2.乳腺科;
3.武汉大学中南医院肿瘤科
2.Department of Breast Surgery;
3.Department of Surgical Oncology,Zhongnan Hospital,Wuhan University
三阴性乳腺癌(Triple negative breast cancer,TNBC) 是ER、PR、HER2 蛋白表达均为阴性的乳腺癌。 由于其缺乏雌激素受体表达,对内分泌治疗不敏 感,预后相对较差,多以内脏转移为特点,近年 来引起广泛关注。不过,该类型乳腺癌的生物学 异质性也很强,不同个体间的临床表现差异很 大,需要寻找对其进一步区分的方法,并从分子 水平加深对其生物学机制的认识。
上皮间叶转化(Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions, EMT)是癌症发生转移的可能机制之一,它以上皮 细胞极性的丧失及间质特性的获得为重要特征。 E-cadherin、β-catenin及Vimentin均为EMT相关的 重要指标,本研究检测其在三阴性乳腺癌中的表 达。 1 资料与方法 1.1 一般资料
采用本研究团队的一组240例乳腺癌病例数据 库,前期系列研究[1]已收集完整临床病理参数, 并完成ER、PR、HER2的检测,本研究取其中的51例三阴性乳腺癌原发灶石蜡包埋标本,检测 E-cadherin、β-catenin及Vimentin的表达,具体如下。
51例三阴性乳腺癌为2002年1月—2003年12 月在湖北省肿瘤医院乳腺科住院治疗患者。均为 女性,年龄29~69岁,中位年龄50岁;绝经前 34例,绝经后17例。原发灶直径≤2 cm者4例, 2.1~5 cm者36例,>5 cm者11例;17例接受过 1~4周期的新辅助化疗。全部患者均经手术治 疗,其中根治术7例,改良根治术44例。这些患者 均经病理学确诊为乳腺癌,其中导管浸润癌非特 殊型44例、小叶浸润癌1例、导管浸润癌特殊型6 例;病理分级Ⅰ级3例,Ⅱ级23例,Ⅲ级25例。腋 窝淋巴结阳性25例,阴性26例。术后均给予辅助 化疗,其中46例为含蒽环类和(或)紫杉类化疗药 物方案。淋巴结阳性患者给予放疗。 1.2 随访
将手术治疗作为随访起始时间,以5年内发现 局部或远处复发为终止事件,随访截止日期为2009 年12 月30 日。共24例出现局部复发或远处转移, 其中肺转移4例,肝转移1例,骨转移4例,脑转移 2例,其他部位复发13例。 1.3 免疫组织化学染色
E-cadherin、β-catenin和Vimentin单克隆抗体均 购自北京中杉金桥生物技术公司。实验步骤:取 51例乳腺癌原发灶石蜡包埋标本,切片厚4 μm, 微波煮沸抗原修复,置于PBS中;滴加3%过氧化 氢阻断内源性过氧化物酶,孵育10 min;蒸馏水漂 洗,置于PBS中10 min,加一抗室温孵育1 h;PBS 漂洗10 min,滴加EnVision 试剂孵育30 min;PBS 漂洗10 min,二氨基联苯胺光学显微镜控制下显 色;蒸馏水洗,复染、封片。 1.4 结果判定
由两位病理医生独立阅片,确定免疫组织化 学结果。两位阅片专家意见不一致时则经商讨决 定结果。
采用半定量计分法判定,以癌细胞染色百 分比及染色强度两方面分别计分,综合评判。 其中癌细胞染色<5%为0分;5%~35%为1分; >35%~70%为2分;>70%为3分;癌细胞按染色强 度分为4等:0分为无染色;1分为浅黄色;2分为 棕黄色;3分为棕褐色。综合计分:染色强度计分 ×染色百分比计分。将0~2分定为阴性,2分以上 定为阳性。 1.5 统计学方法
采用SPSS 12.0统计软件进行分析。单因素生 存分析采用Kaplan-Meier法计算,Log-rank检验。 多因素分析采用Cox回归模型计算,P<0.05为差异 有统计学意义。 2 结果 2.1 E-cadherin和β-catenin在三阴性乳腺癌中的表达及与Vimentn的联合表达情况
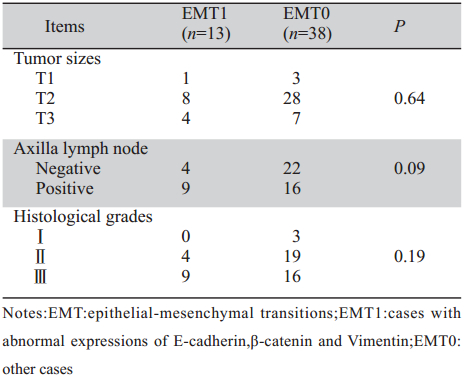
E-cadherin和β-catenin在三阴性乳腺癌中均以细 胞膜表达为主,伴随部分细胞质表达,未见细胞核表 达,见图1。其阳性表达例数分别为27例(52.94%), 7例(13.73%)。正常情况下,Vimentin在间质细胞 中呈阳性反应,而癌细胞中呈阴性反应,本实验 以癌细胞中的Vimentin表达进行计分,间质细胞中 的表达不作统计。结果,我们检测到Vimentin阳性 表达有31(60.78%)例。
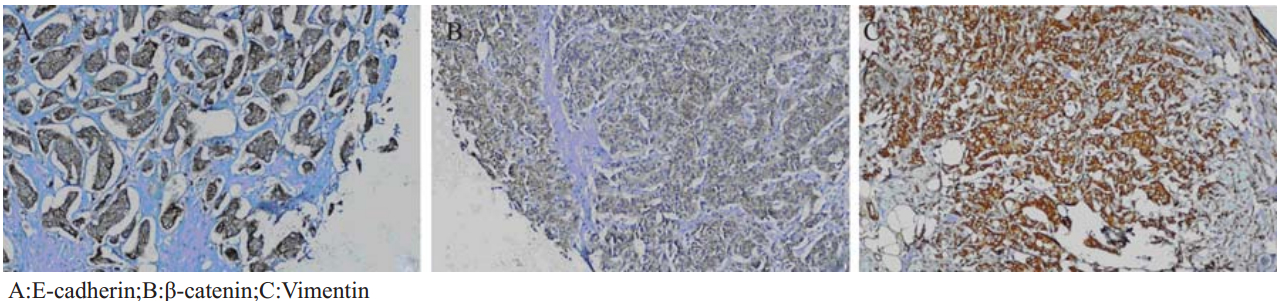 |
图1 E-cadherin、ß-catenin、Vimentin在三阴性乳腺癌中的表达(Envision法×100) Figure 1 Positive expressions of E-cadherin, ß-catenin and Vimentin in triple-negative breast cancer(Envision ×100) |
如果定义E-cadherin阴性、β-catenin阴性或 Vimentin阳性为异常表达,则在本组病例中,三项 均正常、一或二项不正常以及三项均不正常的分 别有1例(1.96%)、37例(72.55%)、13例(25.49%)。 将三项表达均不正常的病例定义为EMT1组,共13 例;其余为EMT0组,共38例,见图2。
 |
图2 E-cadherin、ß-catenin、Vimentin在EMT分组中的表达及复发情况 Figure 2 Expressions of E-cadherin, ß-catenin and Vimentin and recurrence in EMT groups |
以5年无瘤生存(5-year DFS)为参数指标做比 较,单因素分析,EMT1组的复发病例数较EMT0 组明显增多,差异有极显著统计学意义(Log-rank 检验,P<0.01),其Kaplan Meier无瘤生存(DFS) 曲线见图3。进一步通过Cox模型多因素分析,比较 两组的传统预后相关指标:肿瘤大小、腋窝淋巴结 状态和组织学分级等发现,它们在两组间的差异无 统计学意义(P>0.05),见表1。
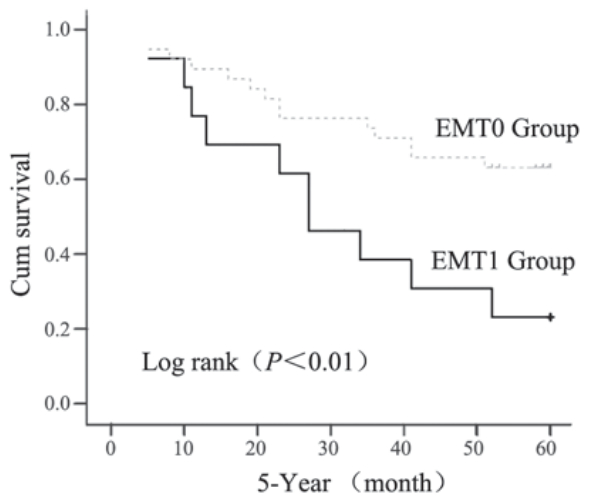 |
图3 单因素分析EMT分组与5年无瘤生存的关系 Figure 3 单因素分析EMT分组与5年无瘤生存的关系 |
|
|
表1 Cox模型多因素分析比较EMT1及EMT0结果 Table 1 Cox regression model analysis results |
三阴性乳癌患者约占乳腺癌人群的10% ~16%[2]。其总体临床病理特征是:肿瘤体积较 大,组织学分级较高,较非三阴性乳腺癌患者无 瘤生存率和总生存率均显著降低;与其他类型乳 腺癌相比,亦较早发生局部复发和远处转移[3, 4, 5, 6], 内脏转移率高于骨转移,易发生脊髓、脑膜、 脑、肝和肺转移,但其机制尚不明确。
Thompson 等[6]将波形蛋白在上皮性肿瘤细胞 的表达,以及促进肿瘤细胞侵袭转移的现象定义为 EMT,即上皮-间叶转化。它以上皮细胞极性的丧 失及间质特性的获得为重要特征[7]。 E-cadherin为重要的细胞黏附分子,是一类建
立细胞间紧密连接,维持细胞极性,保持组织结构 完整的钙依赖性跨膜糖蛋白. 作为抑癌基因,其 所介导的黏附系统已被公认为“浸润抑制系统”[8], 能抑制肿瘤细胞从原发灶脱落,为重要的肿瘤转 移抑制因素之一。E-cadherin的功能不仅需要钙 离子存在,还需要与其配体-连接素(β-catenin)结 合成E-cadherin-β-catenin复合体才能发挥作用。 β-catenin在细胞膜上与E-cadherin形成复合体, 共同参与细胞之间的黏附作用。E-cadherin、 β-catenin的表达下调使得细胞间的黏附能力下降, 转移和侵袭能力增强。在多种肿瘤中(如结肠 癌、肺癌等)也发现E-cadherin/β-catenin复合体的 破坏,与肿瘤的复发转移密切相关[7, 9, 10, 11]。
EMT的另一个重要标志是间叶标记的表达, 如Vimentin等,许多研究显示,波形蛋白的表达与 肿瘤的分化程度以及细胞侵袭的表现型和肿瘤患 者的生存期缩短相关[12, 13]。
在本组三阴性乳腺癌中,我们发现绝大部分 病例伴随着不同程度的E-cadherin/β-catenin复合 体的破坏和(或)Vimentin的异常表达。我们认 为这可能是癌细胞在浸润转移过程中发生EMT的 结果,而这也很可能是其预后较差的重要原因。 E-cadherin、β-catenin和Vimentin都是上皮间叶转化 的重要标志物,其表达异常已在多种肿瘤中分别 被证实与预后相关[14, 15]。但将它们联合检测并用于 预后判断的研究很少见。本组51例中同时检测到 三种标志物异常表达的有13例(25.49%),其5年无 瘤生存率明显低于其他病例。我们分析认为,这 些标志物同时异常表达或部分异常表达可能代表着EMT发生的不同水平状态。由于病例数较少, 我们不能分析其中两种或一种标志物异常时的预 后与它们之间的差异。也可能正是这个原因,在 多因素分析中,我们没有看到统计学上的差异。
不过,EMT受庞大的细胞信号网络的调节, 其作用机制十分复杂,EMT的发生可以是瞬时 的,并且可以被微环境的调节所逆转[8],其在肿瘤 转移中所起的作用也存在一定争议,Lou 等[16]研 究发现,大量原发乳腺癌细胞67NR表达Vimentin, 不表达E-cadherin,但是不发生转移; 4T1细胞表达 E-cadherin但可以转移;66cl4 细胞表达混合型表型 且发生肺转移。这一结果提示,乳腺癌细胞的转移 能力并不与EMT严格相关。
稳态的肿瘤细胞要进入细胞间质完成浸润必 需挣脱细胞之间的黏附,突破基底膜屏障。EMT为 这个破环过程的潜在机制提供了一个新的视野。 已知EMT 相关的上调和下调蛋白与肿瘤的发展相 关。三阴性乳腺癌其实是一个异质性很强的乳腺 癌群体,其中也包括了一部分预后良好的患者, 只是目前还缺乏有效的分类方法。EMT相关蛋白 在三阴性乳腺癌中的表达异常可能从一个方面预 示着其容易发生转移的机制,其适当应用可能对 区分该类型乳腺癌的异质性有一定价值。当然, 本研究病例数有限,所得结论有待进一步验证。
| [1] | Chen C, Xia HS, Gong YP, et al. The quantitative detection of total HER2 load by quantum dots and the identification of a new subtype of breast cancer with different 5-year prognosis[J]. Biomaterials,2010,31(33):8818-25. |
| [2] | Bauer KR,Brown M,Cress RD,et a1.Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor(ER)-negative, progesterone receptor(PR)-negative, and HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative phenotype: a population-based study from the California cancer Registry[J]. Cancer,2007,109(9):1721-8. |
| [3] | Rakha EA,El-Sayed ME,Green AR.Prognostic markers in triplenegative breast cancer[J]. Cancer,2007,109(1):25-32. |
| [4] | Nielsen TO,Hsu FD,Jensen K,et a1.Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma[J]. C1in Cancer Res,2004,10(16):5367-74. |
| [5] | Dent R,Trudeau M,Pritchard KI,et a1.Triple-negative breast cancer:clinical features and patterns of recurrence[J]. Clin Cancer Res,2007,13(15 Pt 1):4429-34. |
| [6] | Thompson EW, Newgreen DF, Tarin D. Carcinoma invasion and metastasis: a role for epithelial-mesenchymal transition?[J]. Cancer Res, 2005, 65(14) : 5991- 95. |
| [7] | Hugo H, Ackland ML, Blick T, et al. Epithelial--mesenchymal and mesenchymal--epithelial transitions in carcinoma progression[J]. J Cell Physiol. 2007, 213(2):374-83. |
| [8] | Baumgart E, Cohen MS, Silva Neto B, et al. Identification and prognostic significance of an epithelial-mesenchymal transition expression profile in human bladder tumors[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2007, 13(6): 1685-94. |
| [9] | Aamodt R, Bondi J, Andersen SN, et al. The prognostic impact of protein expression of E-cadherin-catenin complexes differs between rectal and colon carcinoma[J]. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2010,2010. |
| [10] | Kang H, Min BS, Lee KY, et al. Loss of E-cadherin and MUC2 expressions correlated with poor survival in patients with stages ⅡandⅢcolorectal carcinoma[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2010, 18(3): 711-9. |
| [11] | Chelidonis G, Kavantzas N, Patsouris E, et al. DNA ploidy, E-cadherin, beta-catenin expression and their clinicopathologic significance in imprints of non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Anal Quant Cytol Histol, 2009, 31(5): 332-9. |
| [12] | Moody SE, Perez D, Pan TC, et al. The transcriptional repressor Snail promotes mammary tumor recurrence[J]. Cancer Cell, 2005, 8(3): 197-209. |
| [13] | Willipinski-Stapelfeldt B, Riethdorf S, Assmann V, et al. Changes in cytoskeletal protein composition indicative of an epithelialmesenchymal transition in human micrometastatic and primary breast carcinoma cells[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2005, 11(22): 8006-14. |
| [14] | Gong YP,Qi CB,Wang MW,et al.Prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer and its relevance to epithelial-mesenchymal transitions[J].Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu,2012,39(2):173-6.[龚益平,漆楚波,王明伟,等.三阴性乳腺癌的预后与上皮间叶转化的相关性[J].肿瘤防治研究,2012,39(2):173-6.] |
| [15] | Wu Y,Li M,Tian YZ,et al.The expression of CD44v6 and E-cadherin are related with prognosis in invasive breast cancer[J].Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu,2006,33(11):791-4.[吴岳,李敏,田育璋,等.CD44v6、E-cadherin表达与乳腺浸润性癌预后的关系[J].肿瘤防治研究,2006,33(11):791-4.] |
| [16] | Lou Y, Preobrazhenska O, auf dem Keller U, et al. Epithelialmesenchymal transition (EMT) is not sufficient for spontaneous murine breast cancer metastasis[J]. Dev Dyn, 2008, 237(10): 2755-68. |
 2014, Vol.41
2014, Vol.41