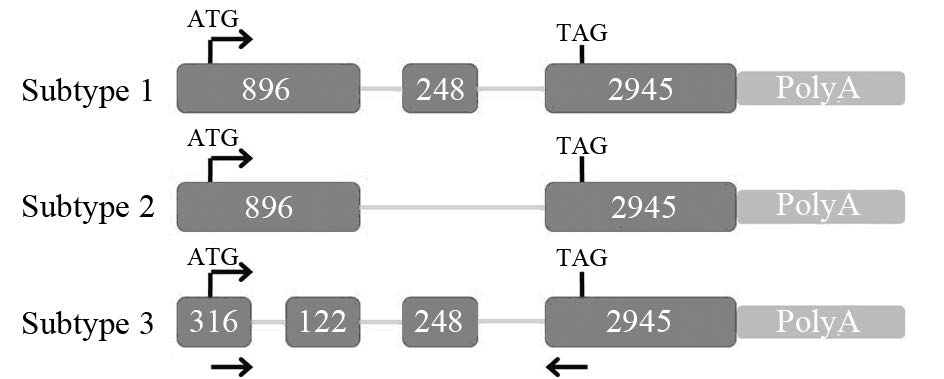
2 结果 2.1 mcl1基因mRNA剪接异构体在结肠肿瘤中的表达mcl1三种mRNA剪接异构体的PCR扩增条带,见图 2。其中mcl1基因亚型1在结肠肿瘤组织及相应旁组织中的表达均高于正常组(P=0.009),且腺癌组中的表达亦高于腺瘤组(P=0.004);亚型2在结肠肿瘤组织及相应旁组织中的表达均高于正常组(P=0.002),且腺癌组中的表达亦高于腺瘤组(P<0.001)。亚型3在结肠肿瘤组织及相应旁组织中的表达均高于正常组(P=0.027),但腺癌组和腺瘤组分别与相应旁组织之间以及腺癌组与腺瘤组之间的比较差异均无统计学意义。
|
| M: Marker; 1: mcl1 mRNA expression in normal colon tissues; 2: mcl1 mRNA expression in colorectal adenoma tissues; 3: mcl1 mRNA expression in relative para-colorectal adenoma tissues; 4: mcl1 mRNA expression in colorectal adenocarcinoma tissues; 5: mcl1 mRNA expression in relative para-colorectal adenocarcinoma tissues; *: P<0.05, compared with normal tissues; #: compared with adjacent tissues; &: adenoma tissues vs. adenocarcinoma tissues 图 2 RT-PCR检测不同组织中mcl1 mRNA的表达 Fig. 2 RT-PCR analysis of mcl1 mRNA expression in different tissues |
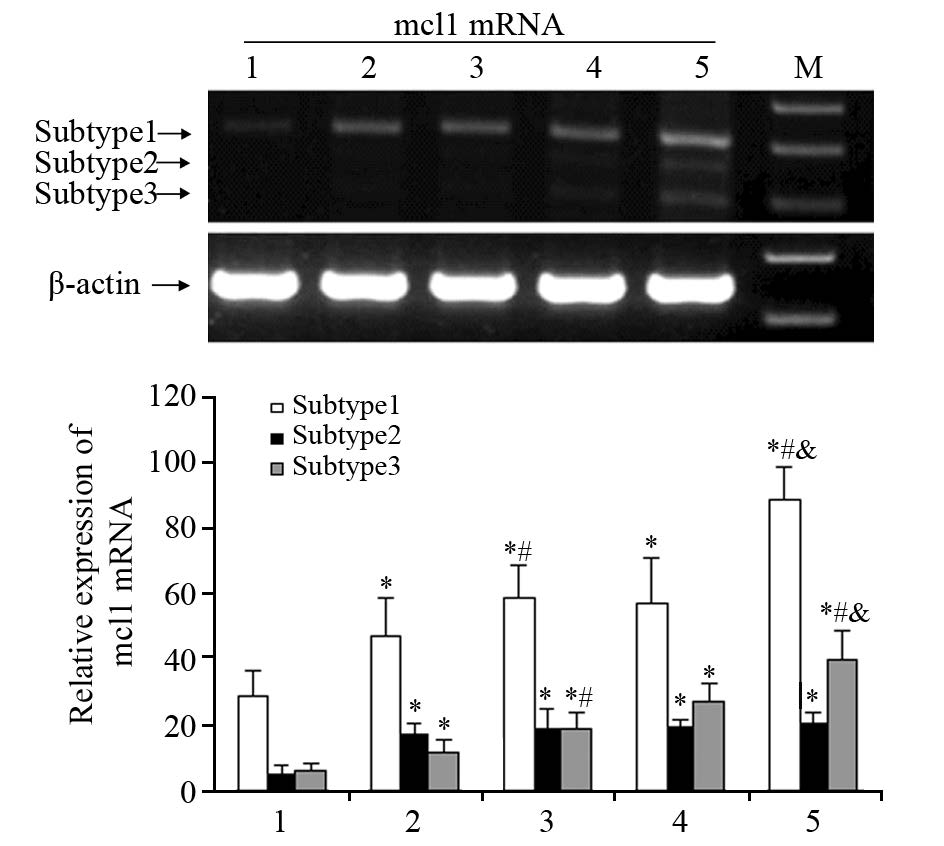
mcl1三种剪接异构体的蛋白印迹条带,见图 3。mcl1基因亚型1在结肠肿瘤组织及相应旁组织中的蛋白表达均高于正常组(P=0.022),且腺癌组中的表达亦高于腺瘤组(P=0.034);亚型2在结肠肿瘤组织及相应旁组织中的蛋白表达均高于正常组(P=0.011),且腺癌组中的表达亦高于腺瘤组(P=0.007)。亚型3在结肠肿瘤组织及相应旁组织中的表达均高于正常组(P=0.045),但腺癌组和腺瘤组分别与相应旁组织之间以及腺癌组与腺瘤组之间比较,差异均无统计学意义。
|
| 1: mcl1 protein expression in normal colon tissues; 2: mcl1 protein expression in colorectal adenoma tissues; 3: mcl1 protein expression in relative para-colorectal adenoma tissues; 4: mcl1 protein expression in colorectal adenocarcinoma tissues; 5: mcl1 protein expression in relative para-colorectal adenocarcinoma tissues; *: P<0.05, compared with normal tissues; #: compared with adjacent tissues; &: adenoma tissues vs. adenocarcinoma tissues 图 3 Western blot检测不同组织中mcl1蛋白水平的表达 Fig. 3 Western blot analysis of mcl1 protein expression in different tissues |
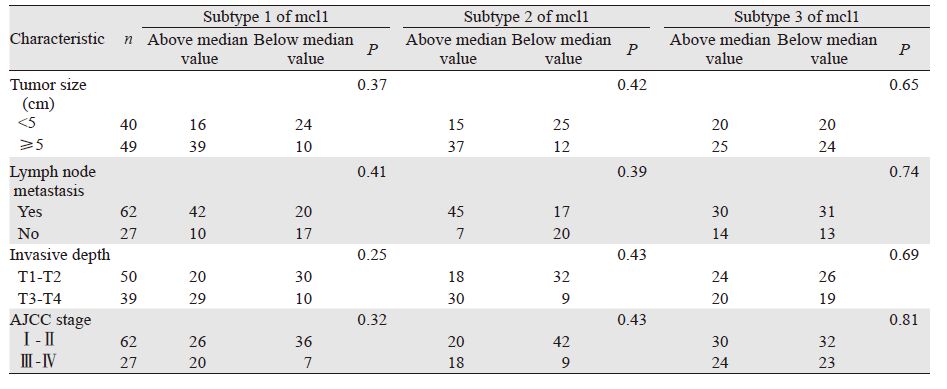
mcl1亚型1和亚型2对结肠癌肿瘤恶性程度呈正相关,而亚型3可以作为肿瘤早期诊断的标志物,但其表达水平与恶性程度无明显相关性,见表 1。
 |
髓细胞白血病基因-1(myeloid cell leukemin-1,mcl-1)是Bcl-2家族中抗凋亡蛋白成员之一,mcl1可以螯合促凋亡蛋白Bax/Bak异二聚化[3],抑制肿瘤细胞的凋亡;可以与CDK-1和增殖细胞核抗原相互作用,调控细胞的分化[4]。因此mcl1的表达与肿瘤的恶性程度呈正相关,许多肿瘤细胞均过度表达mcl1蛋白,越来越多的证据显示mcl1在肿瘤的临床诊断中可以作为一个有效的预测指标[5]。减少mcl1的表达可以有效的抑制肿瘤的恶性增殖[6]。研究表明mcl-2与结肠癌肿瘤的存在呈正相关,与肿瘤的恶性程度及转移情况呈正相关[7]。
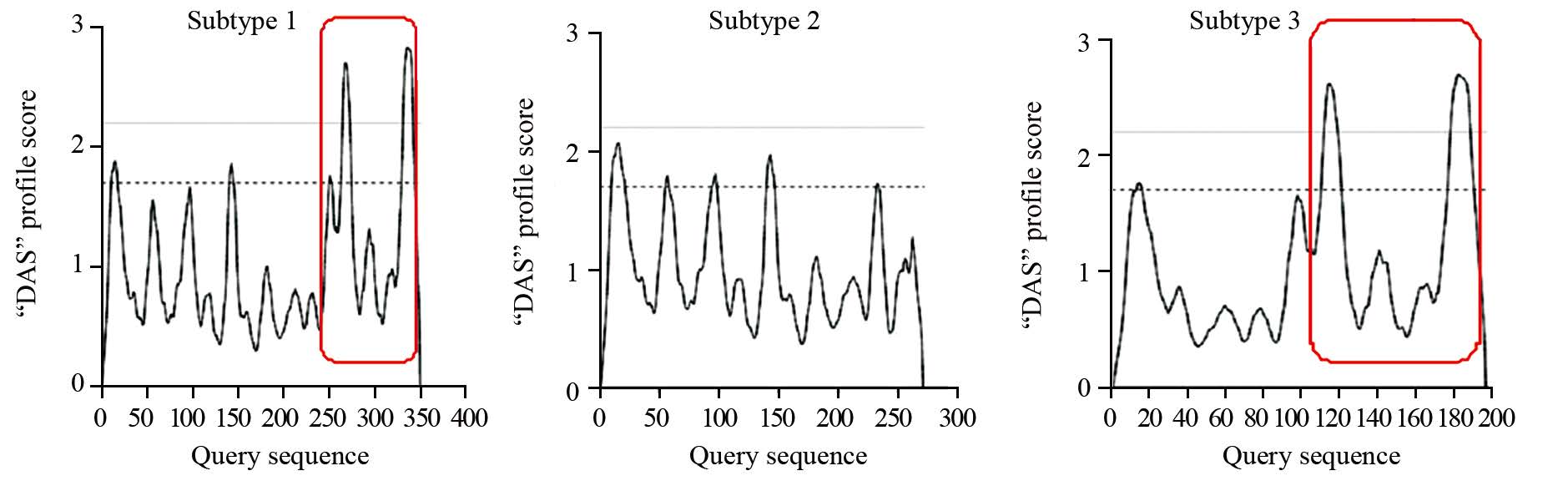
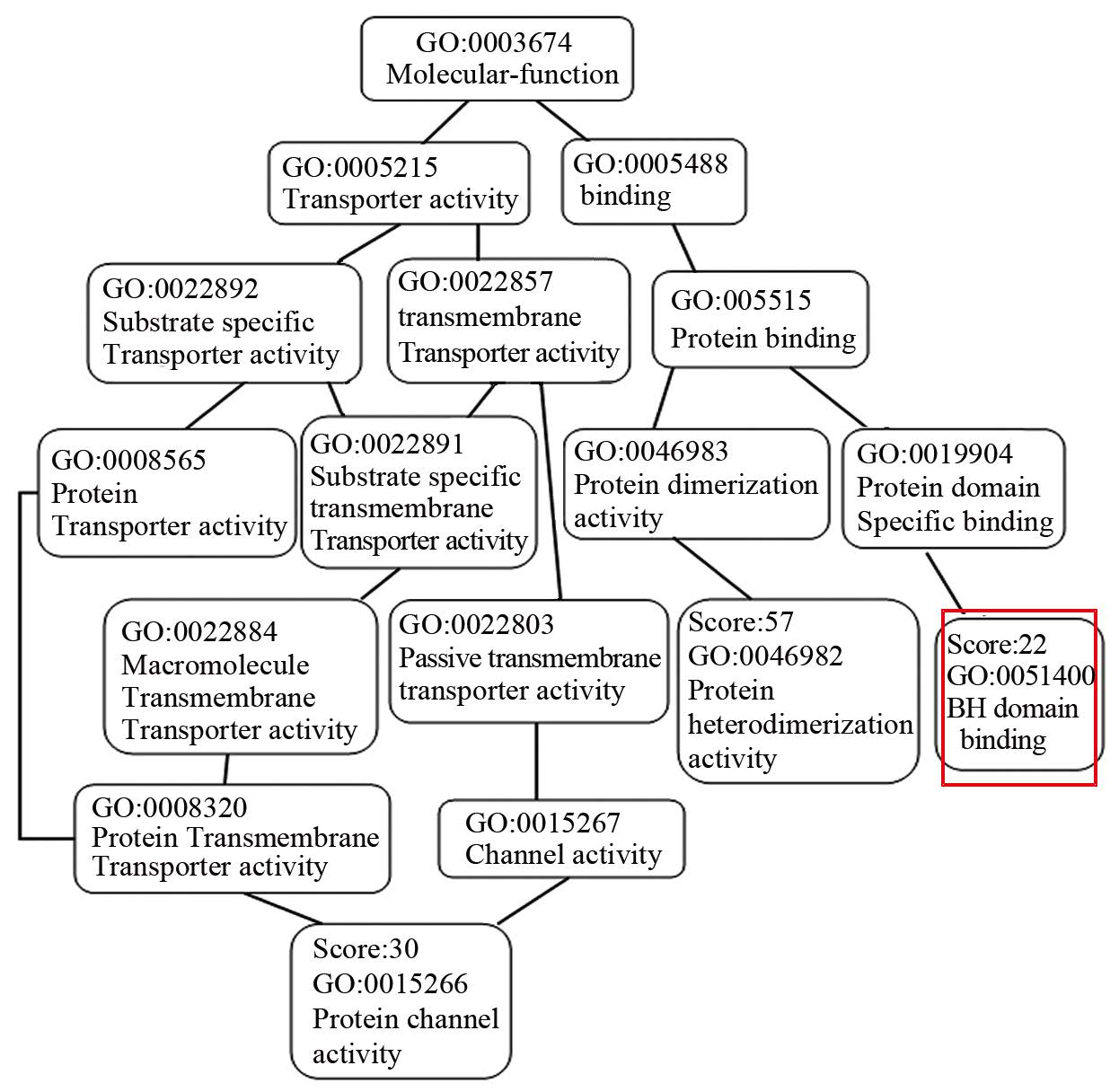
人mcl1基因的mRNA与蛋白具有三种亚型,见图 1,亚型1最为完整,亚型2缺少第二外显子长达248 bp的一段序列,亚型3缺少第一外显子内部458 bp的一段序列。由于MCL1蛋白在胞膜,胞质以及胞核内均有表达。因此通过“DAS”(http://www.sbc.su.se/~miklos/DAS/)以及“The PredictProtein Server”(https://www.predictprotein.org/)对其不同蛋白亚型的功能预测分析后,可以发现第二外显子248 bp编码的氨基酸序列主要功能为跨膜结构,见图 4,第一外显子所缺失的458 bp编码的氨基酸序列主要功能包括BH(Bcl2 homology)结合域(GO:0051400),见图 5。
|
| Dotted and full lines represented the prediction of transmembrane structure; Red frame represented amino acid sequence in exon2 of mcl1 图 4 2号外显子编码的氨基酸序列功能预测 Fig. 4 Function prediction of amino acid sequence in exon2 of mcl1 |
|
| Red frame represented binding clomain of BH 图 5 1号外显子内部458bp编码的氨基酸序 列功能预测(主要包括蛋白异源二聚化活 性、通道活性以及BH结合域) Fig. 5 Function prediction of amino acid sequence of 458bp in exon1 of mcl1(including activity of protein heterodimerization ,activity of channel and binding domain of BH) |
人mcl1基因其拥有三种转录本,分别编码两种蛋白亚型。其中亚型1和亚型3主要分布于细胞核内,与CDK-1和增殖细胞核抗原(PCNA)相互作用,调控细胞分化,而亚型2主要分布在线粒体膜以及细胞膜上[8],可以螯合凋亡蛋白Bax/Bak异二聚化,这与我们对mcl1不同亚型氨基酸序列功能分析结果是一致的,见图 2~3。已证实Mcl-1在多种肿瘤组织中均存在过度表达,提示其与肿瘤的发生密切相关[9, 10],此外,mcl1与多发性骨髓瘤的复发、慢性粒细胞白血病和结肠癌肝转移的耐药有关[11]。mcl1基因在临床诊断结肠癌目前已经在国内外得到广泛认可和应用[2, 12, 13, 14, 15]。
本研究进一步发现mcl1各亚型在结肠癌组中较正常结肠组有显著高表达,这提示在肿瘤发生早期,膜定位表达的亚型3与核定位表达的亚型2均参与了肿瘤形成的应答反应,亚型2和亚型3均可以作为肿瘤早期的诊断指标之一,而亚型3的表达在不同分期的结肠肿瘤中与其恶性程度无显著相关性,在肿瘤与对应旁组织的表达也无显著性差异,提示亚型3作为一种跨膜蛋白主要发挥信号传递的功能,在肿瘤形成以后,可能不再起主要作用;而亚型2作为核表达蛋白,发挥转录因子的作用,维持并调控肿瘤细胞一系列基因的表达,因此在不同分级类型的结肠肿瘤中呈显著性差异,其与亚型1与肿瘤的恶性程度及转移情况呈正相关。
本研究通过对mcl1基因各亚型在结肠癌中表达的分析,提示亚型1和2,主要集中在1号外显子内458 bp的检测可以作为早期诊断结肠癌及其恶性程度有效判定指标之一。
根据mcl-1在结肠癌中的表达研究,是否可以通过抑制mcl-1某种亚型的表达,为结肠癌的新的治疗方案提供理论依据,将是未来研究方向之一,阻断mcl-1亚型基因的表达将可能为肿瘤新药开发提供新的治疗靶点,尚需大规模的临床研究进一步验证。
| [1] | Tárraga López PJ, Albero JS, Rodríguez-Montes JA. Primary and secondary prevention of colorectal cancer[J]. Clin Med Insights Gastroenterol, 2014, 7: 33-46. |
| [2] | Zhao Y, Shen XY. The anti apoptotic function of Mcl-1 and its role in cancer treatment[J]. Sheng Ming De Hua Xue, 2011, 31(6): 863-7. [赵燕, 沈晓云. Mcl-1蛋白的抗凋亡作用与癌症的治疗[J]. 生命的化学, 2011, 31(6): 863-7.] |
| [3] | Bingle CD, Craig RW, Swales BM, et al. Exon skipping in Mcl-1 results in a bcl-2 homology domain 3 only gene product that promotes cell death[J]. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275(29): 22136-46. |
| [4] | Jamil S, Sobouti R, Hojabrpour P, et al. A proteolytic fragment of Mcl-1 exhibits nuclear localization and regulates cell growth by interaction with Cdk1[J]. Biochem J, 2005, 398(Pt 3): 659-67. |
| [5] | Kitada S, Andersen J, Akar S, et al. Expression of apoptosis-regulating proteins in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Correlations with in vitro and in vivo chemoresponses[J]. Blood, 1998, 91(9): 3379-89. |
| [6] | Taniai M, Grambihler A, Higuchi H, et al. MCL-1 mediates tumor necrosis factor-related aptoptosis-indcing ligand resistance in human cholangicarcinoma cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2004, 64(10): 3517-24. |
| [7] | Zhang Y. The expression andclinicopathological significance of eIF3a, mcl-1 and CD83 in colorectal carcinoma tissue and serum[D]. Suzhou Da Xue, 2014, 36-37. [张叶. eIF3a, mcl-1和CD83在结肠癌组织和血清中的表达及其临床病理意义[D].苏州大学, 2014, 36-37.] |
| [8] | Germain M, Duronio V. The N terminus of the anti-apoptotic BCL-2 homologue MCL-1 regulates its localization and function [J]. J Biol Chem, 2007, 282(44): 32233-42. |
| [9] | Song L, Coppola D, Livingaton S, et al. Mcl-1 regulates survival and sensitivity to diverse apoptotic stimuli in human non-small cell lung cancer cells[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2005, 4(3): 267-76. |
| [10] | Schulze-Bergkamen H, Flerscher B, Schuchmann M, et al. Suppression of mcl-1via RNA interference sensitizes human heaptocellular carcinoma cells towards apoptosis induction[J].BMC Cancer, 2006, 6: 232. |
| [11] | Yoon JH, Werneburg NW, Higuchi H, et al. Bile acids inhibit Mcl-1protein turnover via an epidermal growth factor receptor/Raf-1 dependent mechanism[J]. Cancer Res, 2002, 62(22): 6500-5. |
| [12] | Hernandez JM, Farma JM, Coppola D, et al. Expression of the antiapoptotic protein survivin in colon cancer[J]. Clin Colorectal Cancer, 2011, 10(3): 188-93. |
| [13] | Eichhorn JM, Alford SE, Sakurikar N, et al. Molecular analysis of functional redundancy among anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins and its role in cancer cell survival[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2014, 322(2): 415-24. |
| [14] | Feng N, Zhang XJ. Progress of Mcl-1 gene in targeted therapy of tumor[J]. Zhonghua Lin Chuang Yi Shi Za Zhi(Dian Zi Ban), 2009, 3(11): 1883-7. [冯楠, 张学军. Mcl-1基因在肿瘤靶向治疗中的研究进展[J]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2009, 3(11): 1883-7.] |
| [15] | Ma XT, Yu LW, Wang S, et al. The role of bcl-2 in the inhibition of cell apoptosis of colon cancer through Stat5b signaling pathway [J]. Zhonghua Shi Yan Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2005, 22(10): 1167-9. [马向涛, 余力伟, 王杉,等. Stat5b信号通路调控bcl-2成员表达抑制结肠癌细胞凋亡的作用及其机制[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2005, 22(10): 1167-9.] |
 2016, Vol. 43
2016, Vol. 43