Influence of Limonin on Malignant Biological Behavior of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells by Regulating JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway
-
摘要:目的
探讨柠檬苦素调节JAK2/STAT3信号通路对非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)细胞恶性生物学行为的影响。
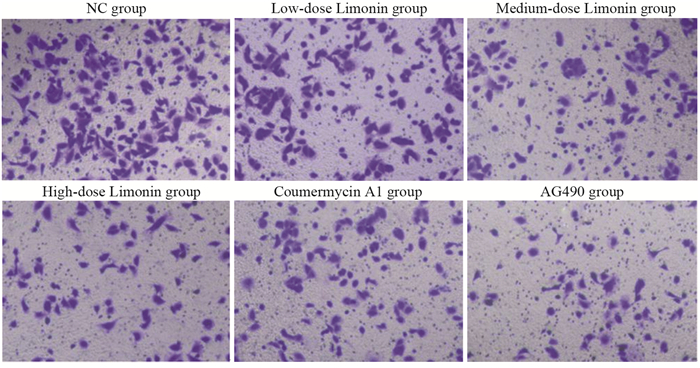
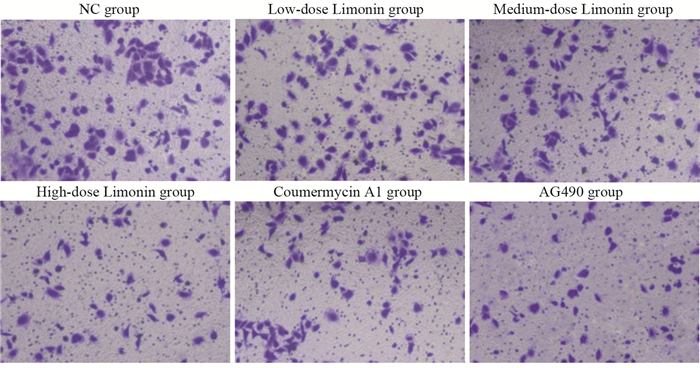
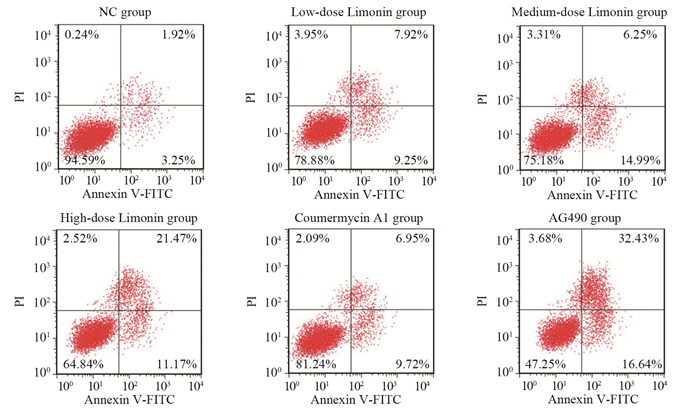
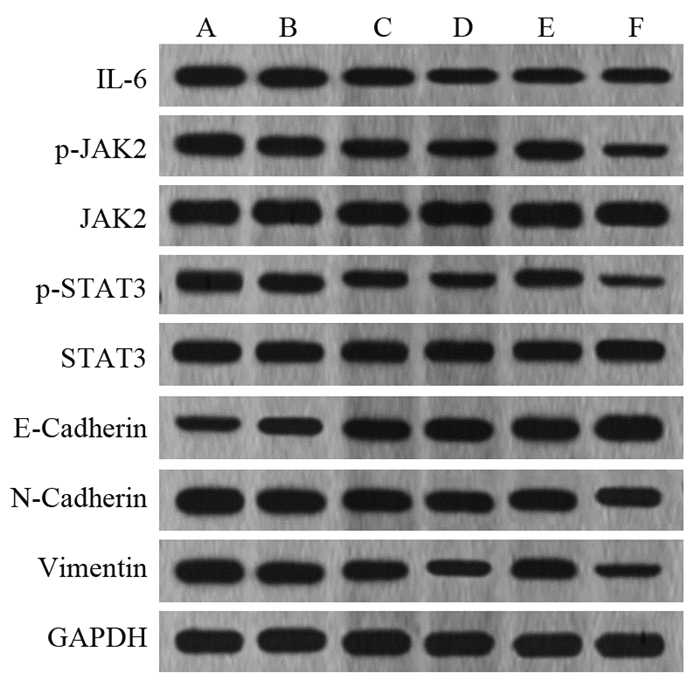
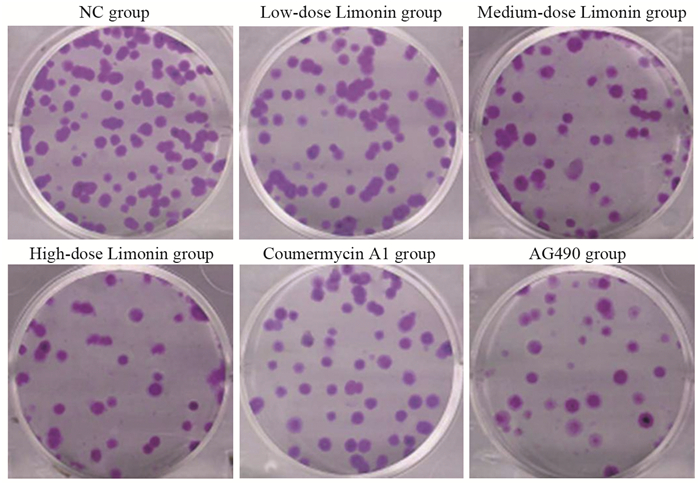
方法CCK-8法检测不同浓度的柠檬苦素(0、5、10、25、50、75、100 μmol/L)干预对A549细胞存活率的影响;将A549细胞分为NC组(正常培养)、柠檬苦素低剂量组(10 μmol/L柠檬苦素干预细胞24 h)、柠檬苦素中剂量组(25 μmol/L柠檬苦素干预细胞24 h)、柠檬苦素高剂量组(50 μmol/L柠檬苦素干预细胞24 h)、Coumermycin A1组(10 μmol/L JAK2激活剂Coumermycin A1+50 μmol/L柠檬苦素干预细胞24 h)、AG490组(10 μmol/L JAK2抑制剂AG490+50 μmol/L柠檬苦素干预细胞24 h);克隆形成实验检测各组细胞克隆情况;Transwell小室检测各组细胞迁移和侵袭;流式细胞术检测各组细胞凋亡情况;Western blot检测各组细胞JAK2、p-JAK2、STAT3、p-STAT3、E-Cadherin、N-Cadherin和Vimentin蛋白表达情况。
结果与0 μmol/L柠檬苦素组相比,A549细胞存活率呈柠檬苦素浓度依赖性降低(P < 0.05),IC50为(45.16±1.66)μmol/L,选择10、25和50 μmol/L进行后续实验;与NC组相比,柠檬苦素低、中、高剂量组A549细胞克隆数、迁移和侵袭数以及IL-6、p-JAK2、p-STAT3、N-Cadherin和Vimentin蛋白表达降低,细胞凋亡率和E-Cadherin蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05);JAK2激活剂Coumermycin A1减弱了柠檬苦素对A549细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭等恶性生物学行为的抑制能力,减弱细胞凋亡能力;JAK2抑制剂AG490增强了柠檬苦素对A549细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭等恶性生物学行为的抑制能力,增强了细胞凋亡能力。
结论柠檬苦素可通过抑制JAK2/STAT3通路进而抑制NSCLC细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭等恶性生物学行为。
-
关键词:
- 柠檬苦素 /
- JAK2/STAT3信号通路 /
- 非小细胞肺癌 /
- 恶性生物学行为
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the influence of limonin on the malignant biological behavior of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells by regulating the protein tyrosine kinase 2 (JAK2)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathway.
MethodsCCK-8 method was applied to detect the survival rate of A549 cells treated with different concentrations of limonin (0, 5, 10, 25, 50, 75, 100 μmol/L). A549 cells were separated into normal culture (NC) group, low-dose limonin group (treatment with 10 μmol/L limonin for 24 h), medium-dose limonin group (treatment with 25 μmol/L limonin for 24 h), high-dose limonin group (treatment with 50 μmol/L limonin for 24 h), coumermycin A1 group (treatment with 10 μmol/L JAK2 activator coumermycin A1+50 μmol/L limonin for 24 h), and AG490 group (treatment with 10 μmol/L JAK2 inhibitor AG490+50 μmol/L limonin for 24 h). Clone formation assay was applied to detect the clones of each group of cells. Transwell assay was applied to detect cell migration and invasion, and flow cytometry was applied to detect apoptosis. Western blot analysis was applied to detect the protein expression levels of JAK2, p-JAK2, STAT3, p-STAT3, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and vimentin in each group.
ResultsThe viability of A549 cells decreased significantly in a limonin concentration-dependent manner (P < 0.05), with IC50 of 45.16±1.66 μmol/L. Concentrations of 10, 25, and 50 μmol/L were selected for subsequent experiments. The numbers of clones, migration, and invasion of A549 cells and the protein expression levels of IL-6, p-JAK2, p-STAT3, N-cadherin, and vimentin in the low-, medium-, and high-dose limonin groups significantly decreased, compared with those in the NC group, and the apoptosis rate and E-cadherin protein expression significantly increased (P < 0.05). The JAK2 activator coumermycin A1 attenuated the ability of limonin to inhibit the proliferation, migration, invasion, and other malignant biological behavior of A549 cells and attenuated the apoptosis ability. The JAK2 inhibitor AG490 enhanced the ability of limonin to inhibit the proliferation, migration, invasion, and other malignant biological behavior of A549 cells and enhanced the apoptosis ability.
ConclusionLimonin can inhibit the malignant biological behavior of NSCLC cells, such as proliferation, migration, and invasion, by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 pathway.
-
0 引言
胶质瘤是中枢神经系统最常见的原发性肿瘤,约80%的病例表现为胶质母细胞瘤(glioblastoma, GBM),其浸润性强、恶性程度高、预后差,患者的平均生存期仅为15个月[1-2]。目前标准治疗方案是手术联合放疗(radiotherapy, RT)和化疗,但患者的总体生存率改善有限。随着免疫治疗在其他肿瘤治疗中取得了突破性进展,在GBM中利用免疫治疗同样引起了学者们的兴趣。然而由于GBM的高异质性、低突变负荷、强大的免疫抑制性肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment, TME)及中枢神经系统特有的天然防御系统——血脑屏障(blood-brain barrier, BBB)使免疫治疗在GBM的研究中仍处于起步阶段[3-4]。已有证据表明,RT可诱导抗肿瘤免疫反应,为免疫治疗提供新的靶点,在抗肿瘤治疗中,可与免疫检查点抑制剂发挥协同效应[5]。鉴于此,本文将着重描述放疗对肿瘤微环境的影响及放疗联合免疫检查点抑制剂治疗对GBM的作用,以期寻找更适合的治疗方案。
1 放射治疗与胶质母细胞瘤
1.1 放疗
RT是治疗恶性肿瘤的主要手段之一。目前基本放疗技术包括常规放疗(conventional radiotherapy, CRT)、三维适形放疗(three dimensional conformal radiotherapy, 3D-CRT)、调强放疗(intensity-modulated radiotherapy, IMRT)和立体定向放疗(stereotactic body radiotherapy, SBRT)。相关研究表明常规分割虽然可以达到治疗效果,但也会带来很多不良反应,而3D-CRT和IMRT相较于常规RT都可以提高生存率,减少不良反应,且IMRT比3D-CRT显示出更好的目标覆盖率[6]。SBRT通常被用于复发性GBM的治疗,可减少治疗体积并控制肿瘤生长以提高肿瘤患者的总体生存率[7]。
1.2 放疗与免疫微环境
当肿瘤细胞暴露于RT的射线时,靶组织表型及周围环境发生改变,使肿瘤细胞更易受到免疫反应的影响。首先,辐射可上调肿瘤细胞表面的MHCⅠ类分子、钙网蛋白及FAS表面分子表达及高迁移率族蛋白B1(high mobility group box-1 protein, HMGB1)的释放,同时可诱导CD8+细胞毒性T细胞识别并杀死肿瘤细胞,激活树突细胞(dendritic cell, DC)并促进其对肿瘤细胞的吞噬作用,而FAS的表达则会进一步诱导细胞凋亡[8-9];其次,辐射诱导肿瘤细胞死亡,可释放抗原及一系列共刺激分子激活DC(辐射诱导释放的抗原足以达到交叉呈递所需的阈值)促进抗原交叉呈递[10]。活化的DC迁移到淋巴结,通过细胞溶质和液泡途径将抗原进行加工后加载到MHCⅠ类分子上[11],进而交叉呈递给CD8+T细胞。此外,由于抗原特异性免疫反应的诱导并不足以消灭肿瘤,需要克服外周耐受(主要为物理屏障)使适应性免疫细胞能够浸润至肿瘤。RT可通过三种不同的作用机制影响免疫细胞浸润:黏附分子表达增加、趋化因子分泌及血管结构的改变[12-13]。第一种作用机制,RT通过诱导炎性细胞因子如白介素-1β、肿瘤坏死因子以及Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型干扰素,影响肿瘤内皮上的血管细胞黏附分子1(intercellular adhesion molecules 1, ICAM-1)或自然杀伤细胞活化性受体(natural killer cell group 2D, NKG2D)配体的上调[14]。第二种作用机制,RT上调肿瘤细胞中的趋化因子(CXC基序)配体9(CXCL9)、-10和-16以促进T细胞募集到受照射的肿瘤中[12]。第三种作用机制,RT还可以改变血管表型,肿瘤通常表现出无组织的脉管系统,低剂量的RT可以使血管正常化,也可刺激血管生成,进而促进T细胞浸润[15-16]。GBM相较于其他肿瘤,还有BBB的存在。相关研究表明RT可改变BBB,诱导其通透性增加,允许外周T细胞浸润或进入中枢神经系统肿瘤,这对中枢神经系统肿瘤的治疗起到关键作用[17]。
从以上研究我们发现,将RT与免疫检查点抑制剂结合,可以产生协同治疗作用,从而对肿瘤产生抑制作用。这为RT联合免疫治疗提供了新思路。
2 放疗联合免疫检查点分子对胶质母细胞瘤的影响
单纯RT治疗对于胶质母细胞瘤患者的生存改善微乎其微,因为RT不但可以促进免疫激活,还可以诱导免疫抑制。不同剂量辐射对抗肿瘤免疫反应产生不同影响,现有研究认为RT每次剂量超过10 Gy可以有效增强抗肿瘤免疫反应并为免疫治疗提供相关靶点,但低剂量辐射可以诱导免疫抑制性TME[18]。研究发现,RT联合不同免疫检查点抑制剂治疗的最佳时机各不相同。在评估放疗和抗PD-1治疗理想时机的报告中得出,相同剂量辐射情况下,同步治疗优于序贯治疗。但在放疗和抗CTLA-4的治疗中发现,在单次20 Gy剂量辐射前7天给予联合用药最有效,而不是同步治疗或在放疗后给予用药;而在同一模型中,放疗后1天给予抗OX40药物治疗效果最佳[19]。这一结论在GBM治疗中是否有效,需要我们进一步验证,但据目前临床前及临床数据显示,RT联合免疫检查点抑制剂对GBM具有积极的抗肿瘤作用[20]。
2.1 放疗与CTLA-4
细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关抗原4(CTLA-4)是第一个进入临床的免疫检查点受体,仅在T淋巴细胞上表达,主要调节T细胞活化早期阶段的幅度,限制T细胞增殖,减少细胞因子的产生,并下调辅助性T细胞的活性,上调调节性T细胞(regulatory T cell, Treg)免疫抑制性,抗CTLA-4抗体可以通过减弱CTLA-4的抑制功能和Treg的抑制作用来减轻T细胞耗竭[17, 20]。CTLA-4抑制剂对免疫原性较差的肿瘤产生抗肿瘤活性需要与其他干预措施相结合。RT联合CTLA-4阻断可诱导CXCL16的分泌,CXCL16可与TH1辅助细胞表面的CXCR6+结合并共同刺激CD8+T细胞募集到肿瘤部位,导致原发肿瘤和转移灶的消退[21]。
RT与抗CTLA-4联合治疗在多种实体瘤治疗中取得了良好的疗效。在不同肿瘤类型中,RT都有一个最佳剂量来诱导免疫和与免疫抑制剂结合[22]。在GBM实验中,肿瘤植入后第10天给予小鼠单次放射治疗,剂量为10 Gy,于第11、17、23天给予800 μg抗CTLA-4抗体,结果显示接受RT和CTLA-4阻断联合治疗的小鼠的中位生存期为29天,与对照组相比其生存期明显延长,且接受联合治疗30天后50%的小鼠依然存活,而给予抗CTLA-4抗体和局灶性RT的对照组小鼠均于肿瘤植入后30天内死亡。实验说明联合治疗可以提高小鼠的生存期,该实验组同时对抗CTLA-4抗体的最佳治疗时间进行了研究,发现在第10天首先用局部放疗治疗,然后在第12、14和15天用CTLA-4阻断治疗的动物中位生存期为27.5天(与未治疗相比)。当CTLA-4阻断剂在第10天与RT同时给药,然后在第12和14天再注射时,中位生存期从21.5天延长至29天。CTLA-4阻断剂在肿瘤植入后的第8天也就是放疗前第2天开始给药,随后在肿瘤植入后的第10和12天再注射,其中位生存期为29.5天[23]。然而与之前研究不同的是,在此实验中发现抗CTLA-4抗体与RT联合治疗的时间顺序对于小鼠的生存期影响似乎并不太明显,对此我们需要进行大量的临床试验进行验证,从而探索联合治疗在GBM治疗中的最佳方案。目前针对放疗后应用抗CTLA-4药物(Ipilimumab)和替莫唑胺的疗效对比的临床Ⅱ期试验(ISCTN84434175)研究正在进行中[24]。
2.2 放疗与PD-1/PD-L1
程序性死亡蛋白1(PD-1)是一种在活化的T细胞、B细胞、巨噬细胞、Treg和自然杀伤(natural killer, NK)细胞表面上表达的跨膜蛋白质,与程序性死亡配体1(PD-L1)的结合有效地阻断了T细胞的增殖和细胞因子的产生,进而促进肿瘤免疫逃逸的发生[25]。针对PD-1/PD-L1的阻断可以有效引发抗肿瘤T细胞反应,并在晚期癌症患者治疗中产生较好的疗效,一些研究将RT与PD-1/PD-L1抑制剂进行结合[26]。
RT除了通过诱导免疫原性细胞死亡来激活宿主免疫外,还可以通过JAK-STAT-IRF途径诱导IFN-γ产生进而使PD-L1上调达到免疫抑制。但相关研究表明抗PD-1/PD-L1抗体可以抵消这种免疫抑制,这进一步阐明了RT与免疫检查点抑制剂联合治疗的重要意义[27]。在GBM小鼠的对照实验中,于肿瘤植入后的第10天给予小鼠大脑单剂量10 Gy辐射,放射后立即注射10 mg/kg抗PD-1抗体,并于肿瘤植入后的第12天及14天再加两次,结果显示,与其他对照组相比,SBRT+抗PD-1组的小鼠生存期及存活率显著提高且平均肿瘤体积生长明显延迟[28]。相对于PD-1阻断在GBM治疗中的影响,大多数学者认为抗PD-L1更有效,在对GBM患者的外周血与肿瘤细胞进行的流式细胞实验中发现,PD-L1在荷瘤小鼠和GBM患者的循环单核细胞和肿瘤巨噬细胞上高表达[29]。为明确PD-L1在GBM治疗中的意义,Ding等测量了60例患者中51例血浆样本中的可溶性程序性死亡配体1(sPD-L1),发现RT(30±10 Gy, 2 Gy/f)后的sPD-L1平均浓度显著高于RT前的基线sPD-L1水平,并使用60例患者的肿瘤组织进行了小鼠实验,给予小鼠RT(20 Gy)+200 μg抗PD-L1抗体,与对照实验相比sPD-L1浓度显著下调,且降低了小鼠肿瘤的生长[30]。临床前实验均表明联合治疗的有效性,RT为免疫治疗提供相关表型,而免疫检查点抑制剂通过直接激活巨噬细胞中的抗肿瘤表型和促炎表型来增强辐射诱导的远隔反应[31]。但对于临床应用实施,则需要更多数据指导。目前有两项临床试验正在进行:一项Ⅲ期随机开放研究,比较两种治疗(抗PD-1药物nivolumab+RT与替莫唑胺+RT)在O-6-甲基鸟嘌呤-DNA甲基转移酶(O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase, MGMT)未甲基化胶质母细胞瘤患者中的总生存期(CheckMate-498);另一项临床试验是评估低分割立体定向放疗和抗PD-L1药物(durvalumab)在复发性胶质母细胞瘤(试验编号STERIMGLI)患者中的安全性。
2.3 放疗与Tim-3
T淋巴细胞免疫球蛋白黏蛋白分子3(Tim-3)是一种跨膜蛋白,也是免疫细胞上的抑制性受体,主要在分泌干扰素γ的CD4+T辅助细胞1和CD8+T细胞毒性细胞上选择性表达,也可在单核/巨噬细胞、DC、Treg、肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞上表达,其主要作用是诱导T细胞衰竭[32-33]。Tim-3在胶质瘤患者外周血及肿瘤的T细胞上过表达,与低级别胶质瘤相比,高级别胶质瘤上Tim-3表达显著上调[34-35]。
Tim-3在GBM治疗中具有重要地位,在对RT+抗PD-L1耐药机制研究中发现经RT+抗PD-L1治疗后早期和晚期采集的肿瘤标本中,表达Tim-3的CD4+细胞的比例分别增加了1.83和2.40倍。Tim-3在CD8+T细胞上的平均荧光强度在早期和晚期肿瘤中分别增加了2.19和2.80倍,且在对肿瘤进行RNA测序后发现,其他T细胞共抑制受体未表达[36]。与之相同的是,体内小鼠模型实验在抗PD-1治疗之前给予SBRT(10 Gy)以诱导炎性反应为随后的免疫治疗提供肿瘤微环境,于肿瘤植入后的第10、12、14天给予每只动物200 μg抗PD-1抗体,第7、11、15天给予每只动物250 μg抗Tim-3抗体,结果显示与单独治疗组相比,RT+抗PD-1抗体+抗Tim-3抗体组中CD4+和CD8+T细胞频率显著增加,且小鼠生存期明显提高[37]。实验发现,Tim-3阻断可作为PD-1/PD-L1耐药的一种替代治疗,但联合治疗需确定RT的剂量、顺序及时间,有学者针对IMRT和SBRT对Tim-3表达的影响进行研究,发现患者在接受IMRT(2 Gy)或SBRT(7.25 Gy)治疗后6 h内,IMRT诱导的Tim-3表达高于SBRT,其余试验时间段Tim-3在SBRT中的表达更高,但总体研究显示RT诱导Tim-3呈缓慢持续性增加状态[38]。
2.4 放疗与TIGIT
T细胞免疫球蛋白和ITIM结构域蛋白(T-cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains, TIGIT)是一种抑制性免疫球蛋白受体,在活化的T细胞和NK细胞上表达,主要抑制活化的T细胞和NK细胞并促进Treg功能恢复。目前研究发现TIGIT在人GBM中高表达,成为癌症免疫治疗的新候选靶点[39-40]。对于该靶点进行的小鼠实验发现,单独使用抗TIGIT治疗对控制肿瘤生长产生较小影响,且小鼠的长期生存率为0[41]。放疗可以增加T细胞活化,促进抗肿瘤免疫反应。在CT26结肠肿瘤的小鼠实验中发现,在RT(3×8 Gy)方案下TIGIT的表达增加,而在RT(18×2 Gy)方案下TIGIT的表达显著降低。当在抗PD-L1和RT(3×8 Gy)联合治疗时,抗TIGIT才会产生显著的抗肿瘤作用。而当与RT(18×2 Gy)或RT(18×2 Gy)和抗PD-L1联合治疗时,抗TIGIT没有显著的抗肿瘤作用[42]。
RT和抗TIGIT联合治疗对于GBM治疗的影响,目前仍缺乏相关临床前及临床试验。
2.5 放疗与其他免疫检查点分子
除了以上几种免疫检查点,临床前研究在使用吲哚胺2, 3双加氧酶(indoleamine2, 3-dioxygenase, IDO)、淋巴细胞活化因子3(lymphocyte activation gene-3, LAG-3)或OX-40的抗体的GBM小鼠模型中也实现了最佳客观缓解率。
IDO是一种细胞内酶,于高龄GBM患者的脑实质中高表达,一般通过降低色氨酸水平抑制T细胞增殖并导致T细胞凋亡和Treg积累[43]。Ahlstedt等对IDO抑制剂与RT联合治疗疗效进行研究,在小鼠接种肿瘤的第7天将10 mg IDO抑制剂注入小鼠腹腔,持续10天,并于接种后第7、11天给予RT(8 Gy),发现小鼠肿瘤较对照组及单次RT+IDO抑制剂组明显变小,且具有明显的生存优势[44]。
LAG-3也是一种抑制性受体,通过与主要组织相容性复合体Ⅱ类(MHCⅡ类)分子结合来下调T细胞活性。此外,LAG-3还增强了Tregs的内在抑制活性。一项正在进行的Ⅰ期研究(NCT03250832)单独评估了抗LAG-3抗体TSR-033以及与抗PD-1抗体的组合[45]。在其他实体肿瘤上目前已有实验证明了RT和抗LAG-3联合治疗取得的良好效果[46],但在GBM治疗中仍缺少相关实验。
OX-40是一种TNF家族共刺激因子,在激活记忆CD4+ T细胞和CD4+FoxP3+调节性T细胞上表达,与其配体OX40L相互作用充当共刺激信号[47]。Shibahara等[48]将人GBM细胞与OX40L共培养后得出,在GBM细胞中表达的OX40L可诱导T细胞活化,从而增强抗肿瘤适应性免疫反应。但RT与抗OX-40抗体联合治疗在GBM治疗中的具体方案并无相关研究,不过一项抗PD-1耐药的肺肿瘤模型研究将实验分成三组:15 Gy分3次5 Gy分割(较低的立体定向剂量)、15 Gy分5次3 Gy分割(常规剂量)、24 Gy分两次12 Gy(更高的立体定向剂量)。结果显示,24 Gy分两次12 Gy对原发性肿瘤生长产生了最大的抑制,对照组和仅抗OX40组(5次100 μg瘤内注射,间隔4天)对肿瘤生长没有明显影响。对上述实验治疗顺序带来的效果分别进行观察,认为首先给予RT,然后给予抗OX40在抑制小鼠抗PD-1耐药性肿瘤的生长方面最有效[49]。这为随后的GBM实验研究提供了有效的思路。
3 总结与展望
由于GBM呈侵袭浸润生长,与周围正常脑组织界限不清,故手术难以将其完全切除,而放疗和化疗又存在放射抵抗和耐药性,所以人GBM仍然是预后最差的肿瘤之一。RT可以在杀伤肿瘤细胞的同时激活抗肿瘤免疫反应,与免疫检查点抑制剂产生协同抗肿瘤作用,并在GBM的临床前实验中取得良好疗效。然而放射治疗对肿瘤的影响复杂多变,为优化免疫治疗效果,我们需进一步明确放疗的分割剂量、最佳时间、顺序,并探讨与不同免疫检查点抑制剂的组合应用,从而为GBM的治疗提供新的有效策略。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。作者贡献:胡会杰:课题设计、实验操作、文章撰写及修改郑晓璐、雷立峰:数据及文献汇总分析 -
表 1 不同浓度柠檬苦素对A549细胞增殖的影响(x±s)
Table 1 Effect of different concentrations of limonin on proliferation of A549 cells (x±s)

表 2 柠檬苦素对A549细胞克隆形成的影响(x±s)
Table 2 Effect of limonin on clonogenic ability of A549 cells (x±s)

表 3 柠檬苦素对A549细胞迁移和侵袭的影响(x±s)
Table 3 Effect of limonin on migration and invasion of A549 cells (x±s)

-
[1] Hernandez D, Cheng CY, Hernandez-Villafuerte K, et al. Survival and comorbidities in lung cancer patients: Evidence from administrative claims data in Germany[J]. Oncol Res, 2023, 30(4): 173-185.
[2] Alduais Y, Zhang H, Fan F, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A review of risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2023, 102(8): e32899. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032899
[3] Chen Q, Wu B, Ge P, et al. Ubenimex Combined with Pemetrexed Upregulates SOCS1 to Inhibit Lung Adenocarcinoma Progression via the JAK2-STAT3 Signaling Pathway[J]. Dis Markers, 2022, 2022: 5614939.
[4] Kang DY, Sp N, Lee JM, et al. Antitumor Effects of Ursolic Acid through Mediating the Inhibition of STAT3/PD-L1 Signaling in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells[J]. Biomedicines, 2021, 9(3): 297. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9030297
[5] Aung TN, Qu Z, Kortschak RD, et al. Understanding the Effectiveness of Natural Compound Mixtures in Cancer through Their Molecular Mode of Action[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(3): 656. doi: 10.3390/ijms18030656
[6] Chen Y, Liang J, Liang X, et al. Limonin induces apoptosis of HL-60 cells by inhibiting NQO1 activity[J]. Food Sci Nutr, 2021, 9(4): 1860-1869. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2109
[7] Akihisa T, Yokokawa S, Ogihara E, et al. Melanogenesis-Inhibitory and Cytotoxic Activities of Limonoids, Alkaloids, and Phenolic Compounds from Phellodendron amurense Bark[J]. Chem Biodivers, 2017, 14(7): e1700105. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201700105
[8] Gong C, Qi L, Huo Y, et al. Anticancer effect of Limonin against benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung carcinogenesis in Swiss albino mice and the inhibition of A549 cell proliferation through apoptotic pathway[J]. J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2019, 33(12): e22374. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22374
[9] Zhang T, Chen Y, Cai J, et al. SOCS2 Inhibits Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation via Suppressing LepR/JAK2/AMPK Signaling Pathway in Mouse Adipocytes[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2020, 2020: 3742542.
[10] Wang Z, Wei Y, Lei L, et al. RANKL expression of primary osteoblasts is enhanced by an IL-17-mediated JAK2/STAT3 pathway through autophagy suppression[J]. Connect Tissue Res, 2021, 62(4): 411-426. doi: 10.1080/03008207.2020.1759562
[11] Zhang Y, Ma P, Duan Z, et al. Ginsenoside Rh4 Suppressed Metastasis of Lung Adenocarcinoma via Inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 Signaling[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(4): 2018. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042018
[12] Qiu Z, Zhong Z, Zhang Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-335-5p attenuates the inflammation and tubular epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation of renal tubular epithelial cells by reducing ADAM19 protein levels[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2022, 13(1): 373. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03071-z
[13] Li Y, Yang M, Lin H, et al. Limonin Alleviates Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Reducing Lipid Accumulation, Suppressing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 12: 801730. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.801730
[14] Chidambara Murthy KN, Jayaprakasha GK, Safe S, et al. Citrus limonoids induce apoptosis and inhibit the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells[J]. Food Funct, 2021, 12(3): 1111-1120. doi: 10.1039/D0FO02740E
[15] Fan CW, Tang J, Jiang JC, et al. Pentagalloylglucose suppresses the growth and migration of human nasopharyngeal cancer cells via the GSK3β/β-catenin pathway in vitro and in vivo[J]. Phytomedicine, 2022, 102: 154192. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154192
[16] Chen J, Liu BX, Shen Q, et al. Limonin inhibits angiogenesis and metastasis of human breast cancer cells by suppressing the VEGFR2/IGFR1-mediated STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Transl Cancer Res, 2020, 9(11): 6820-6832. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-1992
[17] Bae JR, Park WH, Suh DH, et al. Role of limonin in anticancer effects of Evodia rutaecarpa on ovarian cancer cells[J]. BMC Complement Med Ther, 2020, 20(1): 94. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-02890-y
[18] Gao L, Sang JZ, Cao H. Limonin enhances the radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via attenuating Stat3-induced cell stemness[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 118: 109366. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109366
[19] 姜姗, 刘淼, 张黎, 等. 蟛蜞菊内酯通过抑制JAK2/STAT3信号通路诱导人肺腺癌A549细胞凋亡[J]. 华中科技大学学报(医学版), 2021, 50(4): 488-492. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYX202104016.htm Jiang S, Liu M, Zhang L, et al. Wedelolactone induces apoptosis of human lung adenocarcinoma a 549 cells via inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 pathway[J]. Hua Zhong Ke Ji Da Xue Xue Bao (Yi Xue Ban), 2021, 50(4): 488-492. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJYX202104016.htm
[20] Hou J, Lv A, Deng Q, et al. TROP2 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of glioblastoma cells by activating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Oncol Rep, 2019, 41(2): 753-764.
[21] Huang B, Lang X, Li X. The role of IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in cancers[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 1023177.
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 梁帅,尹怡,刘湘花,汪保英,骆文龙,龙云凯,任振杰,王祥麒. 升降理肺消瘤汤对Lewis肺癌小鼠免疫炎性反应和JAK2/STAT3信号通路的影响. 辽宁中医药大学学报. 2024(04): 27-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张彩蝶,靳艳,张德德. 润肺益肾饮对肺癌荷瘤大鼠的抑瘤作用和肿瘤免疫微环境的影响. 天津医药. 2024(04): 362-366 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 孙喜,王召路,贾谨睿,王梦洋,孙润卓,王鹏,史新娥. 虫草素及其在生猪养殖中的应用. 畜牧兽医杂志. 2024(04): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 兰春燕,杨小兰,贺雪峰,赵丹,杨海燕. 甘草苷对胃癌荷瘤小鼠免疫功能的调节作用及机制研究. 中国药房. 2024(15): 1862-1867 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张景淇,郭静,陈娅欣,蒲玥衡,向俊杰. 中药调控肺癌相关信号通路研究进展. 中国实验方剂学杂志. 2024(19): 233-244 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张孟恩,韩睿,徐超,庞训胜,王世琴. 地顶孢霉培养物在反刍动物生产中的应用研究进展. 中国畜牧杂志. 2024(12): 70-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 高铭,丁美灵,雷紫琴,胡靖文,栾飞,曾南. 荆防败毒散及其中成药制剂研究进展. 中药药理与临床. 2023(05): 112-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 朱亚兰,吕世文,曾晨欣,徐媛青. 苍术素对非小细胞肺癌细胞上皮间质转化的影响及机制研究. 浙江医学. 2023(10): 1013-1018 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 陈才伟,陈家亮,李华娟,方芳,文方玲. 虫草素调节MAPK/AP-1信号通路对慢性阻塞性肺疾病大鼠肺组织损伤的影响. 临床肺科杂志. 2023(11): 1656-1661 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 李翔子,王西双,范建伟,杨田野,王丽娟,孙颖,姚景春. 荆防合剂通过抑制JAK2-STAT3信号通路调节荨麻疹小鼠脾脏T淋巴细胞亚群的平衡. 中国中药杂志. 2022(20): 5473-5480 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 沈栩岚,黄凌霞. 虫草素的抗癌机理. 蚕桑通报. 2022(02): 33-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: