Association of Leukemia Incidence and Mortality Rate in 2022 and Human Development Index in Global Countries
-
摘要:目的
比较不同国家或地区2022年人类发展指数(HDI)与白血病发病率和死亡率的关联,以及不同HDI等级国家白血病发病率和死亡率随年龄变化的趋势。
方法根据GLOBOCAN 2022全球不同国家或地区白血病发病和死亡相关数据与HDI进行Pearson相关分析和Kruskal-Wallis检验。各年龄段发病率和死亡率及其随年龄变化趋势使用Joinpoint Regression模型分析。
结果四组HDI等级国家的年龄标化发病率(ASIR)、年龄标化死亡率(ASMR)和标化死亡发病比(M/I)的差别具有统计学意义(P<0.001);HDI与全球国家的ASIR和ASMR呈正相关,与M/I呈负相关。在各个年龄段上,四组HDI等级国家的发病率和死亡率随年龄变化具有相似的趋势,且15岁前与40岁后为白血病高发年龄。中国在各个年龄段上白血病发病率与其他高HDI国家有所差异,而死亡率均低于其他高HDI国家。
结论HDI高的国家或地区具有更高的ASIR和ASMR,同时由于其具有较好医疗水平,也具有更低的M/I。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo compare the association of the incidence and mortality of leukemia and the human development index (HDI) in different countries or regions in 2022, and the trend of leukemia incidence and mortality with age in countries with different HDI levels.
MethodsGLOBOCAN 2022 data related to leukemia incidence and mortality in different countries or regions worldwide and HDI were evaluated by Pearson correlation analysis and Kruskal–Wallis test. The incidence and mortality rates of each age and the age change trend were analyzed using the Joinpoint Regression model.
ResultsAge-standardized incidence rate (ASIR), age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR), and mortality to incidence ratio (M/I) were statistically significantly different among the four groups of HDI countries (P<0.001). HDI was positively correlated with ASIR and ASMR and negatively correlated with M/I. Among all ages, ASIR and ASMR of leukemia of the four groups had similar trends with age, and the risk of leukemia was high at ages less than 15 and more than 40. The incidence of leukemia in all age groups in China differed from those in other countries with high HDI, while the mortality rate was lower than those in other countries with high HDI.
ConclusionCountries or regions with higher HDI have higher ASIR and ASMR and lower M/I because of their better medical condition.
-
Key words:
- Leukemia /
- Human development index /
- Incidence rate /
- Mortality rate /
- Mortality to incidence ratio
-
0 引言
白血病是一种异质性的造血系统恶性肿瘤,肿瘤细胞克隆扩增发生在骨髓和血液中[1]。白血病分为急性髓系白血病(Acute myeloid leukemia, AML)、急性淋巴细胞白血病(Acute lymphocytic leukemia, ALL)、慢性髓系白血病(Chronic myelocytic leukemia, CML)和慢性淋巴细胞白血病(Chronic lymphocytic leukemia, CLL)。2022年全球白血病发病数和死亡数在所有癌症中排第13位和第10位,与2020年基本持平[2]。
与大多数肿瘤一样,年龄的增长是白血病重要的危险因素,其中成人白血病中AML占80%[3]。白血病的主要危险因素包括电离辐射、化学致癌物(苯、甲醛、1,3-丁二烯等)、化疗药物、家族史、生活方式(如吸烟和肥胖)等,虽然一些暴露与特定的白血病有关,但上述危险因素对白血病的若干亚型都有影响[4]。此外,白血病是15岁以下儿童中常见的癌症,是该年龄段发病率和死亡率较高的恶性肿瘤[5-6]。与成人白血病不同,儿童白血病中ALL占80%[7]。儿童白血病的发生很大程度归因于遗传、胎儿发育过程中产生的变异和病毒感染等[8]。此外,父亲吸烟也与儿童白血病的发生有关[9]。
人类发展指数(Human development index, HDI)是由联合国开发计划署提出的,是衡量人类发展关键方面的总结性指标,包括健康、知识水平和生活品质三方面指标。已有研究表明,国家的HDI指数与多种癌症的发病率具有相关性,包括肺癌[10]、前列腺癌[11]、肾癌[12]、结直肠癌[13]等。本研究使用世界卫生组织(World Health Organization, WHO)全球癌症观察(Global Cancer Observatory, GCO)的CANCER TODAY网站上2022年全球各个国家或不同HDI地区的白血病年龄标准化发病率(Age-standardized incidence rate, ASIR)、年龄标准化死亡率(Age-standardized mortality rate, ASMR)和死亡发病比(Mortality to incidence ratio, M/I)等数据,探索不同国家HDI白血病ASIR、ASMR和M/I等的差异,及其随年龄变化的趋势,以进一步了解全球白血病发病和死亡的流行病学特征。
1 资料与方法
1.1 数据来源
最新HDI数据来自Human Development Report网站(https://hdr.undp.org/data-center/human-development-index#/indicies/HDI)中2021年的数据。根据HDI的数值,将HDI分为四个不同等级:极高HDI(HDI≥0.8)、高HDI(0.8>HDI≥0.7)、中HDI(0.7>HDI≥0.55)和低HDI(HDI<0.55)。
GLOBOCAN 2022全球不同国家或地区白血病发病和死亡相关数据来自CANCER TODAY网站(https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home)中2022年全球癌症数据统计,共有185个国家或地区纳入统计,其中有2021年HDI数据的有175个,62个极高HDI国家,41个高HDI国家,40个中HDI国家,32个低HDI国家。
1.2 统计学方法
CANCER TODAY网站上的发病率和死亡率已根据世界标准人口进行标准化,因此可直接进行比较。统计学分析使用IBM SPSS Statistics 25软件。四组HDI等级国家的总人群、男性和女性ASIR、ASMR和M/I不完全符合正态分布,因此不同HDI等级国家的白血病ASIR、ASMR和M/I的差异分析使用非参数检验方法(Kruskal-Wallis检验)。HDI指数与白血病发病率和死亡率的关联采用Pearson相关分析。2022年白血病年龄别发病率和死亡率的变化趋势(slope)使用Joinpoint Regression Program 4.9.1.0软件。统计图采用GraphPad Prism 8软件绘制。双侧检验,检验水准α=0.05。
2 结果
2.1 2022年不同HDI等级国家白血病发病率和死亡率的比较
2022年全球白血病ASIR为5.26/105,ASMR为3.09/105,其中男性的ASIR和ASMR(6.23/105和3.70/105)均大于女性(4.38/105和2.55/105)。在四组HDI等级国家中,极高HDI组ASIR和ASMR(8.07/105和3.31/105)大于高HDI组(4.95/105和3.00/105)大于中HDI组(3.68/105和2.69/105)大于低HDI组(2.77/105和2.22/105),呈递减趋势;而对于M/I,由极高HDI组到低HDI组呈现逐渐升高趋势,分别为0.41、0.61、0.73和0.80。对于男性和女性亚组的ASIR、ASMR和M/I,也有相似趋势,见表1。
表 1 2022年全球不同HDI等级国家白血病发病和死亡情况Table 1 Leukemia incidence and mortality rate in countries with different HDI levels worldwide in 2022HDI level Gender Incidence ASIR
(/105)Mortality ASMR
(/105)M/I Very high
HDIMale 127 669 9.84 68 449 4.23 0.43 Female 94 174 6.53 51 721 2.57 0.39 Total 221 843 8.07 120 170 3.31 0.41 High HDI Male 89 906 5.69 60 591 3.53 0.62 Female 68 534 4.24 45 430 2.51 0.59 Total 158 440 4.95 106 021 3.00 0.61 Medium
HDIMale 45 951 4.21 33 600 3.05 0.72 Female 34 435 3.16 25 949 2.34 0.74 Total 80 386 3.68 59 549 2.69 0.73 Low HDI Male 14 491 3.02 10 571 2.41 0.80 Female 11 944 2.53 8 953 2.03 0.80 Total 26 435 2.77 19 524 2.22 0.80 Global Male 278 120 6.23 173 289 3.70 0.59 Female 209 174 4.38 132 116 2.55 0.58 Total 487 294 5.26 305 405 3.09 0.59 Notes: HDI: human development index; ASIR: age-standardized incidence rate; ASMR: age-standardized mortality rate; M/I: mortality to incidence ratio. 中国和印度人口数之和约占全世界一半,分别属于高HDI和中HDI国家。如表2所示,在去除中国和印度后,高HDI、中HDI的ASIR分别为5.43/105和3.88/105,ASMR分别为3.76/105和2.93/105。中国的ASIR和ASMR分别为4.54/105和2.37/105,M/I为0.52,均低于去除中国后高HDI国家水平。
表 2 2022年中国、印度以及去除中国后全球高HDI国家和去除印度后中HDI国家白血病发病和死亡情况Table 2 Leukemia incidence and mortality rate in China, India, high HDI countries but China, and medium HDI countries but India in 2022Countries Gender Incidence ASIR
(/105)Mortality ASMR
(/105)M/I China Male 46 976 5.14 29 158 2.78 0.54 Female 34 970 3.94 20 916 1.97 0.50 Total 81 946 4.54 50 074 2.37 0.52 India Male 29 487 4.19 21 549 2.99 0.71 Female 20 396 3.01 15 322 2.19 0.73 Total 49 883 3.61 36 871 2.60 0.72 High HDI
countries
but ChinaMale 42 930 6.38 31 433 4.50 0.71 Female 33 564 4.59 24 514 3.13 0.68 Total 76 494 5.43 55 947 3.76 0.69 Medium HDI
countries
but IndiaMale 16 464 4.33 12 051 3.25 0.75 Female 14 039 3.47 10 627 2.65 0.76 Total 30 503 3.88 22 678 2.93 0.76 2.2 2022年全球国家HDI指数与白血病发病率和死亡率的相关分析
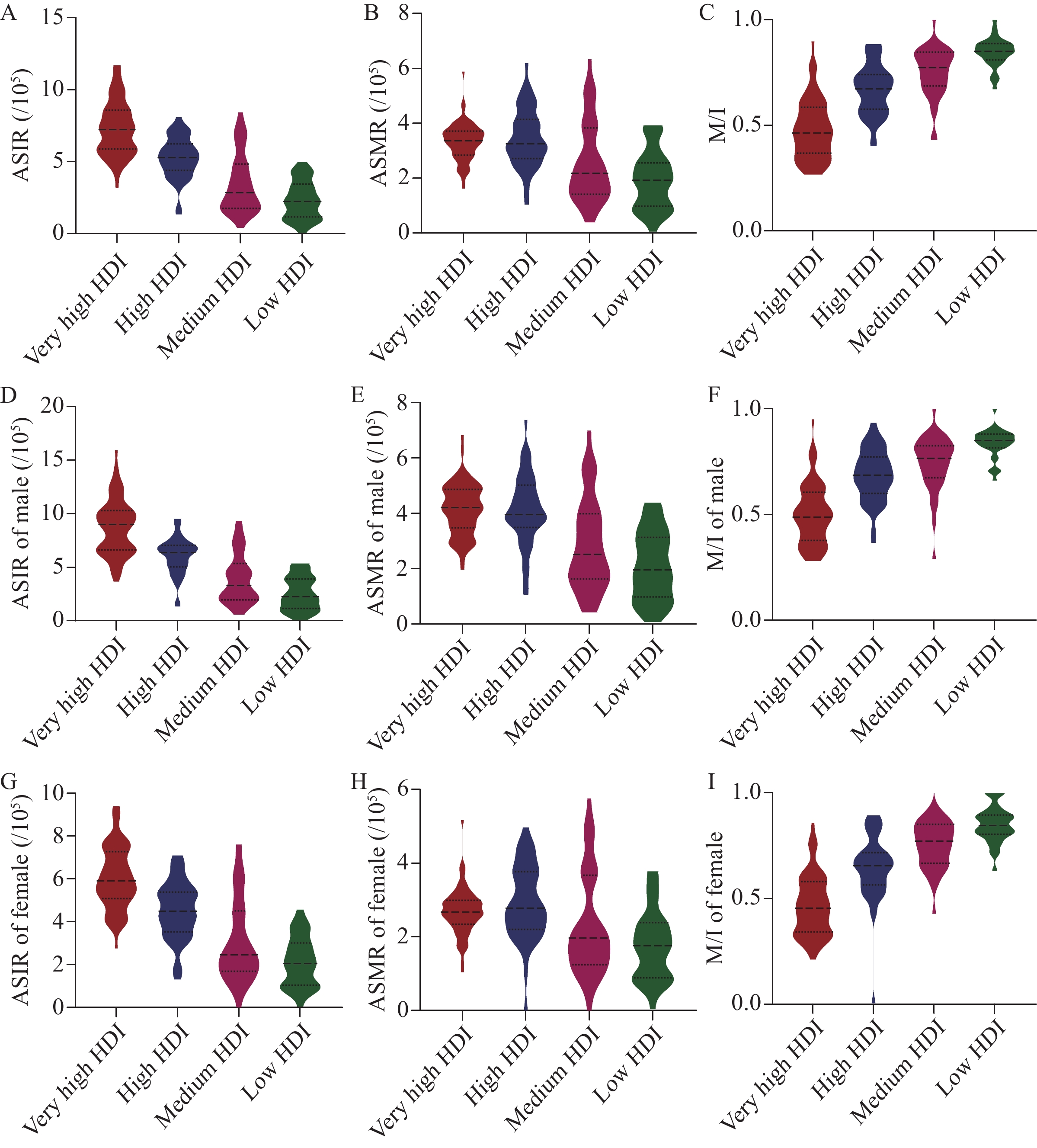
2022年全球不同HDI等级国家白血病的总人群(图1A~C)、男性(图1D~F)和女性(图1G~I)的ASIR、ASMR和M/I的分布均存在显著性差异(均为P<0.001)。从极高HDI组到低HDI组,ASIR和ASMR逐渐降低而M/I逐渐升高(各组的中位数及四分位数),与表1所描述的趋势一致。
对175个国家的ASIR、ASMR和M/I与HDI制成散点图,见图2。ASIR(图2A)、ASMR(图2B)和M/I(图2C)均与HDI有相关性(分别为r=0.781, P<0.001; r=0.417, P<0.001; r=−0.806, P<0.001),同时男性(图2D~F)和女性(图2G~I)ASIR、ASMR和M/I与HDI也具有相关性(分别为r=0.789, P<0.001; r=0.508, P<0.001; r=−0.772, P<0.001; r=0.740, P<0.001; r=0.281, P<0.001; r=−0.745, P<0.001)。因此,HDI与ASIR和ASMR呈正相关,而与M/I则呈负相关。此外,ASIR和M/I与HDI的相关性较大(图2A和2C),而ASMR与HDI的相关性较小(图2B)。
2.3 2022年全球不同HDI等级国家各年龄段白血病发病率和死亡率及其随年龄变化趋势的比较
2.3.1 总体比较
对于白血病发病率,在0~15岁逐渐降低,15~40岁保持较低水平,40岁后则明显升高。15岁前,极高HDI和高HDI的发病率大于中HDI组、低HDI组;15~40岁,极高HDI、高HDI和中HDI组的发病率接近;40岁后,极高HDI组发病率则大于其他三组;50岁前,低HDI组发病率低于其他三组;55岁后,低HDI组发病率则接近中HDI组,见图3A。
对于白血病死亡率,0~25岁保持在较低水平,30岁后则逐渐升高。55岁前极高HDI组和低HDI组死亡率保持在较低水平,60岁后极高HDI组明显升高,超过其他三组。20岁前高HDI组死亡率大于中HDI组,20~60岁HDI组死亡率大于高HDI组,60岁后高HDI组死亡率则再次大于中HDI组。低HDI死亡率一直维持在较低水平,见图3B。
2022年不同HDI等级国家白血病发病率随年龄变化趋势见表3。四组HDI等级国家的发病率随年龄变化都呈现先下降(20岁前)、再升高的趋势(40岁后)。其中高HDI组(slope=2.2,95%CI: −0.2~4.6,P=0.065)和中HDI组(slope=1.8,95%CI: −1.8~5.4,P=0.277)白血病发病率在20~40岁稳定,而极高HDI组(slope=3.5,95%CI: 0.6~6.5,P=0.024)和低HDI组(slope=3.7,95%CI: 3.1~4.4,P<0.001)发病率在20~40岁也缓慢上升。
表 3 2022年不同HDI等级国家白血病发病率随年龄变化趋势Table 3 Variations in leukemia incidence in countries with different HDI levels in 2022 with ageGroup Trend 1 Trend 2 Trend 3 Trend 4 Age
(years)slope 95%CI P Age
(years)slope 95%CI P Age
(years)slope 95%CI P Age
(years)slope 95%CI P Very high
HDI0-20 −6.0 −7.7-4.3 <0.001 20-40 3.5 0.6-6.5 0.024 40-65 8.7 6.8-10.7 <0.001 65- 4.0 2.1-5.9 0.001 High HDI 0-20 −5.1 −6.4-−3.7 <0.001 20-40 2.2 −0.2-4.6 0.065 40-70 6.1 5.0-7.2 <0.001 70- 1.8 −0.6-4.2 0.117 Medium HDI 0-20 −3.1 −4.2-−2 <0.001 20-35 1.8 −1.8-5.4 0.277 35-70 4.6 4.0-5.3 <0.001 70- 2.6 0.8-4.4 0.012 Low HDI 0-20 −2.7 −3.3-−2.1 <0.001 20-45 3.7 3.1-4.4 <0.001 45-60 6.2 4.2-8.3 <0.001 60- 3.4 3.0-3.9 <0.001 China 0-15 −6.2 −9.1-−3.1 0.002 15-40 1.3 −0.8-3.3 0.185 40-70 6.3 4.7-7.8 <0.001 70- 0.9 −2.3-4.2 0.542 India 0-20 −4.3 −5.4-−3.3 <0.001 20-40 2.8 1.0-4.6 0.007 40-65 4.9 3.7-6.0 <0.001 65- 2.1 0.9-3.2 0.003 High HDI
countries
(but China)0-20 −5.0 −6.5-−3.5 <0.001 20-35 0.6 −4.2-5.7 0.769 35-70 6.3 5.4-7.2 <0.001 70- 3.2 0.6-5.7 0.021 Medium HDI
countries
(but India)0-20 −2.8 −3.9-−1.6 0.001 20-40 2.1 0.2-4.1 0.032 40-70 5.8 4.9-6.7 <0.001 70- 2.8 0.8-4.7 0.011 2022年不同HDI等级国家白血病死亡率随年龄变化趋势见表4,高HDI等级国家的死亡率随年龄变化呈现先下降、然后稳定、再升高的趋势,其余三组的死亡率则先稳定,再升高。
表 4 2022年不同HDI等级国家白血病死亡率随年龄变化趋势Table 4 Variations in leukemia mortality in countries with different HDI levels in 2022 with ageGroup Trend 1 Trend 2 Trend 3 Trend 4 Age
(years)slope 95%CI P Age
(years)slope 95%CI P Age
(years)slope 95%CI P Age
(years)slope 95%CI P Very high
HDI0-30 0.6 0-1.2 0.053 30-50 4.8 2.9-6.7 <0.001 50-70 12.1 10.1-14.2 <0.001 70- 6.7 4.8-8.7 <0.001 High HDI 0-20 −1.5 −2.9-−0.2 0.034 20-40 1.8 −0.4-4.1 0.092 40-75 6.9 6.1-7.7 <0.001 75- 2.2 −2.2-6.8 0.289 Medium HDI 0-15 −0.4 −1.8-0.9 0.467 15-40 2.7 1.8-3.6 <0.001 40-70 4.8 4.1-5.4 <0.001 70- 2.8 1.4-4.2 0.002 Low HDI 0-20 −0.7 −1.7-0.3 0.135 20-40 4.0 2.4-5.6 0.001 40-65 6.0 5-7.1 <0.001 65- 3.5 2.5-4.5 <0.001 China 0-40 0.2 −0.5-0.8 0.597 40-70 8.5 7.1-10 <0.001 70- 2.2 −0.8-5.3 0.133 India 0-35 1.0 0.1-1.8 0.026 35-65 4.7 3.2-6.1 <0.001 65- 2.2 0.2-4.3 0.033 High HDI
countries
(but China)0-20 −1.5 −2.7-−0.3 0.022 20-40 2.1 0.2-4.0 0.037 40-75 6.9 6.3-7.6 <0.001 75- 3.3 −0.5-7.3 0.081 Medium HDI
countries
(but India)0-10 −0.5 −4.3-3.4 0.773 10-40 2.3 1.4-3.2 <0.001 40-70 6.0 5.1-6.9 <0.001 70- 3.2 1.2-5.2 0.006 2.3.2 2022年中、印及去除中、印后全球高和中HDI国家各年龄段发病率和死亡率及其随年龄变化趋势的比较
中国白血病发病率在25岁前和35岁后低于其他高HDI国家,25~35岁间高于其他高HDI国家;印度白血病发病率在20岁前白血病发病率高于其他中HDI国家,在20岁后发病率低于其他中HDI国家,见图3C。
中国白血病死亡率在全年龄段都低于其他高HDI国家;印度白血病死亡率在25岁前高于其他中HDI国家,25~45岁与其他中HDI国家接近,45岁后则低于其他中HDI国家,见图3D。
中国白血病发病率随年龄变化趋势与除中国外高HDI国家基本一致,都呈现先下降、然后稳定、再升高的趋势,见表3。中国白血病死亡率在0~40岁稳定(slope=0.2,95%CI: −0.5~0.8,P=0.597),40~70岁逐渐升高(slope=8.5,95%CI: 7.1~10.0,P<0.001),70岁后稳定(slope=2.2,95%CI: −0.8~5.3,P=0.133);而在去除中国后其他高HDI国家白血病死亡率在0~20岁下降,在20~40岁缓慢升高,在40~75岁快速升高,75岁后稳定。见表4。
3 讨论
无论是不同HDI等级区域,还是不同国家分开比较,HDI与白血病ASIR呈正相关,拥有HDI高的国家其白血病发病率也相应较高。而ASMR不仅受ASIR影响,还包括当地经济水平、医疗卫生水平等影响HDI的因素。在HDI较高的国家,吸烟、低体力活动、肥胖、空气污染和接触芳香族环烃致癌物等污染物是患白血病的潜在危险因素;由于教育水平和社区意识较高,较高HDI国家的居民更关注自己的健康,更趋于定期体检,并能够在出现不适时及时就医,从而得到确诊[14]。然而低HDI国家往往资源匮乏,低白血病发病率可能与未及时确诊或误诊有关[15]。
尽管HDI高的国家白血病发病率高,但其医疗水平也相应较高,其ASMR受HDI影响较小。相应地,HDI高的国家拥有较高的医疗水平,因此M/I与HDI呈负相关。Amini的研究只纳入56个国家,也显示白血病的M/I与HDI呈负相关,但并未对ASIR和ASMR进行研究[15]。HDI较高的国家拥有较高的预期寿命和人口老龄化,可解释更高的白血病发病率,尤其是AML、CML和CLL[16]。在高收入国家,白血病的治疗已由传统的化疗转为化疗和免疫治疗的联合治疗,白血病死亡率都有了实质性改善[4,17]。然而对于低HDI国家,尽管白血病发病率较低,其较低的医疗水平导致其白血病M/I较高,仍是未来需要解决的重要问题。
2005到2015年,全球白血病发病数增加26%,而人口增长和老龄化只占了其中的3%[18],而大部分国家白血病ASMR都有所降低[19]。1990—2019年中国HDI由0.484升至0.762,而白血病标化发病率降低17.67%,标化死亡率降低41.65%,这与近年来医疗卫生条件改善以及对接触化学致癌物劳动者的保护密切相关[20]。
尽管近些年白血病ASMR有所下降,但白血病依旧是人类面临的主要恶性肿瘤之一。白血病主要有2个高发年龄段,15岁前儿童以淋巴系白血病为主,35岁后成年人以髓系白血病为主。ALL的发病率随年龄增长而成降低,对于15岁以下儿童,极高HDI、高HDI和中HDI国家有着更高的白血病发病率。对于35岁以上成年人,极高HDI国家白血病发病率明显高于其他三组国家,以髓系白血病为主。尽管不同HDI等级国家各年龄段发病率和死亡率的趋势相似,但本研究Joinpoint分析显示不同年龄段还存在一定差异,这可能与不同国家社会结构、经济结构、产业结构、医疗系统等方面的差异密切相关,需要进一步研究来解释此现象。男性在发病率和死亡率上都高于女性,与职业接触电离辐射或化学致癌物密切相关[17]。不仅不同HDI等级国家白血病ASIR和ASMR存在差异,而且其随年龄变化趋势也有所不同。中国与其他高HDI国家白血病发病率在各个年龄段上有所差异,而中国白血病死亡率在各个年龄段上均低于其他高HDI国家。未来中国的经济会进一步发展,HDI指数会继续升高,控制白血病发病率和死亡率将成为重要难题。一方面应改善居民的生活居住环境,主要包括监测空气污染水平、检测日用化学产品中致癌物、检测房屋装修时遗留的致癌副产物,以及鼓励居民戒烟;另一方面要增加运动的普及率,提倡健康饮食;此外,还应对职业暴露者进行重点保护,定期进行体检,严格做到“三级预防”。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。作者贡献:何奕达:数据采集和分析、图表绘制、文章撰写朱小琼:数据分析、技术支持李 政:图表绘制、数据分析柳东红:数据分析、论文修改曹广文:研究指导、论文修改、经费支持 -
表 1 2022年全球不同HDI等级国家白血病发病和死亡情况
Table 1 Leukemia incidence and mortality rate in countries with different HDI levels worldwide in 2022
HDI level Gender Incidence ASIR
(/105)Mortality ASMR
(/105)M/I Very high
HDIMale 127 669 9.84 68 449 4.23 0.43 Female 94 174 6.53 51 721 2.57 0.39 Total 221 843 8.07 120 170 3.31 0.41 High HDI Male 89 906 5.69 60 591 3.53 0.62 Female 68 534 4.24 45 430 2.51 0.59 Total 158 440 4.95 106 021 3.00 0.61 Medium
HDIMale 45 951 4.21 33 600 3.05 0.72 Female 34 435 3.16 25 949 2.34 0.74 Total 80 386 3.68 59 549 2.69 0.73 Low HDI Male 14 491 3.02 10 571 2.41 0.80 Female 11 944 2.53 8 953 2.03 0.80 Total 26 435 2.77 19 524 2.22 0.80 Global Male 278 120 6.23 173 289 3.70 0.59 Female 209 174 4.38 132 116 2.55 0.58 Total 487 294 5.26 305 405 3.09 0.59 Notes: HDI: human development index; ASIR: age-standardized incidence rate; ASMR: age-standardized mortality rate; M/I: mortality to incidence ratio. 表 2 2022年中国、印度以及去除中国后全球高HDI国家和去除印度后中HDI国家白血病发病和死亡情况
Table 2 Leukemia incidence and mortality rate in China, India, high HDI countries but China, and medium HDI countries but India in 2022
Countries Gender Incidence ASIR
(/105)Mortality ASMR
(/105)M/I China Male 46 976 5.14 29 158 2.78 0.54 Female 34 970 3.94 20 916 1.97 0.50 Total 81 946 4.54 50 074 2.37 0.52 India Male 29 487 4.19 21 549 2.99 0.71 Female 20 396 3.01 15 322 2.19 0.73 Total 49 883 3.61 36 871 2.60 0.72 High HDI
countries
but ChinaMale 42 930 6.38 31 433 4.50 0.71 Female 33 564 4.59 24 514 3.13 0.68 Total 76 494 5.43 55 947 3.76 0.69 Medium HDI
countries
but IndiaMale 16 464 4.33 12 051 3.25 0.75 Female 14 039 3.47 10 627 2.65 0.76 Total 30 503 3.88 22 678 2.93 0.76 表 3 2022年不同HDI等级国家白血病发病率随年龄变化趋势
Table 3 Variations in leukemia incidence in countries with different HDI levels in 2022 with age
Group Trend 1 Trend 2 Trend 3 Trend 4 Age
(years)slope 95%CI P Age
(years)slope 95%CI P Age
(years)slope 95%CI P Age
(years)slope 95%CI P Very high
HDI0-20 −6.0 −7.7-4.3 <0.001 20-40 3.5 0.6-6.5 0.024 40-65 8.7 6.8-10.7 <0.001 65- 4.0 2.1-5.9 0.001 High HDI 0-20 −5.1 −6.4-−3.7 <0.001 20-40 2.2 −0.2-4.6 0.065 40-70 6.1 5.0-7.2 <0.001 70- 1.8 −0.6-4.2 0.117 Medium HDI 0-20 −3.1 −4.2-−2 <0.001 20-35 1.8 −1.8-5.4 0.277 35-70 4.6 4.0-5.3 <0.001 70- 2.6 0.8-4.4 0.012 Low HDI 0-20 −2.7 −3.3-−2.1 <0.001 20-45 3.7 3.1-4.4 <0.001 45-60 6.2 4.2-8.3 <0.001 60- 3.4 3.0-3.9 <0.001 China 0-15 −6.2 −9.1-−3.1 0.002 15-40 1.3 −0.8-3.3 0.185 40-70 6.3 4.7-7.8 <0.001 70- 0.9 −2.3-4.2 0.542 India 0-20 −4.3 −5.4-−3.3 <0.001 20-40 2.8 1.0-4.6 0.007 40-65 4.9 3.7-6.0 <0.001 65- 2.1 0.9-3.2 0.003 High HDI
countries
(but China)0-20 −5.0 −6.5-−3.5 <0.001 20-35 0.6 −4.2-5.7 0.769 35-70 6.3 5.4-7.2 <0.001 70- 3.2 0.6-5.7 0.021 Medium HDI
countries
(but India)0-20 −2.8 −3.9-−1.6 0.001 20-40 2.1 0.2-4.1 0.032 40-70 5.8 4.9-6.7 <0.001 70- 2.8 0.8-4.7 0.011 表 4 2022年不同HDI等级国家白血病死亡率随年龄变化趋势
Table 4 Variations in leukemia mortality in countries with different HDI levels in 2022 with age
Group Trend 1 Trend 2 Trend 3 Trend 4 Age
(years)slope 95%CI P Age
(years)slope 95%CI P Age
(years)slope 95%CI P Age
(years)slope 95%CI P Very high
HDI0-30 0.6 0-1.2 0.053 30-50 4.8 2.9-6.7 <0.001 50-70 12.1 10.1-14.2 <0.001 70- 6.7 4.8-8.7 <0.001 High HDI 0-20 −1.5 −2.9-−0.2 0.034 20-40 1.8 −0.4-4.1 0.092 40-75 6.9 6.1-7.7 <0.001 75- 2.2 −2.2-6.8 0.289 Medium HDI 0-15 −0.4 −1.8-0.9 0.467 15-40 2.7 1.8-3.6 <0.001 40-70 4.8 4.1-5.4 <0.001 70- 2.8 1.4-4.2 0.002 Low HDI 0-20 −0.7 −1.7-0.3 0.135 20-40 4.0 2.4-5.6 0.001 40-65 6.0 5-7.1 <0.001 65- 3.5 2.5-4.5 <0.001 China 0-40 0.2 −0.5-0.8 0.597 40-70 8.5 7.1-10 <0.001 70- 2.2 −0.8-5.3 0.133 India 0-35 1.0 0.1-1.8 0.026 35-65 4.7 3.2-6.1 <0.001 65- 2.2 0.2-4.3 0.033 High HDI
countries
(but China)0-20 −1.5 −2.7-−0.3 0.022 20-40 2.1 0.2-4.0 0.037 40-75 6.9 6.3-7.6 <0.001 75- 3.3 −0.5-7.3 0.081 Medium HDI
countries
(but India)0-10 −0.5 −4.3-3.4 0.773 10-40 2.3 1.4-3.2 <0.001 40-70 6.0 5.1-6.9 <0.001 70- 3.2 1.2-5.2 0.006 -
[1] Kowalczyk A, Zarychta J, Lejman M, et al. Electrochemical and Optical Sensors for the Detection of Chemical Carcinogens Causing Leukemia[J]. Sensors (Basel), 2023, 23(7): 3369. doi: 10.3390/s23073369
[2] Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024, 74(3): 229-263.
[3] Wu Y, Li Y, Gao Y, et al. Immunotherapies of acute myeloid leukemia: Rationale, clinical evidence and perspective[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2024, 171: 116132. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116132
[4] Bispo JAB, Pinheiro PS, Kobetz EK. Epidemiology and Etiology of Leukemia and Lymphoma[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 2020, 10(6): a034819. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a034819
[5] Lin L, Yan L, Liu Y, et al. Incidence and death in 29 cancer groups in 2017 and trend analysis from 1990 to 2017 from the Global Burden of Disease Study[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2019, 12(1): 96. doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0783-9
[6] 於坛春, 林琳, 刘韫宁, 等. 基于GBD数据分析1990和2019年中国不同年龄人群恶性肿瘤死亡和伤残调整寿命年差异[J]. 中国肿瘤, 2024, 33(1): 44-52. [Yu TC, Lin L, Liu YN, et al. Change of the Mortality and DALY of Malignant Tumors Among Different Age groups in China Based on GBD data in 1990 and 2019[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Liu, 2024, 33(1): 44-52.] doi: 10.11735/j.issn.1004-0242.2024.01.A007 Yu TC, Lin L, Liu YN, et al. Change of the Mortality and DALY of Malignant Tumors Among Different Age groups in China Based on GBD data in 1990 and 2019[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Liu, 2024, 33(1): 44-52. doi: 10.11735/j.issn.1004-0242.2024.01.A007
[7] Marcotte EL, Spector LG, Mendes-de-Almeida DP, et al. The Prenatal Origin of Childhood Leukemia: Potential Applications for Epidemiology and Newborn Screening[J]. Front Pediatr, 2021, 9: 639479. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.639479
[8] Paul S, Kantarjian H, Jabbour EJ. Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia[J]. Mayo Clin Proc, 2016, 91(11): 1645-1666. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2016.09.010
[9] Orsi L, Rudant J, Ajrouche R, et al. Parental smoking, maternal alcohol, coffee and tea consumption during pregnancy, and childhood acute leukemia: the ESTELLE study[J]. Cancer Causes Control, 2015, 26(7): 1003-1017. doi: 10.1007/s10552-015-0593-5
[10] 朱小琼, 蒋栋铭, 沈佳莹, 等. 不同人类发展指数国家肺癌发病率和死亡率分析[J]. 上海预防医学, 2023, 35(4): 305-313. [Zhu XQ, Jiang DM, Shen JY, et al. Incidence and mortality of lung cancer in countries with different human development index[J]. Shanghai Yu Fang Yi Xue, 2023, 35(4): 305-313.] Zhu XQ, Jiang DM, Shen JY, et al. Incidence and mortality of lung cancer in countries with different human development index[J]. Shanghai Yu Fang Yi Xue, 2023, 35(4): 305-313.
[11] Huang J, Chan EO, Liu X, et al. Global Trends of Prostate Cancer by Age, and Their Associations With Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Human Development Index (HDI), Smoking, and Alcohol Drinking[J]. Clin Genitourin Cancer, 2023, 21(4): e261-e270. e50.
[12] 胡明, 范君言, 周雄, 等. 2020年全球肾癌发病与死亡分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2023(4): 575-580. [Hu M, Fan JY, Zhou X, et al. Global incidence and mortality of renal cell carcinoma in 2020[J]. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi, 2023(4): 575-580.] doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20220624-00558 Hu M, Fan JY, Zhou X, et al. Global incidence and mortality of renal cell carcinoma in 2020[J]. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi, 2023(4): 575-580. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20220624-00558
[13] 周雄, 胡明, 李子帅, 等. 2020年全球及中国结直肠癌流行状况分析[J]. 海军军医大学学报, 2022, 43(12): 1356-1364. [Zhou X, Hu M, Li ZS, et al. Colorectal cancer in the world and China in 2020: an analysis of epidemic status[J]. Hai Jun Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao, 2022, 43(12): 1356-1364.] Zhou X, Hu M, Li ZS, et al. Colorectal cancer in the world and China in 2020: an analysis of epidemic status[J]. Hai Jun Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao, 2022, 43(12): 1356-1364.
[14] Namayandeh SM, Khazaei Z, Lari Najafi M, et al. GLOBAL Leukemia in Children 0-14 Statistics 2018, Incidence and Mortality and Human Development Index (HDI): GLOBOCAN Sources and Methods[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2020, 21(5): 1487-1494. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.5.1487
[15] Amini M, Sharma R, Jani C. Gender differences in leukemia outcomes based on health care expenditures using estimates from the GLOBOCAN 2020[J]. Arch Public Health, 2023, 81(1): 151. doi: 10.1186/s13690-023-01154-8
[16] Hao T, Li-Talley M, Buck A, et al. An emerging trend of rapid increase of leukemia but not all cancers in the aging population in the United States[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 12070. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48445-1
[17] Sharma R, Jani C. Mapping incidence and mortality of leukemia and its subtypes in 21 world regions in last three decades and projections to 2030[J]. Ann Hematol, 2022, 101(7): 1523-1534. doi: 10.1007/s00277-022-04843-6
[18] Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration, Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2017, 3(4): 524-548. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5688
[19] Ou Z, Yu D, Liang Y, et al. Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study highlights the trends in death and disability-adjusted life years of leukemia from 1990 to 2017[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2020, 40(11): 598-610. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12094
[20] 喻静, 姜海虹, 刘欢, 等. 1990—2019年中国白血病疾病负担变化趋势及危险因素分析[J]. 公共卫生与预防医学, 2022, 33(5): 23-28. [Yu J, Jiang HH, Liu H, et al. Trends and risk factors of leukemia disease burden in China, 1990-2019[J]. Gong Gong Wei Sheng Yu Yu Fang Yi Xue, 2022, 33(5): 23-28.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2483.2022.05.005 Yu J, Jiang HH, Liu H, et al. Trends and risk factors of leukemia disease burden in China, 1990-2019[J]. Gong Gong Wei Sheng Yu Yu Fang Yi Xue, 2022, 33(5): 23-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2483.2022.05.005



 下载:
下载: