Nomogram for Predicting Early Death in Patients with Metastatic Colon Cancer Based on SEER Database
-
摘要:目的
构建预测转移性结肠癌(mCC)患者早期死亡的列线图模型。
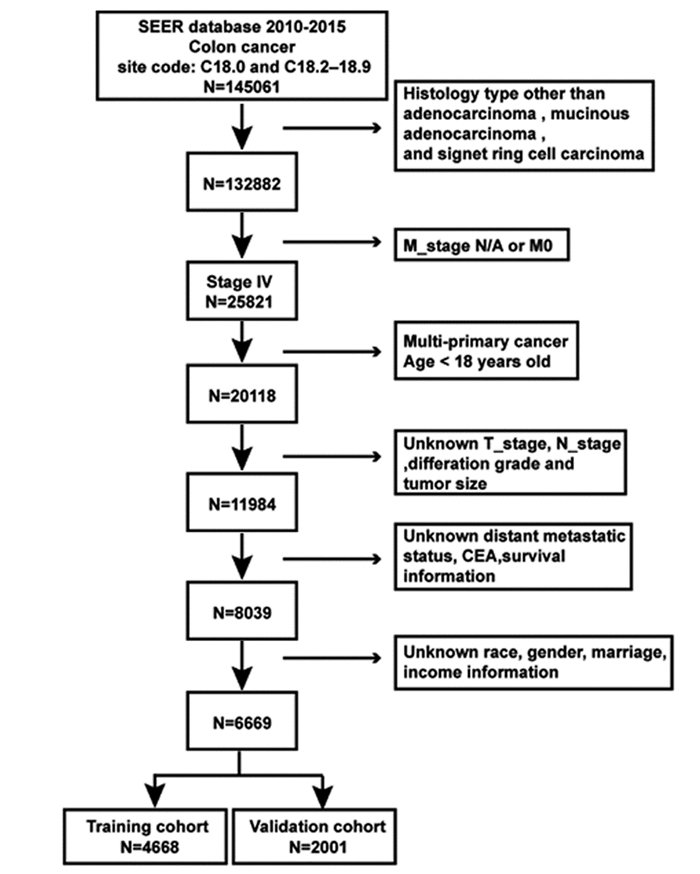
方法从SEER数据库中选择6 669例符合条件的mCC患者。根据多因素Logistic回归中的危险因素构建列线图。通过C-index、校准曲线和临床决策曲线分析(DCA)评估列线图的预测性能。
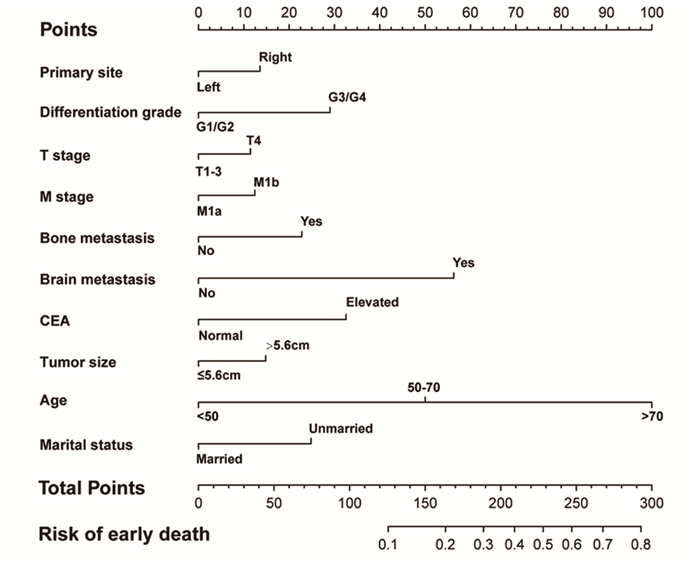
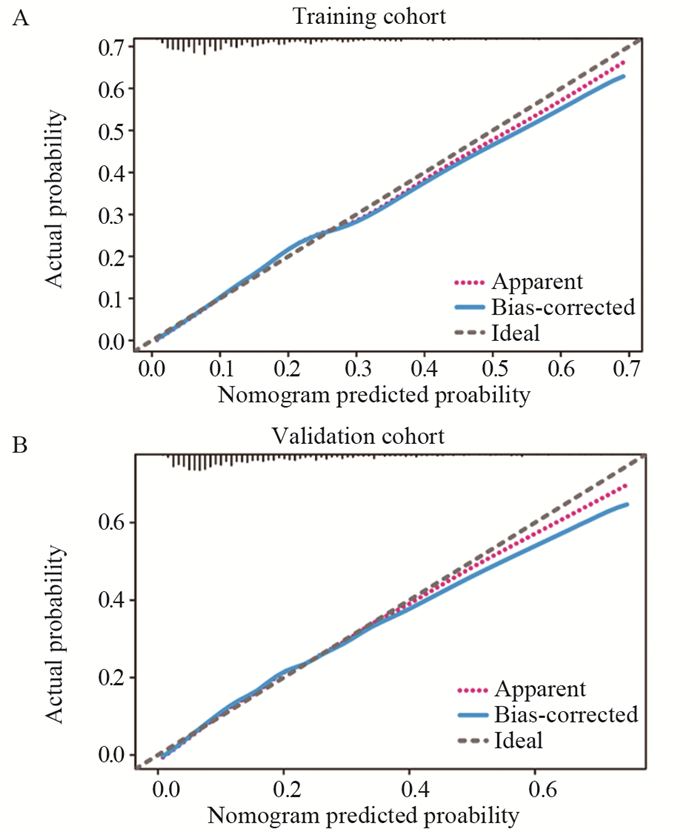
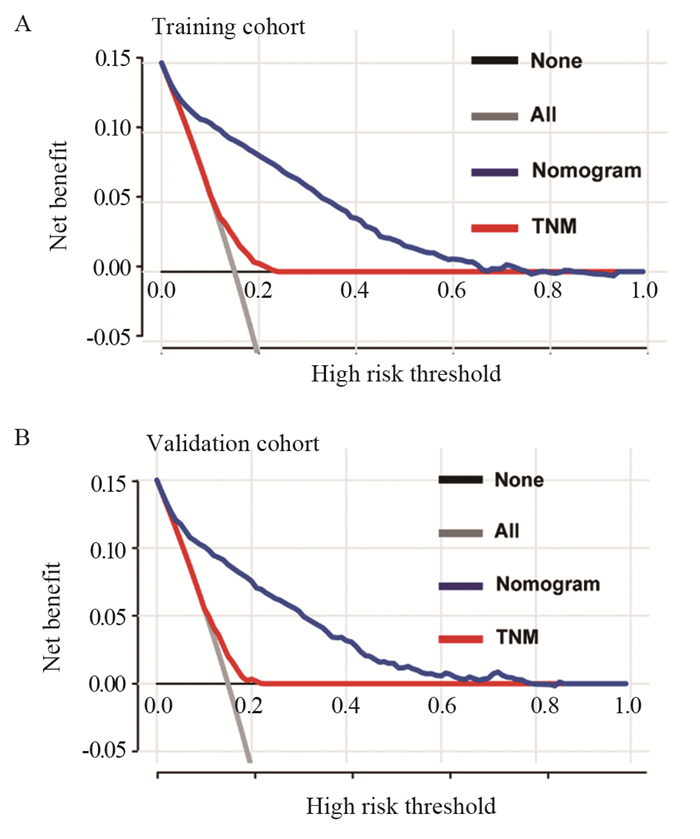
结果原发肿瘤位置、肿瘤分化、T分期、M分期、骨转移、脑转移、CEA、肿瘤大小、年龄和婚姻状态是mCC患者早期死亡的独立影响因素。基于这些变量构建列线图,C-index和校准曲线显示模型具有很好的预测能力,DCA曲线显示列线图可以使患者有较好的临床获益。
结论该列线图具有良好的预测能力,能够帮助医生识别可能早期死亡的高危mCC患者,有助于制定个性化治疗策略。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo construct a Nomogram model that can accurately predict early death of metastatic colon cancer (mCC).
MethodsA total of 6 669 patients from the SEER database were identified using inclusion and exclusion criteria. Multivariate logistic regression was used to identify risk factors for early mortality and to construct a Nomogram. The predictive performance of the Nomogram was evaluated by C-index, calibration curve, and decision curve analysis (DCA).
ResultsPrimary tumor location, differentiation grade, T stage, M stage, bone metastases, brain metastases, CEA, tumor size, age and marital status were independent factors for early death in patients with mCC. A Nomogram was constructed based on these variables. The C-index and the calibration curve of the Nomogram showed the good predictive ability of the nomogram. DCA showed that the Nomogram had a superior clinical net benefit in predicting early death compared with TNM stage.
ConclusionThe developed Nomogram has good predictive ability and can help guide clinicians to identify patients with high-risk mCC for individualized diagnosis and treatment.
-
Key words:
- Metastasis colon cancer /
- SEER /
- Nomogram /
- Early death
-
0 引言
免疫检查点抑制剂(immune checkpoint inhibitors, ICIs)可以解除免疫检查点的“免疫刹车”作用,使免疫系统能够识别并杀伤肿瘤细胞。根据作用位点的不同,常用的ICIs可分为PD-1单抗、PD-L1单抗和CTLA-4单抗三类。ICIs对存在错配修复基因缺陷(deficient mismatch repair, dMMR)或微卫星高度不稳定(microsatellite instability high, MSI-H)的结直肠癌患者治疗效果确切。也有研究发现,部分错配修复基因无缺陷(proficient mismatch repair, pMMR)或微卫星稳定型(microsatellite stability, MSS)结直肠癌患者也能从ICIs的治疗中获益[1-2],如何筛选出能够从ICIs治疗获益的MSS结直肠癌患者成为当前研究的热点。
通过预测标志物的检测可以发现潜在的对ICIs治疗有效的微卫星稳定型结直肠癌患者,扩大免疫治疗获益人群。在MSS结直肠癌患者ICIs疗效预测方面,部分标志物已经显示出较好的潜能和价值。本文将对微卫星稳定型结直肠癌ICIs疗效预测标志物的相关研究进行全面梳理和总结,为MSS结直肠癌患者免疫治疗提供参考。
1 基因水平预测标志物
1.1 肿瘤突变负荷
肿瘤突变负荷(tumor mutational burden, TMB)是指基因组每百万个碱基发生的体细胞基因突变个数。
KEYNOTE158研究采用帕博利珠单抗治疗非结直肠癌患者,结果发现高TMB患者客观缓解率显著高于低TMB患者(29% vs. 6%)[3]。因此,美国FDA批准了帕博利珠单抗用于肿瘤组织存在高TMB(≥10 mut/Mb)的难治性进展期实体瘤的治疗。MSS结直肠癌是实体瘤的一种,其肿瘤组织中的TMB同样能够对帕博利珠单抗的疗效进行预测。
在结直肠癌中,高TMB结直肠癌患者中仅有16%的患者为MSI-H型,其余84%的结直肠癌患者为MSS型,这些高TMB MSS结直肠癌患者可以从ICIs治疗中获益[4-5]。Fabrizio等[6]研究发现TMB对ICIs治疗结直肠癌疗效预测方面优于MSI状态检测,以上这些研究均表明TMB是预测ICIs治疗MSS结直肠癌患者的疗效标志物。目前,研究者对TMB临界值的设定并未达成共识,常用的临界值有10、16、20 mut/Mb。
1.2 POLE/POLD1基因突变
DNA聚合酶ε(DNA polymerase epsilon, POLE)和δ(DNA polymerase delta 1, POLD1)基因编码DNA聚合酶的核酸外切酶结构域,参与DNA的复制和校对,当POLE/POLD1基因发生突变时,DNA复制受到直接影响。皮肤癌、子宫内膜癌、结直肠癌等多种肿瘤均可发生该基因突变,在结直肠癌中约有1%的患者存在POLE/POLD1突变,且多见于年轻的右半结肠癌患者,POLE/POLD1突变与MSI突变相互排斥,因此主要存在于MSS结直肠癌患者中[7]。POLE/POLD1突变的肿瘤组织中存在大量细胞毒性T细胞(CD8+)和记忆T细胞(CD45RO+),并且存在较高水平的突变新抗原[8]。
相关研究表明,在非小细胞肺癌、子宫内膜癌和其他实体瘤治疗中POLE/POLD1突变能够对ICIs疗效进行预测[9-11]。在MSS mCRC治疗中,POLE/POLD1突变对ICIs疗效的预测价值也已经得到证实,多个研究结果显示使用帕博利珠单抗治疗存在POLE/POLD1突变的MSS转移性结直肠癌效果显著[12-13],表明POLE/POLD1突变是预测ICIs治疗MSS结直肠癌患者的疗效标志物。
1.3 结直肠癌分子亚型
根据基因表达特点国际结直肠癌分型联盟将结直肠癌分为4种共识分子亚型(consensus molecular subtypes, CMS):CMS1型:免疫型,以高TMB和突变新抗原、高度免疫细胞浸润以及BRAF V600E突变为特征,MSI状态多数为dMMR/MSI-H。CMS2型:经典型,其特征是WNT和MYC通路激活,该亚型中MSI-H的患者比例很低,不超过2%。CMS3型:代谢型,其特征是癌细胞代谢失调和KRAS突变。CMS4型:间质型,其特征是基质浸润、转化生长因子β激活和血管生成[14]。CMS1和CMS4型肿瘤组织中均存在高度的免疫细胞浸润,有可能从免疫疗法中获益,是潜在的免疫治疗疗效预测标志物。但是CMS1和CMS4型免疫微环境是截然不同的,CMS1表现为免疫活化状态,CMS4表现为免疫抑制状态。
CMS1型肿瘤组织中存在CD8+T细胞和CD68+巨噬细胞浸润,而且与肿瘤发生免疫逃避相关的免疫检查点分子CTLA-4、PD-1和PD-L1表达升高[15]。有研究采用恩考芬尼(BRAF抑制剂)、西妥昔单抗(EGFR抑制剂)联合纳武单抗治疗MSS型BRAF-V600E突变的转移性结直肠癌,入组患者分子亚型均为CMS1型,BRAF抑制剂与EGFR抑制剂联合诱导出短暂的MSI-H表型,从而提高了PD-1抗体的反应率[16],表明CMS1型MSS结直肠癌患者采用ICIs与靶向药物联合治疗效果较好。
CMS4型的免疫浸润模式与CMS1型不同,主要是存在抑制性的髓源性抑制细胞(myeloid-derived suppressor cells, MDSCs)、调节性T细胞(T regulatory lymphocytes, Tregs)、单核细胞源性细胞和Th17细胞浸润。在肿瘤组织中免疫抑制因子TGF-β和CXCL12与趋化因子白细胞介素17和23表达上调[17]。当前有多个研究结果显示,CMS4型转移性结直肠癌患者采用ICIs治疗效果并不理想[18-19]。
1.4 甲基化
O6-甲基鸟嘌呤-DNA甲基转移酶(O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase, MGMT)是烷化剂诱导的DNA损伤修复机制中的关键蛋白,MGMT甲基化的胶质瘤患者采用替莫唑胺治疗疗效较好[20]。约有40%的结直肠癌患者存在MGMT甲基化,但是单独采用替莫唑胺治疗MGMT甲基化的结直肠癌患者效果不佳[21]。
MAYA研究采用替莫唑胺序贯ICIs治疗MGMT甲基化的MSS转移性结直肠癌,结果显示在接受替莫唑胺治疗2个疗程后疾病稳定、获得后续纳武单抗联合伊匹单抗治疗的33位患者中,客观缓解率为45%,中位OS和PFS分别为18.4和7个月[22]。提示使用替莫唑胺能够诱导并获得超突变表型,具有将冷肿瘤转变为热肿瘤的疗效。同时也说明ICIs对MGMT甲基化的MSS mCRC具有较好的疗效,MGMT甲基化具有作为MSS结直肠癌ICIs疗效预测标志物的潜能。
2 蛋白水平预测标志物
2.1 PD-1和PD-L1的表达
程序性死亡受体1(PD-1)是一种跨膜蛋白,表达于活化的T细胞、B细胞和自然杀伤细胞表面。程序性死亡配体1(PD-L1)是PD-1的配体,通常在肿瘤细胞表面表达[23],此外肿瘤免疫微环境中的淋巴细胞、巨噬细胞和间质细胞等也会表达PD-L1。PD-1与PD-L1结合能抑制效应T细胞的增殖和功能,促进效应T细胞向调节性T细胞转化,抑制肿瘤细胞的凋亡,从而逃避免疫系统的监视和攻击[24]。
PD-L1表达水平通常采用综合阳性评分(combined positive score, CPS)、肿瘤细胞阳性比例评分(tumor cell proportion score, TPS)或免疫细胞阳性比例评分(immune cell proportion score, IPS)来评价,在胃癌、非小细胞肺癌以及食管癌中采用上述评分系统能够对ICIs疗效进行预测[25]。但在结直肠癌中,PD-L1的表达水平与dMMR/MSI-H并不存在相关性,采用PD-L1单项指标不能预测ICIs的疗效[26]。
Llosa等[27]发现MSS mCRC患者的肿瘤组织高表达PD-L1同时肿瘤中存在PD-1高表达的T细胞(CD8+)浸润时,肿瘤免疫微环境与dMMR/MSI-H患者类似,患者能够从帕博利珠单抗治疗中获益。提示联合检测肿瘤组织PD-L1表达水平和PD-1高表达T细胞能够预测ICIs治疗MSS结直肠癌患者的疗效。
2.2 突变新抗原
突变新抗原(mutation-associated neoantigens, MANA)存在于癌细胞表面,能够被树突状细胞递呈给免疫效应细胞,引起肿瘤浸润性淋巴细胞(tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, TILs)细胞的浸润[28],因此,T细胞对MANA的识别与ICIs的疗效相关。
存在高水平MANA的肺癌和黑色素瘤患者采用ICIs治疗的效果较好[9, 29-30]。Luksza等[31]为了更好的预测ICIs的疗效建立了突变新抗原模型,通过该模型可以预测ICIs治疗肺癌和黑色素瘤患者的疗效。在当前的结直肠癌临床研究中通常同时检测MANA、TMB和TILs水平以评价ICIs疗效,MANA具有作为ICIs治疗MSS结直肠癌疗效预测标志物的潜能。
2.3 T细胞受体库
T细胞受体(T cell receptor, TCR)由4条多肽链组成,包括α、β、γ和δ,编码4条多肽链的TCR基因发生重排使TCR具有多样性和特异性。因此,研究者根据TCR基因的特异性建立了T细胞受体库。研究表明肿瘤微环境中T细胞受体库呈现多样化时免疫治疗疗效更好[32]。此外,还有研究发现在治疗前可以采用液体活检方法检测T细胞受体库对ICIs的疗效进行预测[33]。
Chen等[34]对TCR多样性在转移性结直肠癌患者疗效预测方面的价值进行了评估,发现TCR多样性水平高或化疗后TCR多样性快速下降的患者治疗效果更好。另一项采用肿瘤疫苗联合奥沙利铂治疗进展期结直肠癌的研究结果显示,TCR多样性评分高的患者具有较好的疗效[35]。这些研究提示T细胞受体库可能是结直肠癌ICIs治疗疗效潜在的预测标志物,确切结论尚需进一步研究证实。
3 肿瘤微环境预测标志物
肿瘤微环境(TME)是指肿瘤癌巢和间质中存在的免疫细胞、间质细胞、细胞外基质及活性介质。TME在肿瘤的发生发展过程中起着重要作用,目前发现多种免疫治疗标志物与肿瘤微环境有关。
3.1 肿瘤浸润性淋巴细胞和免疫评分
在肿瘤实质和间质中通常存在多种淋巴细胞的浸润,这些淋巴细胞统称为TILs,TILs包括T细胞、B细胞、NK细胞、树突状细胞、巨噬细胞等多个亚群,是肿瘤免疫微环境的重要组成部分。
在结直肠癌组织中出现细胞毒性T细胞和Th1细胞的浸润以及IFN-γ表达上调时提示ICIs的疗效较好,表明TILs能够对免疫治疗的疗效进行预测[36]。有研究表明,在抗PD-1抗体治疗有效的乳腺癌和膀胱癌组织中CD8和PD-L1的表达水平显著升高[37-39]。当前,PD-L1阳性细胞和CD8+T细胞共同浸润已经用于ICIs治疗结直肠癌等肿瘤疗效的预测[40-41]。以上这些研究表明,TILs具有作为ICIs治疗MSS结直肠癌疗效预测标志物的潜能。
为了更精确对ICIs的疗效进行预测,研究者提出了根据TILs的分布进行免疫评分的方法,该方法对位于肿瘤核心区域及交界区域中的CD8+T细胞、CD3+T细胞和CD45RO+记忆性T细胞的数量进行分级。将两个区域内淋巴细胞群的密度从低到高评为1~4分[42]。目前,有多个研究采用免疫评分系统对ICIs疗效进行预测[43-45]。免疫评分能否作为ICIs治疗MSS结直肠癌疗效预测标志物尚需更多的证据加以证实。
3.2 肠道和肿瘤菌群
在宿主免疫系统的维持和发展过程中肠道菌群起着重要作用,ICIs治疗肿瘤的疗效与肠道菌群有关[46-47]。一项研究表明,胃肠肿瘤患者肠道的普氏杆菌与拟杆菌属的比例与ICIs疗效相关,患者能从免疫治疗中获益很可能与细菌代谢产物有关[48-49]。另一项研究显示,从人肠道微生物群中收集的含有11种细菌的菌群,在小鼠肠道中能够诱导出产生干扰素γ的CD8+T细胞,从而增强了ICIs的抗肿瘤疗效[50]。
除了肠道菌群外,结直肠肿瘤组织内也存在菌群。其中关于具核梭杆菌的研究较多,该菌是结直肠癌中一种肿瘤驻留菌。相关研究表明,具核梭杆菌能够激活干扰素刺激因子信号通路,进而诱导PD-L1表达并增加IFN-γ+CD8+TILs的浸润,从而提高肿瘤对ICIs的敏感度,当肿瘤组织中存在高水平具核梭杆菌时,患者ICIs的治疗效果好,且不需检测MSI状态[51]。提示具核梭杆菌可以对包括MSS在内的结直肠癌ICIs疗效进行预测。
4 结语
免疫检查点抑制剂在MSI-H结直肠癌治疗中显示出的良好疗效让研究者认识到免疫治疗所蕴含的巨大潜力和价值。目前研究者正在试图通过筛选ICIs预测标志物、开发新的ICIs药物以及将ICIs与化疗、放疗或靶向治疗联合使用来提高MSS结直肠癌的治疗效果,从而获得最佳的MSS结直肠癌免疫治疗方案。其中,TMB、POLE/POLD1基因已显示出对MSS结直肠癌ICIs疗效具有较好的预测作用。除了本文中的标志物以外,循环肿瘤DNA(circulating tumor DNA, ctDNA)也能对MSS结直肠癌ICIs的疗效进行较好的监测,ctDNA水平较低的患者疾病稳定,ctDNA升高的患者通常会出现快速进展[52]。
然而,现有的ICIs疗效预测标志物还存在一些问题:(1)用于MSS结直肠癌预测的相关研究较少,需要更多的临床研究进行验证。(2)TMB、TILs等预测标志物的临界值尚未形成共识,需要进一步明确。相信随着对免疫系统及其调节机制的不断深入了解、免疫治疗理念的逐步发展和完善,免疫检查点抑制剂在MSS结直肠癌的应用将更加科学和规范。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.作者贡献:王磊:资料收集、文献查阅、数据分析及论文撰写韩晖琼:文献查阅、资料收集审阅秦艳茹:研究方案设计、审阅 -
表 1 mCC患者的临床病理学特征(n(%))
Table 1 Clinicopathological characteristics of mCC patients (n(%))

表 2 训练队列中早期死亡风险因素的单变量和多变量Logistic回归分析
Table 2 Univariate and Multivariate Logistic Regression for Analyzing the Risk Factors for Early Death in the Training Cohort

-
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2022, 72(1): 7-33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21708
[2] Ciardiello F, Ciardiello D, Martini G, et al. Clinical management of metastatic colorectal cancer in the era of precision medicine[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2022, 72(4): 372-401. doi: 10.3322/caac.21728
[3] Riedesser JE, Ebert MP, Betge J. Precision medicine for metastatic colorectal cancer in clinical practice[J]. Ther Adv Med Oncol, 2022, 14: 17588359211072703.
[4] Wang X, Mao M, Xu G, et al. The incidence, associated factors, and predictive nomogram for early death in stage Ⅳ colorectal cancer[J]. Int J Colorectal Dis, 2019, 34(7): 1189-1201. doi: 10.1007/s00384-019-03306-1
[5] Kanth P, Inadomi JM. Screening and prevention of colorectal cancer[J]. BMJ, 2021, 374: n1855.
[6] Biller LH, Schrag D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Review[J]. JAMA, 2021, 325(7): 669-685. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.0106
[7] Datta J, Narayan RR, Kemeny NE, et al. Role of Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy in Treatment of Initially Unresectable Colorectal Liver Metastases: A Review[J]. JAMA Surg, 2019, 154(8): 768-776. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.1694
[8] Hari DM, Leung AM, Lee JH, et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual 7th edition criteria for colon cancer: do the complex modifications improve prognostic assessment?[J]. J Am Coll Surg, 2013, 217(2): 181-190. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2013.04.018
[9] Tai Q, Xue W, Li M, et al. Survival Nomogram for Metastasis Colon Cancer Patients Based on SEER Database[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 832060. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.832060
[10] Wang Y, Yang L, Zhou M, et al. Disparities in survival for right-sided vs. left-sided colon cancers in young patients: a study based on the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database (1990-2014)[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2018, 10: 1735-1747. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S163302
[11] Meguid RA, Slidell MB, Wolfgang CL, et al. Is there a difference in survival between right- versus left-sided colon cancers?[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2008, 15(9): 2388-2394. doi: 10.1245/s10434-008-0015-y
[12] 徐洪丽, 胡俊杰, 徐慧婷, 等. 不同原发部位结肠癌的临床病理及预后分析[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2018, 45(9): 672-675. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2018.18.0017 Xu HL, Hu JJ, Xu HT, et al. Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Colon Cancer Patients with Different Primary Locations[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2018, 45(9): 672-675. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2018.18.0017
[13] Chen F, Wang F, Bailey CE, et al. Evaluation of determinants for age disparities in the survival improvement of colon cancer: results from a cohort of more than 486, 000 patients in the United States[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2020, 10(10): 3395-3405.
[14] Patel SG, Ahnen DJ. Colorectal Cancer in the Young[J]. Curr Gastroenterol Rep, 2018, 20(4): 15. doi: 10.1007/s11894-018-0618-9
[15] Tilg H, Adolph TE, Gerner RR, et al. The Intestinal Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer[J]. Cancer Cell, 2018, 33(6): 954-964. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.03.004
[16] Krajc K, Miroševič Š, Sajovic J, et al. Marital status and survival in cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Cancer Med, 2022. Online ahead of print.
[17] Goldberg RM, Sargent DJ, Morton RF, et al. A randomized controlled trial of fluorouracil plus leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin combinations in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2004, 22(1): 23-30. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.09.046
[18] Colucci G, Gebbia V, Paoletti G, et al. PhaseⅢ randomized trial of FOLFIRI versus FOLFOX4 in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: a multicenter study of the Gruppo Oncologico Dell'Italia Meridionale[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2005, 23(22): 4866-4875. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.07.113
[19] Arnold D, Lueza B, Douillard JY, et al. Prognostic and predictive value of primary tumour side in patients with RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer treated with chemotherapy and EGFR directed antibodies in six randomized trials[J]. Ann Oncol, 2017, 28(8): 1713-1729. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx175
[20] Saltz LB, Clarke S, Díaz-Rubio E, et al. Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy as first-line therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: a randomized phase Ⅲstudy[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2008, 26(12): 2013-2019. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.14.9930
[21] Overman MJ, McDermott R, Leach JL, et al. Nivolumab in patients with metastatic DNA mismatch repair-deficient or microsatellite instability-high colorectal cancer (CheckMate 142): an open-label, multicentre, phase 2 study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2017, 18(9): 1182-1191. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30422-9
[22] Qiao Y, Qiao Y, Li H, et al. Survival benefit of primary and metastatic tumor resection for colon cancer with liver metastases: A population based, propensity score-matched study[J]. Front Surg, 2022, 9: 959826. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.959826
[23] Ruo L, Gougoutas C, Paty PB, et al. Elective bowel resection for incurable stage Ⅳ colorectal cancer: prognostic variables for asymptomatic patients[J]. J Am Coll Surg, 2003, 196(5): 722-728. doi: 10.1016/S1072-7515(03)00136-4
[24] Decker KM, Lambert P, Nugent Z, et al. Time Trends in the Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer With Obstruction, Perforation, and Emergency Admission After the Introduction of Population-Based Organized Screening[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2020, 3(5): e205741. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.5741
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 胡婉彦,汪溢,秦晓燕,郑志昂. 膀胱移行细胞癌患者血cGAS、STING基因表达与癌组织CD44阳性的剂量—效应关系. 疑难病杂志. 2025(02): 214-219 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 耿改丽,连文晓,陈蕊. 个案护理对膀胱肿瘤患者自我护理能力和生命质量的影响. 齐鲁护理杂志. 2024(01): 41-44 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 韦兴发,李智强,陈从其,林云侨,陈锦添. 卡介苗灌注联合经尿道红激光汽化切除术治疗非肌层浸润性膀胱癌的效果. 国际泌尿系统杂志. 2024(04): 628-631 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 郑宏,王栋洋. 膀胱癌组织中miR-451表达及其对患者术后生存预后的预测价值分析. 国际泌尿系统杂志. 2024(06): 1024-1027 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: