Clinicopathological Characteristics and Therapeutic Effect of Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and Uncommon EGFR Mutations
-
摘要:目的
探讨表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)基因罕见突变非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)患者的临床病理特征及治疗效果。
方法采用荧光定量PCR法检测674例NSCLC中EGFR基因状态, 分析EGFR罕见突变与临床病理特征的相关性。
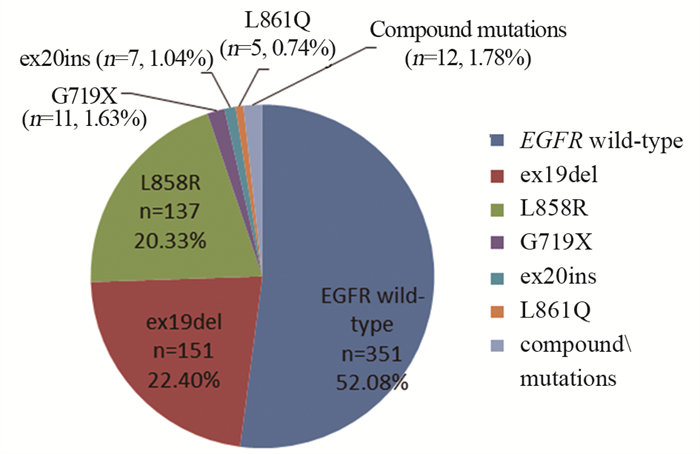
结果EGFR突变阳性率为47.92%, 其中EGFR罕见突变率为5.19%, 包括ex18 G719 A/S/C (G719X)(1.63%)、ex20ins (1.04%)、ex21 L861Q (0.74%)、含一个以上EGFR突变位点的复合突变(1.78%)。相关性分析显示, EGFR罕见突变更多见于女性、无吸烟史、高-中分化、腺癌患者, 易发生脑、骨转移(均P < 0.05);与常见敏感突变相比, 各临床病理特征比较差异均无统计学意义(均P > 0.05)。35例EGFR罕见突变患者中有31例获得随访资料, 中位随访时间10个月, 其中23例为晚期患者, 8例G719X突变晚期患者中, 7例一线使用EGFR-酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(EGFR-TKIs)(其中5例为阿法替尼), 中位PFS为12个月, 1例采用培美曲塞加卡铂化疗方案, PFS为7个月, 低于TKI组; 4例L861Q晚期患者中1例未治疗, 其余3例一线使用TKI, 中位PFS为8个月, 其中使用阿法替尼及贝伐珠单抗靶向治疗的患者, 随访11个月疾病仍稳定; 2例EGFR ex20ins晚期患者行化疗及贝伐珠单抗治疗; 9例复合突变晚期患者使用TKI治疗, 其中5例含T790M的复合突变患者使用三代TKI, 中位PFS大于10个月。
结论EGFR各罕见突变类型与临床病理特征的相关性不尽相同, 晚期EGFR罕见突变(除EGFR ex20ins外)患者, 临床一线治疗一般选择TKI, 其中具有G719X、L861Q突变的晚期NSCLC患者, 推荐使用阿法替尼; 含T790M的复合突变患者三代TKI有显著疗效。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the clinicopathological characteristics and treatment effect of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene mutations.
MethodsReal-time fluorescence quantitative PCR was used to detect the mutation of EGFR in 674 samples of patients with NSCLC.The correlation between uncommon EGFR mutations and clinicopathological characteristics was analyzed.
ResultsThe EGFR mutation rate was 47.92%, of which the incidence of uncommon EGFR mutations was 5.19%, showed the presence of ex18 G719 A/S/C (G719X)(1.63%), ex20ins (1.04%), ex21 L861Q (0.74%), and compound mutations (1.78%).Correlation analysis showed that uncommon EGFR mutations were more common in women, non-smokers, patients with high-medium differentiation and adenocarcinoma, and patients were more prone to brain and bone metastasis (all P < 0.05).NSCLC with uncommon EGFR mutations showed no significant differences in clinical and pathological features compared with those with common sensitive mutations (all P > 0.05).Follow-up information was available on 31 patients, with a median follow-up time of 10 months, of which 23 were in advanced stage.Among eight patients with G719X mutation in late stage, seven patients used EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR TKIs)(five of them used afatinib) in the first line and had a median PFS of 12 months; one patient received chemotherapy with pemetrexed and carboplatin and had PFS of seven months, which was lower than that of the TKI group.Among four patients with L861Q mutation in late stage, one patient was untreated and the three remaining were treated with TKI in the first line and had a median PFS of eight months.The patient who was treated with afatinib and bevacizumab was still stable after 11 months of follow-up.Two patients with EGFR ex20ins in advanced stage were treated with chemotherapy and bevacizumab.Nine patients with compound mutations in advanced stage were treated with TKI; among which, five patients harboring T790M compound mutations were treated with third-generation TKI and had a median PFS of more than 10 months.
ConclusionThe correlation between specific uncommon EGFR mutation and clinical pathological characteristics varies.For advanced patients with uncommon EGFR mutations (except for ex20ins), TKI is generally chosen as the first-line clinical treatment.Afatinib is recommended for advanced NSCLC patients with G719X and L861Q mutations.Third-generation TKI has significant efficacy in patients with complex mutations containing T790M.
-
0 引言
骨肉瘤(osteosarcoma)是骨科最常见的恶性肿瘤[1],其发生、发展是一个复杂的、涉及多基因调控网络失衡导致的细胞异常代谢的结果。基因表达受转录水平及翻译水平的调控,转录因子(transcription factors, TFs)及microRNAs(miRNAs)在调控基因的表达方面扮演了重要的角色。TFs和miRNAs之间存在广泛的相互作用和合作调控,共同组成复杂的调控网络,对于了解细胞的生理过程、生物学功能、疾病的发生机制等都起到了重要作用。目前面临的首要难题是骨肉瘤往往不能做到早期诊断,诊断不及时会耽误治疗时机,严重影响患者预后[2-3]。因此,建立新的、有效的骨肉瘤防治措施势在必行,还需寻找并发现新的功能基因靶向治疗骨肉瘤,根据治疗效果建立分子水平预后指标,开发安全的不同于传统治疗骨肉瘤的放化疗药物,是当前科研及临床研究中的热门话题[4-5]。本研究将利用高通量基因芯片技术分析骨肉瘤中差异表达的基因和miRNAs,结合生物信息学软件预测与调控骨肉瘤相关的TFs、miRNAs及其靶基因,分析调控网络中的关键基因及关键miRNAs的功能,构建骨肉瘤发生发展的“TFs-miRNAs”共调控网络。
1 材料与方法
1.1 miRNA数据来源
收集美国国家生物技术信息中心(National Center of Biotechnology Information, NCBI)维护的GEO数据库中的两组数据库(GPL8227、GPL19631)中所有骨肉瘤miRNA数据,收集数据时间截至2016年12月31日。
1.2 数据库资源
用基因本体论数据库(gene ontology, GO)对所分析得到的差异表达基因进行功能注释;使用京都基因与基因组百科全书(kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes, KEGG)数据库对差异表达基因进行代谢通路富集分析;使用转录作用元件数据库(transcriptional regulatory element database, TRED)对差异表达基因进行转录因子筛选。
1.3 方法
1.3.1 差异表达基因筛选及注释
为探究骨肉瘤细胞发生发展的分子机制,用R语言下载GEO数据库中GSE28425、GSE65071数据集的原始数据。使用MAS 5.0算法对数据集中的原始数据进行标准化预处理。使用Limma程序包中所提供的统计分析函数,计算与健康者细胞系相比,骨肉瘤患者中表达水平发生变化的基因。选取差异表达倍数≥2.0(Fold Change≥2.0)为筛选阈值,筛选获得差异表达的miRNA。通过差异表达分析获得两组平台共有的骨肉瘤细胞系表达水平发生显著性改变的miRNA,利用DIANA TOOLS数据库中收录的人类基因信息,找到具有显著差异的miRNA靶基因。利用R语言,将筛选得到的差异表达基因与GEO数据库提供的GPL平台注释信息进行匹配,对差异表达基因进行信息注释。
1.3.2 差异表达基因KEGG代谢通路富集分析
为进一步探究差异表达基因参与生物代谢的代谢通路,对筛选得到的差异表达基因进行KEGG代谢通路富集分析。提取差异表达基因GPL平台注释信息中的“Entrez_Gene_ID”信息,应用R语言KEGG程序包与KEGG数据库信息,对每一个差异表达基因向已知的代谢通路进行富集映射,探究差异表达基因集中映射的细胞代谢通路,初步推测骨肉瘤所影响的主要代谢通路,并筛选出与肿瘤通路关系密切的基因,进行GO功能注释分析。
1.3.3 差异表达基因GO功能注释分析
为探究差异表达且与肿瘤通路关系密切的基因所参与的生物功能,对筛选得到的与肿瘤通路关系密切的差异表达基因进行GO功能注释分析。提取差异表达基因GPL平台注释信息中的“Entrez_Gene_ID”信息,使用R语言GO程序包与GO数据库信息,对每一个差异表达基因进行功能注释,探究骨肉瘤组织与正常组织差别的基因功能,初步推测骨肉瘤作用的分子机制。
1.3.4 分子共调控网络构建
为进一步挖掘骨肉瘤的分子调控模式,探究差异表达基因之间的相互调控作用关系,提取TRED数据库中所收录的所有人类转录因子数据。通过Pearson相关性分析,提取基因间分子共调控作用关系。使用Cytoscape version 3.4.0软件对得到的分子共调控作用关系进行可视化展示,构建出最终的分子共调控网络。
2 结果
2.1 差异表达基因的筛选
本研究分别从GPL8227、GPL19631两组数据库中筛选出差异表达miRNA 232个(上调129个、下调103个)和265个(上调205个、下调60个)。共筛选得到两组均包含的差异表达miRNA52个,其中31个miRNA上调表达,21个miRNA下调表达见表 1。
表 1 差异表达的miRNAs信息Table 1 Information of differentially-expressed miRNAs
2.2 差异表达基因KEGG代谢通路富集分析
将筛选出的52个差异表达miRNA结合DIANA TOOLS数据库中收录的人类基因信息进行分析。其中KEGG代谢通路富集分析结果见图 1,差异表达基因主要参与肿瘤相关的诸多代谢通路。差异表达的52个miRNA的整体调控模式及每个miRNA所调控的代谢通路情况见图 2。肿瘤代谢通路的分子调控关系网络见图 3。
2.3 差异表达基因GO功能注释分析
将上述筛选出与肿瘤通路关系最紧密的5个miRNA及其靶基因进行GO功能注释分析。注释分析结果显示这些基因主要参与维生素E的代谢路径(response to vitamin E)、RNA聚合酶Ⅱ启动子的转录调控反应(regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase Ⅱ promoter in response etc)、调控神经元的成熟(regulation of neuron maturation)、受体激动剂活性(receptor agonist activity)、正调控血管内皮生长因子受体活性(positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor activity)、通过MAPK级联非经典Wnt信号途径(non-canonical wnt signaling pathway via MAPK cascade)、间充质上皮细胞信号转导(mesenchymal-epithelial cell signaling)、Ⅳ型胶原(collagen type Ⅳ)、细胞对生长激素刺激的反应(cellular response to growth hormone stimulus)、蛋白激酶活性的激活(activation of protein kinase A activity)等生物功能,见图 4。
2.4 分子共调控网络构建
最后基于与肿瘤通路密切相关的差异表达基因及TRED数据库中所收录的人类转录因子信息,对差异表达基因进行分子偶联,构建了分子共调控网络,见图 5。
3 讨论
目前miRNA被广泛认为是血液学和肿瘤组织的生物标志物。miRNA有可能通过扭曲、突变、成纤维细胞生长因子(FGF)和骨形态发生蛋白(BMP)信号参与骨的形成。研究发现miRNA与多种骨科疾病有关系,比如有研究认为miRNA-140与骨性关节炎有关,miRNA-503、miRNA-3960与骨质疏松有关,miRNA-34、miRNA-146等与类风湿关节炎有关[6]。研究表明众多的miRNA在骨肉瘤发病的机制中异常表达,被miRNA决定的许多基因被上调或下调。比如Karbasy等[7]通过研究发现miR-125b和miR-300的下调与骨肉瘤的进展相关且两者都起到抑癌基因的作用。Goudarzi等[8]通过研究发现miR-185上调miR-218下调与软骨肉瘤的进展相关联,并且两者均可以作为软骨肉瘤的抑癌基因。Bahador等[9]通过研究发现在青少年、儿童以及青年人骨肉瘤患者中,如果miR-29b和miR-422a的表达下调往往表明患者的预后较差。Taheriazam等[10]通过研究发现下调microRNA-26a和微小RNA-27A的上调有助于判断人类骨肉瘤的攻击性进展。高表达的miR-130b水平和miR-218的低表达与差的临床病理特征有关。此外,有研究表明miR-130b可对预测骨肉瘤的进展起关键作用[10-11]。另有研究表明miR-145、miR-128、miR-34a在骨肉瘤中的表达均发生了改变。miR-335、miR-128、miR-340、miR-214等均与骨肉瘤的侵袭性有重要关系,表达增高后预示骨肉瘤的恶性程度较高,可以较早发生转移,患者的生存期缩短[12]。并且近期有研究表明血浆中miR-34b表达下降可能与骨肉瘤已经发生转移有密切的联系[13],如果能明确这种作用关系会对骨肉瘤的早期诊断起到非凡的作用。就目前研究现状来看骨肉瘤发生发展的分子作用机制尚不十分明确,本研究利用高通量基因芯片技术,通过生物信息学手段,系统性预测构建了一张与肿瘤通路关系密切的TF、miRNA及其靶基因共调控网络蓝图。该分子共调控网络从整体的角度鸟瞰与肿瘤通路关系密切的miRNA及其靶基因的相互作用关系,展示了差异表达基因主要参与肿瘤相关的诸多代谢通路及与肿瘤通路有关的基因主要参与的生物功能。为骨肉瘤诊断标志物簇的筛选提供可靠的选择方向;为临床诊断及预后分析分子靶点的筛选提供实用工具,同时也为其他癌症的同类研究提供新思路。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。作者贡献:孙文佳:数据收集及分析、论文撰写岳君秋:文章撰写指导王满香:文章审阅及修改 -
表 1 EGFR罕见突变与EGFR野生型、EGFR经典突变NSCLC患者临床病理特征比较
Table 1 Clinicopathological features comparation of patients with NSCLC and uncommon EGFR mutations, wildtype EGFR or common EGFR mutation

表 2 各EGFR罕见突变与EGFR野生型NSCLC患者临床病理特征比较
Table 2 Clinicopathological features comparison of patients with NSCLC and uncommon EGFR mutations or wildtype EGFR

表 3 23例晚期EGFR罕见突变NSCLC患者治疗及随访
Table 3 Treatment and follow-up of 23 patients with advanced NSCLC and uncommon EGFR mutations

-
[1] 中华医学会病理学分会, 国家病理质控中心, 中华医学会肿瘤学分会肺癌学组, 等. 非小细胞肺癌分子病理检测临床实践指南(2021版)[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2021, 50(4): 323-332. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112151-20201220-00945 Chinese Pathological Society, National Pathological Quality Control Center, Lung Cancer Group, Oncology Branch, Chinese Medical Association, et al. Guidelines on clinical practice of molecular tests in non-small cell lung cancer in China[J]. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi, 2021, 50(4): 323-332. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112151-20201220-00945
[2] Wei B, Ren P, Zhang C, et al. Characterization of common and rare mutations in EGFR and associated clinicopathological features in a large population of Chinese patients with lung cancer[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2017, 213(7): 749-758. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2017.04.007
[3] Harrison PT, Vyse S, Huang PH. Rare epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2020, 61: 167-179. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.09.015
[4] Yuan M, Huang LL, Chen JH, et al. The emerging treatment landscape of targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2019, 4: 61. doi: 10.1038/s41392-019-0099-9
[5] 杜文兴, 沃杨, 卢通, 等. EGFR-TKIs治疗非小细胞肺癌EGFR罕见突变的研究进展[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2019, 22(9): 590-599. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FAIZ201909009.htm Du WX, Wo Y, Lu T, et al. A Review of EGFR-TKIs Therapy of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with Uncommon EGFR Mutations[J]. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi, 2019, 22(9): 590-599. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FAIZ201909009.htm
[6] Shah R, Lester JF. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Clash of the Generations[J]. Clin Lung Cancer, 2020, 21(3): e216-e228. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2019.12.003
[7] Hou J, Li H, Ma S, et al. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: current status and perspectives[J]. Biomark Res, 2022, 10(1): 21. doi: 10.1186/s40364-022-00372-6
[8] Vasconcelos PENS, Gergis C, Viray H, et al. EGFR-A763_Y764insFQEA Is a Unique Exon 20 Insertion Mutation That Displays Sensitivity to Approved and In-Development Lung Cancer EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors[J]. JTO Clin Res Rep, 2020, 1(3): 100051.
[9] Passaro A, Mok T, Peters S, et al. Recent Advances on the Role of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in the Management of NSCLC With Uncommon, Non Exon 20 Insertions, EGFR Mutations[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2021, 16(5): 764-773. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2020.12.002
[10] Chiu CH, Yang CT, Shih JY, et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Treatment Response in Advanced Lung Adenocarcinomas with G719X/L861Q/S768I Mutations[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2015, 10(5): 793-799. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000504
[11] Pang LL, Gan JD, Tan JR, et al. Efficacy and potential resistance mechanisms of afatinib in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with EGFR G719X/L861Q/S768I[J]. Cancer, 2022, 128(21): 3804-3814. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34451
[12] Attili I, Passaro A, Pisapia P, et al. Uncommon EGFR Compound Mutations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Systematic Review of Available Evidence[J]. Curr Oncol, 2022, 29(1): 255-266. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29010024
[13] Zhou Y, Ge F, Du Y, et al. Unique Profile of Driver Gene Mutations in Patients With Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Qujing City, Yunnan Province, Southwest China[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 644895. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.644895
[14] Hayashi T, Kohsaka S, Takamochi K, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of lung adenocarcinoma with compound EGFR mutations[J]. Hum Pathol, 2020, 103: 42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2020.07.007
[15] Yang JC, Sequist LV, Geater SL, et al. Clinical activity of afatinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring uncommon EGFR mutations: a combined post-hoc analysis of LUX-Lung 2, LUX-Lung 3, and LUX-Lung 6[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2015, 16(7): 830-838. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00026-1



 下载:
下载: