miR-18a-5p Regulates Colorectal Cancer Proliferation and Progression by Targeting RORA
-
摘要:目的
探讨miR-18a-5p和RORA在结直肠癌增殖中的作用机制及临床意义。
方法采用qRT-PCR、FISH、IHC方法检测miR-18a-5p和RORA在结直肠癌细胞和组织中的表达情况。通过EdU和CFSE实验检测细胞增殖能力、FCM实验检测细胞凋亡情况,细胞划痕实验和Transwell侵袭实验检测细胞迁移和侵袭能力。进一步通过双荧光素酶报告实验、细胞功能挽救实验、RT-PCR和Western blot实验验证miR-18a-5p对RORA的靶向调控作用。最后运用生物信息学探究miR-18a-5p调控RORA促进结直肠癌恶性增殖和侵袭进展的分子机制。
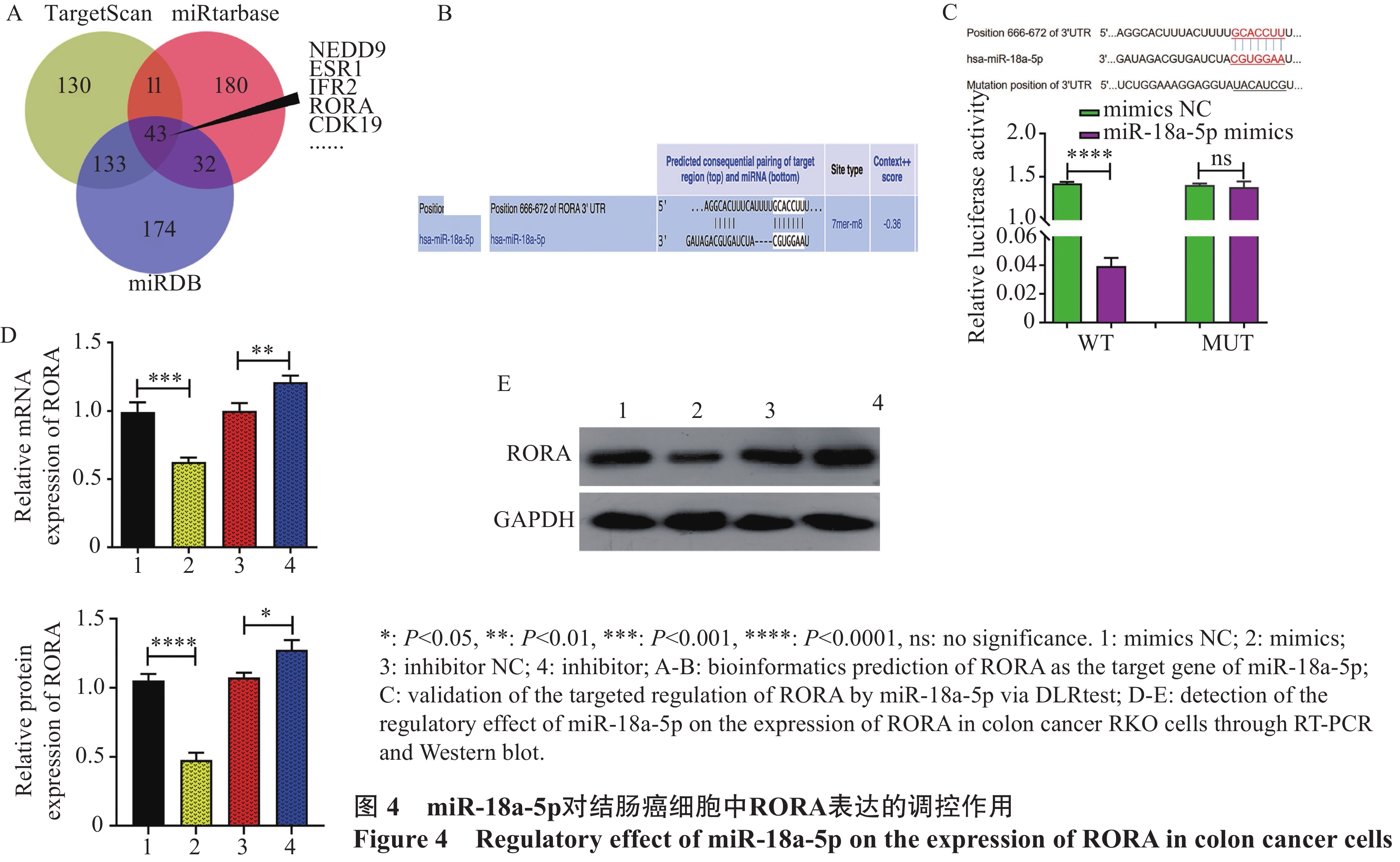
结果miR-18a-5p在结直肠癌组织和细胞中高表达(P<0.05),并且能够促进结直肠癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭(P<0.05)。此外RORA是miR-18a-5p的靶基因,过表达RORA能够有效消减miR-18a-5p促结直肠癌细胞恶性生物学表型的作用(P<0.05)。RORA在结直肠癌组织中的表达与CD8+T细胞浸润及其表面标志蛋白CD8A的表达显著正相关(P<0.05)。
结论miR-18a-5p可能通过靶向调控 RORA促进结直肠癌的进展;miR-18a-5p/RORA调控通路可能参与了结直肠癌免疫微环境的塑造,是结直肠癌的潜在治疗靶点。
-
关键词:
- miR-18a-5p /
- RORA /
- 结直肠癌 /
- 增殖
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the mechanism and clinical significance of miR-18a-5p and retinoid acid receptor-related orphan receptor-α (RORA) in the proliferation and progression of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells.
MethodsThe expressions of miR-18a-5p and RORA in CRC cells and tissues were detected via qRT-PCR, FISH, and IHC. Cell proliferation capability was detected through EdU and CFSE assay, cell apoptosis by flow cytometry assay, and cell migration and invasion abilities by cell scratch and Transwell invasion assays, respectively. The targeted regulation of miR-18a-5p on RORA was further verified via dual-luciferase reporter assay, cell function rescue test, RT-PCR, and Western blot assay. Finally, bioinformatics was used to explore the molecular mechanism of miR-18a-5p promoting malignant proliferation, invasion, and progression of CRC via regulating RORA.
ResultsmiR-18a-5p exhibited a high expression in CRC tissues and cells (P<0.05) and promoted the proliferation, migration, and invasion of CRC cells (P<0.05). In addition, RORA served as the target gene of miR-18a-5p, and its overexpression effectively reduced the promoting function of miR-18a-5p in the malignant biological phenotype of CRC cells (P<0.05). The expression of RORA in CRC tissues showed a significantly positively correlation with the infiltration of CD8+T cells and the expression of its surface marker protein CD8A.
ConclusionThe targeted regulation of RORA by miR-18a-5p promotes the proliferation and progression of CRC. The miR-18a-5p/RORA regulatory pathway possibly contributes to the immune microenvironment of CRC, which can be a potential therapeutic target for CRC.
-
Key words:
- miR-18a-5p /
- RORA /
- Colorectal cancer /
- Proliferation
-
0 引言
胆囊癌是来源于胆囊底部、体部、颈部和胆囊管上皮细胞的恶性肿瘤,其发生与胆囊结石、胆胰管汇流异常、慢性炎性反应刺激等因素有关。随着胆囊结石的发病率日益增高,胆囊癌的发生率亦呈增高趋势,位居消化系统恶性肿瘤第六位[1]。胆囊癌早期无特殊表现,发病时约45%的患者出现淋巴结转移,超过60%的患者为局部进展期,50%的患者伴有远处转移,加之治疗手段有限,导致胆囊癌患者的预后极差,整体5年生存率不足10%[2]。根治性切除仍然是胆囊癌患者获得长期生存的最有效手段,但由于胆囊癌部位不同,其手术方式和手术范围差异甚大,即便相同部位、相同分期的胆囊癌,在不同中心所采取的手术方案也不尽相同。本文将针对胆囊癌外科治疗的争议问题,结合东方肝胆外科医院临床经验进行讨论,以期对胆囊癌的外科治疗有所帮助。
1 胆囊癌的T分期和临床分型与外科治疗的关系
美国癌症联合委员会/国际抗癌联盟(AJCC/UICC)的TNM分期系统是应用最广的胆囊癌分期系统,其基于循证医学的基础,能够为胆囊癌的手术方案选择、患者预后的判断及辅助治疗方案的选择提供指导。AJCC/UICC的TNM分期第8版在第7版的基础上进行了修订,基于肿瘤不同发生部位及侵犯方向将胆囊癌T2期进一步分为T2a(腹腔侧肿瘤侵及肌周结缔组织而未超出浆膜)和T2b(肝脏侧肿瘤侵及肌周结缔组织而未超出浆膜)[3]。中华医学会外科学分会胆道外科学组制订的2019版胆囊癌诊断和治疗指南中依据胆囊癌的T分期来指导手术切除范围[4],但准确的T分期多依赖于术后病理,即便是行术中快速冰冻病理切片检查,能够提供准确T分期的中心甚少,往往需要依据术者的经验结合术中探查情况来制定手术方案。
起源于胆囊底部、体部、颈部和胆囊管的进展期胆囊癌,其肿瘤侵犯的器官及组织结构存在差异,临床表现和预后各不相同,手术方式和范围亦有差异。2019版胆囊癌诊断和治疗指南中提出,建议T2期及以上胆囊癌根据肿瘤起源部位及侵犯方向分为4型:腹腔型、肝脏型、肝门型和混合型,对手术方案的制定有一定参考价值[4]。
Kondo等[5]将胆囊癌分为6型,包括肝床型、肝门型、肝门和胆囊床型、淋巴结型、胆囊管型、局限型。根据该分型,处于相同临床分期的不同分型的肿瘤,在邻近脏器侵犯、肝脏侵犯、胆管侵犯、门静脉侵犯、淋巴结转移以及肿瘤分化程度上均有差异,因而根治性切除手术方式也不一样,其预后亦不尽相同,局限型5年存活率高达73%,而肝门型仅为12%。
在东方肝胆外科医院的一项回顾性研究中,根据肿瘤的原发部位将382例胆囊癌患者分为左半部分胆囊癌组163例(包括胆囊颈和胆囊管癌)和右半部分胆囊癌组219例(包括胆囊底部和体部癌),结果发现左半部分胆囊癌和右半部分胆囊癌的临床特点不同,右半部分胆囊癌的肿瘤侵犯深度为T4的较多,而左半部分胆囊癌淋巴结转移较多、临床分期较差、病理分化程度也较差(P < 0.05); 右半部分胆囊癌行常规根治术的比例较高,扩大根治术以联合结肠切除为主,而左半部分胆囊癌接受扩大根治术的比例较高,其中以联合半肝切除、肝胰十二指肠切除和联合胆管“T”字吻合为主[6]。研究发现左半部分胆囊癌患者的预后较右半部分胆囊癌患者差,但若能达到R0切除,两组患者生存时间无显著性差异[6]。
因此,在临床工作中,我们应结合胆囊癌的部位、浸润深度和术中探查情况来制定手术方案。
2 肝脏切除的范围
胆囊癌行肝脏切除的范围包括:胆囊床周围肝组织(> 2 cm)楔形切除、S4b+S5段切除、右半肝或扩大右半肝切除。根据肿瘤浸润深度的T分期来指导肝脏切除范围有助于统一标准,便于不同中心之间进行比较。
对于原位癌和T1a期胆囊癌,单纯胆囊切除术已足够,无需联合肝脏切除。在一项基于SEER(The National Cancer Institute's Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results, SEER)数据库的回顾性研究中发现,T1a期胆囊癌行单纯胆囊切除、胆囊切除+淋巴结清扫和胆囊癌根治术(任何类型的肝切除+淋巴结清扫)三组间的疾病特异性生存期无显著性差异(P=0.614),而对于T1b期胆囊癌,三组不同手术方式间,患者的疾病特异性生存期存在显著性差异(P=0.0002)[7]。NCCN指南建议T1b期胆囊癌常规行胆囊切除联合肝脏部分切除及区域淋巴结清扫[8]。日本肝胆胰协会胆道恶性肿瘤临床实践指南亦提出,对于侵犯到黏膜下层及以上的胆囊癌应考虑行根治性手术[9]。但在一项荟萃分析中发现,对T1b期胆囊癌,行单纯胆囊切除和根治术之间风险率无显著性差异[10]。胆囊癌属于少见疾病,T1b期胆囊癌术前确诊难度较大,其多以“意外胆囊癌”的形式出现,开展前瞻性临床研究困难重重,故手术方式的确定缺乏强有力的循证医学证据。鉴于当前的研究证据,我们建议胆囊切除+胆囊床周围肝组织楔形切除+区域淋巴结清扫应作为T1b期胆囊癌的标准术式。
Shindoh等[11]最早报道了腹膜侧T2期胆囊癌患者的5年生存率显著高于肝脏侧T2期患者(64.7% vs. 42.6%, P=0.0006),基于此项研究,许多学者对T2a期患者是否需行肝脏切除提出质疑。此外,T2a期和T2b期胆囊癌患者的肝脏切除范围是否应一致,亦存在争议。在一项纳入了937例T2期胆囊癌的国际多中心回顾性研究中发现,根治手术组的5年无疾病生存率显著优于单纯胆囊切除组(73.0% vs. 61.5%, P=0.012); 细分为T2a期和T2b期后,根治手术组与单纯胆囊切除组的5年无疾病生存率分别为(76.5% vs. 66.1%, P=0.094)和(68.2% vs. 56.2%, P=0.084),根治手术组优于单纯胆囊切除组,但无显著性差异。在根治手术组中,胆囊床周围肝组织楔形切除的患者和S4b+S5段切除患者的5年无疾病生存率无显著性差异(74.1% vs. 71.5%, P=0.720)[12]。Horiguchi等[13]报道了85例pT2N0的胆囊癌患者,55例行胆囊床周围肝组织楔形切除,30例行S4b+S5段切除,两组患者5年总体生存率(76.2% vs. 65.9%, P=0.298)和无疾病生存率(74.4% vs. 63.3%, P=0.235)无显著性差异。因此,T2期患者能够从根治性手术中获益,对于T2a期患者可行胆囊切除+胆囊床周围肝组织楔形切除+区域淋巴结清扫,对于T2b期患者,应根据技术条件和术中情况,行胆囊切除+胆囊床周围肝组织楔形切除或S4b+S5段切除+区域淋巴结清扫。
T3期肿瘤已穿透浆膜和(或)直接侵入肝脏和(或)一个邻近器官或结构,如胃、十二指肠、结肠、胰腺、网膜或肝外胆管,根据肝脏侵犯程度,施行胆囊切除S4b+S5段切除或扩大右半肝切除+区域淋巴结清扫,若合并其他脏器侵犯,需行联合脏器切除。T4期胆囊癌侵犯门静脉或肝动脉或侵犯两个或更多肝外器官或结构,难以根治性切除,应以综合治疗为主。
胆囊癌患者肝脏切除的范围历来存在争议,理论上可依据T分期进行划分,而实践中由于准确的T分期术前难以获得、术中难以判断,往往需要术者根据术中探查的情况确定肝脏切除的范围,因此需要由经验丰富的胆道外科医师作出合理的术中决策。
3 淋巴结的标准清扫与扩大清扫
在2019版胆囊癌诊断和治疗指南中[4],将胆囊癌的淋巴结转移分为3站:第1站为胆囊颈部(12c组)、胆总管旁(12b组)淋巴结; 第2站为门静脉后方(12p组)、肝总动脉旁(8组)、肝固有动脉(12a)、胰头后上方(13a组)、肝门部(12h)淋巴结; 第3站为腹腔动脉(9组)、胰头周围(13b、17、18组)、肠系膜上动脉周围(14组)、腹主动脉周围(16组)淋巴结。第1、2站转移为区域淋巴结转移,第3站转移为远处转移,其中区域淋巴结转移范围的定义与日本肝胆胰协会胆囊癌分期的范围一致[14]。在第8版AJCC/UICC TNM分期中,将N1定义为1~3个区域淋巴结转移,N2定义为≥4个区域淋巴结转移,考虑到淋巴结获取数目以及淋巴结阳性率对预后判断的重要性,建议至少获取6枚淋巴结送检[15]。
胆囊癌易发生淋巴结转移,肿瘤浸润深度与淋巴结转移发生率呈正相关,T1a期、T1b期、T2期和T3/T4期淋巴结转移发生率分别为0~4%、12.5%~20.0%、20%~62%及60%~81%[16-17]。基于T1b期胆囊癌淋巴结转移发生率明显增高,2019版胆囊癌诊断和治疗指南[4]、CSCO胆道系统肿瘤诊断治疗专家共识[18]、NCCN指南[8]均建议T1b期及以上分期的胆囊癌行区域淋巴结清扫。近年来,东方肝胆外科医院对可根治性切除的T1b期及T2期胆囊癌患者常规实施标准的区域淋巴结清扫,力争做到肝十二指肠韧带胆管和血管骨骼化; 对能达到R0切除的进展期胆囊癌患者,若9组、16a2组和16b1组有可疑转移的第3站淋巴结,亦可考虑施行相应区域的扩大清扫,再超出此范围的转移淋巴结不建议行清扫。对于经验丰富的胆道专科医师而言,选择性的扩大淋巴结清扫范围并不会增加手术并发症发生率,还能够更准确地指导分期,部分患者可能从中获益。但由于扩大淋巴结清扫的循证医学证据并不充分,仅限于在大的胆道肿瘤中心进行临床研究,不建议推广应用。
4 扩大切除和姑息切除的意义
对于绝大多数T3、T4期胆囊癌患者,需采取扩大切除才有可能获得阴性切缘,包括联合肝外胆管切除、联合邻近脏器切除、右半肝或扩大右半肝切除、肝胰十二指肠切除以及扩大淋巴结清扫区域的手术。
胆囊颈及胆囊管的肿瘤易侵犯肝外胆管,导致梗阻性黄疸,此时需联合肝外胆管切除以达到根治性切除的目的。但对于肝外胆管未受累的患者,预防性肝外胆管切除并不能给患者带来生存获益,故不建议施行[19-20]。
进展期胆囊癌可累及大网膜、结肠、胃窦、十二指肠,若为肿瘤直接浸润可行联合脏器扩大切除,若为转移淋巴结侵犯相应脏器,预后较差,不建议行扩大切除[21]。
当肿瘤累及胆管下段和胰腺,或胰头后方的转移性淋巴结融合成团难以清扫时,可考虑行肝胰十二指肠切除(整块切除肝脏、胆囊、肝外胆管和胰十二指肠)。日本学者对肝胰十二指肠切除的定义是指包括肝门部胆管在内所有肝外胆管切除的术式,与西方学者的定义有所不同。大范围肝胰十二指肠切除是指切除3段以上的肝组织,若联合血管切除重建,则手术难度更大、术后并发症发生率和死亡率显著增加,而患者生存获益并不明确。肝胰十二指肠切除术后并发症发生率和死亡率分别为35%~100%和0~47%不等,故建议该术式仅在大的肝胆胰中心、由经验丰富的专科医师施行[22]。考虑到胆囊癌恶性程度高,施行肝胰十二指肠切除术更应慎重。
目前多数指南对不能获得R0切除的胆囊癌患者不建议行减瘤手术,这是基于对残余肿瘤缺乏有效后续治疗手段前提下的合理抉择。随着二代测序技术的进步以及免疫治疗和靶向治疗的飞速发展,姑息性的胆囊切除亦有一定的应用价值,东方肝胆外科医院在此方面也进行了初步的探索。首先,姑息性胆囊切除后,可获取充足的样本进行二代测序了解患者基因突变情况,指导术后开展免疫治疗和靶向治疗; 其次,减瘤手术后,对伴有腹膜转移的胆囊癌患者实施腹腔热灌注化疗有可能延长患者生存时间,改善生活质量[23-24]; 最后,很多胆囊癌患者存在胆囊颈部结石嵌顿、胆囊肿大积脓,有发热、腹痛等症状,姑息性胆囊切除可缓解症状,提高患者生存质量。因此,结合患者具体情况,有选择性的施行姑息性胆囊切除对晚期胆囊癌患者仍有积极的意义。
在胆囊癌外科治疗中,对有希望达到R0切除的进展期病变要积极进行手术,但同时又要避免盲目扩大手术范围,导致患者术后生活质量急剧下降。在肿瘤综合治疗效果日益趋好的时代,手术切除不再是胆囊癌治疗的唯一选择,给患者留有接受免疫治疗和靶向治疗的余地,可能会获得更好的生活质量和生存期。
5 腹腔镜手术的是与非
胆囊癌是否应行腹腔镜手术一直是外科领域争论的热点。日本肝胆胰协会胆道恶性肿瘤临床实践指南[9]明确指出,对于术前怀疑胆囊癌的患者应行开腹手术。从技术层面而言,开展腹腔镜胆囊癌根治术完全可行,但考虑到胆囊癌易发生腹腔转移及Trocar切口种植转移的生物学特性,我们反对开展腹腔镜胆囊癌根治术。
胆囊癌患者在腹腔镜切除术后Trocar切口种植转移的发生率为10%左右[25],笔者所在科室曾多次接诊在外院行腹腔镜切除术后短期内即出现Trocar切口种植转移的胆囊癌患者,在深感痛心的同时,也在不断思考腹腔镜在胆囊癌患者中的应用价值。对于Tis和T1a期胆囊癌,由于术前难以诊断,绝大多数患者接受了腹腔镜胆囊切除术,实践证明效果确切; 对于T3和T4期胆囊癌,术前诊断并不困难,目前主流的观点仍然是行开腹手术。当前的争议主要集中在T1b和T2期胆囊癌患者初次和再次手术方式的选择。近年来,有文献报道对T1b和T2期患者、甚至部分T3期患者开展腹腔镜手术取得良好效果,总体生存率和疾病无复发生存率与开腹手术无显著性差异。但这些研究多为小样本、单中心的经验总结和回顾性研究,仍需要高质量的前瞻性临床研究来进一步证实[26-29]。
腹腔镜探查手术在胆囊癌治疗中有一定价值。在一项前瞻性研究中,Agarwal等[30]对409例胆囊癌患者行诊断性腹腔镜探查,其中23.2%的病例在探查中发现腹腔转移而避免了开腹手术,腹腔镜探查的准确率约为55.9%。笔者认为,对于术前影像学判断可行根治性切除的患者,不建议腹腔镜探查,以避免腹腔转移及Trocar切口种植转移的发生; 对于术前影像学判断可能无法行根治手术的胆囊癌患者,腹腔镜探查是可行的,若证实术前判断,可行活检手术; 若探查后考虑可根治性切除,建议行开腹手术。
6 意外胆囊癌的处理
意外胆囊癌是指初诊为良性疾病而行胆囊切除术,经组织病理学检查诊断为胆囊癌。据报道意外胆囊癌发生率为0.2%~2.8%[31],总体可占胆囊癌总数的50%以上[32],其中以早期胆囊癌为主,还包括部分T3、T4期的胆囊癌。
但笔者认为T3、T4期“意外”胆囊癌绝大多数是由于术前检查不完善所导致,不应定义为意外胆囊癌; 对于Tis和T1a期意外胆囊癌施行单纯的胆囊切除术,无论是腹腔镜或开腹手术,均可以达到治愈,亦不是讨论的焦点。目前对于T1b和T2期意外胆囊癌需追加手术已成共识,主要的争议集中于再次手术的时机和方式。
Ethun等[33]在一项多中心回顾性研究中纳入207例意外胆囊癌,根据再次手术的时机分为 < 4周、4~8周和 > 8周三组,该研究发现4~8周组的中位总体生存期(40.4月)明显优于其他两组(17.4月和22.4月),多因素回归分析亦提示手术时机是影响生存期的危险因素。但根据我们的经验和临床观察,早期施行补救性手术并不影响患者生存期,还需要更高质量的研究来证实手术时机对生存期的影响。
虽然有文献报道,与开腹手术相比,再次手术时采用腹腔镜技术可获得非劣效的3年总体生存率(87% vs. 62%, P=0.502)[34],但考虑到再次手术为补救性手术,区域淋巴结清扫的难度远大于初次手术,故选择开腹手术更为合理。
尽管腹腔镜意外胆囊癌术后Trocar切口发生转移的概率从18.6%(1991—1999年)降至10.3%(2000—2014年)[25],但这仍然是非常高的比例,再次手术时是否需要预防性切除Trocar切口也存在争论。有文献报道,常规切除Trocar切口并未改善患者生存[31],但对于存在高危因素的患者,如术中胆汁溢出、肿瘤突破浆膜层、胆囊未使用标本袋取出者,仍建议联合Trocar切口切除[35]。
7 结语
胆囊癌可防难治,鉴于胆囊癌的预后极差,针对引起胆囊癌的高危因素进行预防显得尤为重要。在当前形势下,外科治疗仍然是胆囊癌治疗的核心部分,胆囊癌的术式并非一成不变,对于有争议的情形,需要结合病变部位和浸润程度、患者个体情况以及医师的技术能力来制定最佳手术方案。在胆囊癌外科治疗中,手术方式的选择远比手术技巧更为重要,对于可获得根治性切除的胆囊癌不建议行腹腔镜手术。在目前进展期胆囊癌居多的情况下,开展综合治疗、加强对胆囊癌患者的全程管理亦是外科医师需要重视的工作。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。作者贡献:陈一锋、王涛:研究设计,文章撰写王帅、柴明明、张迪、王春霞、赵丽霞、张洪来、杨熊飞:实验操作,数据分析张维胜:提供研究资料 -
表 1 慢病毒序列信息
Table 1 Lentivirus sequence information
Lentiviral
vectorsPrimer(5′- 3′) miR-18a-5p
mimicsSense UAAGGUGCAUCUAGUGCAGAUAG Anti-
senseAUCUGCACUAGAUGCACCUUAUU mimics NC Sense CCCTGCTGTGTGCCGTGATAAC Anti-
senseAGTGTGTTGTGCCTGCTGAAGTG mi-18a-5p
inhibitorCUAUCUGCACUAGAUGCACCUUA Inhibitor NC GGAACGATACAGAGAAGATTAGC 表 2 PCR引物序列
Table 2 PCR primer sequences
Genes Primer (5′- 3′) Lengths
(bp)RORA 109 Forward CTATCCCTCCAAGGCACAAGTGAAC Reverse ACACAAGACTGACGAGCACATCAAG miR-18a-5p AAGCGCCTTAAGGTGCATCTAG U6 68 Forward GGAACGATACAGAGAAGATTAGC Reverse TGGAACGCTTCACGAATTTGCG GAPDH 206 Forward AGGGCTGCTTTTAACTCTGGT Reverse CCCCACTTGATTTTGGAGGGA 表 3 miR-18a-5p表达与结直肠癌临床病理特征的关系
Table 3 Relationship between miR-18a-5p expression and clinicopathological characteristics of CRC
Characteristics N miR-18a-5p P 2−∆∆Ct Gender 0.21 Male 13 1.76±0.19 Female 17 1.68±0.16 Age(years) 0.76 ≤60 8 1.70±0.18 >60 22 1.72±0.18 Tumor size(cm) 0.97 ≤3 5 1.72±0.31 >3 25 1.72±1.75 Lymph node metastasis 0.02 Yes 5 1.88±0.19 No 25 1.68±0.16 Tumor location 0.29 Colon 18 1.69±0.20 Rectum 12 1.76±0.14 T stage 0.10 T1-T2 5 1.60±0.22 T3-T4 25 1.74±0.16 N stage 0.46 N0 16 1.69±0.18 N1-N2 9 1.74±0.17 TNM stage 0.03 Ⅰ/Ⅱ 15 1.63±0.17 Ⅲ/Ⅳ 15 1.77±0.16 Vascular invasion 0.26 Yes 20 1.77±0.23 No 10 1.69±0.14 Nerve invasion 0.69 Yes 24 1.72±0.14 No 6 1.69±0.29 Serum CEA (ng/ml) 0.30 ≤5 15 1.69±0.15 >5 15 1.76±0.21 -
[1] Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(3): 229-263. doi: 10.3322/caac.21834
[2] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(1): 7-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21332
[3] Qi B, Dong Y, Qiao XL. Effects of miR-18a on proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer cells by regulating RUNX1[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(19): 9957-9964.
[4] Cui M, Qu F, Wang L, et al. MiR-18a-5p Facilitates Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting CPEB3[J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2021, 20: 2091181432.
[5] Liang C, Zhang X, Wang HM, et al. MicroRNA-18a-5p functions as an oncogene by directly targeting IRF2 in lung cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2017, 8(5): e2764. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.145
[6] Lee JM, Kim H, Baek SH. Unraveling the physiological roles of retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor α[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2021, 53(9): 1278-1286. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00679-8
[7] Byun JK, Choi YK, Kang YN, et al. Retinoic acid-related orphan receptor alpha reprograms glucose metabolism in glutamine-deficient hepatoma cells[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 61(3): 953-964. doi: 10.1002/hep.27577
[8] Mao W, Xiong G, Wu Y, et al. RORα Suppresses Cancer-Associated Inflammation by Repressing Respiratory Complex I-Dependent ROS Generation[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(19): 10665. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910665
[9] Jiang Y, Zhou J, Zhao J, et al. MiR-18a-downregulated RORA inhibits the proliferation and tumorigenesis of glioma using the TNF-α-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. EBioMedicine, 2020, 52: 102651. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102651
[10] Xiao W, Geng W, Zhou M, et al. POU6F1 cooperates with RORA to suppress the proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma by downregulation HIF1A signaling pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(5): 427. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04857-y
[11] Muljo SA, Kanellopoulou C, Aravind L. MicroRNA targeting in mammalian genomes: genes and mechanisms[J]. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med, 2010, 2(2): 148-161. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.53
[12] Zhang J, He J, Zhang L. The down-regulation of microRNA-137 contributes to the up-regulation of retinoblastoma cell proliferation and invasion by regulating COX-2/PGE2 signaling[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 106: 35-42. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.099
[13] Kang Y, Zhang Y, Sun Y. MicroRNA-198 suppresses tumour growth and metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting CDK4[J]. Int J Oncol, 2021, 59(1): 39. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5219
[14] Wang X, Chang K, Gao J, et al. MicroRNA-504 functions as a tumor suppressor in oral squamous cell carcinoma through inhibiting cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting CDK6[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2020, 119: 105663. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2019.105663
[15] Zhang W, Hsu P, Zhong B, et al. MiR-34a Enhances Chondrocyte Apoptosis, Senescence and Facilitates Development of Osteoarthritis by Targeting DLL1 and Regulating PI3K/AKT Pathway[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 48(3): 1304-1316. doi: 10.1159/000492090
[16] Otto T, Candido SV, Pilarz MS, et al. Cell cycle-targeting microRNAs promote differentiation by enforcing cell-cycle exit[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2017, 114(40): 10660-10665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1702914114
[17] Zhu Q, Zhang Q, Gu M, et al. MIR106A-5p upregulation suppresses autophagy and accelerates malignant phenotype in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Autophagy, 2021, 17(7): 1667-1683. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1781368
[18] Jiao P, Wang XP, Luoreng ZM, et al. miR-223: An Effective Regulator of Immune Cell Differentiation and Inflammation[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2021, 17(9): 2308-2322. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.59876
[19] Ali SZ, Langden S, Munkhzul C, et al. Regulatory Mechanism of MicroRNA Expression in Cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(5): 1723. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051723
[20] Dong H, Li Y, Zhou J, et al. MiR-18a-5p Promotes Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Endometrial Cancer Cells by Targeting THBD[J]. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr, 2021, 31(2): 63-73. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2021037776
[21] Liang B, Zhou C, Cui S, et al. Upregulation of miR-18a-5p promotes the proliferation of prostate cancer via inhibiting the expression of SLC40A1[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2021, 224: 153448. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153448
[22] Gao S, Zhu D, Zhu J, et al. miR-18a-5p Targets FBP1 to Promote Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Liver Cancer Cells and Inhibit Cell Apoptosis[J]. Comput Math Methods Med, 2021, 2021: 3334065.
[23] Li J, Zhong Y, Cai S, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling in the colorectal normal-adenoma-carcinoma transition[J]. Oncol Lett, 2019, 18(2): 2013-2018.
[24] Humphreys KJ, McKinnon RA, Michael MZ. miR-18a inhibits CDC42 and plays a tumour suppressor role in colorectal cancer cells[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(11): e112288. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112288
[25] 玛依努尔·达吾提, 胡尼其古丽·阿巴克, 阿依努尔·玉苏普, 等. 过表达miR-18a-5p对结肠癌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响及其作用机制[J]. 山东医药, 2018, 58(8): 10-13. [Mayinur Dawut, Ghunichigul Abak, Aynur Yusup, et al. Effect of miR-18a-5p overexpression on cell proliferation and apoptosis of colon cancer cells[J]. Shandong Yi Yao, 2018, 58(8): 10-13.] Mayinur Dawut, Ghunichigul Abak, Aynur Yusup, et al. Effect of miR-18a-5p overexpression on cell proliferation and apoptosis of colon cancer cells[J]. Shandong Yi Yao, 2018, 58(8): 10-13.
[26] Kochan DZ, Kovalchuk O. Circadian disruption and breast cancer: an epigenetic link?[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(19): 16866-16882. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4343
[27] Xian H, Li Y, Zou B, et al. Identification of TIMELESS and RORA as key clock molecules of non-small cell lung cancer and the comprehensive analysis[J]. BMC Cancer, 2022, 22(1): 107. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09203-1
[28] Wang X, Jia R, Chen K, et al. RORα and REV-ERBα are Associated With Clinicopathological Parameters and are Independent Biomarkers of Prognosis in Gastric Cancer[J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2021, 20: 2091185738.
[29] Zhao J, Jiang Y, Chen L, et al. The EIF4A3/CASC2/RORA Feedback Loop Regulates the Aggressive Phenotype in Glioblastomas[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 699933. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.699933
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 张亚奇,潘明胜,田彦军,张国荣. 双氢青蒿素对消化道肿瘤作用及其机制的研究进展. 医学信息. 2023(14): 173-177+187 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 赵良涛,程张军. 胆囊癌术后复发的影响因素. 中国实用外科杂志. 2023(11): 1299-1304 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李雪川,陈炜,刘颖斌. 胆囊癌临床研究基础与现状. 肿瘤. 2023(06): 472-477 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 时志刚,李晓勇,陈艳军,程冰冰,陈升阳,胡水全,仝昊. 纳米刀消融术治疗晚期胆囊癌的疗效及安全性分析. 重庆医学. 2022(19): 3293-3297 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 邢跃栊,曲赛,倪德生,陈国梁,张凯,杨佳. 胆囊癌切除术围手术期输血与术后生存和无瘤生存的关系. 中国医药导报. 2022(28): 28-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: