Prognostic Predictive Value of ITPKB Mutation's Variant Allele Frequency in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
-
摘要:目的
探讨弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)ITPKB突变变异等位基因频率(VAF)与预后的相关性。
方法纳入2014年6月—2020年12月在新疆维吾尔自治区人民医院初次诊断的155例DLBCL患者,获取石蜡包埋的肿瘤组织标本。提取肿瘤组织DNA,应用二代测序技术检测包括ITPKB在内的475种热点基因,分析高频突变基因VAF与无进展生存(PFS)和总生存(OS)的关系。
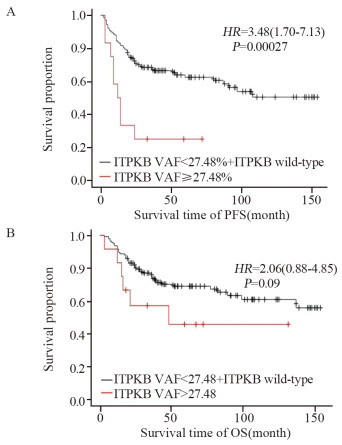
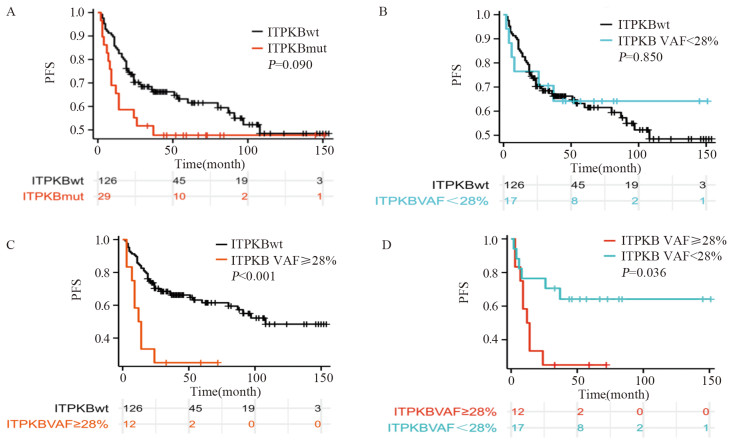
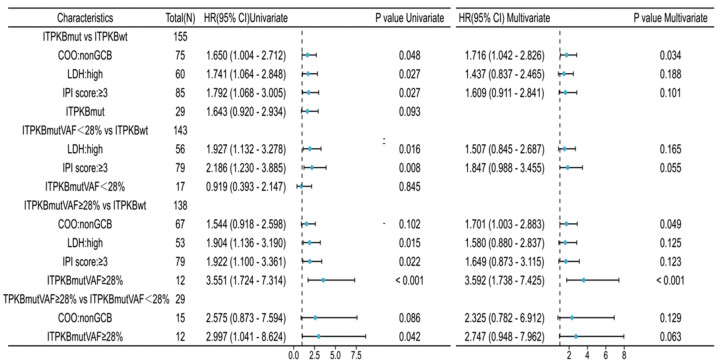
结果ITPKB的突变频率为18.71%,ITPKB突变患者的PFS较未突变患者的PFS明显缩短,但差异无统计学意义(37.00 vs. 108.00个月;HR=1.643, 95%CI: 0.920~2.934, P=0.093)。通过基于R语言的网页工具探寻可区分患者预后的最佳VAF截断值,将患者依据VAF值分成对应的两组(高VAF组 vs. 低VAF+野生型组),ITPKB最佳VAF的截断值为27.48%(HR=3.48, 95%CI: 1.70~7.13, P=0.00027),纳入年龄、性别、COO分型、IPI、LDH等临床指标行多因素Cox分析,结果显示PFS与高ITPKB VAF(≥28%)相关(HR=3.592, 95%CI: 1.738~7.425, P < 0.001),是PFS独立的不良预测因素。
结论ITPKB突变高负荷为DLBCL患者PFS的独立危险因素,ITPKB突变的VAF在DLBCL患者中具有预后预测价值。
-
关键词:
- 弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤 /
- 变异等位基因突变频率 /
- 预后 /
- 基因突变
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the correlation between ITPKB mutation's variant allele frequency (VAF) and prognosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
MethodsThis study included 155 patients with DLBCL initially diagnosed in the People's Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region from June 2014 to December 2020. Paraffin-embedded tumor tissue specimens were obtained, and tumor tissue DNA was extracted. A total of 475 hotspot genes including ITPKB were detected by the next generation sequencing to analyze the relationship of the VAF of high-frequency mutant gene with progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS).
