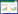文章信息
- 王雷, 王林, 米源.
- WANG Lei, WANG Lin, MI Yuan.
- Gli抑制剂GANT61对肺癌细胞生长的抑制作用
- GANT61 as Inhibitor of Gli Inhibits Growth of Lung Cancer Cells
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2016, 43(02): 112-115
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2016, 43(02): 112-115
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2016.02.004
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2015-05-12
- 修回日期: 2015-08-31
80%左右的肺癌患者是非小细胞肺癌(鳞癌、腺癌为主),且确诊时多为中晚期,传统的手术和放化疗效果不理想。近年来靶向治疗已经使部分腺癌患者受益,但如何找到更好的治疗靶点成为研究热点。研究表明Hedgehog(Hh)信号通路在胃癌、肺癌、头颈部癌和胰腺癌等多种癌组织中异常活化,与肿瘤的发生发展、转移密切相关[1, 2, 3, 4]。Hh信号转导通路主要包括4个部分:Hedgehog配体、Patched受体、Smoothened蛋白、核转录因子Gli以及下游目的基因等组成[5]。普遍认为Gli1上调是Hedgehog通路激活的重要标志,促进了肿瘤的进展和转移。GANT61是近年研制的Hh通路抑制剂,它的靶点是特异性针对Gli[6, 7]。本研究通过GANT61特异性阻断人肺癌细胞系H1703和A549中的Gli1和Gli2的表达,观察其对肺癌细胞生长、增殖及侵袭的影响,初步探讨其作用机制,为肺癌的靶向治疗提供一个新思路。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料人肺鳞癌细胞系H1703和腺癌细胞系A549 由河北医科大学第四医院肿瘤研究所提供。RPMI 1640培养液(美国Gibco公司),胎牛血清(美国Gibco公司),胰蛋白酶(美国Gemini公司),二甲基亚砜( DMSO美国MPBIO 公司),GANT61,2'-[[Dihydro-2-(4-pyridinyl)-1,3(2H,4H)-pyrimidinediyl]bis(methylene)]bis(N,N-dimethylbenzenamine) 美国Selleckchem公司,Gli-1兔抗人多克隆抗体(美国abcam公司),Gli-2 鼠抗人单克隆抗体(美国Santa Cruz公司),GAPDH鼠抗人单克隆抗体(美国Santa Cruz公司),CellTiter-Glo®发光法细胞活力检测试剂盒(美国Promega公司),GloMax-96 Microplate Luminometer(美国Promega公司),Pierce-BCA 蛋白分析试剂盒(美国Thermo Scientific公司),M-PER培养细胞总蛋白提取试剂(美国Thermo Scientific公司),蛋白酶抑制剂(德国roche公司),Mini-PROTEAN TGX预制胶(美国BIO-RAD公司),Tris/甘氨酸/电泳缓冲液(美国BIO-RAD公司),Tris/甘氨酸缓冲液(美国BIO-RAD公司),Matrigel胶(美国Corning公司),Transwell膜嵌套(美国Corning公司)。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 细胞培养
将人肺癌细胞系H1703和A549细胞培养于37℃、5%CO2培养箱中,培养液为RPMI 1640培养液,10%胎牛血清,青-链霉素各100 mg/ml,取对数生长期细胞计数后用无血清培养液于每孔5 000个细胞接种于96孔板和0.3×106接种到6孔板进行实验。
1.2.2 MTS法检测细胞生长抑制率
将H1703和A549细胞以每孔5 000个细胞密度接种于96孔培养板中,50 μl培养液/孔,每个浓度设3个复孔,并设空白对照组(DMSO);于培养箱培养过夜后待细胞贴壁生长状态良好,用无血清培养液稀释GANT61后每孔50 μl加入不同终浓度GANT61溶液(1.1705、1.7558、2.6337、3.9506、5.9259、8.8888、13.3333、20、30 μmol/L),培养72 h后将96孔板放置室温10 min后每孔加入CellTiter-Glo®发光法细胞活力检测试剂100 μl,于10 min后置于GloMax-96 Microplate Luminometer仪器检测,应用GraphpadPrism 6软件进行数据分析,计算GANT61对H1703和A549的IC50值。
1.2.3 Westernblot方法检测细胞蛋白表达
于6孔板内呈对数生长期的H1703和A549细胞加浓度为10 μmol/L的GANT61处理24 h,对照组为DMSO组。用PBS洗涤细胞后加细胞总蛋白提取试剂和蛋白酶抑制剂,BCA法测定蛋白浓度。于Mini-PROTEAN TGX预制胶中行蛋白上样,每泳道上样为10 μg蛋白,在电泳槽中经Tris/甘氨酸/电泳缓冲液SDS进行电泳后,在Tris-甘氨酸缓冲液中将蛋白电转移印迹到PVDF膜上,再用5%脱脂奶粉/TBST液封闭PVDF膜1 h,Gli1工作浓度为 1:1 000,Gli2工作浓度为1:250,GAPDH工作浓度为1:10 000 ,4℃过夜,第二天加二抗,二抗工作浓度为1:20 000,孵育1 h后用TBST洗膜,ECL试剂发光,暗室曝光显影。
1.2.4 Transwell侵袭实验
用50 mg/L Matrigel 1:4稀释液包被Transwell小室基底膜,将浓度为10 μmol/L的GANT61处理 24 h后的细胞和DMSO处理的细胞消化后,用无血清培养液悬浮细胞并计数,于每个上室接种7.5×104细胞:于下室放置10%血清培养液,常规培养细胞24 h后,用棉签擦去基质胶和上室内的细胞,再用0.1%结晶紫染色后对穿过Matrigel胶和膜的细胞进行计数,于显微镜下每个孔取5个高倍镜视野(×400)计数,计算平均值。
1.2.5 统计学方法
实验数据采用SPSS17.0统计软件进行处理,应用χ2检验方法。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 MTS法实验结果检测不同浓度的GANT61作用72 h对H1703和A549细胞生长的影响,通过Graphpad Prism软件进行数据分析,H1703和A549的IC50值分别是8.6 μmol/L和8.2 μmol/L,见图 1。
|
| Cell lines were treated with a range of concentrations of GANT61. Cell viability was tested 72h after treatment. All samples were triplicate and data were standardized to that of DMSO treated cells. IC50 of GANT61 was 8.6 and 8.2μmol/L in H1703 and A549 cell lines respectively 图 1 不同剂量GANT61作用后H1703和A549细胞的药物剂量反应曲线 Fig. 1 Drug-response curves of H1703 and A549 cell lines treated with different doses of GANT61 |
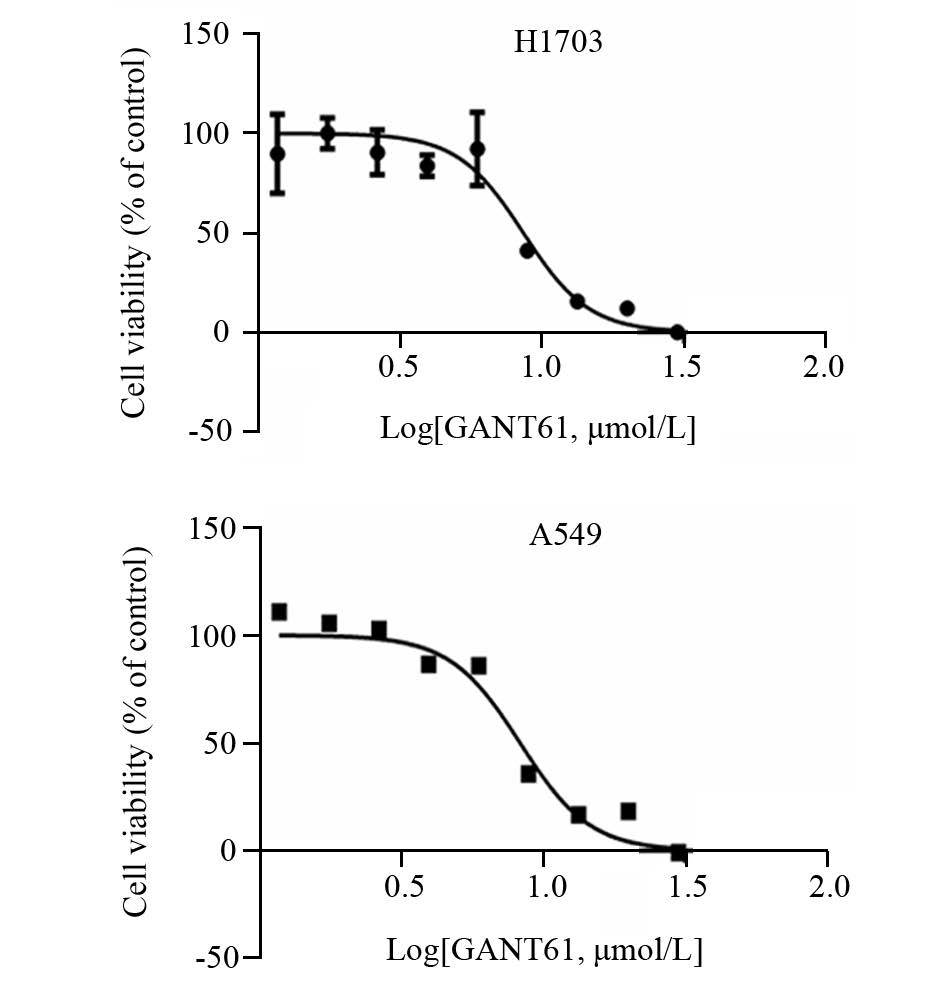
应用GANT61处理H1703和A549细胞24 h后Gli1和Gli2蛋白表达显著减少,而内参GAPDH蛋白表达无明显变化。DMSO组Gli1、Gli2和内参GAPDH蛋白表达无明显变化,见图 2。
|
| In both H1703 and A549 cell lines,the expression of Gli1and Gli2 were decreased significantly after treated with corresponding GANT61 (10μmol/L) 图 2 H1703和A549细胞的Gli1、Gli2蛋白表达 Fig. 2 Expression of Gli1 and Gli2 proteins in H1703 and A549 cell lines |
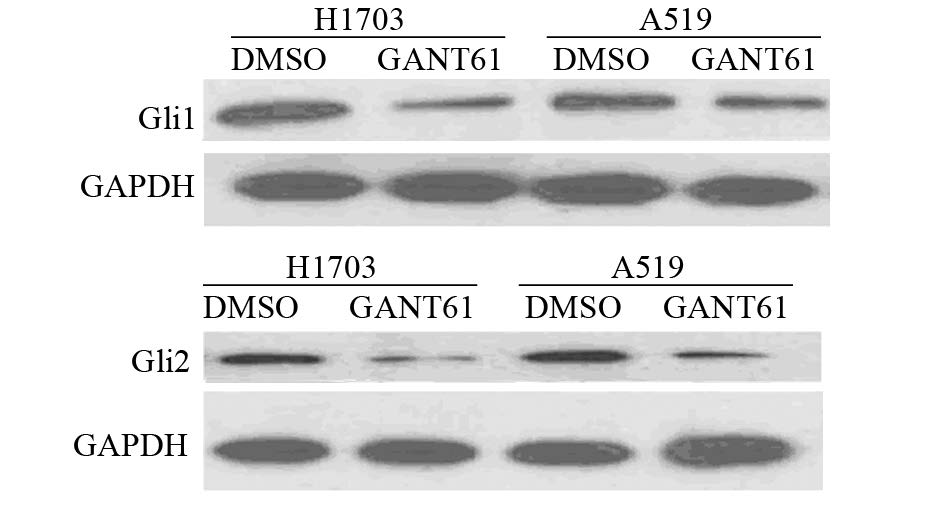
H1703和A549细胞接种在Transwell小室24 h 之后,观察到H1703实验组平均穿膜细胞数[(45.0±3.0 ) 个]较空白对照组[(126.0 ± 4.8)个]明显降低,差异有统计学意义(P=0.000);A549实验组平均穿膜细胞数[(63.0±2.8)个]较空白对照组[(156.0±3.2)个]明显降低,差异有统计学意义(P=0.000)。
|
| Lung cancer cells were plated onto the matrigel-coated membrane on the top of transwell chamber and treated with GANT-61 (10μmol/L) for 24h. Cells invaded to the lower chamber were fixed with methanol,stained with crystal violet and counted 图 3 H1703和A549细胞的Transwell侵袭实验 Fig. 3 Transwell invasion assay of H1703 and A549 cell lines |
Hh通路处于静止状态时Ptch与Smo结合抑制Hh功能,当内源性Hh过表达时与受体Ptch相结合导致解除Ptch对Smo的抑制作用,活化的Smo激发了一系列复杂的细胞内信号转导事件导致转录因子Gli家族的活化。大量研究表明Hh通路对肿瘤的生长和转移发挥关键作用,因此近年来研发了针对Hh通路的靶向药GDC-0449[8]、cyclopamine[9]等去阻断Hh信号的转导,其中GDC-0449被美国FDA批准临床治疗基底细胞癌,但是由于天然或获得性Smo突变导致针对Hh上游通路Hh、Smo的靶向药GDC-0449、cyclopamine等效果不佳。Gli1和Gli2是Gli家族的转录因子,在Hh通路中发挥着中枢作用,目前认为,Gli1基因是Hh通路重要的靶基因,其上调是该通路激活的重要标志,可将Hh信号转导至核内后对靶基因起转录激活作用。Gli2是Hh信号调节的主要转录激活子,可以启动Hh信号通路下游靶基因的转录,Gli1是其靶基因之一,因此通过针对以Gli1和Gli2为靶点对Hedgehog信号通路进行调控可以起到精确高效作用[10, 11]。
Lauth等[12]研究发现GANT61比Hh信号通路上游拮抗剂cyclopamine有更高的拮抗效率,在体外实验可以显著抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖,体内试验也可以明显抑制前列腺癌转移瘤的生长。Fu等[13]应用GANT-61对胰腺癌干细胞进行研究,发现GANT-61可以抑制Gli的转录活性,通过激活caspase-3等诱导肿瘤干细胞凋亡,此外GANT61可以上调DR4和DR5表达,抑制Gli1、Gli2、Bcl-2、CCND2和Zeb1从而抑制肿瘤干细胞的增长。
本研究结果显示GANT61可以明显抑制H1703和A549细胞的细胞活力并且Western blot方法显示GANT61可以明显抑制Gli1和Gli2蛋白的表达,因为Gli可通过调控下游靶基因的转录进而影响肿瘤细胞的生长增殖和转移,GANT61作为Gli转录的抑制剂可能是通过特异性下调Hh信号通路下游的Gli1和Gli2的基因和蛋白表达来实现对H1703和A549细胞的生长抑制作用。此外,有研究表明[14, 15]Gli与上皮-间质转化(EMT)有关,Gli可以调节癌细胞的EMT转化从而促进侵袭转移,本研究显示GANT61处理组细胞的侵袭能力明显下降,可能与GANT61通过影响Gli1和Gli2的表达从而调控肺癌细胞的EMT有关。对信号转导途径中靶点的治疗已经成为治疗肿瘤的重要策略之一,由于Gli在Hh 信号转导通路中起关键作用且在肺癌细胞中也存在Gli1和Gli2的活化状态,因此GANT61可能成为肺癌靶向治疗的新药物。
| [1] | Stanton BZ, Peng LF. Small-molecule modulators of the Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway[J]. Mol Biosyst, 2010, 6(1): 44-54. |
| [2] | Jiang WG, Ye L, Ruge F, et al. Expression of Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) in human lung cancer and the impact of YangZheng XiaoJi on SHH-mediated biological function of lung cancer cells and tumor growth[J]. Anticancer Res, 2015, 35(3): 1321-31. |
| [3] | Kageyama-Yahara N, Yamamichi N, Takahashi Y, et al. Gli regulates MUC5AC transcription in human gastrointestinal cells[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(8): e106106. |
| [4] | Schneider S, Thurnher D, Kloimstein P, et al. Expression of the Sonic hedgehog pathway in squamous cell carcinoma of the skin and the mucosa of the head and neck[J]. Head Neck, 2011, 33(2): 244-50. |
| [5] | Ng JM, Curran T. The Hedgehog’s tale: developing strategies for targeting cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2011, 11(7): 493-501. |
| [6] | Mazumdar T, DeVecchio J, Shi T, et al. Hedgehog signaling drives cellular survival in human colon carcinoma cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2011, 71(3): 1092-102. |
| [7] | Von Hoff DD, LoRusso PM, Rudin CM, et al. Inhibition of the hedgehog pathway in advanced basal-cell carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2009, 361(12): 1164-72. |
| [8] | LoRusso PM, Rudin CM, Reddy JC, et al. Phase I trial of hedgehog pathway inhibitor vismodegib (GDC-0449) in patients with refractory, locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2011, 17(8): 2502-11. |
| [9] | Matsushita S, Onishi H, Nakano K, et al. Hedgehog signaling pathway is a potential therapeutic target for gallbladder cancer[J]. Cancer Sci, 2014, 105(3): 272-80. |
| [10] | Stecca B, Ruiz I Altaba A. Context-dependent regulation of the GLI code in cancer by HEDGEHOG and non-HEDGEHOG signals[J]. J Mol Cell Biol, 2010, 2(2): 84-95. |
| [11] | Li H, Lui N, Cheng T, et al. Gli as a novel therapeutic target in malignant pleural mesothelioma[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(3): e57346. |
| [12] | Lauth M, Bergström A, Shimokawa T, et al. Inhibition of GLI-mediated transcription and tumor cell growth by small-molecule antagonists[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2007, 104(20): 8455-60. |
| [13] | Fu J, Rodova M, Roy SK, et al. GANT-61 inhibits pancreatic cancer stem cell growth in vitro and in NOD/SCID/IL2R gamma null mice xenograft[J]. Cancer Lett, 2013, 330(1): 22-32. |
| [14] | Chen JS, Li HS, Huang JQ, et al. Down-regulation of Gli-1 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2014, 393(1-2): 283-91. |
| [15] | Lei J, Ma J, Ma Q, et al. Hedgehog signaling regulates hypoxia induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition and invasion in pancreatic cancer cells via a ligand-independent manner[J]. Mol Cancer, 2013, 12: 66. |
 2016, Vol. 43
2016, Vol. 43