2.华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院肿瘤中心
2.Cancer Center, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology
鼻咽癌是我国常见的头颈部肿瘤之一,随着 诊疗设备及技术的不断进步,鼻咽癌患者五年生 存率得到了显著提高。但其局部浸润及转移仍然 是治疗失败的主要原因。肿瘤细胞的侵袭、转 移过程十分复杂,是多因素共同作用的结果, 有研究表明上皮间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)可能在肿瘤细胞侵袭和转移过程中 起着关键性作用[1]。EMT是指在生理和病理状态下 上皮细胞向间质转化,同时伴有细胞形态学及相 关基因表达的改变。E-钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)和N- 钙黏蛋白(N-cadherin)是EMT中两个标志性蛋白。 在多项研究中[2, 3, 4]均发现E-cadherin的低表达和 N-cadherin异常表达与肿瘤的浸润和转移有关。 但有关E-钙黏蛋白和N-钙黏蛋白在鼻咽癌组织中 的表达及其临床意义尚未见报道。本实验通过 研究鼻咽癌和慢性鼻咽炎性组织中E-cadherin、 N-cadherin的表达情况与鼻咽癌临床病理特征之间 的相关性,探讨他们在预测鼻咽癌侵袭及转移潜 能中的意义。 1 资料与方法 1.1 一般资料
收集2006年1月1日—2011年12月31日华中科 技大学同济医学院附属协和医院耳鼻喉科鼻咽镜 活检确诊的鼻咽癌标本72例,所有病例确诊前均 未行放化疗,临床资料齐全;另取慢性鼻咽黏膜 炎症组织12例作对照。所有标本均为病理科包埋 好的石蜡切片。在72例鼻咽癌标本中,男56例, 女16例;年龄15~76岁,≥50岁38例,<50岁34 例;角化性鳞癌(WHOⅠ型)2例,分化型非角 化性癌(WHOⅡ型)5例,未分化癌(WHOⅢ 型)65例。浸润深度T1~T2的25例,T3~T4的47 例;N0~N1有18例,N2~N3有54例;临床分期在 Ⅰ+Ⅱ期的6例,Ⅲ+Ⅳ期的66例。TNM分期及临床 分期以2002年AJCC分期为标准。 1.2 免疫组织化学染色
免疫组织化学技术采用SABC法,操作按试 剂盒说明书进行。单克隆兔抗人E-cadherin购自 美国Cell Signaling Technology公司,多克隆羊抗 人N-cadherin购自美国R&D公司,免疫组织化学 SABC试剂盒购自武汉博士德生物有限公司。大 概步骤如下:石蜡包埋组织切片、脱蜡、水化, 3%H2O2消除内源性过氧化物酶活性,枸橼酸盐缓 冲液修复抗原,5%BSA封闭液,室温放置20~30 min。每张切片滴加单克隆兔抗人E-cadherin稀 释液(1:200)、多克隆羊抗人N-cadherin稀释液 (1:400)各100 μl,4℃过夜。滴加SABC盒中生 物素化二抗IgG,37℃ 30 min。DAB染色,苏木精 对比染色,封片,光学显微镜下观察。 所有切 片均在相同条件及相同批次完成免疫组织化学染 色,以PBS液代替一抗作为阴性对照。 1.3 结果判断
免疫组织化学结果以阳性细胞所占的百分数 以及染色强度进行分级。在光学显微镜下对切片 染色情况进行评估,免疫组织化学反应以细胞 膜、细胞质或细胞核出现棕黄色颗粒为阳性。其 结果判断标准如下:用高倍镜(40×10)在每张切片 上观察5个视野,计数100个癌细胞。染色强度: 根据着色的强弱程度评分,无着色为0分,淡黄 色为1分,棕黄色为2分,棕褐色为3分。阳性细胞 率:按阳性细胞所占百分比计分,阳性细胞率≤ 10%为1分,>10%且≤50%为2分,>50%为3分; 根据染色强度和阳性细胞所占百分比两项得分的 乘积划分为两组:弱表达或无表达为0~4分, 阳性 表达为6、9分。 1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS17.0统计学软件进行处理。应用χ2 检验分析E-cadherin、N-cadherin在鼻咽癌组织及 慢性鼻咽炎性组织中的表达情况及与患者临床病 理特征之间的关系;应用Spearman等级相关分析 E-cadherin与N-cadherin表达之间的相关性。以P <0.05为差异有统计学意义。 2 结果 2.1 鼻咽癌组织和鼻咽炎性组织中E-cadherin和 N-cadherin的表达
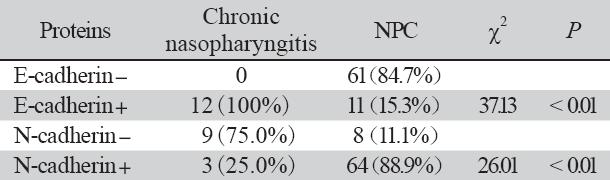
E-cadherin阳性表达位于胞膜或胞质,上皮细 胞均可见阳性表达呈连续的线状,为淡黄色到棕 黄色颗粒,见图1A。N-cadherin阳性表达主要位 于胞质和细胞核内,呈浅黄色到棕黄色颗粒均匀 分布,见如图1D。E-cadherin在慢性鼻咽炎性组 织中的表达率为100%(12/12)明显高于鼻咽癌 组织中表达率15.3%(11/72),差异具有统计学 意义P<0.05。N-cadherin在鼻咽癌组织中表达率为 88.9%(64/72)高于慢性鼻咽炎性组织表达率25% (3/12),两者差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05), 见表1。
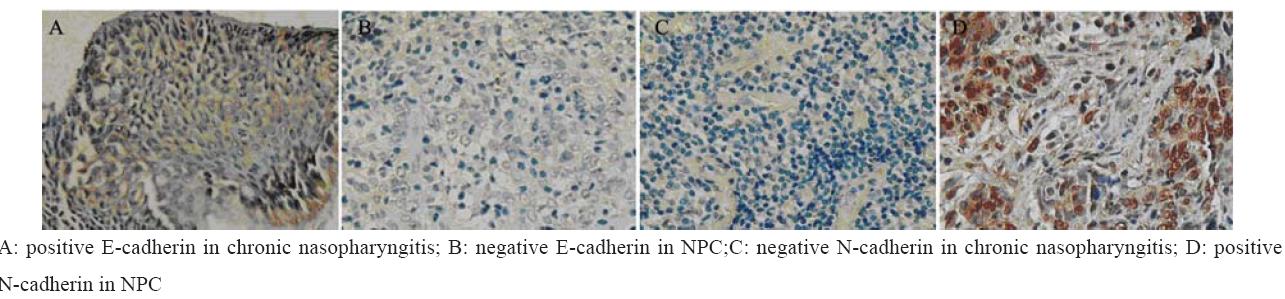 |
图1 E-cadherin和N-cadherin在鼻咽癌和鼻咽炎性组织中的表达情况 Figure1 The expression of E-cadherin and N-cadherin in samples of NPC and chronic nasopharyngitis |
|
|
表1 E-cadherin、N-cadherin在鼻咽慢性炎性组织和鼻咽癌组织中表达差异比较 Tab1e1 The different expression of E-cadherin and N-cadherin in samples of NPC and chronic nasopharyngitis |
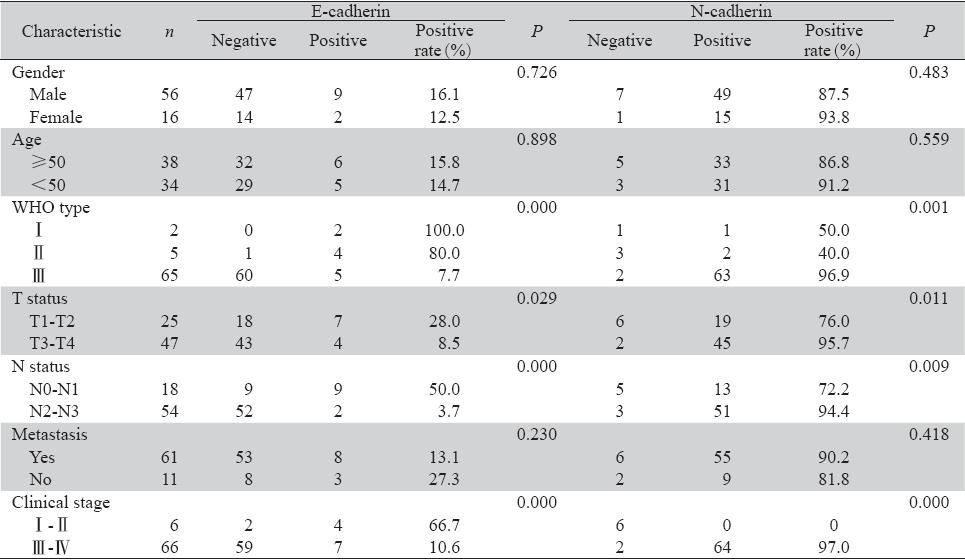
E-cadherin蛋白的表达与鼻咽癌的性别、年 龄及远处转移无明显相关(P>0.05),与WHO分 型、淋巴结转移、肿瘤T分期及临床分期显著相关(P<0.05)。在原发灶分期为T3~T4、淋巴结转 移分期N2~N3及临床分期为Ⅲ~Ⅳ期的癌组织中, E-cadherin的表达程度显著低于T1~T2期和N0~N1 期。
鼻咽癌患者中N-cadherin蛋白的表达与性别、 年龄及远处转移无明显相关(P>0.05),与病理 分型、淋巴结转移、肿瘤大小及临床分期显著相 关(P<0.05)。在原发灶分期为T3~T4、淋巴结 转移分期N2~N3及临床分期为Ⅲ~Ⅳ期的癌组织中 N-cadherin的表达程度明显高于T1~T2期、N0~N1 期和Ⅰ~Ⅱ期,见表2。
|
|
表2 E-cadherin、N-cadherin的表达与鼻咽癌不同临床病理特征的关系 Table2 The relationship between E-cadherin or N-cadherin and pathological features |
本组E-cadherin阳性表达11例中,N-cadherin 亦阳性表达者5例;E-cadherin阴性表达61例中, N-cadherin亦阴性者2例,经Spearman等级相关分 析,相关系数r=-0.587,P=0.000,两种蛋白表达 水平具有负相关性。 3 讨论
E-cadherin是一种跨膜糖蛋白,能与Ca特异性 地结合而发挥细胞黏附功能。E-cadherin普遍存在 于各类正常的上皮细胞中,介导同型细胞之间的 连接,在维持正常的上皮细胞形态、稳定细胞极性 及保持组织结构的完整性方面发挥着重要作用[5]。 最早在1989年Hashimoto等[6]首先在高侵袭性卵巢 癌细胞中发现E-cadherin表达下降,后来许多学者 在结直肠癌[7]、肺癌[8]、胃癌[9]、宫颈癌[10]等恶性 肿瘤的研究中发现E-cadherin的表达均有不同程度 的下调,同时表明E-cadherin的下调程度与肿瘤的 分化程度、分期、远处转移、侵袭性以及预后有 着密切的关系。
N-cadherin的高表达与肿瘤的浸润和转移密 切相关,其与E-cadherin的作用恰好相反,研究发 现,N-cadherin可促使肿瘤细胞从肿瘤原位中脱离 出来并与内皮或基质成分黏附,使上皮细胞向间 质细胞转化,从而具有侵袭性表型并且易于远处 转移[11]。多个体外实验中也表明了在N-cadherin表 达阴性的肿瘤细胞转染N-cadherin后,细胞的侵袭 能力明显增强,同时E-cadherin介导的细胞间黏附 作用缺失,E-cadherin的表达明显下降[12, 13, 14]。Hanan等[15]在乳腺癌的研究中发现,N-cadherin在乳腺癌 组织中的表达率为51.9%,明显高于正常乳腺上皮 组织,N-cadherin的高表达同肿瘤分化程度不良、 淋巴结转移数量、较差的预后相关。
本实验中我们通过免疫组织化学检测发现, E-cadherin在慢性鼻咽炎性组织中阳性表达率高 于鼻咽癌组织,而N-cadherin在慢性鼻咽炎性组 织中阳性表达率低于鼻咽癌组织。E-cadherin在 T3~T4、N2~N3分期中蛋白表达率明显低于T1~T2 和N0~N1期,而N-cadherin在T3~T4、N2~N3分期 中蛋白表达率明显高于T1~T2和N0~N1期,差异 具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。随着T及N分期的增 加,E-cadherin表达呈下降趋势。N-cadherin表达 的趋势则与前者恰好相反,说明E-cadherin表达 下调和N-cadherin表达的增加可能与鼻咽癌的淋 巴结转移率增加及肿瘤浸润深度的加深有密切关 系。本实验还通过Spearman相关性得出E-cadherin 与N-cadherin的表达呈负相关(r=-0.587, P=0.000),进一步证实在鼻咽癌的发生发展过程 中EMT的存在。 近些年的研究[16]显示,在肠癌、 肝癌和乳腺癌等多种肿瘤中EMT与肿瘤细胞的局 部浸润和转移有着密切的关系。而E-cadherin和 N-cadherin是EMT的重要标志物[17]。上皮间质转化 过程中E-cadherin表达下调的同时N-cadherin表达 上调,被称为钙黏蛋白转换。钙黏蛋白转换同时 肿瘤细胞骨架系统排列会发生变化,细胞的生物 性状也会发生改变,其黏附能力下降,随之容易 脱离原发部位,向远处浸润或转移。
总之,上述研究提示,联合检测鼻咽癌中的 E-cadherin、N-cadherin在预测鼻咽癌的侵袭性和 淋巴结转移风险方面有一定的参考价值。本实验 也间接提示鼻咽癌进展过程中EMT的存在,下一 步我们将从细胞通路的分子机制中进一步证实鼻 咽癌中的EMT,并寻找阻断EMT潜在的靶点。
| [1] | Zhao RZ. Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition and Tumor etastasis[J]. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi,2011,14(7):620-4. |
| [2] | Araki K, Shimura T, Suzuki H, et al.E/N-cadherin switch mediates ancer progression via TGF-β-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal ransition in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[J].Br J Cancer,2011 105(12):1885-93. |
| [3] | ElMoneim HM, Zaghloul NM. Expression of E-cadherin, -cadherin and snail and their correlation with clinicopathological ariants: an immunohistochemical study of 132 invasive ductal reast carcinomas in Egypt[J].Clinics (Sao Paulo),2011,66(10): 765-71. |
| [4] | Li S,Jiao J. Effects of N-cadherin expression on cell cycle, cell poptosis and invasiveness and metastasis of tongue squamous ell carcinoma cell line Tca8113 cells[J].Zhong Hua Kou Qiang i Xue Za Zhi,2011,46(6):365-9.[李莎, 焦静. 神经钙黏素表达下 对舌鳞状细胞癌细胞生物学能力的影响[J].中华口腔医学杂 ,2011,46(6):365-9.] |
| [5] | Ray ME, Mehra R, Sandler HM, et al. E-cadherin protein xpression predicts prostate cancer salvage radiotherapy utcomes[J]. J Urol,2006,176(4Pt 1): 1409-14. |
| [6] | Hashimoto M,Niwa O,Nitta Y,et a1.Unstable expression of -cadherin adhesion molecules in metastatic ovarian tumor ells[J]. Jpn J Cancer Res,1989,80(5):459-63. |
| [7] | Gao H,Liang H. Evaluation of E-cadherin in the prediction of liver etastasis of colorectal carcinoma[J]. Tianjin Yi Ke Da Xue Xue ao, 2007,13(3):422-4. [高浩,梁寒.E-钙粘蛋白在预测结直 癌肝转移中的价值[J]..天津医科大学学报,2007,13(3):422-4.] |
| [8] | Liu D,Huang C,Kameyama K,et a1.E-cadherin expression ssociated with diferentiation and prognosis in patients with nonsmall ell lung cancer[J]. Ann Thorac Surg,2001,71(3):949-54. |
| [9] | Ma Z,Wu H,Wei R. The research on the relationship among -cadherin,VEGF-C and gastric cancer clinical pathology[J]. hanxi Zhong Yi Xue Yuan Xue Bao,2009,10(4):56-7. [马钊,武华, 瑞. E-cadherin、VEGF-C与胃癌临床病理学关系的研究[J].山西中医学院学报,2009,10(4):56-7.] |
| [10] | Zhang Q,Zhang CJ.The expression and its sinifi cance of P120ctn nd E-cad in the tissues and cell lines of cervical squamous cell aicinoma[J]. Shi Yong Yi Xue Jin Xiu Za Zhi,2007,35(4):213-8. |
| [11] | Shih W, Yamada S. N-cadherin as a key regulator of ollective cell migration in a 3D environment[J]. Cell Adh igr,2012,6(6):513-7. |
| [12] | Hazan RB, Phillips GR, Qiao RF,et al. Exogenous expression of -cadherin in breast cancer cells induces cell migration,invasion nd metastasis[J]. J Cell Biol,2000,148(4):779-90. |
| [13] | Nieman MT, Prudoff RS, Johnson KR,et al. N-cadherin promotes otility in human breast cancer cells regardless of their E-cadherin xpression[J]. J Cell Biol,1999,147(3):631-44. |
| [14] | Li G, Satyamoorthy K, Herlyn M. N-cadherin-mediated ntercellular interactions promote survival and migration of elanoma cells[J]. Cancer Res,2001,61(9):3819-25. |
| [15] | ElMoneim HM, Zaghloul NM. Expression of E-cadherin, -cadherin and snail and their correlation with clinicopathological ariants: an immunohistochemical study of 132 invasive ductal reast carcinomas in Egypt[J]. Clinics (Sao Paulo),2011,66(10): 765-71. |
| [16] | Yap AS, Crampton MS, Hardin J. Making and breaking contacts: he cellular biology of cadherin regulation[J].Curr Opin Cell iol,2007,19(5):508-14. |
| [17] | Prasad CP,Rath G,Mathur S,et al. Expression analysis of -cadherin, Slug and GSK3beta in invasive ductal carcinoma of reast[J]. BMC Cancer,2009, 9:325. |
 2014, Vol.41
2014, Vol.41