ResultsThe mutation frequency of ITPKB was 18.71%. The PFS was significantly shorter in the patients with ITPKB mutations than in those without mutations (37 months vs. 108 months; HR=1.643, 95%CI: 0.920-2.934, P=0.093). The R-language based web tool was used to find the best VAF cutoff to differentiate prognosis. The patients were divided into two groups (VAF High vs. VAF Low+Wt) according to their VAF values. The optimal VAF threshold for ITPKB was 27.48% (HR=3.480, 95%CI: 1.70-7.13, P=0.00027). Multivariate Cox analysis was conducted using clinical indicators such as age, gender, COO classification, IPI, and LDH, and the results showed that PFS was associated with high ITPKB VAF (≥28%) (HR=3.592, 95%CI: 1.738-7.425, P < 0.001) which was an independent adverse predictor of PFS.
ConclusionThe high load of ITPKB mutation is an independent risk factor for the PFS of patients with DLBCL, and the VAF of ITPKB mutation has a prognostic predictive value for patients with DLBCL.
-
Key words:
- Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma /
- Variant allele frequency /
- Prognosis /
- Gene mutation
-
0 引言
前列腺癌常见于50岁以上的男性,其发病率居全球男性恶性肿瘤首位,死亡率居第二位[1]。中高危前列腺癌常伴有淋巴结转移,有研究表明淋巴结转移的数量与无进展生存期及总生存期相关[2]。联合应用前列腺特异性膜抗原(prostate-specific membrane antigen, PSMA)正电子发射计算机体层摄影(positron emission tomography/computed tomography, PET/CT)和前哨淋巴结活检,可使中高危前列腺癌患者淋巴结分期的准确性达到94%[3]。68Ga标记的PSMA对前列腺癌淋巴结转移具有较好的诊断性能[4-5],但68Ga的半衰期为68分钟,远程运输存在一定的挑战,而18F标记的PSMA半衰期为110分钟,有利于长距离运输,而且患者接受的辐射相对更少,图像分辨率更高[6-7]。同时,18F标记的PSMA对膀胱的放射性剂量相对更低,尤其是18F-PSMA-1007在尿路的清除率极低[8],对盆腔内区域淋巴结转移的诊断可能具有较高的准确性。为进一步了解18F标记的PSMA PET/CT对前列腺癌区域淋巴结转移的诊断价值,我们进行此次Meta分析,以便为临床实践提供参考。
1 资料与方法
1.1 资料的纳入与排除标准
纳入标准:(1)18F标记的PSMA PET/CT用于评估前列腺癌区域淋巴结转移或分期的文献;(2)所有病灶以穿刺活检或术后病理或临床影像学随访作为诊断金标准;(3)能够直接或间接获取真阳性数(TP)、假阳性数(FP)、假阴性数(FN)及真阴性数(TN)的四格表数据;(4)以患者为分析单位的文献,病例数不少于10例。
排除标准:(1)与本研究目的无关的文章;(2)综述性文章、读者来信、病例报告、会议摘要、动物实验;(3)以患者为分析单位的文献,病例数少于10例;(4)数据不齐全、无法直接或间接提取四格表数据的文献。
1.2 文献检索
两名研究者独立通过计算机检索中英文数据库,数据库包括:中国知网(CNKI)、万方、维普、PubMed、Embase、Cochrane Library、Web of Science等。检索时间为2000年1月1日至2021年5月31日。英文检索词:prostatic neoplasms、prostate cancer、prostate carcinoma、PSMA、prostate-specific membrane antigen、18F-DCFPyL、18F-PSMA-1007、18F-DCFBC、positron emission tomography、PET、computed tomography、CT、lymph node。中文检索词:前列腺癌、前列腺特异性膜抗原、正电子发射计算机体层摄影。检索方式为主题词与自由词结合,经过多次预检索后确定最终的检索策略,并根据各数据库的特点进行适当调整。以PubMed为例,检索策略为:#1 Prostatic Neoplasms [Mesh] OR Prostate cancer OR Prostate carcinoma;#2 PSMA OR Prostate-specific membrane antigen;#3 DCFPyL OR PSMA-1007 OR DCFBC;#4 Positron emission tomography/computed tomography OR PET/CT;#5 Lymph node;#6 #1 AND #2 AND #3 AND #4 AND #5。
1.3 文献筛选与数据提取
利用EndNote X9删除重复文献后,所有文献均由两名研究者独立进行筛选,先浏览文献的标题和摘要,根据纳入标准和排除标准筛选出合适的文献,并进行全文阅读及提取相关数据。提取数据包括:第一作者、国家、发表年份、患者群体(新发或复发)、样本量、年龄、研究类型、诊断标准、示踪剂、TP、FP、FN、TN、分析单位。如研究中提供了两名或以上观察者的数据,则取平均值,遇到分歧时共同讨论得出一致的结论,若仍有异议则请第三方决定。
1.4 文献质量评价
使用Cochrane推荐的QUADAS-2(第2版诊断准确性研究质量评估工具)进行文献质量评价,该工具包括病例选择、待评价试验、金标准、病例流程和进展情况四个方面。分别由两名评价者独立对纳入文献进行质量评价,若偏倚风险低或适用性好则评估为“低风险”、若偏倚风险不清楚则评估为“不确定”,若偏倚风险高或适用性差则评估为“高风险”。
1.5 数据分析
采用Meta-disc1.4和Stata 16.0软件分析提取的四格表数据。首先,使用Spearman相关系数及综合受试者工作特征曲线(summary receiver operating characteristic, SROC)检验纳入文献是否存在阈值效应,若P < 0.05,提示存在阈值效应,则拟合SROC曲线;若P > 0.05,提示不存在阈值效应,则使用Stata 16.0软件包midas命令统计分析四格表数据,计算各研究的合并敏感度(sensitivity, Sen)、合并特异性(specificity, Spe)、合并阳性似然比(positive likelihood ratio, PLR)、合并阴性似然比(negative likelihood ratio, NLR)、诊断比值比(diagnostic odds ratio, DOR)和SROC曲线下面积(AUC)。通过异质性指数I2和χ2检验评估各研究的异质性。I2 < 25%为不存在异质性,25% < I2 < 50%为异质性较小,50% < I2 < 75%为存在一定的异质性,I2 > 75%则为存在较大的异质性。若异质性较明显,则进行Meta回归分析明确异质性的来源,如分析单位、研究类型、不同示踪剂等,计算各亚组之间的Sen、Spe。使用Stata 16.0制作漏斗图评估发表偏倚,检验水准P=0.05。
2 结果
2.1 文献检索结果
通过检索中英文数据初步检出相关文献664篇,使用Endnote X9软件进行文献管理,删除重复文献122篇,经过阅读标题和摘要排除不相关文献484篇,对剩下的可能符合要求的58篇文献阅读全文,根据排除标准剔除无法直接或间接提取四格表数据的50篇文献,最终筛选出符合纳入标准的文献8篇,见图 1。
2.2 纳入文献基本特征
共纳入文献8篇,其中英文文献7篇,中文文献1篇;前瞻性研究5篇,回顾性研究3篇;共纳入分析754例前列腺癌患者的2 101枚淋巴结。只纳入新发病例的文献5篇,只纳入复发病例的文献1篇,同时纳入了新发和复发病例的文献2篇。以淋巴结为分析单位的文献3篇,以患者为分析单位的文献4篇,以患者和淋巴结为分析单位的文献1篇。以病理作为唯一诊断标准的文献7篇,以病理、影像学及临床随访资料作为诊断标准的文献1篇。5篇文献使用18F-DCFPyL作为示踪剂,3篇使用18F-PSMA-1007作为示踪剂,见表 1。
表 1 纳入研究的基本特征Table 1 Characteristics of included studies
2.3 纳入文献的质量评价
采用RevMan 5.3软件,根据QUADAS-2[16]中的条目对纳入的8篇文献进行质量评价,结果显示:大部分纳入文献在病例选择、待评价试验方面偏倚较小,而在金标准、病例流程和进展情况两个方面可能存在一定的偏倚,见图 2。一篇文献金标准的解读未使用盲法[9],部分文献没有足够的信息判断是否使用盲法[12, 14-15]。部分病例因病情变化未完成手术,或因治疗方案改变等原因无法获得病理结果而未被纳入最终的分析[8, 10, 13-14],其中一篇文献并非以病理作为唯一的诊断标准[11]。各纳入文献在病例的选择、待评价试验及金标准三方面的临床适用性较好。
2.4 Meta分析结果
2.4.1 异质性分析
阈值分析结果提示Spearman相关系数为0.117(P=0.765),SROC曲线显示各研究的数据点不呈“肩臂状”分布,说明不存在阈值效应,见图 3。Sen和Spe的异质性结果显示,PSen < 0.01,ISen2=89.51%;PSpe < 0.01,ISen2=97.38%,提示各纳入文献的Sen和Spe存在高度异质性,见图 4。
2.4.2 诊断的准确性
18F标记的PSMA PET/CT诊断前列腺癌区域淋巴结转移的结果显示:Sen=0.82(95%CI: 0.61~0.93)、Spe=0.98(95%CI: 0.91~1.00)、PLR=45.7(95%CI: 9.0~231.3)、NLR=0.18(95%CI: 0.07~0.45)、DOR=251(95%CI: 34~1851)、AUC=0.97(95%CI: 0.95~0.98),见图 4。
2.4.3 Meta回归分析
对本研究可能引起异质性的原因进行Meta回归分析,分析因素包括:研究类型、分析水平、放射性示踪剂、是否只纳入新发病例及术前淋巴结分期。结果显示:以淋巴结为分析单位是引起Sen异质性的主要原因,而前瞻性研究、使用放射性示踪剂18F-PSMA-1007、只纳入新发病例及术前淋巴结分期是引起Spe异质性的主要原因,见表 2。
表 2 18F标记的PSMA PET/CT诊断前列腺癌区域淋巴结转移的Meta回归分析结果Table 2 Meta-regression analysis results of 18F-labeled PSMA PET/CT for diagnosis of regional lymph node metastasis in prostate cancer
2.4.4 发表偏倚评估
使用Stata 16.0软件绘制发表偏倚漏斗图,其中横坐标为DOR,纵坐标为有效样本量的平方根的倒数(1/ESS1/2),见图 5。所有纳入篇文献中,P=0.56(t=-0.61, 95%CI: -38.29, 22.67),说明发表偏倚存在的可能性较小。
3 讨论
中高危前列腺癌患者易发生区域或远处转移,部分临床复发的患者,复发部位最先发生于前列腺床和盆腔淋巴结,因此对淋巴结转移的准确诊断至关重要,关系患者的管理及预后[2, 17]。根据美国临床肿瘤学会(American Society of Clinical Oncology, ASCO)指南,对于常规影像学检查不明确或前列腺癌术后常规影像学检查阴性而前列腺特异性抗原(prostate-specific antigen, PSA)升高的患者,推荐行PSMA显像,尤其是有意愿行挽救性放疗的患者[18]。用于PSMA显像的放射性示踪剂主要有两类,包括68Ga和18F标记的药物。68Ga标记的PSMA主要缺点是半衰期较短、患者量多时生产成本较高及在膀胱的放射性相对较高,而18F标记的药物可以弥补这样的缺点[6]。有Meta分析表明,68Ga标记的PSMA PET/CT对前列腺癌术前淋巴结分期具有中度敏感度和高度特异性[19-20],尚未有研究系统性总结18F标记的PSMA PET/CT对前列腺癌区域淋巴结转移的诊断性能,本文就此进行Meta分析。
18F标记的PSMA PET/CT示踪剂主要有3种,分别是18F-PSMA-1007、18F-DCFPyL和18F-DCFBC,本研究纳入文献只包括前两种。相对而言,18F-PSMA-1007在膀胱的放射性剂量最低,对观察骨盆内的病灶可能更有优势,而其余两种示踪剂在膀胱内均可有放射性积聚[8, 21]。18F-PSMA-1007对前列腺癌根治术后的生化复发具有较高的检出率,能够检测出盆腔或腹膜后的转移淋巴结[22]。在高危前列腺癌患者中,18F-DCFPyL PET/CT对前列腺内肿瘤的检测具有很高的敏感度,可以检测到部分多参数磁共振成像(multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging, mpMRI)上漏诊的肿瘤[23]。同时,18F-DCFPyL PET/CT能检测出CT检查阴性的病灶,对一些CT显示没有肿大的淋巴结,仍可表现为阳性,该检查手段可作为原发性高危前列腺癌患者的一线成像方式,而且大部分患者不需要再进行额外的诊断性成像[24]。
CT及MRI等常规影像学检查方法均可用于评估前列腺癌患者的淋巴结分期,既往Meta分析表明CT和MRI诊断前列腺癌淋巴结转移具有较低的敏感度,分别为0.42和0.39[25]。一项研究表明,18F-PSMA-1007 PET/CT、全身MRI及增强CT对前列腺癌盆腔淋巴结转移诊断的敏感度分别为0.87、0.37和0.26,前者具有较明显的诊断优势,且能检出上述两种检查方法均呈阴性的转移淋巴结[11]。18F-DCFPyL PET/CT对前列腺癌盆腔淋巴结的检出率较mpMRI更高,在经活检证实的淋巴结病灶中,前者诊断敏感度更高(1.00 vs. 0.57)[14]。
本研究中,18F标记的PSMA PET/CT诊断前列腺癌区域淋巴结转移的敏感度为0.82,特异性为0.98,AUC值为0.97,说明18F标记的PSMA PET/CT对前列腺癌区域淋巴结转移具有较高的诊断性能,尤其特异性很高,这意味着影像上诊断淋巴结阴性时,能更有效地排除淋巴结转移的可能。一项纳入6篇研究的Meta分析中[19],其中5篇研究应用68Ga标记的PSMA PET/CT作为成像方式,该研究对前列腺癌淋巴结转移诊断的敏感度为0.71,特异性为0.95,与本研究有相似的高特异性,但本研究的Sen相对更高。18F标记的PSMA半衰期相对更长,考虑到运输过程,18F标记的示踪剂可能更适用于临床。
本研究所纳入的文献存在高度异质性,对可能引起异质性的因素进行Meta回归分析,结果显示以淋巴结为分析单位的敏感度高于以患者为分析单位(0.94 vs. 0.66),而特异性在两个分析单位之间相差不大(0.99 vs. 0.97)。Tu等[20]应用68Ga标记的PSMA PET/CT进行相关的Meta分析,结果也表明以淋巴结为分析单位的敏感度相对更高(0.70 vs. 0.63),且特异性亦较高(0.99 vs. 0.93),与本研究结果类似,但本研究的敏感度相对更高。这也说明以淋巴结为分析单位用于临床诊断前列腺癌区域淋巴结转移及进行临床分期的准确性更高。在临床研究中,由于研究方法存在差异,部分研究仅以患者或仅以淋巴结为分析单位,两者均可作为诊断的性能指标[19-20],本Meta分析的数据可为相关研究方法的选择提供一些参考信息。关于特异性的分析结果显示,前瞻性研究的特异性低于回顾性研究(0.93 vs. 1.00),这可能是因为在前瞻性研究中,部分纳入患者因病情的变化无法按计划进行手术或中途退出研究,导致少部分数据不能纳入最终的分析,在一定程度上影响诊断的性能。同时,回顾性研究可能会出现选择偏倚,导致诊断的性能偏高。应用放射性示踪剂18F-PSMA-1007的特异性较18F-DCFPyL相对更高(0.99 vs. 0.95),可能是由于后者通过尿路排泄,在膀胱内有一定的放射性积聚,影响盆腔内病灶的观察,对盆腔内转移淋巴结的诊断可能会出现假阳性的结果。只纳入新发病例的亚组较包含复发病例的亚组特异性相对更高(0.99 vs. 0.97),可能因为部分复发病例失去手术指征,更多地通过活检方式获得组织病理学结果,而体积较小或影像学阴性的病灶在临床上有更大的可能性不选择活检,这也可能出现选择性偏倚,影响最终的统计结果。也可能是由于复发病例接受过不同的治疗方案,转移前列腺癌细胞的PSMA表达出现了一定的差异。18F标记的PSMA PET/CT对前列腺癌术前淋巴结分期具有中度敏感度及高度特异性,有助于准确评估疾病的临床分期,指导治疗方案的选择。对于复发或转移性前列腺癌,因本Meta分析纳入的研究数量及样本量较少,未进行统计分析,有待进一步的扩大研究补充说明。
本Meta分析的局限性:(1)纳入的文献相对较少,可能存在一定偏倚,仍需更多的研究进一步证实。(2)其中一篇纳入文献并非以病理作为唯一的诊断金标准,在一定程度上影响了Meta分析的准确性。(3)少部分研究金标准的解读未使用盲法或无法判断是否使用盲法,结果解读可能存在偏倚。
综上,18F标记的PSMA PET/CT对前列腺癌区域淋巴结转移的诊断具有较高的敏感度及特异性,其药物半衰期及代谢特点具有较好的临床适用性,有望在临床上推广应用,有助于准确评估淋巴结分期,帮助临床医生根据不同患者的病情制定个体化的治疗方案。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。作者贡献:张玲珑:收集及整理数据、调查设计、文献检索、统计分析、撰写文章漆小龙:收集及整理数据、统计分析寇珍、热那古力·阿不来提、聂玉玲、木合拜尔·阿布都尔、翟顺生、安利、毛敏:收集数据、统计分析李燕:收集数据、统计分析、审核文章 -
表 1 155例DLBCL患者的ITPKB突变VAF与临床特征的关系(n=155)
Table 1 Relationship between ITPKB mutation VAF and clinical characteristics of 155 DLBCL patients (n=155)

-
[1] Solimando AG, Annese T, Tamma R, et al. New insights into diffuse large B-cell lymphoma pathobiology[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2020, 12(7): 1869. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071869
[2] Koh Y. Genomics of diffuse large B cell lymphoma[J]. Blood Res, 2021, 56(S1): S75-S79. doi: 10.5045/br.2021.2021049
[3] Miao Y, Medeiros LJ, Li Y, et al. Genetic alterations and their clinical implications in DLBCL[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2019, 16(10): 634-652. doi: 10.1038/s41571-019-0225-1
[4] 黄耀慧, 赵维莅. 二代测序在弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤中的应用[J]. 临床血液学杂志, 2016, 29(5): 694-698. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1004-2806.2016.09.002 Huang YW, Zhao WL. Application of the next-generation sequencing in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Lin Chuang Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi, 2016, 29(5): 694-698. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1004-2806.2016.09.002
[5] 胡文明, 阚海华, 王伟, 等. 等位基因功能差异的统计遗传学分析及应用[J]. 作物学报, 2014, 40(1): 72-79. Hu WM, Kan HH, Wang W, et al. Statistical Genetics Approach for Functional Difference Identification of Allelic Variations and Its Application[J]. Zuo Wu Xue Bao, 2014, 40(1): 72-79.
[6] Deng J, Wu X, Ling Y, et al. The prognostic impact of variant allele frequency (VAF) in TP53 mutant patients with MDS: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Haematol, 2020, 105(5): 524-539. doi: 10.1111/ejh.13483
[7] 中华医学会血液学分会, 中国抗癌协会淋巴瘤专业委员会. 中国弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤诊断与治疗指南(2013年版)[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2013, 34(9): 816-819. Society of Hematology, Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Anti-Cancer Association Lymphoma Committee. Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of difuse large B cell lymphoma (2013)[J]. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi, 2013, 34(9): 816-819.
[8] Budczies J, Klauschen F, Sinn BV, et al. Cutoff Finder: a comprehensive and straightforward Web application enabling rapid biomarker cutoff optimization[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(12): e51862. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051862
[9] Wang Y, Feng W, Liu P. Genomic pattern of intratumor heterogeneity predicts the risk of progression in early stage diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2019, 40(11): 1427-1434. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgz068
[10] Mareschal S, Dubois S, Viailly PJ, et al. Whole exome sequencing of relapsed/refractory patients expands the repertoire of somatic mutations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 2016, 55(3): 251-267. doi: 10.1002/gcc.22328
[11] Maréchal Y, Pesesse X, Jia Y, et al. Inositol 1, 3, 4, 5-tetrakisphosphate controls proapoptotic Bim gene expression and survival in B cells[J]. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A, 2007, 104(35): 13978-13983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704312104
[12] Rae DT, Hocum JD, Bii V, et al. A novel retroviral mutagenesis screen identifies prognostic genes in RUNX1 mediated myeloid leukemogenesis[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(31): 30664-30674. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5133
[13] Zhang W, Huang C, Liu J, et al. Genomic Mutation Landscape of Primary Breast Lymphoma: Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis[J]. Dis Markers, 2022, 2022: 6441139.
[14] Pan C, Jin L, Wang X, et al. Inositol-triphosphate 3-kinase B confers cisplatin resistance by regulating NOX4-dependent redox balance[J]. J Clin Invest, 2019, 129(6): 2431-2445. doi: 10.1172/JCI124550
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 陈泽玲,刘慧. 逆向法定位穿刺点在蝶翼针植入输液港中的应用. 中国当代医药. 2024(08): 175-178+182 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 连蕊,张军军,韩敏,李琳,汪京萍. 国内外完全植入式输液港研究可视化对比分析. 军事护理. 2024(07): 68-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 吴娇,祝中荣,吴晓霞,肖娜,黄晓波. 床旁超声引导下锁骨下静脉输液港置管术在恶性肿瘤患者中的应用效果. 癌症进展. 2024(24): 2704-2707 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: