Prediction of Responses of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy by T-cell Invigoration to Tumour Burden Ratio
-
摘要:目的
探讨抗PD-1治疗后肝细胞癌患者外周血T细胞活化及其与肿瘤负荷比值对免疫治疗疗效的预测价值。
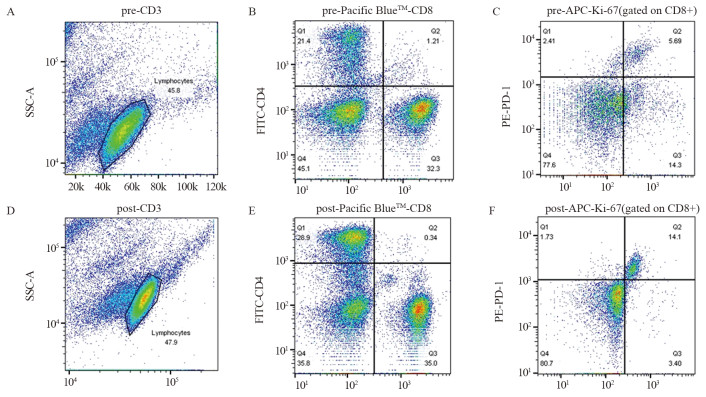
方法分析85例接受抗PD-1治疗的肝细胞癌(HCC)患者治疗前后的血清样本,通过流式细胞仪分析其外周血细胞亚群、T细胞活化,结合影像检查X-tile软件选取截断值,生存分析评估患者预后情况。
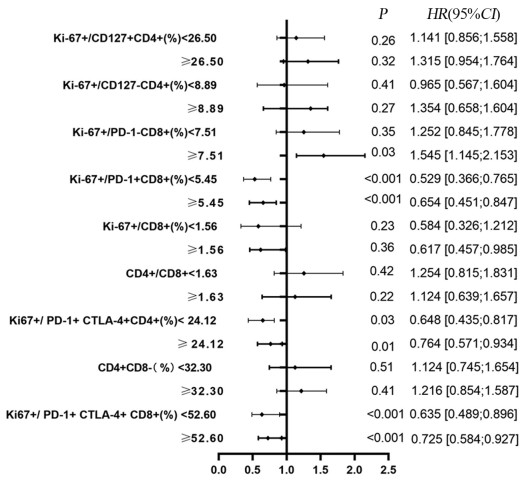
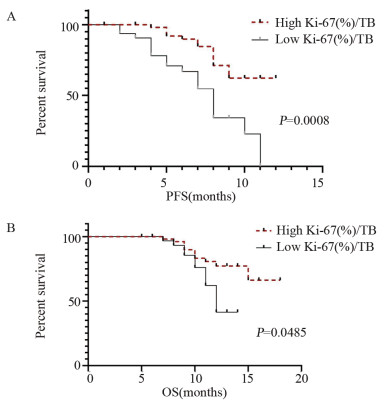
结果治疗周期中Ki-67+/PD-1+/CD8+ T细胞的最大倍数变化和通过影像确定的肿瘤负荷与免疫治疗的生存获益相关。在抗PD-1免疫治疗的第一个周期,T细胞Ki-67+/PD-1+/CD8+表达与肿瘤负荷比大于0.6与PFS和OS的改善相关(P < 0.05)。
结论免疫治疗后外周血T细胞的活化与肿瘤负荷比可能与肝细胞癌抗PD-1免疫治疗的临床疗效相关。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the predictive value of T cell activation in peripheral blood of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC) after anti PD-1 therapy and its ratio to tumor burden on the efficacy of immunotherapy.
MethodsSerum specimens were obtained before and after treatment from 85 patients with HCC who received anti-PD-1 treatment. Indicators such as cell subpopulations and T cell activation were detected by flow cytometry. Combined with imaging analysis, cutoff value was obtained by X-tile software. Survival analysis was used to evaluate patients' outcomes.
ResultsThe maximum fold change of Ki-67+/PD-1+/CD8+ T cells in treatment cycles and the tumor burden determined by imaging were associated with prognoses. The ratio of T cell Ki-67+/PD-1+/CD8+ expression to tumor burden ratio greater than 0.6 at the first cycle of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy was associated with improvements in progression-free survival and overall survival (P < 0.05).
ConclusionThe ratio of activationa in T cells in peripheral blood after immunotherapy to the tumor burden may be related to the clinical efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy for HCC.
-
Key words:
- Immunotherapy /
- Peripheral blood biomarkers /
- Tumour burden /
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
-
0 引言
目前,化学治疗仍是三阴性乳腺癌的主要治疗方法之一,但是肿瘤细胞对化疗药物的耐药性严重影响了治疗效果,化疗药物与肿瘤细胞的接触是诱导继发性耐药的主要原因[1]。由于阿霉素是乳腺癌化学方案的常用药物[2],本研究观察阿霉素对三阴性乳腺癌耐药性的诱导作用并探究其机制。
ATP结合盒(ABC)转运蛋白在耐药的发展中起着至关重要的作用。ATP结合盒亚家族G成员2(ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G member 2, ABCG2)能排出大量异质化合物,导致耐药,引起治疗抵抗[3]。细胞耐药性的产生及耐药蛋白的表达受多种转录因子的调控。有研究报道cMyc能够调控包括ABCG2在内的ABC转运蛋白的表达[4]。cMyc是一个多功能的转录因子,参与调节细胞对阿霉素的敏感度[5],而cMyc的表达受其上游基因Stat3的调控。Stat3在肿瘤组织中异常激活,引发其下游靶基因cMyc转录,从而使正常细胞转化为癌细胞,并增加肿瘤细胞的耐药性[6]。因此,本研究观察阿霉素对MDA-MB-468细胞耐药性的诱导作用并探讨Stat3-cMyc通路是否介导了耐药性的发生。
1 材料与方法
1.1 细胞株、试剂、仪器
人乳腺癌MDA-MB-468细胞株购自美国标准细胞库(American type culture collections, ATCC)。本研究实验剂和仪器包括:RPMI 1640培养基(Hyclone,美国)、青霉素/链霉素(索莱宝,北京,中国)、胎牛血清(四季青,杭州,中国)、阿霉素(索莱宝,北京,中国)、RIPA裂解液/苯甲基磺酰氟(索莱宝,北京,中国)、聚偏二氟乙烯膜(Millipore,Billerica,美国)、ABCG2抗体(Abcam,Cambridge,美国)、WP1066抑制剂(Selleckchem,上海,中国)和二甲基亚砜(索莱宝,北京,中国)等。
1.2 细胞培养
人乳腺癌MDA-MB-468细胞用含10%FBS和1%青霉素/链霉素的RPMI 1640在37℃、5%CO2培养箱中培养。以不同浓度的阿霉素(0、0.05、0.1和0.5 μmol/L)孵育细胞24 h,观察并筛选最适阿霉素浓度进行后续实验。
1.3 MTT法检测
细胞以3 000个/孔的密度接种至96孔板,然后分别加入终浓度为0、0.05、0.1和0.5 μmol/L的阿霉素。24 h后,每孔加入20 μl MTT溶液(5 mg/ml)继续培养4 h,吸弃培养液,每孔加150 μl DMSO溶液,振荡15 min后测定570 nm处的吸光度(OD570)。
1.4 细胞爬片及免疫荧光染色
将盖玻片置于24孔板孔底,分别将MDA-MB-468和MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞以1×104个/孔接种,待细胞爬满盖玻片后进行免疫荧光染色。用PBS轻轻冲洗后在4%多聚甲醛中固定15 min。PBS洗涤爬片3次,山羊血清封闭1 h。将细胞用ABCG2一抗在4℃冰箱中孵育、过夜。PBS洗涤后,用二抗于37℃温育1 h。PBS洗涤细胞,用DAPI染色10 min,再次洗涤3次后滴加荧光防淬灭剂,观察免疫荧光染色并拍照。
1.5 蛋白质印迹分析
抽提各组细胞的总蛋白,利用BCA法测定总蛋白浓度,以每个泳道20 μg浓度的蛋白样品上样,经SDS-PAGE电泳后,利用半干电转化法将蛋白转移至PVDF膜上,经过封闭、一抗(稀释倍数1:1 000)孵育、TBST洗脱、HRP标记的二抗(稀释倍数1:5 000)孵育、TBST再洗脱等步骤后,用增强化学发光法检测信号及X线片曝光,并且经定影显影处理,获得清晰条带。
1.6 统计学方法
运用SPSS13.0统计软件进行分析,所有结果采用(x±s)表示,组间均数的比较采用独立t检验(双侧),P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 持续低剂量阿霉素刺激诱导MDA-MB-468细胞产生耐药性
不同浓度阿霉素作用于MDA-MB-468细胞24 h后可见0.05 μmol/L与0.1 μmol/L浓度的阿霉素未引起细胞明显的损伤,大部分细胞生长良好。当浓度增加到0.5 μmol/L时,几乎所有细胞都受损,可见大量坏死细胞;MTT法测得在0.05 μmol/L、0.1 μmol/L及0.5 μmol/L浓度下阿霉素对MDA-MB-468细胞的抑制率分别为0.14、0.20、0.38,而且阿霉素对MDA-MB-468细胞的半数最大效应浓度(concentration for 50% of maximal effect, EC50)为0.94 μmol/L(P=0.038)。综合以上结果,我们选用0.1 μmol/L的阿霉素继续进行后续研究。
用0.1 μmol/L的阿霉素持续刺激MDA-MB-468细胞4周后获得耐药细胞,命名为MDA-MB-468/ADM。MTT实验检测MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞对阿霉素敏感度,结果显示MDA-MB-468/ADM的EC50为5.2 μmol/L,较MDA-MB-468的EC50(0.94 μmol/L)显著升高(P=0.041),说明长期使用0.1 μmol/L的阿霉素后,MDA-MB-468细胞对阿霉素的敏感度显著下降,产生耐药,见图 1。
2.2 MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞中高表达耐药蛋白ABCG2
与正常MDA-MB-468细胞相比,MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞中代表ABCG2表达水平的红色荧光明显增多增强,见图 2A。Western blot检测结果也表明了MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞中ABCG2的高表达,见图 2B。提示用0.1 μmol/L阿霉素持续刺激后,三阴性乳腺癌MDA-MB-468细胞对阿霉素产生耐药。
![]() 图 2 MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞中耐药蛋白ABCG2的表达Figure 2 Expression of drug resistance protein ABCG2 in MDA-MB-468/ADM cellsA: Immunofluorescence staining results showed the increased expression of ABCG2 (red) in MDA-MB-468/ADM cells, staining with DAPI (blue); B: Western blot analysis results showed high expression of ABCG2 in MDA-MB-468/ADM cells (n=3, *: P < 0.05)
图 2 MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞中耐药蛋白ABCG2的表达Figure 2 Expression of drug resistance protein ABCG2 in MDA-MB-468/ADM cellsA: Immunofluorescence staining results showed the increased expression of ABCG2 (red) in MDA-MB-468/ADM cells, staining with DAPI (blue); B: Western blot analysis results showed high expression of ABCG2 in MDA-MB-468/ADM cells (n=3, *: P < 0.05)2.3 MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞高表达p-Stat3与cMyc
为探究MDA-MB-468细胞对阿霉素产生耐药的机制,我们进一步检测了MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞中转录因子p-stat3与cMyc的表达水平,观察MDA-MB-468细胞对阿霉素耐药性的产生是否与Stat3-cMyc途径有关。Western blot结果显示,MDA-MB-468/ADM中p-Stat3与cMyc的表达均明显升高,而两组细胞中总的Stat3表达水平未见显著变化。这些结果表明Stat3的激活和cMyc表达的增多可能参与了MDA-MB-468细胞对阿霉素耐药性的产生,见图 3。
2.4 抑制Stat3活化可下调cMyc及ABCG2的表达
为进一步证明Stat3-cMyc途径在阿霉素诱导三阴性乳腺癌MDA-MB-468细胞耐药性产生中的作用,我们用Stat3磷酸化的抑制剂WP1066抑制Stat3活化,观察转录因子cMyc的表达是否受到影响。结果显示WP1066(1.25 μmol/L)作用于MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞后,磷酸化的Stat3显著降低(P=0.014),同时cMyc表达水平明显下降(P=0.044)。另外WP1066处理后MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞耐药蛋白ABCG2的表达也显著减少(P=0.000)。这些结果进一步说明阿霉素通过Stat3-cMyc途径诱导了MDA-MB-468细胞耐药性的产生,而抑制Stat3的活化后,耐药蛋白表达减少,细胞的耐药性减弱,见图 4。
2.5 抑制Stat3活化增强了MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞对阿霉素的敏感度
由于WP1066下调了耐药蛋白ABCG2的表达,因此我们进一步通过MTT法检测MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞对阿霉素敏感度的变化。结果显示,阿霉素对MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞的EC50为6.774 μmol/L,而在使用WP1066之后的EC50降低至1.29 μmol/L(P=0.000),这表明WP1066抑制Stat3的活化增强了MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞对阿霉素的敏感度,见图 5。
3 讨论
目前肿瘤细胞的耐药性是临床治疗的难点与研究的热点,阐明肿瘤耐药的机制可以为肿瘤的治疗提供新的治疗方向和靶点。
本研究应用低剂量阿霉素持续诱导人三阴性乳腺癌MDA-MB-468细胞,导致细胞产生耐药性,对阿霉素的敏感度显著下降,耐药蛋白ABCG2表达增高。为探究MDA-MB-468细胞对阿霉素产生耐药的机制,本实验进一步检测了MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞中转录因子p-stat3与cMyc的表达水平,观察MDA-MB-468细胞对阿霉素耐药性的产生与Stat3-cMyc途径有关。为进一步证明Stat3-cMyc途径在阿霉素诱导三阴性乳腺癌MDA-MB-468细胞耐药性产生中的作用,实验用Stat3磷酸化的抑制剂WP1066抑制Stat3活化,发现转录因子cMyc的表达也受到影响。进一步的机制研究揭示了Stat3-cMyc通路在阿霉素诱导的耐药中具有重要作用。
文献报道,Stat3信号通路与肿瘤细胞对化疗的耐药性有关[7]。Stat3的激活可以帮助癌细胞逃避由药物引起的死亡,从而诱发耐药性。Yue等[8]证明了Stat3的过度活化可以促进顺铂耐药的卵巢癌进展,相反,如果抑制Stat3信号通路则会促进耐药性癌细胞的凋亡,增加癌细胞对各种药物的敏感度。Li等[9]研究也有相似的发现,抑制Stat3信号通路后人胃癌细胞的凋亡增强,耐药性减弱。那么Stat3在三阴性乳腺癌耐药性的产生中有何作用?文献报道,乳腺癌组织中Stat3的活化增强与乳腺癌的临床分期和侵袭转移密切相关[10]。多种致癌性细胞因子与细胞膜的相应受体结合后导致Stat3与酪氨酸磷酸化通道相偶联后被激活,激活后的Stat3可在核内与特异性DNA启动子相结合,调节cMyc、Oct4、Sox2等相关基因表达[11]。作为调节多种转录因子功能的重要枢纽,Stat3有望成为肿瘤基因治疗中的有效靶点。有研究表明,在肿瘤中cMyc的表达水平与耐药性有关[4, 12-13],cMyc能够调控ABC转运蛋白的表达水平,而ABCG2与肿瘤细胞的耐药性直接相关,但Stat3/cMyc在三阴性乳腺癌产生耐药性方面的影响及机制却未见报道。
本研究发现低浓度(0.1 μmol/L)阿霉素持续刺激使MDA-MB-468细胞对阿霉素的敏感度明显降低,MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞中p-Stat3和cMyc的表达较MDA-MB-468细胞显著增加,这些发现与上述文献中对Stat3和cMyc在肿瘤耐药性中的作用相一致。另外,刘丽等[6]在喉鳞癌细胞的研究中也揭示了Stat3-cMyc通路的重要作用,与本研究的结果相吻合。由此推测,MDA-MB-468/ADM对阿霉素耐药的机制很可能与Stat3的激活和p-Stat3介导的cMyc表达的增多有关。为进一步证明Stat3-cMyc通路在阿霉素诱导的乳腺癌耐药性中的关键作用,本实验应用WP1066抑制MDA-MB-468/ADM中Stat3的活化,发现随着p-Stat3的降低,cMyc和ABCG2的表达也相应下降,这与Granato等[14]证实抑制Stat3信号可下调cMyc的表达一致。再次MTT检测发现WP1066作用后MDA-MB-468/ADM细胞对阿霉素的敏感度显著增强,这与Li等[9]研究结果一致。
总之,本实验结果表明阿霉素可以诱导Stat3活化,上调转录因子cMyc及耐药蛋白ABCG2的表达,促进了三阴性乳腺癌MDA-MB-468细胞对阿霉素耐药性的产生。因此,抑制Stat3的表达与活化可有效逆转乳腺癌对阿霉素的耐药性,特异性靶向Stat3-cMyc途径联合化疗药物治疗有望成为一种有效治疗乳腺癌的新措施,改善乳腺癌患者的预后。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。作者贡献:吴慧:实验设计与实施、数据分析、论文撰写及修改孙丽娜:数据收集、统计学分析及流式细胞检测潘璋驰:实验设计、临床数据筛选施纯玫:课题设计、数据审核及指导论文撰写 -
表 1 85例肝细胞癌患者T细胞活化与肿瘤负荷比与临床病理特征的关系
Table 1 Relationship between T-cell invigoration to tumour burden ratio and clinicopathological features in 85 cases of HCC

-
[1] Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
[2] Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(2): 115-132. doi: 10.3322/caac.21338
[3] Ma W, Gilligan BM, Yuan J, et al. Current status and perspectives in translational biomarker research for PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint blockade therapy[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2016, 9(1): 47. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0277-y
[4] Sharma P, Allison JP. The future of immune checkpoint therapy[J]. Science, 2015, 348(6230): 56-61. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa8172
[5] Liu Z, Meng X, Tang X, et al. Intratumoral tertiary lymphoid structures promote patient survival and immunotherapy response in head neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2023, 72(6): 1505-1521. doi: 10.1007/s00262-022-03310-5
[6] Dolina JS, Van Braeckel-Budimir N, Thomas GD, et al. CD8(+) T Cell Exhaustion in Cancer[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 715234. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.715234
[7] 沈仕俊, 王巧丽, 杨金江, 等. 肿瘤突变负荷对PD-1/PD-L1抑制剂治疗非小细胞肺癌临床疗效预测的Meta分析[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2021, 48(3): 281-287. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2021.20.0765 Shen SJ, Wang QL, Yang JJ, et al. Predictive Value of Tumor Mutation Burden for PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors Treatment on Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-analysis[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2021, 48(3): 281-287. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2021.20.0765
[8] 许晶, 金顺花. 循环肿瘤DNA在消化系统肿瘤中的应用进展[J]. 医学研究生学报, 2022, 35(8): 883-888. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLYB202208017.htm Xu J, Jin SH. Advances in the application of circulating tumor DNA in digestive system tumors[J]. Yi Xue Yan Jiu Sheng Xue Bao, 2022, 35(8): 883-888. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLYB202208017.htm
[9] 王亚东, 杨笑盈, 贾梓淇, 等. 循环肿瘤细胞PD-L1表达在非小细胞肺癌免疫治疗中的应用[J]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2021, 28(1): 110-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXYX202101021.htm Wang YD, Yang XY, Jia ZQ, et al. Clinical utility of PD-L1 expression in circulating tumor cells in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with immunotherapy[J]. Zhongguo Xiong Xin Xue Guan Wai Ke Lin Chuang Za Zhi, 2021, 28(1): 110-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXYX202101021.htm
[10] Pinter M, Jain RK, Duda DG. The Current Landscape of Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2021, 7(1): 113-123. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.3381
[11] Khagi Y, Goodman AM, Daniels GA, et al. Hypermutated Circulating Tumor DNA: Correlation with Response to Checkpoint Inhibitor-Based Immunotherapy[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2017, 23(19): 5729-5736. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1439
[12] Yue C, Jiang Y, Li P, et al. Dynamic change of PD-L1 expression on circulating tumor cells in advanced solid tumor patients undergoing PD-1 blockade therapy[J]. Oncoimmunology, 2018, 7(7): e1438111. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1438111
[13] Bullwinkel J, Baron-Lühr B, Lüdemann A, et al. Ki-67 protein is associated with ribosomal RNA transcription in quiescent and proliferating cells[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2006, 206(3): 624-635. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20494
[14] Blackburn SD, Shin H, Haining WN, et al. Coregulation of CD8+ T cell exhaustion by multiple inhibitory receptors during chronic viral infection[J]. Nat Immunol, 2009, 10(1): 29-37. doi: 10.1038/ni.1679
[15] Twyman-Saint Victor C, Rech AJ, Maity A, et al. Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer[J]. Nature, 2015, 520(7547): 373-377. doi: 10.1038/nature14292
[16] Marei HE, Hasan A, Pozzoli G, et al. Cancer immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs): potential, mechanisms of resistance, and strategies for reinvigorating T cell responsiveness when resistance is acquired[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2023, 23(1): 64. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02902-0
[17] Kim KH, Cho J, Ku BM, et al. The First-week Proliferative Response of Peripheral Blood PD-1+CD8+ T Cells Predicts the Response to Anti-PD-1 Therapy in Solid Tumors[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 25(7): 2144-2154. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1449
[18] Sharma P, Allison JP. Immune checkpoint targeting in cancer therapy: toward combination strategies with curative potential[J]. Cell, 2015, 161(2): 205-214. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.030
[19] Hack SP, Zhu AX, Wang Y. Augmenting Anticancer Immunity Through Combined Targeting of Angiogenic and PD-1/PD-L1 Pathways: Challenges and Opportunities[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 598877. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.598877
[20] Wang W, Green M, Choi JE, et al. CD8(+) T cells regulate tumour ferroptosis during cancer immunotherapy[J]. Nature, 2019, 569(7755): 270-274. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1170-y
[21] Yi L, Huang P, Zou X, et al. Integrative stemness characteristics associated with prognosis and the immune microenvironment in esophageal cancer[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2020, 161: 105144. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105144
[22] Guo W, Tan F, Huai Q, et al. Comprehensive Analysis of PD-L1 Expression, Immune Infiltrates, and m6A RNA Methylation Regulators in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 669750. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.669750
[23] Chi H, Zhao S, Yang J, et al. T-cell exhaustion signatures characterize the immune landscape and predict HCC prognosis via integrating single-cell RNA-seq and bulk RNA-sequencing[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1137025. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1137025
[24] Huang AC, Postow MA, Orlowski RJ, et al. T-cell invigoration to tumour burden ratio associated with anti-PD-1 response[J]. Nature, 2017, 545(7652): 60-65. doi: 10.1038/nature22079
[25] Bengsch B, Seigel B, Ruhl M, et al. Coexpression of PD-1, 2B4, CD160 and KLRG1 on exhausted HCV-specific CD8+ T cells is linked to antigen recognition and T cell differentiation[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2010, 6(6): e1000947. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000947




 下载:
下载: