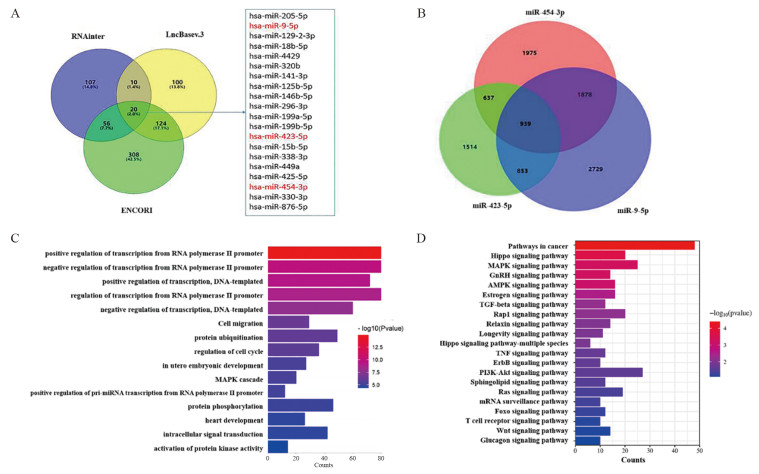
Effects of KCNQ1OT1 Gene Knockout Combined with Bruceine D on Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells
-
摘要:目的
探讨KCNQ1OT1基因敲除联合鸦胆子素D对乳腺癌MDA-MB-231细胞生物学行为的影响及其机制。
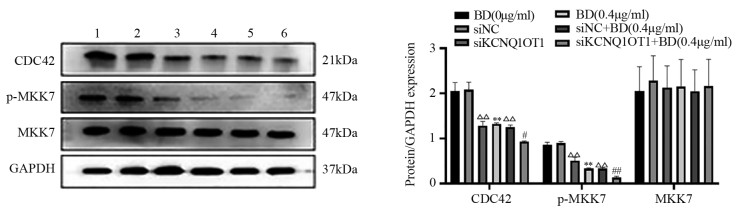
方法CCK8、划痕和Transwell侵袭实验分别检测鸦胆子素D和siKCNQ1OT1对MDA-MB-231细胞活力、迁移和侵袭能力的影响;qRT-PCR检测鸦胆子素D、siKCNQ1OT1对MDA-MB-231细胞中KCNQ1OT1表达的影响;Western blot法检测EMT相关蛋白及CDC42、p-MKK7、MKK7蛋白的表达情况。
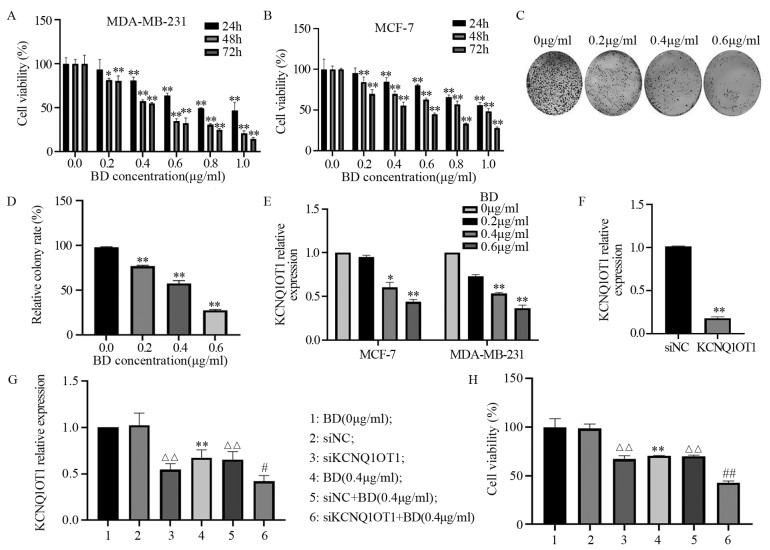
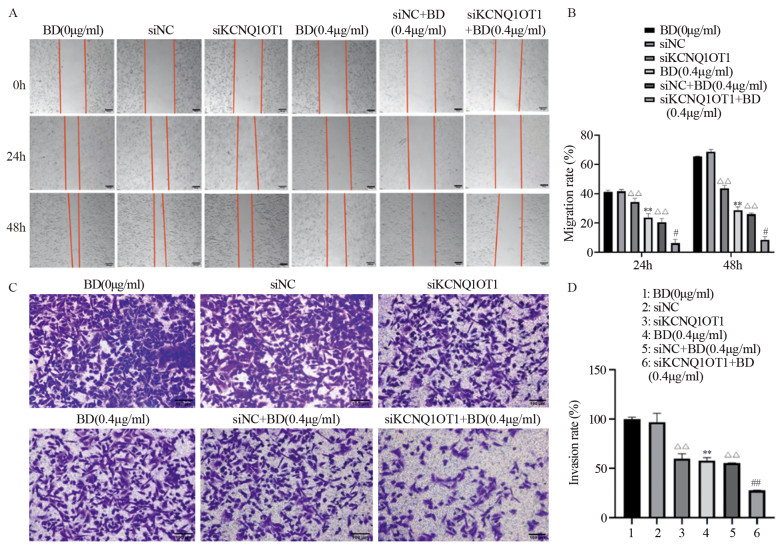
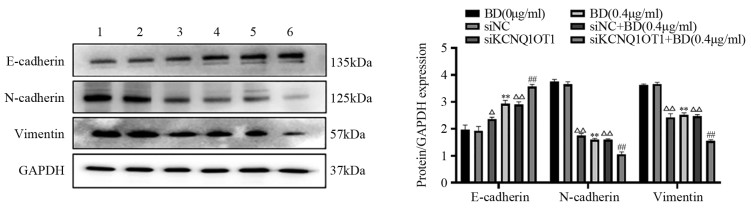
结果鸦胆子素D和siKCNQ1OT1处理的MDA-MB-231细胞活力、迁移和侵袭能力受到显著抑制,且二者联用时抑制作用更强(均P < 0.05);鸦胆子素D处理后KCNQ1OT1在MDA-MB-231细胞中的表达下调(均P < 0.05);鸦胆子素D联合siKCNQ1OT1处理组MDA-MB-231细胞中CDC42、p-MKK7、N-cadherin和Vimentin的表达显著下调,E-cadherin的表达上调(均P < 0.05)。
结论鸦胆子素D联合siKCNQ1OT1抑制人乳腺癌MDA-MB-231细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭和EMT,其分子机制可能与CDC42/MKK7信号通路的阻断有关。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the effect of KCNQ1OT1 gene knockout combined with bruceine D on the proliferation, migration, and invasion of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells.
MethodsCell Counting Kit-8, wound healing, and Transwell invasion assay were used to detect the effects of bruceine D and siKCNQ1OT1 on the viability, migration, and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells. Effect of bruceine D and siKCNQ1OT1 on the expression of KCNQ1OT1 in MDA-MB-231 cells was detected by qRT-PCR. Western blot was used to detect the effect of bruceine D and siKCNQ1OT1 on the expression of EMT-related proteins and CDC42, p-MKK7, MKK7 proteins in MDA-MB-231 cells.
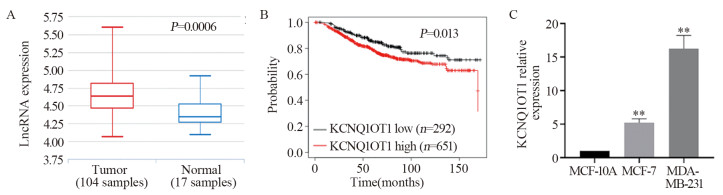
ResultsBruceine D and siKCNQ1OT1 could significantly inhibit the viability, migration, and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells, and the inhibitory effect was enhanced when they were combined (all P < 0.05); bruceine D downregulated the expression of KCNQ1OT1 in MDA-MB-231 cells (all P < 0.05); bruceine D combined with siKCNQ1OT1 significantly decreased CDC42, p-MKK7, N-cadherin, and Vimentin expression in MDA-MB-231 cells and increased the expression of E-cadherin (all P < 0.05).
ConclusionBruceine D combined with siKCNQ1OT1 significantly inhibit the proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells, and its molecular mechanism may be related to the blocking of CDC42/MKK7 signaling pathway.
-
Key words:
- Breast cancer /
- Bruceine D /
- KCNQ1OT1 /
- Migration /
- Invasion
-
0 引言
细胞外基质(extracellular matrix, ECM)是所有组织和器官的基本核心组成部分,是多细胞生物存在的必要条件,它调节体内每一个细胞的发育、衰老和死亡。肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment, TME)中,ECM在生物化学、生物力学、组织拓扑结构中发生显著改变。近年来随着研究的深入,ECM在实体肿瘤中的重要性不断加强,其主要成分—胶原蛋白在肿瘤的恶性转化和药物耐受中发挥的作用日益受到关注,胶原蛋白受体之一的盘状结构域受体(discoidin domain receptor, DDR),尤其是DDR1在炎性反应、肿瘤细胞增殖、转移及免疫微环境中的功能被不断探索。随着研究ECM之间以及细胞-ECM间相互作用的技术进步,我们也开始看到以ECM和其细胞受体为中心开展靶向肿瘤ECM治疗的新探索。
1 细胞外基质的主要成分
ECM是细胞间复杂的大分子网络,包绕着器官和组织内每一个细胞。基因中与编码ECM和ECM相关蛋白质的基因被称为“基质组(matrisome)”。哺乳动物基质组中有约1 100个基因,可以广泛地分为核心ECM基因(约300个基因)和ECM相关基因(约800个基因)[1]。这些基因所编码的基质成分约占人类蛋白质组的4%。ECM可以广泛分为两个主要类别:间质基质(interstitial matrix)和高度异化的器官/组织特异性基质。每个基质成分都有独特的特征,其性质由其生物化学和生物物理学性能共同决定。在生物物理层面,ECM能够作为支架发挥细胞外机械力承载功能;生物化学层面,给细胞提供附着点并可以作为相互作用的配体参与细胞内和细胞间的信号转导,见图 1[2]。
1.1 胶原蛋白
胶原蛋白(Collagen)是ECM最主要的结构成分,决定了ECM的骨架结构。迄今已鉴定出28种人类胶原蛋白[3]。与正常组织相比,肿瘤中常观察到胶原蛋白在沉积、降解、翻译后修饰和重排中的变化[4]。胶原蛋白提供机械强度和生物活性位点利于细胞粘附,参与调节细胞迁移功能[5-6]。Ⅰ型胶原蛋白是肿瘤ECM的主要组成部分,在多种类型的肿瘤中发挥促进肿瘤细胞生存和转移的作用。在正常组织ECM中,纤维性胶原蛋白通常具有异向性,而肿瘤中的胶原蛋白往往高度整齐且具有同向性[7]。不同类型胶原蛋白的含量和相对比例控制着组织微环境稳态和肿瘤ECM的顺应性、硬度、粘弹性和生物化学等特性。研究者认为胶原蛋白助于肿瘤的侵袭和转移。例如胆管癌中可以观察到大量的ECM尤其是胶原蛋白沉积,致密地排列在肿瘤细胞周围,可以隔绝化疗药物以及免疫细胞进入肿瘤实质[8],胶原蛋白还会助于头颈部鳞状细胞癌和乳腺肿瘤转移过程中的休眠和再激活[9]。在一些肿瘤中,含有胶原蛋白和层粘连蛋白的基底膜构成了组织的边界,将上皮层与间质分隔,肿瘤细胞必须突破基底膜才能向远处转移。光学显微镜下,围绕癌前病变的基底膜通常更薄,且含有较少的胶原蛋白,胰腺导管腺癌ECM中Ⅰ型胶原的减少加快胰腺上皮内瘤变和胰腺导管腺癌进程,降低了总生存率[10]。精原细胞瘤分泌的COL15A1通过抑制上皮间质转化(EMT)过程抑制肿瘤转移[11]。
1.2 糖蛋白和蛋白聚糖
糖蛋白(Glycoprotein)和蛋白聚糖(Proteoglycan)由重复的糖基(二糖)链连接到蛋白质核心组成。糖蛋白由短的、分支的寡糖链共价连接到中央多肽侧链上。相比之下,蛋白聚糖是由核心蛋白和一个或多个共价连接的长链糖基氨基糖链组成的糖基化蛋白质[12]。
糖蛋白包括了蛋白聚糖,可以填充ECM空间,并通过它们的侧链和抵抗压缩力的能力产生高粘度,缓冲ECM的物理应力,不仅调节细胞的粘附、运动、增殖和分化,还可以通过多价阴离子电荷结合生长因子、细胞因子和双价阳离子共同构建ECM的网络结构,在许多实体肿瘤中发挥促进或抑制肿瘤作用[13]。糖蛋白还可以作为辅助受体,帮助配体结合到细胞表面受体,从而调节下游的胞内信号转导。在肿瘤中,研究较多的糖蛋白是透明质酸(Hyaluronan),肿瘤细胞和基质细胞通常过度分泌透明质酸,不同分子量决定了它是抗肿瘤还是促肿瘤效应。CD44是透明质酸的特异性受体之一,已发现将透明质酸分子量提高到1 MDa可以增加与CD44的结合亲和力。CD44激活多条下游信号通路,包括PI3K-AKT和ERK信号,以及RhoA、RAS、NF-κB和SRC的途径,因此CD44可以促进肿瘤存活、肿瘤细胞干性、化疗耐药性、浸润以及EMT[14]。
在肿瘤中表达异常的其他糖蛋白和蛋白聚糖还包括层粘连蛋白、纤连蛋白、纤维蛋白原、基质素、玻璃蛋白、骨质素(也称为富含半胱氨酸的分泌蛋白)、凝血调节蛋白、骨架聚糖等[15]。糖蛋白和蛋白聚糖确切的促肿瘤或抗肿瘤作用与组织类型和肿瘤类型有关,并且可能受到不同阶段和不同基质成分的影响。
2 细胞外基质的转录后修饰
ECM的生物化学和生物力学特性受不同器官特异性成分的分布、浓度和组合方式调节。这些特性会受基质成分的转录后修饰所调控,包括羟化、糖基化、转酰胺化、硫酸化和交联,以及裂解和降解而发生调节[16]。转录后修饰由多个家族酶完成,包括但不限于细胞内的胶原脯氨酸羟化酶和赖氨酸羟化酶[17],以及细胞外的赖氨酸氧化酶、转酰胺酶、硫酸酶、肝素酶和金属基质蛋白酶超家族等[18-20]。ECM的持续修饰是维持其动态平衡至关重要的基础,也是细胞微环境持续修复和更新的基础。因此,任何一种或多种修饰酶家族的失调引起的基质改变都可能促进肿瘤的进展[21]。ECM的修饰可以由恶性和非恶性细胞驱动,可以影响局部范围内的肿瘤细胞以及非肿瘤细胞(例如免疫细胞),异常的ECM翻译后修饰有助于区分不同肿瘤的特性。
2.1 赖氨酸氧化酶
赖氨酸氧化酶(lysyl oxidase, LOX)家族的基质交联相关酶对成熟的胶原纤维和弹性蛋白的沉积与稳定至关重要。该家族酶的失调与多种肿瘤有关,包括乳腺癌、结直肠癌和胰腺导管腺癌[22-24]。LOX家族介导的基质交联也可以减缓基质降解、改变细胞迁移和侵袭、血管生成和治疗耐药性,并增加肿瘤内液体压力,降低药物渗透性[25]。
2.2 糖基化
糖基化(Glycosylation)是一种自发的非酶促的基质交联形式,是ECM中游离性还原糖通过形成Schiff碱,经Amadori重排和Maillard反应与氨基酸、脂质和核酸等生成晚期糖基化终产物(Advanced glycation end products, AGEs)。AGEs包含各种细胞受体,主要分布在内皮细胞、平滑肌细胞和单核-巨噬细胞等,调节细胞周期、分化和基因转录等过程[26-27]。通过交联作用,AGEs会阻止ECM的正常生理功能,限制胶原纤维的运动和弹性导致基质硬化,激活细胞力学转导通路。它们对肿瘤的调控作用是一个重要的研究领域[27-28]。
2.3 谷氨酰胺转氨酶
谷氨酰胺转氨酶(Transglutaminase, TG)通过在组装多种分子(包括纤连蛋白、肝素硫酸蛋白聚糖、纤维蛋白原和胶原蛋白)时通过转移或去氨基酸残基作用来稳定基质。谷氨酰胺转氨酶在基质中纤维排列和增加基质硬度方面非常重要,它们可以使基质成分对抗蛋白水解作用,从而维持稳定和保持力学特性[29]。谷氨酰胺转氨酶可以影响细胞的黏附和迁移,在侵袭性胰腺癌中,TG2的表达升高可以增强纤连蛋白的交联和纤维形成促进ECM纤维化,通过YAP/TAZ信号通路促进肿瘤细胞的增殖[30]。
3 细胞外基质的降解
ECM降解和循环是维持微环境稳态的重要部分。ECM的降解和循环由几种酶协调进行,降解过少或过多会导致组织纤维化和组织结构破坏,影响肿瘤的发生发展过程。肿瘤相关的异常基质积累会导致“正常”基质的快速降解,去除物理屏障(如基底膜),以便于肿瘤细胞的生长和远处播散[31-32]。ECM还通过与生长因子结合成为一个重要的配体储存库。基质降解可以局部释放结合的生长因子并激活细胞内的信号转导。
3.1 基质金属蛋白酶
在Metzincin超家族中,基质金属蛋白酶(matrix metalloproteinases, MMPs)是主要的基质降解蛋白酶。人类有23种MMPs,它们的结构通常包括一个前肽、一个Zn2+结合的催化域、四个类血红素结合蛋白结构域,部分MMPs还含有一个跨膜和细胞质结构域[33]。MMPs广泛降解ECM包括胶原蛋白、纤维蛋白和蛋白聚糖,可选择性地释放细胞表面结合的细胞因子、生长因子或其受体,影响基质完整性、细胞行为和表型。
生理情况下,MMPs的表达在转录水平和转录后水平都受到严格调控,确保其时空分布和活性受到限制。然而,在许多肿瘤中这种调控被打破,使MMPs参与癌症的发生和进展。肿瘤ECM成分的降解既可以促癌也可以抗癌。例如,MMP8的过度表达,可降解Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ型胶原蛋白,抑制了舌癌的发生[34]。MMP9的上调则会促进肿瘤肝转移的发生[35]。这些相互矛盾的结果可能揭示了为什么MMPs抑制剂在临床试验中表现不佳。
3.2 透明质酸酶
透明质酸酶(Hyaluronidase)是一类主要降解透明质酸的糖苷酶。透明质酸是一种糖胺聚糖(glycosaminoglycan, GAG),由葡萄糖醛酸和N-乙酰葡糖胺的重复二糖单位组成。透明质酸的代谢速度很快,其正常代谢对ECM稳态非常重要,而肿瘤中经常可以观察到异常的透明质酸增多或代谢失衡,导致大量的透明质酸沉积[36-37]。除了经典的透明质酸酶外,一些在实体瘤中高表达的膜蛋白也表现出透明质酸酶活性,这些生物活性肽段可以促进血管生成,刺激炎性反应细胞因子的产生,并激活肿瘤相关的细胞内信号通路。例如,CEMIP的异常积累会影响乳腺癌细胞的凋亡、代谢和运动等功能,缩短患者生存时间[38]。透明质酸酶抑制剂可以阻碍微管聚合,导致G2/M期阻滞,有效抑制皮肤癌细胞增殖[39]。
3.3 Adamalysin样金属蛋白酶
Adamalysin样金属蛋白酶家族包括21种ADAM(a disintegrin and metalloproteinase)和19种ADAMTS(ADAM with thrombospondin motifs),与MMP和蛇毒金属蛋白酶结构相似,参与血管基底膜的降解。实体肿瘤中,ADAM的表达和活性异常会影响其他基质相关酶的分泌,并促进基质蛋白质的降解,影响肿瘤的进展[40]。ADAMTS是具有类thrombospondinⅠ型重复序列的分泌型ADAM,多为蛋白聚糖酶,负责加工胶原蛋白前体,因此对于胶原纤维的沉积非常重要[41]。ADAM还可以通过从细胞表面剪切EGFR配体,调节EGF细胞内信号,突显了ECM相关成分与其他信号通路之间的网络性[42]。
3.4 组织蛋白酶
组织蛋白酶(Cathepsins)是由半胱氨酸、丝氨酸和天冬氨酸肽酶组成的蛋白酶家族,作用于溶酶体、胞质和ECM。一般来说,除了分子量为200 kDa的半胱氨酸蛋白酶C外,大多数组织蛋白酶分子量较小,约20~35 kDa[43]。组织蛋白酶可以大量降解多种ECM前体,包括胶原蛋白、弹性蛋白、层粘连蛋白、纤连蛋白、十二指肠素C和nidogen 1,从而调节这些成分在正常和肿瘤环境中的分泌和沉积[44]。
4 细胞外基质和细胞信号转导
肿瘤ECM中的生物化学和生物力学性能会影响癌细胞的增殖和存活,调节其药物抵抗等能力,细胞对ECM变化的响应通常迅速而长久。多种信号刺激与信号网络结合可以增强生物学效应[45-46]。肿瘤细胞会主动参与重构ECM过程,肿瘤ECM的动态改变会进一步导致细胞表面受体的持续聚集和激活[47]。有研究发现,EGF信号激活头颈部鳞状细胞癌细胞引起胶原蛋白收缩,促进侵袭细胞球的形成[48]。
4.1 整合素受体
ECM硬度增加可以激活整合素受体(Integrin)促进多种酪氨酸激酶受体的信号转导,包括EGFR、FGFR和VEGFR等。整合素受体异二聚体是细胞与ECM之间通信的主要枢纽,可以激活多种下游信号网络。整合素的氨基酸序列在进化上是保守的,包含大质量的胞外结构域、短的跨膜结构域和短的细胞内结构域[49]。整合素受体不同的亚单位以异二聚体方式组成,它们的微观距离会影响肿瘤对药物的敏感度,这可能解释了一些肿瘤细胞在化疗后生存能力增强的原因。αvβ3到α5β1 “整合素转换”可以促进肿瘤的进展和耐药性,在胰腺癌中过度表达α5β1整合素会促进肿瘤相关成纤维细胞(cancer-associated fibroblasts, CAF)的激活,造成肿瘤内纤维增生和沉积,减少血液灌注,降低吉西他滨在动物模型中的疗效[50-51]。
整合素在肿瘤中的作用也取决于不同细胞类型和ECM成分的生物化学。E-钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)转换为N-钙黏蛋白(N-cadherin)过程伴随着从α6β4到β1和β3整合素的转换,这种转换使肿瘤细胞更容易在细胞—细胞和细胞—基底膜之间迁移,并更容易附着于Ⅰ型胶原蛋白,从而促进局部侵袭[52]。因此,基于整合素和ECM成分的细胞粘附复合物,与其所连接的细胞骨架形成了一个整合的网络,使细胞能够感知、处理和响应微环境改变。
4.2 非整合素型细胞外基质结合受体
其他基质结合受体,如DDR1和DDR2、破骨细胞相关免疫球蛋白样受体(OSCAR)、多配体蛋白聚糖、尿激酶型纤溶酶原激活剂受体相关蛋白(UPARAP,也称为ENDO180)和白细胞相关免疫球蛋白样受体1(LAIR-1,也称为CD305)等,也参与协调细胞外—胞内信息传递和下游信号通路的激活[53-58]。
5 胶原蛋白受体DDR1
DDR1属于受体酪氨酸激酶(receptor tyrosine kinase, RTK)的DDR家族,包括DDR1和DDR2。DDR与RTK相似,具有细胞外结构域(extracellular domain, ECD)、短的跨膜域(transmembrane, TM)和细胞内酪氨酸激酶结构域(Intracellular domain, ICD)。与其他RTK不同的是,DDR可以与ECM中胶原蛋白配体结合,其激酶激活时间缓慢但磷酸化持续时间久。通常,细胞膜上DDR1天然成簇形成二聚体,胶原蛋白配体结合后会激活胞内结构域使二聚体的胞内段共同磷酸化。DDR1可以被多种胶原蛋白亚型激活,主要包括基底膜中丰富的Ⅰ和Ⅳ型胶原。DDR1常在上皮组织中表达丰富,在胶原蛋白富集的微环境中作为细胞传感器,调节细胞生长和黏附的信号转导[59]。DDR1基因敲除小鼠显示,生理情况下DDR1在乳腺组织发育以及维持胰腺和肾脏微环境稳态中发挥重要功能[60-63]。本课题组前期研究也发现DDR1在HCC的生长以及转移中发挥重要调控作用[64-65]。在肿瘤的发展中,不同类型、不同阶段及瘤内胶原蛋白含量丰富与否,DDR1分别发挥促进或抑制肿瘤的功能,见图 2。
6 DDR1在肿瘤细胞休眠和转移重激活中的作用
肿瘤远处转移是一个效率低下的多步骤过程,整个过程都受到肿瘤细胞与其微环境相互作用的影响,例如原发肿瘤的边缘、基质含量、血管的丰富程度和定植组织的转移性龛的形成。异常的胶原沉积在整个转移过程中起着重要的作用,DDR1则有助于肿瘤细胞对这些富含胶原的微环境做出响应。例如,DDR1促进上皮癌细胞向肿瘤边缘沉积的胶原纤维进行局部侵袭[66]。DDR1上调促进了结肠癌细胞的肝转移,这种转移可能由CAF、TAM、DTC和肿瘤分泌的细胞外囊泡中的胶原蛋白在转移部位沉积进而激活造成,还有研究显示DDR1对肿瘤在肺和骨骼组织中定植也是必要的[63, 67]。
最近有研究揭示了DDR1在转移过程中的另一个重要功能,即通过维持DTCs处于静止状态来实现肿瘤转移。肿瘤细胞的转移可以在肿瘤发生的早期阶段和进展期间发生,这些DTCs可以在转移部位长时间处于非增殖状态(即休眠状态),被特定信号重新激活后,导致肿瘤转移。这一过程的表现是临床中观察到部分患者在手术和化疗根除原发肿瘤后数年才出现转移灶。研究者们在小鼠异种移植实验中,通过HNSCC细胞和乳腺癌细胞的静止和增殖两种模型来评估局部ECM成分在诱导肿瘤休眠状态的作用。比较两种情况下胶原蛋白的结构和组成,他们发现大量Ⅲ型胶原蛋白沉积在非增殖型肿瘤细胞周围,并维持细胞的休眠状态。与之不同的是,增殖型的DTCs被含有大量糖蛋白的胶原纤维所包围,而Ⅲ型胶原蛋白由定植部位的DTCs分泌,这表明它会形成一种自我保护的非增殖性程序。研究者们继续证明DDR1介导了肿瘤基于Ⅲ型胶原蛋白的细胞休眠状态,其中,DDR1的休眠信号转导是依赖于其与Ⅲ型胶原蛋白的结合,不依赖其激酶活性,通过STAT1依赖的前馈回路,DDR1可以诱导COLA31表达。由此,他们提出COL3A1的表达重塑了ECM,使其呈波浪状胶原结构,从而使细胞保持在静止状态。同时,DDR1下调会重新激活DTC的增殖功能,而更重要的是,DDR1对增殖型DTC的存活也是必要的,与DDR1在其转移重激活过程中的功能一致[11]。
本课题组也发现,DDR1与ARF6相互作用,通过招募PSD4激活ARF6,通过ERK/MAPK信号通路促进HCC的肺转移[64]。总的来说,DDR1调节细胞休眠和增殖(转移)状态,具体取决于转移巢中沉积的ECM结构和胶原蛋白比例。
7 DDR1与肿瘤免疫排除
免疫逃逸是侵袭性肿瘤的一个重要特征,其中ECM的沉积发挥了关键作用。最近,有研究报道DDR1在这种恶性转化过程中的重要作用。通过乳腺肿瘤小鼠模型,研究者发现DDR1敲除可以阻止免疫正常小鼠的肿瘤发展,但无法阻碍免疫缺陷小鼠的肿瘤进展,从而揭示了DDR1在肿瘤免疫逃逸中的新功能。作者报道了肿瘤DDR1表达与CD8+T细胞含量之间的负相关关系,并在乳腺癌患者队列中验证了其临床相关性。虽然转录组学分析意义有限,但功能拯救实验揭示了肿瘤中DDR1新的机制,即细胞膜上DDR1可能经历膜剪切,导致DDR1整个细胞外结构域(DDR1-ECD)的释放。结果表明,单独表达DDR1-ECD就足以显示明显的肿瘤免疫排除效应。这种现象与ECM中沉积的致密胶原纤维相关,提示了DDR1-ECD在ECM重塑中的功能。接下来通过证明DDR1-ECD以其多聚体形式高效地重塑胶原纤维,并在体外培养中减少T细胞的运动性验证了这一假设。体内实验中,注射纯化的DDR1-ECD减少了肿瘤异种移植中的免疫细胞浸润。作者通过研发一种阻断性抗DDR1-ECD抗体,验证了DDR1作为肿瘤免疫治疗靶点的作用,这种特异性抗体有效促进免疫细胞浸润并阻碍了体内的肿瘤发展。这项新研究进一步证实了以往的结果,即DDR1在肿瘤免疫逃逸和抗PD-1免疫治疗中的作用,且揭示了DDR1在免疫逃逸中的另一种机制,即重塑胶原蛋白丰富的肿瘤ECM,抑制免疫细胞的浸润[68]。总的来说,这项研究进一步凸显了DDR1在肿瘤免疫逃逸中的重要作用。
8 DDR1介导的肿瘤治疗抵抗
肿瘤细胞具有适应不同微环境和应激压力的能力,这是导致肿瘤对治疗产生抵抗性并导致治疗失败的原因之一。有研究报道,ECM促进黑色素瘤细胞对抗-BRAFV600E产生治疗抵抗,研究者们发现CAF分泌的ECM对黑色素瘤细胞具有药物保护作用,这种耐药性是由于排列整齐且密集的Ⅰ型胶原蛋白导致的,黑色素瘤患者中DDR1和DDR2高表达与不良预后相关,同时DDR1/2表达与黑色素瘤进展、肿瘤浸润和治疗抵抗关联。基于此,他们假设DDR会介导这种药物抵抗反应,结果表明在黑色素瘤细胞与CAF分泌的ECM相互作用中诱导了DDR1/2的成簇和激活。抑制DDR1/2表达或活性能够削弱ECM介导的黑色素瘤细胞对靶向药物的治疗抗性。在体内实验中,小鼠接受酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, TKi)伊马替尼的治疗,可以增强抗-BRAFV600E药物的疗效并延缓肿瘤复发,这种抗肿瘤作用与药物诱导的胶原蛋白重排减少有关,表明DDR1/2和胶原蛋白之间存在反馈环路。然而,其他的伊马替尼药物靶点(例如血小板衍生生长因子受体PDGFR和DDR2)也可能有助于胶原蛋白的沉积。尽管MAPK信号通路不会受到这种耐药机制的影响,但蛋白质组学分析指出,基于DDR1/2的药物抵抗机制受下游的NIK/IKKα/NF-κB2信号通路影响[69]。这种新的DDR1活性在KRAS突变型肺癌中也得到了证实,铂类药物化疗期间肿瘤DDR1表达上调,其表达水平与肺癌患者对化疗耐药相关[70]。在多种肺癌模型中,DDR1抑制剂与化疗联合治疗具有协同抑制肿瘤作用。有报道描述了一种基于四次跨膜蛋白TM4SF1依赖的DDR1在转移性肺癌中上调机制[71]。总之,这些研究证实DDR1在肿瘤治疗抵抗中发挥着重要作用。
9 小结
综上所述,ECM对组织器官的稳态维持非常重要,ECM成分、修饰酶、受体和信号通路的失衡会导致并促进肿瘤的发生和发展。DDR1作为重要的胶原蛋白受体,在肿瘤的耐药、转移以及肿瘤免疫等方面发挥了多种作用,是肿瘤进程中的关键蛋白受体之一,针对DDR1开发靶向药物提高肿瘤治疗疗效亟待更深入的研究。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。作者贡献:龙凤:实验设计、经费支持、统计分析,文章构思、修订及撰写赵玉:实验设计与实施、数据采集、统计分析及解释、文章撰写黄勇:实验指导刘晓燕:文章修订及审校周旋、李雪、叶海琳:文章审校 -
表 1 siKCNQ1OT1序列
Table 1 siKCNQ1OT1 sequences

-
[1] Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
[2] Borri F, Granaglia A. Pathology of triple negative breast cancer[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2021, 72: 136-145. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.06.005
[3] Mahtani R, Kittaneh M, Kalinsky K, et al. Advances in therapeutic approaches for triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Clin Breast Cancer, 2021, 21(5): 383-390. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2020.12.011
[4] Liu TJ, Hu S, Qiu ZD, et al. Anti-Tumor mechanisms associated with regulation of Non-Coding RNA by active ingredients of chinese medicine: A review[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 634936.
[5] Zhao LJ, Li C, Zhang Y, et al. Phytochemical and biological activities of an anticancer plant medicine: Brucea javanica[J]. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 2014, 14(3): 440-458. doi: 10.2174/18715206113136660336
[6] Tan BQ, Huang YY, Lan LH, et al. Bruceine D induces apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer cells through regulating JNK pathway[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 117: 109089. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109089
[7] Lau ST, Lin ZX, Liao Y, et al. Bruceine D induces apoptosis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line PANC-1 through the activation of p38-mitogen activated protein kinase[J]. Cancer Lett, 2009, 281(1): 42-52. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.02.017
[8] Cheng ZY, Yuan X, Qu Y, et al. Bruceine D inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth by targeting β-catenin/jagged1 pathways[J]. Cancer Lett, 2017, 403: 195-205. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.06.014
[9] Luo C, Wang Y, Wei C, et al. The anti-migration and anti-invasion effects of Bruceine D in human triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2020, 19(1): 273-279.
[10] Cagle P, Qi Q, Niture S, et al. KCNQ1OT1: an oncogenic long noncoding RNA[J]. Biomolecules, 2021, 11(11): 1602. doi: 10.3390/biom11111602
[11] Ren ZY, Xu YF, Wang X, et al. KCNQ1OT1 affects cell proliferation, invasion, and migration through a miR-34a/Notch3 axis in breast cancer[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2022, 29(19): 28480-28494. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-18434-x
[12] 王菲菲, 符合, 任进, 等. siRNA药物研究进展[J]. 中国新药杂志, 2022, 31(5): 427-434. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3734.2022.05.004 Wang FF, Fu H, Ren J, et al. Research advances on siRNA drug[J]. Zhongguo Xin Yao Za Zhi, 2022, 31(5): 427-434. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3734.2022.05.004
[13] Feng L, Li HQ, Li F, et al. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 regulates microRNA-9-LMX1A expression and inhibits gastric cancer cell progression[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2020, 12(1): 707-717.
[14] Yin XH, Jiang AM, Ma ZB, et al. Long non-coding RNA-KCNQ1OT1 mediates miR-423-5p/microfibril-associated protein 2 axis in colon adenocarcinoma[J]. Histol Histopathol, 2021, 36(10): 1099-1110.
[15] Yuan F, Lou ZP, Zhou ZF, et al. Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell cisplatin resistance via the miR-454/USP47 axis[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2021, 47(4): 54. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4887
[16] Zhang Y, Tang LL. The Application of lncRNAs in cancer treatment and diagnosis[J]. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov, 2018, 13(3): 292-301. doi: 10.2174/1574892813666180226121819
[17] Wu YY, Bi QJ, Han R, et al. Long noncoding RNA KCNQ1OT1 is correlated with human breast cancer cell development through inverse regulation of hsa-miR-107[J]. Biochem Cell Biol, 2020, 98(3): 338-344. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2019-0271
[18] Wang J, Wong YK, Liao F. What has traditional Chinese medicine delivered for modern medicine?[J]. Expert Rev Mol Med, 2018, 20: e4. doi: 10.1017/erm.2018.3
[19] Sin ZW, Bhardwaj V, Pandey AK, et al. A brief overview of antitumoral actions of bruceine D[J]. Explor Target Antitumor Ther, 2020, 1(4): 200-217. doi: 10.37349/etat.2020.00013
[20] Zhang J, Xu HX, Cho WCS, et al. Brucein D augments the chemosensitivity of gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer via inhibiting the Nrf2 pathway[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 41(1): 90. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02270-z
[21] Mohan CD, Liew YY, Jung YY, et al. Brucein D modulates MAPK signaling cascade to exert multi-faceted anti-neoplastic actions against breast cancer cells[J]. Biochimie, 2021, 182: 140-151. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2021.01.009
[22] Wang M, Dai M, Wang D, et al. The regulatory networks of the Hippo signaling pathway in cancer development[J]. J Cancer, 2021, 12(20): 6216-6230. doi: 10.7150/jca.62402
[23] Lu H, Guo Y, Gupta G, et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK): New insights in Breast Cancer[J]. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol, 2019, 38(1): 51-59. doi: 10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.2018028386
[24] Gillies TE, Pargett M, Silva JM, et al. Oncogenic mutant RAS signaling activity is rescaled by the ERK/MAPK pathway[J]. Mol Syst Biol, 2020, 16(10): e9518.
[25] Maldonado MDM, Dharmawardhane S. Targeting rac and cdc42 GTPases in cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2018, 78(12): 3101-3111. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0619
[26] Foltz IN, Gerl RE, Wieler JS, et al. Human mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7 (MKK7) is a highly conserved c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase (JNK/SAPK) activated by environmental stresses and physiological stimuli[J]. J Biol Chem, 1998, 273(15): 9344-9351. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.15.9344
[27] Xiao XH, Lv LC, Duan J, et al. Regulating cdc42 and its signaling pathways in cancer: small molecules and microRNA as new treatment candidates[J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(4): 787. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040787
[28] Wang X, Zhang J, Liu X, et al. Long noncoding RNAs in endometriosis: biological functions, expressions, and mechanisms[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236(1): 6-14. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29847
[29] Zhong CH, Tao B, Chen YT, et al. B7-H3 regulates glioma growth and cell invasion through a JAK2/STAT3/Slug-dependent signaling pathway[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2020, 13: 2215-2224. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S237841
[30] Serrano-Gomez SJ, Maziveyi M, Alahari SK. Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through epigenetic and post-translational modifications[J]. Mol Cancer, 2016, 15: 18. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0502-x




 下载:
下载: