Effects of Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation from Haploidentical Versus Matched Sibling Donors on High-risk and Refractory/Relapsed Acute Myeloid Leukemia
-
摘要:目的
探讨单倍体相合与同胞全相合外周血造血干细胞移植治疗高危及难治/复发急性髓系白血病(AML)患者的临床疗效。
方法回顾性分析2010年1月1日至2020年6月30日在我中心行清髓预处理单倍体相合外周血造血干细胞移植(Haplo-HSCT)治疗高危及难治/复发AML的疗效,并与同期行同胞全相合外周血造血干细胞移植(MSD-HSCT)的结果进行比较。
结果共纳入98例患者,其中Haplo-HSCT组62例,MSD-HSCT组36例,两组患者中位年龄、预处理方案、MNC及CD34+细胞输注剂量差异具有统计学意义,其余基线指标差异均无统计学意义。Haplo-HSCT组与MSD-HSCT组急性及慢性移植物抗宿主病(GVHD)发生率比较差异均无统计学意义。移植后相关感染并发症两组相比差异均无统计学意义。Haplo-HSCT组的3年累积复发率显著低于MSD-HSCT组(16.2% vs. 41.1%, P=0.036);Haplo-HSCT组、MSD-HSCT组3年DFS分别为66.98%和41.8%,两组差异无统计学意义(P=0.140);Haplo-HSCT组、MSD-HSCT组OS分别为73.37%和51.41%,两组差异无统计学意义(P=0.105)。
结论采用Haplo-HSCT治疗高危及难治/复发AML患者的临床疗效与MSD-HSCT相似,并且Haplo-HSCT可能有更好的GVL效应。
-
关键词:
- 外周血造血干细胞移植 /
- 急性髓系白血病 /
- 高危 /
- 难治性 /
- 复发性
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the clinical efficacy of peripheral blood stem cell transplantation from haploidentical and matched sibling donors for treatment of high-risk and refractory/relapsed acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
MethodsData on the efficacy of haploidentical peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (Haplo-HSCT) with myeloablative conditioning regimen were retrospectively analyzed and compared with that of matched sibling donors' peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (MSD-HSCT) for treatment of high-risk refractory/relapsed AML in our center from January 1st, 2010 to June 30th, 2020.
ResultsA total of 98 patients were enrolled, including 62 patients in the Haplo-HSCT group and 36 patients in MSD-HSCT group. The median age, conditioning regimen, and infusion doses of MNC and CD34+ cells were significantly different between the two groups, but no significant differences in other baseline parameters were found. Transplantation-related infectious complications and the incidence of acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) were also not significantly different between the two groups. The 3-year cumulative relapse in the Haplo-HSCT group was significantly lower than that in the MSD-HSCT group (16.2% vs. 41.1%, P=0.036). The 3-year DFS of the Haplo-HSCT and MSD-HSCT groups were 66.98% and 41.8%, respectively (P=0.140), and their OS were 73.37% and 51.41%, respectively (P=0.105).
ConclusionThe clinical efficacy of Haplo-HSCT for the treatment of high-risk and refractory/relapsed AML is similar to that of MSD-HSCT, and Haplo-HSCT may have better GVL effect.
-
Key words:
- Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation /
- Acute myeloid leukemia /
- High-risk /
- Refractory /
- Relapsed
-
0 引言
对于高危、难治或复发性急性髓系白血病(acute myeloid leukemia, AML)患者来说,异基因造血干细胞移植(allo-HSCT)可能是唯一具有治愈潜力的治疗选择[1]。尽管人类白细胞抗原(human leukocyte antigen, HLA)匹配同胞全相合供者(matched sibling donor, MSD)allo-HSCT是首选,但仅有约30%患者能够找到合适供者[2]。对于缺乏HLA匹配的患者,绝大多数都可以找到单倍体相合供者,并且单倍体相合造血干细胞移植(Haplo-HSCT)已成为广泛接受的替代方案[3]。研究表明,与MSD-HSCT相比,Haplo-HSCT能够取得相似的临床疗效[4-6]。然而,单纯外周血造血干细胞(peripheral blood stem cell, PBSC)作为移植物行Haplo-HSCT对高危及难治/复发AML患者的疗效仍不清楚。因此,本研究评估我中心以高剂量非体外去T细胞PBSC作为移植物,行Haplo-HSCT治疗高危及难治/复发AML患者的临床疗效,并与同一时期实施MSD-HSCT的结果进行比较。
1 资料与方法
1.1 病例资料
回顾性分析2010年1月至2020年6月在新疆医科大学第一附属医院血液病中心进行造血干细胞移植的成人高危及难治/复发AML患者(≥18岁)资料。患者的诊断依据为2016版WHO造血和淋巴组织肿瘤的分型诊断标准[7],高危定义如下:伴有预后差的染色体核型或分子遗传学标志;高白细胞计数 > 50×109/L;前驱血液病史;合并中枢神经系统白血病(central nervous system leukemia, CNSL)。难治、复发AML的诊断标准依据中华医学会血液学分会制定的诊断标准[8]。所有供者、患者均签署知情同意书。
1.2 造血干细胞动员与采集
移植物均为非体外去T细胞PBSC,采用重组人粒细胞集落刺激因子(rhG-CSF)7~10 μg/(kg.d)皮下注射动员PBSC,于动员的第5、6天采集,体重过低的供者于动员第4~6天采集(供受者体重差 < 10 kg)或提前冻存干细胞(供受者体重差≥10 kg)。
1.3 预处理方案
试验分为两组:Haplo-HSCT组采用阿糖胞苷(Ara-C)+白消安(Bu)+环磷酰胺(Cy)+抗胸腺细胞球蛋白(ATG)[9],MSD-HSCT组采用ABu/Cy或者ABu/Cy+ATG或者Bu/Cy+ATG方案。两组患者均采用清髓性预处理方案。
1.4 移植物抗宿主病(GVHD)预处理方案
两组患者均采用环孢素(CsA)或他克莫司(Tac)+甲氨蝶呤(MTX)+霉酚酸酯(MMF)作为基础预防方案:CsA:移植前5天至移植后30天2.5 mg/(kg.d)静脉滴注,30天后改为(4~5)mg/(kg.d)口服,或者Tac 0.02 mg/(kg.d)静脉滴注,移植30天后改为0.1 mg/(kg.d)口服,根据血药浓度调整;MTX:移植后第1天15 mg/(m2.d)静脉滴注,移植后第3天、第6天改为10 mg/(m2.d)静脉滴注;MMF:移植前1天至移植后100天1.0 g/d口服;地塞米松(Glu):移植后1天至移植后15天5 mg/d静脉滴注,之后逐渐减量,MSD组在移植后30天停用,Haplo-HSCT组用至移植后100天。Haplo-HSCT组在上述基础上加用抗CD25单克隆抗体(舒莱)移植当天及移植后第2天12 mg/m2静脉滴注。
1.5 评估标准及指标
动态监测血常规,连续3天中性粒细胞计数绝对值(ANC)≥0.5×109/L为粒系植入时间;不输注血小板情况下血小板计数(PLT)连续7天≥20×109/L为巨核系植入时间。GVHD分级及诊断根据西雅图国际标准进行评分及分级。总生存(OS)为移植后至任何原因导致的死亡时间或随访截止时间。无病生存(DFS)为移植后至随访截止或者复发/死亡时间。
1.6 随访
随访资料来自电话随访、住院/门诊病历。随访截至2021年12月30日。
1.7 统计学方法
采用SPSS25.0和GraphPad Prism 5.0软件进行数据分析。计数和计量资料用频率和中位数等进行描述统计。组间资料比较采用卡方检验或t检验。急性和慢性GVHD、DFS以及OS等采用Kaplan-Meier进行描述和分析。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 患者基本临床特征
本研究共纳入98例患者,其中Haplo-HSCT组62例,MSD-HSCT组36例。两组中位年龄、预处理方案、MNC及CD34+细胞输注剂量差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05),其他临床指标差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05),见表 1。
表 1 98例高危及难治/复发急性髓系白血病患者的临床特征Table 1 Clinical characteristics of 98 patients with high-risk and refractory/relapsed acute myeloid leukemia
2.2 造血重建
本研究中共有4例患者植入失败,均发生在Haplo-HSCT组,两组植入率比较差异无统计学意义(93.5% vs. 100%, P=0.120)。Haplo-HSCT组、MSD-HSCT组中性粒细胞恢复中位时间分别为16(10~21)d和15.5(11~18)d(P=0.452),血小板恢复中位时间分别为15(13~20)d和16(13~22)d(P=0.231),差异均无统计学意义。
2.3 GVHD发生情况
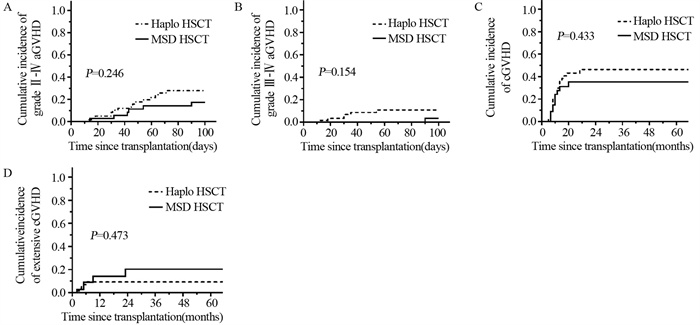
100天内Haplo-HSCT组、MSD-HSCT组Ⅱ~Ⅳ度急性移植物抗宿主病(acute graft- versus-host disease, aGVHD)的发生率分别为27.89%(95%CI: 15.76~40.02)和17.19%(95%CI: 4.65~29.73),两组比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.246),见图 1A。Haplo-HSCT组、MSD-HSCT组Ⅲ~Ⅳ度aGVHD的发生率分别为10.96%(95%CI: 2.60~19.11)和3.45%(95%CI: 0~10.19),两组比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.154),见图 1B。
Haplo-HSCT组、MSD-HSCT组慢性移植物抗宿主病(chronic graft- versus-host disease, cGVHD)的3年累积发生率分别为46.31%(95%CI: 31.86~60.76)和35.16%(95%CI: 18.13~52.19),两组相比差异无统计学意义(P=0.433),见图 1C。Haplo-HSCT组、MSD-HSCT组广泛型cGVHD的3年累积发生率分别为9.15%(95%CI: 1.43~16.87)和20.24%(95%CI: 3.29~37.19),两组比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.473),见图 1D。
2.4 复发情况
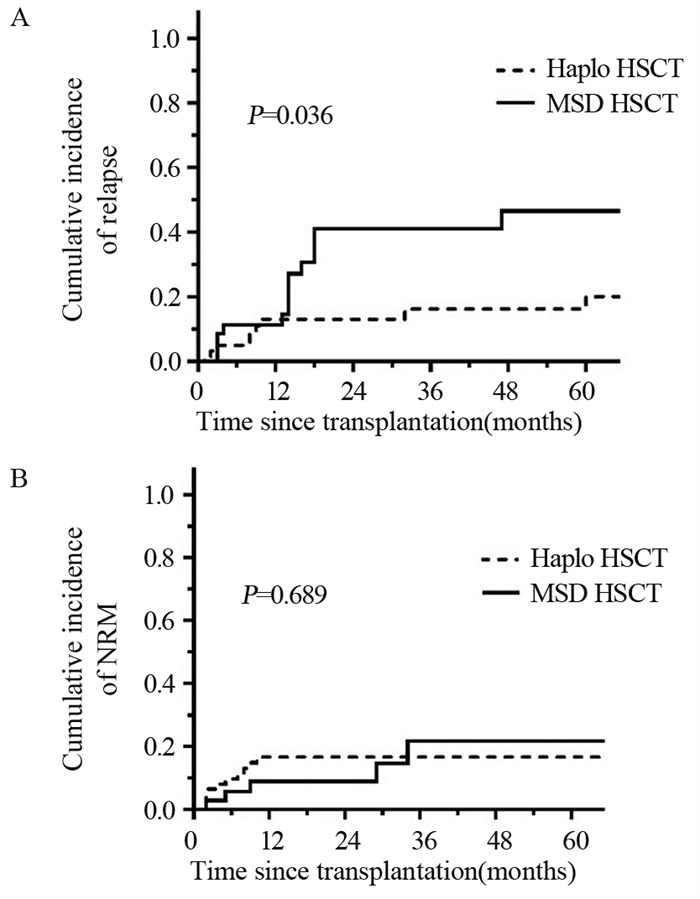
随访期间,Haplo-HSCT组有10例患者复发,其中2例为髓外复发,复发部位分别为淋巴结和中枢神经系统,余8例为骨髓复发。MSD-HSCT组有14例患者复发,其中3例为髓外复发,复发部位分别为腮腺、肝脏和中枢神经系统,余11例为骨髓复发。两组患者3年累积复发率分别为16.2%(95%CI: 5.42~26.98)和41.1%(95%CI: 23.66~58.54),两组相比差异有统计学意义(P=0.036),见图 2A。两组患者3年非复发死亡率(NRM)分别为16.61%(95%CI: 7.18~26.04)和21.71%(95%CI: 3.13~40.29),两组相比差异无统计学意义(P=0.689),见图 2B。
2.5 移植后并发症
本研究中主要并发症为移植后感染,多为细菌和(或)真菌感染,两组相比差异无统计学意义(P=0.129)。28例患者发生出血性膀胱炎,其中Haplo-HSCT组22例、MSD-HSCT组6例,两组相比差异无统计学意义(P=0.063)。两组患者发生间质性肺炎、带状疱疹和CMV血症的差异均无统计学意义,见表 2。
表 2 高危及难治/复发的AML患者移植后并发症Table 2 Post-transplantation complications in patients with high-risk and refractory/relapsed acute myeloid leukemia
2.6 生存分析及影响生存的因素
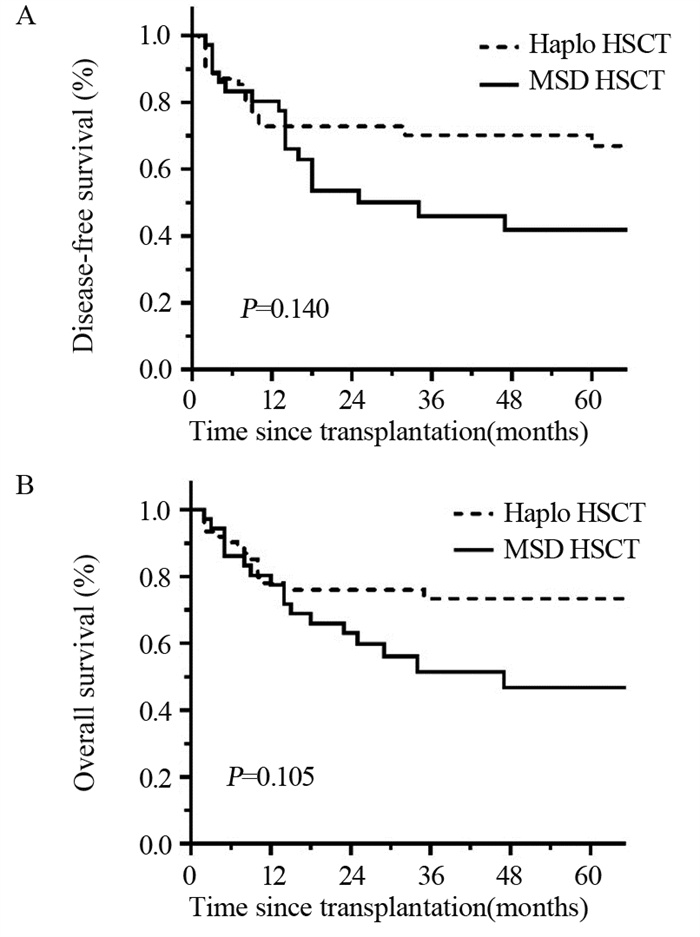
本研究中位随访时间为27(2~119)月。Haplo-HSCT组有17例患者死亡,5人死于复发,8人死于感染,3人死于植入失败,1人死于呼吸循环衰竭。MSD-HSCT组有17例患者死亡,其中9人死于复发,4人死于感染,4人死于脑出血。Haplo-HSCT组、MSD-HSCT组3年DFS率分别为66.98(95%CI: 53.87~80.09)和41.8%(95%CI: 24.1~59.5),两组相比差异无统计学意义(P=0.140),见图 3A。Haplo-HSCT组、MSD-HSCT组3年OS率分别为73.37%(95%CI 61.55~85.19)和51.41%(95%CI: 33.59~69.23),两组相比差异无统计学意义(P=0.105),见图 3B。对可能影响患者预后的因素如患者年龄、供者年龄、供-受者性别匹配、是否发生aGVHD、是否发生cGVHD、输注MNC剂量、输注CD34+细胞剂量等进行多因素Cox回归分析,未发现影响患者生存的独立危险因素,见表 3。
表 3 98例患者DFS和OS影响因素的多因素分析Table 3 Multivariate analysis of risk factors related to DFS and OS of 98 patients
3 讨论
AML是成人最常见的恶性血液病,尽管目前对初诊患者诱导化疗后完全缓解(CR)率可达60%~80%,但对高危以及复发/难治AML患者的疗效仍欠佳[10]。Allo-HSCT是AML患者的最佳潜在治疗方法,尤其是细胞遗传学不良且单独化疗预后非常差的患者[11]。因此,选择合适的移植方式对患者的治疗策略至关重要。
最近,Haplo-HSCT的数量逐渐增加,并取得了不错的效果。越来越多的研究表明,对于AML患者接受Haplo-HSCT与MSD-HSCT疗效相当[12-14]。然而,对于Haplo-HSCT在治疗复发/难治性AML中是否存在与MSD-HSCT同等的疗效,目前相关报道较少。来自欧洲血液和骨髓移植学会(EBMT)的一项研究表明,在中度或高风险细胞遗传学首次完全缓解的AML患者中,Haplo-HSCT与MSD-HSCT的疗效相似[11]。本研究中也取得了类似结果,Haplo-HSCT与MSD-HSCT在植入、GVHD、DFS及OS方面的差异无统计学意义。然而,最近一项研究通过比较Haplo-HSCT与MSD在复发/难治性AML患者的预后发现Haplo-HSCT后OS、DFS较低,NRM较高,导致患者预后较差[15]。不同研究中心取得不同的结果可能与患者类型及移植体系有关。
Haplo-HSCT因供受体之间的HLA差异引起双向免疫屏障,导致发生原发性移植失败的倾向更高。本研究中,Haplo-HSCT组均输注高剂量非体外去T细胞PBSC作为移植物,以克服免疫屏障,促进持续稳定的植入。但是随着输注剂量的增加,GVHD的发生风险也随之增加。我们在经典的GVHD预防方案中添加了抗CD25单克隆抗体(舒莱)及短程低剂量的糖皮质激素以加强GVHD预防。由此,形成本血液病中心独特的移植体系-高剂量非体外去T细胞PBSC作为移植物联合强化的GVHD预防方案。抗CD25单克隆抗体能够抑制同种抗原诱导的T细胞增殖以及抗原特异性细胞毒性T细胞的生成,降低GVHD的发生[16]。Chang等[17]研究表明低剂量糖皮质激素能够显著降低aGVHD的发生率,并在不增加感染的情况下减少不良事件的发生。本研究结果表明,两组间GVHD的发生率比较差异无统计学意义,但是Haplo-HSCT广泛型cGVHD发生率有降低的趋势(9.15% vs. 20.24%, P=0.473),考虑可能与我们强化的GVHD预防方案有关。两组患者移植后并发症的比较未发现显著性差异,提示强化的GVHD预防方案并未增加感染的风险。
近年来,越来越多的研究显示Haplo-HSCT治疗恶性血液病较MSD-HSCT具有更强的移植物抗白血病(GVL)作用。Yu等[18]通过前瞻性多中心的研究表明,Haplo-HSCT治疗首次完全缓解的高风险AML与MSD-HSCT相比复发率更低,提示Haplo-HSCT可能存在更强的GVL效应。本研究中也得到了一致结果,Haplo-HSCT组3年累积复发率显著低于MSD-HSCT组。Guo等[19]通过动物模型发现Haplo-HSCT存在更强GVL作用,是因为自然杀伤(NK)细胞凋亡减少和细胞毒性细胞因子分泌增加。此外,从理论上来看,Haplo-HSCT存在更强GVL效应可通过降低NRM从而提高存活率[20]。本研究中两组的生存情况并无差异,多因素分析也并未发现影响患者预后的危险因素,这可能与样本量较少有关。
总之,本研究初步表明对高危以及复发/难治AML患者接受Haplo-HSCT与MSD-HSCT疗效相似,且haplo-HSCT的复发率更低,可能存在更强的GVL效应。但本研究为回顾性研究且病例数较少,后期仍需要进行前瞻性大样本研究进一步证实此结论。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。作者贡献:苗文艳、蔺思颖:数据收集、文章撰写及修改徐建丽、王洪波:研究设计、文章写作指导及修改江明:实验设计、写作指导 -
表 1 98例高危及难治/复发急性髓系白血病患者的临床特征
Table 1 Clinical characteristics of 98 patients with high-risk and refractory/relapsed acute myeloid leukemia

表 2 高危及难治/复发的AML患者移植后并发症
Table 2 Post-transplantation complications in patients with high-risk and refractory/relapsed acute myeloid leukemia

表 3 98例患者DFS和OS影响因素的多因素分析
Table 3 Multivariate analysis of risk factors related to DFS and OS of 98 patients

-
[1] Yan CH, Wang Y, Sun YQ, et al. Optimized therapeutic strategy for patients with refractory or relapsed acute myeloid leukemia: long-term clinical outcomes and health-related quality of life assessment[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2022, 42(12): 1387-1402. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12376
[2] Gragert L, Eapen M, Williams E, et al. HLA match likelihoods for hematopoietic stem-cell grafts in the U.S. registry[J]. N Engl J Med, 2014, 371(4): 339-348. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1311707
[3] Passweg JR, Baldomero H, Bader P, et al. Use of haploidentical stem cell transplantation continues to increase: the 2015 European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplant activity survey report [J]. Bone Marrow Transplant, 2017, 52(6): 811-817. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2017.34
[4] Sanz J, Galimard JE, Labopin M, et al. Post-transplant cyclophosphamide containing regimens after matched sibling, matched unrelated and haploidentical donor transplants in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first complete remission, a comparative study of the ALWP of the EBMT[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2021, 14(1): 84. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01094-2
[5] Nagler A, Labopin M, Houhou M, et al. Outcome of haploidentical versus matched sibling donors in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a study from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2021, 14(1): 53. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01065-7
[6] Chang YJ, Wang Y, Xu LP, et al. Haploidentical donor is preferred over matched sibling donor for pre-transplantation MRD positive ALL: a phase 3 genetically randomized study[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2020, 13(1): 27. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00860-y
[7] Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia [J]. Blood, 2016, 127(20): 2391-2405. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-03-643544
[8] 中华医学会血液学分会. 急性髓系白血病(复发难治性)中国诊疗指南(2011年版)[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2011, 32(12): 887-888. Hematology Branch of Chinese Medical Association. China Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (Recurrent and Refractory) (2011 Edition)[J]. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi, 2011, 32(12): 887-888.
[9] Duan XL, Pang NN, Xu JL, et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors for acute graft-versus-host disease in related HLA-haploidentical without ex vivo T cell depletion peripheral blood HSCT[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2019, 12(5): 5249-5258.
[10] DeWolf S, Tallman MS. How I treat relapsed or refractory AML[J]. Blood, 2020, 136(9): 1023-1032. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019001982
[11] Salvatore D, Labopin M, Ruggeri A, et al. Outcomes of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from unmanipulated haploidentical versus matched sibling donor in patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission with intermediate or high-risk cytogenetics: a study from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation[J]. Haematologica, 2018, 103(8): 1317-1328. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.189258
[12] Rashidi A, Hamadani M, Zhang MJ, et al. Outcomes of haploidentical vs. matched sibling transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission[J]. Blood Adv, 2019, 3(12): 1826-1836. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000050
[13] Wang Y, Liu QF, Xu LP, et al. Haploidentical vs. identical-sibling transplant for AML in remission: a multicenter, prospective study[J]. Blood, 2015, 125(25): 3956-3962. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-02-627786
[14] Versluis J, Labopin M, Ruggeri A, et al. Alternative donors for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in poor-risk AML in CR1[J]. Blood Adv, 2017, 1(7): 477-485. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2016002386
[15] Battipaglia G, Boumendil A, Labopin M, et al. Unmanipulated haploidentical versus HLA-matched sibling allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia: a retrospective study on behalf of the ALWP of the EBMT[J]. Bone Marrow Transplant, 2019, 54(9): 1499-1510. doi: 10.1038/s41409-019-0459-7
[16] Mo XD, Hong SD, Zhao YL, et al. Basiliximab for steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: A real-world analysis[J]. Am J Hematol, 2022, 97(4): 458-469. doi: 10.1002/ajh.26475
[17] Chang YJ, Xu LP, Wang Y, et al. Controlled, Randomized, Open-Label Trial of Risk-Stratified Corticosteroid Prevention of Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease After Haploidentical Transplantation[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2016, 34(16): 1855-1863. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.63.8817
[18] Yu S, Huang F, Wang Y, et al. Haploidentical transplantation might have superior graft-versus-leukemia effect than HLA-matched sibling transplantation for high-risk acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission: a prospective multicentre cohort study[J]. Leukemia, 2020, 34(5): 1433-1443. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0686-3
[19] Guo H, Chang YJ, Hong Y, et al. Dynamic immune profiling identifies the stronger graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) effects with haploidentical allografts compared to HLA-matched stem cell transplantation[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2021, 18(5): 1172-1185. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-00597-1
[20] Chang YJ, Huang XJ. Is human leukocyte antigen-matched sibling donor transplant always better than haploidentical allograft?[J]. Semin Hematol, 2019, 56(3): 201-208. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2018.07.005
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: