2.肝胆外科;
3.河北省中医院脾胃病科;
4.河北医科大学第二附属医院微创外科
2.Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery,
3.Department of Spleen and Stomach Diseases,Chinese Medicine Hospital of Hebei Province;
4.Department of Minimally Invasive Surgery,The Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University
去甲斑蝥素(norcantharidin,NCTD)是从我国传 统抗肿瘤中药斑蝥中提取的斑蝥素的衍生物,由 于其特殊的升白细胞作用,近年来被广泛应用于 临床对各种肿瘤的治疗和术后的化疗中,同时大 量的体外实验也证实了去甲斑蝥素有抑制肝癌、 乳腺癌、胆管癌[1, 2, 3]等肿瘤细胞生长,促进肿瘤细胞凋亡的作用。但当前对结肠癌细胞的体外研 究报道较少,且其潜在的抑癌机制也有待研究。 STAT3通路的持续活化可导致细胞的异常增生, 抑制细胞凋亡,促使细胞向恶性转化,因此被公 认为是一种癌基因[4, 5, 6],同时大量研究表明在结肠 癌中存在JAK3和STAT3持续高表达,STAT3的持 续活化不仅促进结肠肿瘤的生长,并且促进肿瘤细 胞的扩散[7, 8, 9]。近年来对NCTD抗肿瘤作用的研究 证实:NCTD可以通过调控细胞周期、诱导细胞 凋亡、抗肿瘤血管及淋巴管形成从而阻止肿瘤的 转移来实现其抗肿瘤作用[10]。其中大量研究证实 了去甲斑蝥素可以通过线粒体通路激活caspase系 统引起肿瘤细胞的凋亡[11, 12],同时也有研究证实 NCTD可以通过分别激活JNK激酶依赖性通路、 TRAIL/DR5信号转导通路以及TR3依赖性通路来 抑制肿瘤细胞生长、促进肿瘤细胞凋亡 [13, 14, 15] ,但对 于JAK-STAT通路研究报道较少。 本研究旨在探讨去甲斑蝥素对体外结肠癌LS- 174T细胞的生长抑制作用,同时研究去甲斑蝥素 作用下STAT3及其下游相关抗凋亡蛋白的表达,从 而探讨去甲斑蝥素可能的促凋亡机制,为临床的应 用提供实验依据。 1 材料与方法 1.1 药品与试剂
去甲斑蝥素和DMSO购自美国Sigma公司; RPMI1640购自美国Gibco公司, 四甲基偶氮唑盐 (MTT)购自Biosharp公司,吖啶荧光染料购自罗 莱宝科技有限公司,胎牛血清购自杭州四季青公 司,兔抗人bax、stat3、Mcl-1、survivin多克隆抗 体购自美国Bioworld公司,兔抗人β-actin单克隆抗 体购自美国Abcam公司,Annexinv凋亡检测试剂盒 购自北京宝赛生物试剂有限公司。 1.2 细胞系及细胞培养
人结肠癌LS-174T细胞购自中国生命科学院上 海生命研究所,以含10%胎牛血清、100 u/ml青霉 素和100 μg/ml链霉素的RPMI1640培养液于温度 37℃、5%CO2温箱中培养,待细胞贴壁,取对数 生长期细胞进行实验。 1.3 MTT法检测去甲斑蝥素对LS-174T细胞的生长 抑制作用
取生长对数期的LS-174T细胞,将其消化成 单细胞悬液,调整细胞终浓度为1×105/ml,以每 孔200 μl接种于96孔培养板中,培养24 h,待细胞 贴壁后,弃上清液,分别加入质量浓度为5、10、 20和40 μg/ml的去甲斑蝥素培养,同时设空白组 (DMSO溶剂对照组)和阴性对照组(不加药物 组),每个浓度设6个复孔。加药作用24、48、72 h,每孔加入20 μl MTT(5 mg/ml),于培养箱中继 续培养4 h,弃上清液,每孔加入200 μlDMSO,充 分振荡,使蓝紫色颗粒完全溶解。Ascent酶标仪检 测OD490值,计算细胞生长抑制率IR=(1-实验组 OD值/对照组OD值)×100%,绘制细胞生长曲线。 1.4 荧光显微镜下细胞形态学观察
将对数生长期的LS-174T细胞消化,收集并 调整细胞至1×105个/毫升,接种于6孔板中进行爬 片,培养24 h待细胞贴壁生长后,弃去培养液,分 别加入质量浓度为10、40 μg/ml的去甲斑蝥素,同 时设阴性对照组,培养箱中继续培养24 h后,弃上 清液,PBS洗涤,4%多聚甲醛固定10 min,滴加 AO/EB等体积混合染料,迅速置于荧光显微镜下 观察并拍照。 1.5 透射电子显微镜观察细胞超微结构的变化
收集0、10、40 μg/ml去甲斑蝥素作用24 h 后的结肠癌LS-174T细胞以2 000 r/min,离心10 min,小心吸尽上清液,沿管壁加入2.5%的戊二 醛,4℃保存,之后加入1%的锇酸4℃固定2 h,用 梯度丙酮脱水,用Epon 618纯化树脂浸透,包埋, 烤箱中聚合后,用莱卡(Leica)超薄切片机制成 切片,经醋酸铀和柠檬酸铅双重染色后,用透射 电子显微镜观察及拍照。 1.6 流式细胞术AnnexinV-FITC/PI染色法
收集阴性对照组细胞和药物组(5、10、20、 40 μg/ml)作用24 h后细胞,于室温2 000 r/min, 离心10 min,收集细胞,用预冷PBS重悬细胞, 2 000 r/min离心10 min,洗涤细胞,加入300 μl Binging Buffer 悬浮,加入5 μl AnnexinV-FITC混匀 后,避光,室温孵育15 min,上机前5 min加入5 μl PI,补加200 μl的1×Binding Buffer,上流式细胞仪检 测。 1.7 Western blot法检测 stat3、survivin、Mcl-1、 bax的蛋白表达
收集对照组和药物组(5、10、20、40 μg/ml) 作用24 h后细胞,PBS洗涤两遍,分别加入300 μl 蛋白裂解液,冰上作用1 h,12 000 r/min,离心10 min,取上清液,样品置于-80℃保存,Bradford 法测定蛋白质浓度,每个样品孔加入50 μg蛋白, 进行12%SDS-PAGE分离蛋白,将蛋白转移到 PVDF膜上,1%BSA 37℃封闭1 h,加入1:500稀释 的survivin、stat3、Mcl-1和bax多克隆抗体,室温振荡5 h,洗膜后,荧光二抗(抗兔lgG)避光孵育 1 h,洗膜,发光。 1.8 统计学方法
应用SPSS13.0软件进行统计学分析,检验数 据用单因素方差分析和t检验,数据用均数±标准 差(x±s)表示。 2 结果 2.1 去甲斑蝥素对结肠癌LS-174T细胞的抑制作用
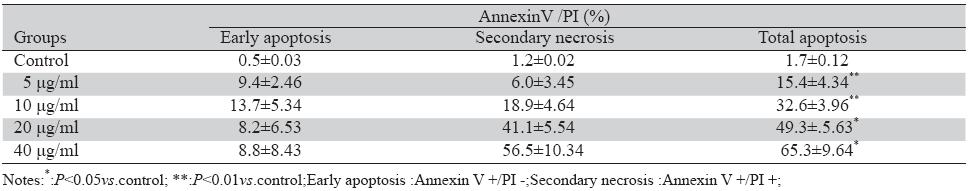
MTT结果表明:药物作用组NCTD(5、10、 20、40 μg/ml)作用24 h后,抑制率分别为(9.04 ±2.4)% 、(18.5 ±3.5) %、(40.1 ±5.8)% 、(58.2 ± 2.7)%;作用72 h后,抑制率分别为(18.14 ±7.4)%、 (36.7 ±4.3)% 、(49.9 ±3.6) %、(72.4±3.1)%(n=3, x±s)。最大抑制率在40 μg/ml作用72 h出现 ,见 图1。去甲斑蝥素对结肠癌LS-174T细胞有明显的 生长抑制作用,并且呈时间-剂量依赖性。 2.2 AO/EB 观察细胞形态学变化 正常组细胞呈均一绿染;10 μg/ml药物组细 胞体积减小,胞质减少,细胞核固缩,染色质浓 集,凋亡细胞增加;40 μg/ml药物组可见细胞核碎 裂以及凋亡小体,出现了典型的“鬼影”细胞,见图2。随着药物浓度的增加凋亡率明显增加。
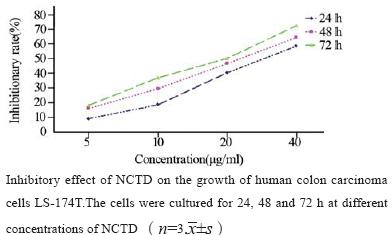 |
图1 去甲斑蝥素对结肠癌LS-174T细胞生长的抑制作用 Figure1 Inhibitory effect of NCTD on cell proliferation of the human colon carcinoma cells LS-174T |
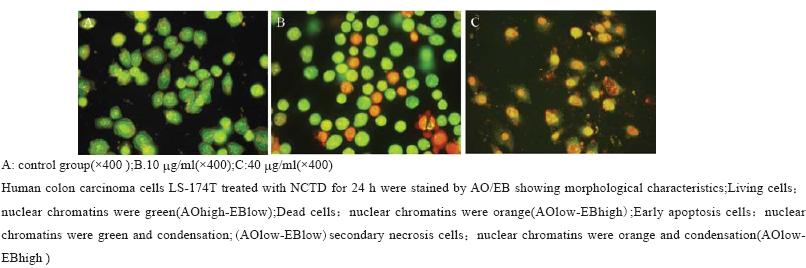 |
图2 AO/EB染色观察结肠癌LS-174T细胞形态学的变化 Figure2 Morphology of human colon carcinoma cells LS-174T was detected by acridine orange/ethidium bromide staining |
阴性对照组细胞的细胞核大、双核且各有一 个大而明显的核仁,细胞表面有些细长突起,10 μg/ml去甲斑蝥素作用24 h后,细胞微绒毛减少, 核体积缩小,核固缩,电子密度增加。40 μg/ml去 甲斑蝥素作用24 h后,核膜破裂,核染色质外排到 细胞质中,见图3。
 |
图3 透射电子显微镜下观察去甲斑蝥素对结肠癌LS-174T细胞凋亡的影响 Figure3 Effects of NCTD on apoptosis of human colon carcinoma cells LS-174T observed under transmission electron |
流式细胞仪AnnexinV-FITC/PI染色法检测药物组和阴性对照组凋亡率,结果显示与阴性对照组 相比不同药物浓度(5、10、20、40 μg/ml)NCTD 作用24 h后,细胞凋亡率明显增加,且呈剂量依 赖性,各药物组之间凋亡率差异有统计学意义 (P<0.05),见图4,表1。
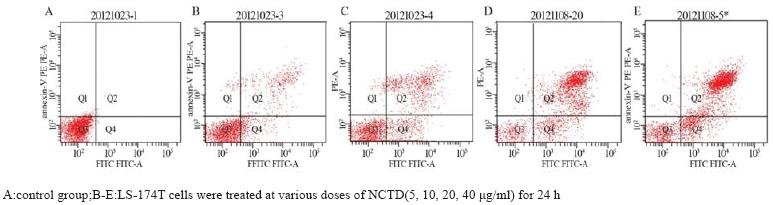 |
图4 AnnexinV/PI法检测NCTD诱导LS-174T细胞的凋亡 Figure4 Effects of NCTD on apoptosis of the human colon carcinoma cells LS-174T detected by AnnexinV/PI staining methods |
|
|
表1 AnnexinV/PI法检测NCTD诱导LS-174T细胞凋亡百分率 (x±s,n=3) Table1 Apoptosis rate of the human colon carcinoma LS-174T cells induced by NCTD was detected by AnnexinV /PI staining methods |
阴性对照组和药物组干预组(NCTD 5、10、 20、40 μg/ml)作用24 h后,检测stat3、survivin、 Mcl-1、bax蛋白表达情况。结果显示:stat3、 survivin、Mcl-1蛋白表达减少,bax蛋白表达增加,且 随药物浓度的增加表达也增加,呈明显的剂量依 赖关系,见图5。
 |
图5 Western blot测定去甲斑蝥素对survivin、stat3、 Mcl-1、bax表达的影响 Figure5 Effects of NCTD on the expression of survivin , stat3,Mcl-1 and bax detected by Western blot |
随着人民生活水平的提高和饮食结构的改 变,结肠癌在我国的发病率呈现出逐年上升趋 势,当前对于结肠癌的治疗主要以手术为主辅以 放化疗,但由于结肠癌的发病比较隐匿,出现症 状时往往已处于中晚期,错过了手术的最佳时 期,而单纯放化疗远期生存率并不理想,并且复 发率及转移率较高,尤其是晚期结肠癌生存率极 低,于是从传统中医药理论出发,用中药及其提 取成分治疗肿瘤为人们提供了新的治疗思路,并 且越来越多地受到国内外医学专家的重视。本实 验通过去甲斑蝥素(NCTD)对体外结肠癌LS-174T 细胞的作用,证实了去甲斑蝥素对结肠癌细胞存 在明显的生长抑制作用,并且呈时间-剂量相关 性。进一步应用AO/EB 染色以及AnnexinV/PI法检 测LS-174T细胞凋亡百分率,结果显示,去甲斑蝥 素作用下早期凋亡,晚期凋亡细胞数量随着药物 浓度的增加明显增加,提示去甲斑蝥素通过增加 凋亡来抑制结肠癌LS-174T细胞生长。同时应用透 射电子显微镜观察细胞超微结构发现,出现了细 胞表面微绒毛减少,胞核固缩、细胞核膜破裂,染色质外排等典型的凋亡形态学改变,更加证实 了去甲斑蝥素对结肠癌细胞的促凋亡作用。 JAK-STAT3 信号转导通路,参与肿瘤的发 生、发展,在许多人类肿瘤中被激活,成为目前 肿瘤信号转导通路研究的热点。 JAK-STAT 信号 通路由JAK酪氨酸激酶家族和STAT信号转导和转 录激活因子家族构成,STAT信号转导通路是表皮 生长因子(EGF)、JAK和IL-6等多个致癌性酪氨酸 激酶信号通道汇聚的焦点[16],STAT3作为重要的信 号转导分子,通过激活靶基因而诱导某些关键产 物的表达来影响肿瘤的发生;重要的靶基因产物 包括影响细胞凋亡的Bcl-2家族成员。本实验应用 Western blot对NCTD作用结肠癌LS-174T细胞后相 关蛋白的表达进行检测,发现NCTD可以明显抑制 STAT3蛋白的表达,且呈剂量相关性,推测NCTD 促进细胞凋亡的机制可能与抑制JAK-STAT3的信 号通路活化有关。
Bcl-2家族包括抑制凋亡和促进凋亡两大类,前 者包括Bcl-2、Bcl-xL、Mcl-1等,后者包括Bax、 Bak、Bcl-xS等[17],髓样细胞白血病-1(Myeloid Cell Leuke-lia-1,MCL-1)基因属于BCL-2抗凋亡家族成 员之一,Mcl-1基因编码的蛋白主要位于细胞内膜 系统,尤其是线粒体膜,通过阻止Smac、细胞色素 C、AIF的释放来抑制细胞的凋亡,该基因的表达 异常与肿瘤的发生发展关系密切,而目前研究表 明JAK-STAT3 信号转导途径是调节Mcl-1表达的主 要途径[18, 19]。既然NCTD可以抑制JAK-STAT3的信 号通路的活化,那么,Mcl-1的表达是否也发生相 应改变呢?Western blot结果显示,NCTD呈剂量 依赖性地抑制Mcl-1的表达,初步证明NCTD促进 细胞凋亡的机制可能与抑制JAK-STAT3的信号通 路、减少Mcl-1表达有关。
Bax为Bcl-2促凋亡家族成员之一,位于细胞 质,当细胞DNA受损时,可与Bcl-2形成同源或者 异源二聚体,拮抗bcl-2蛋白的抗凋亡功能,通过 激活线粒体凋亡通路,引起一系列caspase家族的 级联反应,最终导致细胞凋亡的发生[20, 21]。与我 们预想一致的是NCTD呈剂量依赖性促进Bax的表 达,上述结果进一步说明NCTD诱导细胞凋亡的机 制与激活促凋亡基因和抑制抗凋亡基因的表达有 关。
Survivin为迄今为止发现的最强的凋亡抑制 因子(inhibitor of apoptosis,IAP),在正常分化 成熟的组织中几乎不表达, 而选择性地表达于多 种恶性肿瘤组织。 它除了具有促进细胞的抗凋亡和向恶性转化作用外,还有促细胞增殖、血管生 成和肿瘤转移的作用[22],虽然不属于bcl-2家族, 但研究表明survivin上具有STAT3结合位点,通过 抑制STAT3的表达可以减少survivin蛋白的表达, 从而促进肿瘤细胞的凋亡[23, 24, 25]。本实验也发现, NCTD可以通过抑制STAT3信号通路减少survivin的 表达,与以往的报道相一致。
综上所述,本实验应用Western blot对NCTD 作用结肠癌LS-174T细胞后相关蛋白的表达进行检 测,发现NCTD可以明显抑制STAT3蛋白的表达, 且呈剂量相关性,进一步检测其下游调控蛋白 survivin、Mcl-1的表达,发现显示随着药物浓度的 增加它们的表达也随之减少,而促凋亡蛋白Bax表 达反而增加,这些结果表明去甲斑蝥素可能直接 或者间接参与了对JAK-STAT3凋亡通路的调节, 通过减少STAT3的磷酸化激活,并抑制其与下游抗 凋亡基因启动子结合,使相关凋亡蛋白的表达减 少,同时激活线粒体等凋亡通路,从而诱发结肠 癌细胞的凋亡。
| [1] | Fan YZ, Fu JY, Zhao ZM, et al. Inhibitory effect of norcantharidin n the growth of human gallbladder carcinoma GBC-SD cells in itro[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int ,2007,6(1):72-80. |
| [2] | Fan YZ, Fu JY, Zhao ZM, et al .The in vitro effect of norcantharidin n proliferation and invasion of human gallbladder carcinoma BC-SD cells and its mechanism[J].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 004,26(5):271-4.[范跃祖,傅锦业,赵泽明,等. 去甲斑蝥素 人胆囊癌GBC-SD细胞系增殖及侵袭的影响[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2004,26(5):271-4.] |
| [3] | Chang C, Zhu Y, Tang X, et al. The anti-proliferative effects of orcantharidin on human HepG2 cells in cell culture[J].Mol Biol ep,2011,38(1):163-9. |
| [4] | Chen CL, Cen L, Kohout J, et al.Signal transducer and activator f transcription 3 activation is associated with bladder cancer cell rowth and survival[J].Mol Cancer,2008,7:78. |
| [5] | Fossey SL, Liao AT, McCleese JK, et al. Characterization of STAT3 ctivation and expression in canine and human osteosarcoma[J]. MC Cancer,2009,9:81. |
| [6] | de Araújo VC, Furuse C, Cury PR, et al. STAT3 expression in alivary gland tumours[J]. Oral Oncol,2008,44(5):439-45. |
| [7] | Lin Q, Lai R, Chirieac LR,et al.Constitutive activation of JAK3/ TAT3 in colon carcinoma tumors and cell lines: inhibition of AK3/STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of olon carcinoma cells.[J]. Am J Pathol,2005,167(4):969-80. |
| [8] | Corvinus FM, Orth C, Moriggl R, et al. Persistent STAT3 activation n colon cancer is associated with enhanced cell proliferation and umor growth[J]. Neoplasia,2005,7(6):545-55. |
| [9] | Xiong H, Zhang ZG, Tian XQ, et al. Inhibition of JAK1, 2/STAT3 ignaling induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and reduces tumor ell invasion in colorectal cancer cells[J]. Neoplasia,2008,10(3): 87-97. |
| [10] | Yeh CB, Hsieh MJ, Hsieh YH, et al. Antimetastatic effects of orcantharidin on hepatocellular carcinoma by transcriptional nhibition of MMP-9 through modulation of NF-κB activity[J]. LoS One,2012,7(2):e31055. |
| [11] | An WW,Gong XF,Wang MW,et al.Norcantharidin induces poptosis in HeLa cells through caspase,MAPK,and mitochondrial athways[J].Acta Pharmacol Sin,2004,25(11):1502-8. |
| [12] | Chang C, Zhu YQ, Mei JJ, et al. Involvement of mitochondrial athway in NCTD-induced cytotoxicity in human hepG2 cells[J]. Exp Clin Cancer Res,2010,29:145. |
| [13] | Yan-Nian Chen,Chi-Chih Cheng,Jung-Chou Chen, et al. orcantharidin-induced apoptosis is via the extracellular ignal-regulated kinase and c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase ignaling pathways in human hepatoma HepG2 cells[J]. Br J harmacol,2003,140(3): 461-70. |
| [14] | Liu S, Yu H, Kumar SM, et al. Norcantharidin induces melanoma ell apoptosis through activation of TR3 dependent pathway[J]. ancer Biol Ther,2011,12(11):1005-14. |
| [15] | Yeh CH, Yang YY, Huang YF, et al. Induction of apoptosis in uman Hep3B hepatoma cells by norcantharidin through a p53 ndependent pathway via TRAIL/DR5 signal transduction[J]. hin J Integr Med, 2012,18(9):676-82. |
| [16] | Jing N, Tweardy DJ,et al. Targeting Stat3 in cancer therapy[J]. nticancer Drugs, 2005,16 (6):601-7. |
| [17] | Cory S,Huang DC, Adams JM, et al. The Bcl-2 family: roles n cell survival and oncogenesis[J].Oncogene,2003,22(53): 590-607. |
| [18] | Epling-Burnette PK,Liu JH,Catlett-Falcone R,et al.Inhibition of TAT3 signaling leads to apoptosis of leukemic large granular ymphocytes and decreased Mcl-1 expression[J]. J Clin Invest, 001,107( 3):351-62. |
| [19] | Zhang B,Potyagaylo V,Fenton RG,et al.IL-6-independent xpression of Mcl-1 in human multiple myeloma[J]. ncogene,2003,22(12): 1848-59. |
| [20] | Chipuk JE, Maurer U, Green DR,et al.Pharmacologic activation f p53 elicits Bax-dependent apoptosis in the absence of ranscription[J]. Cancer Cell,2003,4(5):371-81. |
| [21] | Peng LT,Xu X.Effect of Fas,bcl-2 and caspase8 on Norcantharidin nduced Esophageal Cancer Cell Line Eca-109 Apoptosis and olecular Mechanism[J].Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu,2010,37(4): 98-401.[彭林涛,许欣.Fas、bcl-2和caspase8在去甲斑蝥 诱导食管癌细胞凋亡中的作用及机制[ J ] . 肿瘤防治研究,2010,37(4):398-401.] |
| [22] | Wu XY, Fu ZX, Wang XH, et al.Effect of hypoxia-inducible actor 1-α on Survivin in colorectal cancer[J]. Mol Med Rep, 010,3(3):409-15. |
| [23] | Scheper MA, Nikitakis NG, Sauk JJ, et al.Survivin is a ownstream target and effector of sulindac-sensitive oncogenic tat3 signalling in head and neck cancer[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac urg, 2007,36(7):632-9. |
| [24] | Kanda N, Seno H, Konda Y, et al. STAT3 is constitutively activated nd supports cell survival in association with survivin expression n gastric cancer cells[J]. Oncogene, 2004,23(28):4921-9. |
| [25] | Aoki Y, Feldman GM, Tosato G, et al.Inhibition of STAT3 ignaling induces apoptosis and decreases survivin expression in rimary effusion lymphoma[J]. Blood, 2003,101(4):1535-42. |
 2014, Vol.41
2014, Vol.41