Effects of Amarogentin on Residual Liver Cancer Stem Cells After Insufficient Thermal Ablation and Related Mechanism
-
摘要:目的
探讨苦龙胆酯苷(Amarogentin)在热消融不全的残存肝癌细胞对肝癌干细胞的影响及其作用机制。
方法水浴法建立HepG2肝癌细胞热消融不全的残存模型, 流式细胞术检测细胞中CD133阳性细胞比例, qRT-PCR和Western blot法检测肝癌细胞中CD133的mRNA和蛋白的表达水平。分别用低、中和高剂量的苦龙胆酯苷处理上述HepG2细胞24 h后, 流式细胞术分别检测细胞中CD133阳性肝癌细胞比例、肝癌细胞的增殖率和凋亡率, qRT-PCR和蛋白印记法检测肝癌细胞中CD133、TBC1D15和p53的mRNA和蛋白的表达水平。
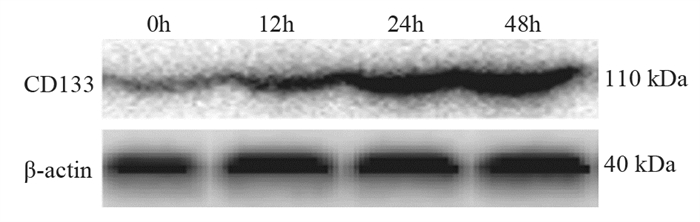
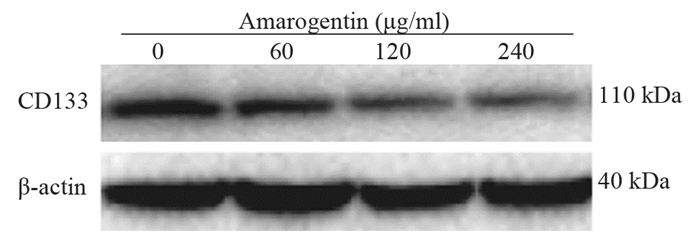
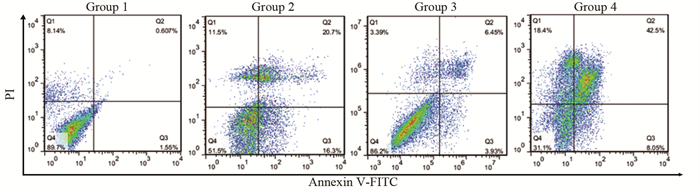
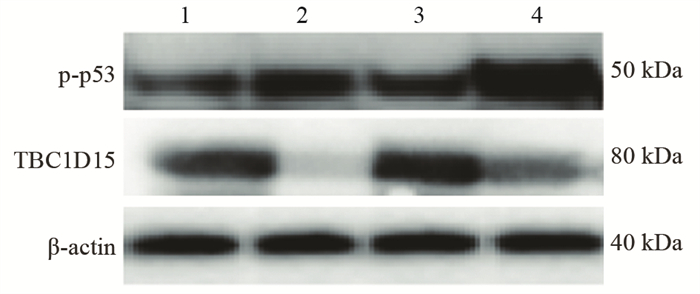
结果随培养时间的延长, 热消融不全的残存肝癌细胞中CD133阳性细胞比例、CD133和TBC1D15 mRNA和蛋白的表达水平显著提高, 而p53磷酸化水平显著下降。苦龙胆酯苷处理后, 热消融不全的残存肝癌细胞中CD133阳性细胞比例、细胞增殖率以及肿瘤干细胞相关分子CD133和TBC1D15的mRNA和蛋白表达水平显著降低(均P < 0.05);凋亡率和p53磷酸化水平提高(均P < 0.05)。
结论苦龙胆酯苷可降低热消融不全的残存肝癌干细胞的比例和肿瘤细胞的增殖, 促进细胞的凋亡, 这可能与其提高肝癌干细胞p53磷酸化和抑制TBC1D15蛋白相关。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo observe the effects of amarogentinon liver cancer stem cells (LCSCs) after insufficient thermal ablation and its mechanism.
MethodsA insufficient thermal ablation model of HepG2 cells was established by water bath method.The percentage of CD133-positive LCSCs and the mRNA and protein levels of CD133 were detected by flow cytometry, qRT-PCR and Western blot.The insufficient thermal ablation model of HepG2 cells was treated with variable doses of amarogentin for 24 h; the percentage of CD133-positive LCSCs, the proliferation and apoptosis of liver cancer cells, and the mRNA and protein levels of CD133, TBC1D15, and p53were detected by flow cytometry, qRT-PCR and Western blot.
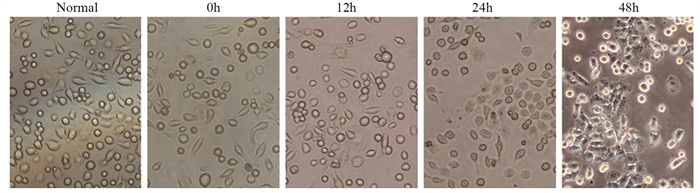
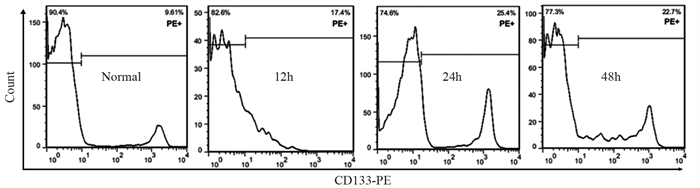
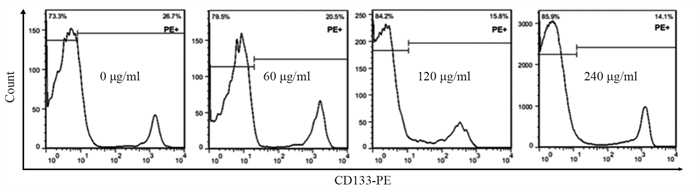
ResultsThe percentage of CD133-positive HepG2 cells and the mRNA and protein levels of CD133 and TBC1D15in the insufficient thermal ablation model were significantly higher than those in the normal HepG2 cells.Amarogentin then markedly decreased the percentage of CD133-positive LCSCs, the proliferation rate of HepG2 cells, and the mRNA and protein levels of CD133 and TBC1D15 in the insufficient thermal ablationresidual model (all P < 0.05);inversely, the apoptosis rate of HepG2 cells and the phosphorylated levels of p53 in the insufficient thermal ablation model were significantly increased (all P < 0.05).
ConclusionAmarogentin could reduce the proportion of LCSCs after insufficient thermal ablation, inhibit the proliferation, and promote the apoptosis of LCSCs, which maybe associated with increasing the phosphorylation of p53 and inhibiting the expression of TBC1D15.
-
Key words:
- Amarogentin /
- Insufficient thermal ablation /
- Liver cancer stem cells /
- TBC1D15 /
- p53
-
0 引言
目前肿瘤患者静脉化疗采用输液港的方式已经被广泛采用,经锁骨下静脉植入输液港较经其他静脉植入的血栓风险更低[1]。在穿刺手法上,通常使用盲穿或超声实时引导技术,由于目前部分地区尚无条件引入超声引导,盲穿成为无法避免的选择,超声实时引导的技术正在逐步普及参与输液港植入的操作。本研究采用较新的改良型锁骨下静脉穿刺方式与超声实时引导穿刺方式植入输液港,比较两者成功率、气胸、动脉损伤、导管异位、局部血肿、夹闭综合征等的差异,为提高锁骨下静脉穿刺的成功率及降低相关并发症提供实际的数据支持。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究设计与对象
本研究为随机、对照临床研究,入组标准:18岁以上肿瘤患者;体力状态评估(ECOG 0~4)。主要排除标准:穿刺部位有感染;穿刺部位及穿刺路径上有明显占位;严重的心肺功能衰竭患者;不能平卧的患者。
试验对象为我院2019年9月—2021年5月行输液港植入术的260例患者,随机数表法分为超声引导组和技术改良组各130例。两组年龄、性别、身高、体重、体重指数(body mass index, BMI)差异无明显统计学差异,见表 1。
表 1 超声引导组和技术改良组患者一般情况(x±s)Table 1 General conditions of ultrasound-guided and technique modified groups (x±s)
1.2 输液港穿刺方式
采用美国巴德公司的8806061输液港或法国贝鲁斯医疗集团公司的3017ISP输液港,Philips超声仪及高频探头,穿刺部位均为右侧锁骨下静脉,头位靠近右肩,脸面转向左侧。
1.2.1 超声引导法
消毒、铺无菌单后,在探头上覆盖无菌套,将探头置于右侧锁骨下方约1 cm的胸部外侧部分,使超声探头与锁骨下静脉的长轴成约90°角,将穿刺针沿探头长轴的中间插入,缓慢使针尖与锁骨下静脉横截面接近[2]。穿刺针在超声上显示为高回声亮点,而静脉及动脉分别显示为边界明显的低回声椭圆形和圆形结构。在超声引导下小心地推进穿刺针,穿刺针刺破静脉前壁时在注射器中抽出静脉血,然后按Seldinger的导管插入技术[3]完成操作,见图 1。
1.2.2 技术改良法
取右侧锁骨下缘中点向下1 cm向外1 cm处为穿刺点,针尖大约指向同侧锁骨上缘与胸锁乳突肌胸骨支外缘所成角的平分线上1 cm处,穿刺针于紧贴锁骨下进针,大约3~5 cm可进入锁骨下静脉,在抽出静脉血后根据Seldinger的技术[3]完成操作,见图 2。
1.3 评估项目
1.3.1 成功率
导管顺利植入静脉,抽到静脉血,并拍摄胸部X线片明确导管已进入静脉系统即为穿刺成功。
1.3.2 气胸
所有患者术后均行胸部X线片检查,片中提示术后出现无肺纹理的肺野为气胸。
1.3.3 动脉损伤
穿刺中抽出动脉血。
1.3.4 导管异位
导管未向上腔静脉方向行进,误入颈内静脉或其他静脉等。
1.3.5 局部血肿
穿刺后因渗血局部出现肿胀。
1.3.6 夹闭综合征
出现锁骨下不适或疼痛,输液速度受体位影响,或输液不畅,胸片可提示为锁骨下导管受压变形。
1.3.7 其他严重并发症
动静脉瘘、恶性心律失常、心力衰竭等。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS23.0统计软件进行数据分析,入组患者的基本资料符合近似正态分布规律,通过单因素方差分析,判断其一致性,P≥0.05为两组基本资料差异无统计学意义,计数资料使用χ2检验,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 超声引导组和技术改良组穿刺成功率比较
超声引导组130例患者,穿刺成功率为100%;其中一针穿刺成功的患者126例(96.92%)。4例患者经二次穿刺全部成功。技术改良组127例患者穿刺成功,穿刺成功率为97.69%(127/130);其中一针穿刺成功的患者112例(86.15%)。8例二次穿刺成功,分别于三次、四次和五次穿刺成功的患者各2例,1例在第八次穿刺成功,3例患者在多次穿刺后未能完成右侧锁骨下静脉下路的穿刺,分别改为右侧颈内后路、右侧锁骨下静脉上路和左侧静脉中路后穿刺后完成穿刺,见表 2。
表 2 超声引导法和技术改良法成功率比较(n(%))Table 2 Comparison of success rate between ultrasound-guided and technique modified methods (n(%))
上述结果显示:超声引导组的成功率优于技术改良组(100% vs. 97.69%),但差异无统计学意义(P=0.081),超声引导组的一针穿刺成功率优于技术改良组(96.92% vs. 86.15%),差异有统计学意义(P=0.002)。
2.2 超声引导组和技术改良组穿刺并发症发生率比较
两组均未出现动静脉瘘及夹闭综合征,技术改良组发生气胸5例、误伤动脉4例,与超声引导组比较,差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05),发生气胸的患者予静卧吸氧后恢复,出现误伤动脉时立即予局部妥善按压。技术改良组发生血肿1例、导管异位2例,与超声引导组比较,差异无统计学意义(均P > 0.05),技术改良组出现导管异位后,予导丝重新引导后纠正易位,并复查胸X线片提示导管位置纠正,见图 3;超声引导组在术中可及时发现导管异位,并马上纠正。超声引导组未出现相关并发症,技术改良组总的并发症发生12例(9.23%),两组比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001),见表 3。
表 3 超声引导法和技术改良法并发症比较(n(%))Table 3 Comparison of complications between ultrasound-guided and technique modified methods (n(%))
在分析技术改良组气胸与患者的摆位相关性中,发现摆位配合差的患者(含胸)出现气胸的风险(66.67%, 2/3)高于摆位配合好的患者(2.36%, 3/127),提示摆位和气胸的发生存在相关性(χ2=32.770, P=0.000)。所有发生气胸的患者均出现在12月份~次年3月份,在这段时间穿刺的55例患者中有5例(9.09%)出现气胸,在4月份~11月份的75例患者中未出现气胸,提示出现气胸可能与季节相关(χ2=7.091, P=0.008)。
3 讨论
在肿瘤患者的输液港植入术中,目前有深静脉穿刺及静脉切开两种方案,静脉切开技术要求清晰地暴露相关血管,技术要求高,耗时长,静脉穿刺相对来说普及性较广,但难以避免穿刺失败及相关并发症的发生[4],其成功率、并发症发生与患者的血管直径、摆位配合程度、有无血管畸形、患者年龄[5]、医生的熟练程度[6]及其他因素[7]相关,参与本次试验的医生均有行两种穿刺技术150例以上的经验,但仍无法避免穿刺失败及并发症的发生。反复穿刺失败的患者可能是血管畸形等因素造成,应及时更改穿刺部位,如安全性更好的颈内静脉、通过上路的锁骨下静脉穿刺,保证顺利完成手术。考虑大多肿瘤患者行输液港植入术是为了便于化疗及长期支持治疗,术前大多已经进行过CT检查,可根据CT术前评估血管情况,选择条件较好的血管穿刺,并及时发现血管变异的情况,这样可提高穿刺成功率。技术改良方法穿刺的成功率仍能部分满足目前的需要,但其存在并发症需要重视。对于有超声实时引导条件的,选择超声实时引导穿刺,可避免绝大多数并发症,并可以发现部分导管异位,减少患者再次手术的痛苦。穿刺术后胸部X线片检查是必要的[8],能及时发现气胸等并发症,并减少出现严重并发症的风险[9],对于发生气胸的患者,及时卧床吸氧及相关治疗可以避免出现呼吸衰竭,并减少闭式引流治疗的痛苦。穿刺术中出现误伤动脉,及时行充足时间的局部按压可降低出现血肿的风险,并缩小血肿的大小,提高局部穿刺的成功率。本研究两组穿刺方法均未出现动静脉瘘及夹闭综合征,故认为上述穿刺方法在动静脉瘘及夹闭综合征上是安全的。亚组分析提示含胸体位的患者行改良方式的穿刺更容易出现气胸,建议行其他方式穿刺以减少气胸风险。在季节上,12月份到次年3月份行改良方式的穿刺气胸风险更大,可能与低气温下的静脉血流减少及肌肉相对僵硬相关,同样建议在这段时间内行其他方式的穿刺以减少气胸风险。
随着超声引导穿刺技术的普及,传统的深静脉穿刺技术在临床中的使用将逐步被取代。而在缺乏超声支持的条件下,传统的深静脉穿刺技术需针对患者的具体情况选择合适的穿刺方案来规避相关的风险及提高置管的成功率,使静脉通路的开通风险进一步降低。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。作者贡献:刘彦:实验实施、文稿撰写秦凡博:实验实施龚建平:数据整理及文章终审张文锋:数据整理、文章终审及基金支持 -
表 1 不同时间点热消融不全HepG2细胞模型中CD133的表达
Table 1 Expression of CD133 in residual HepG2 cell models of insufficient thermal ablation at different time points

表 2 不同浓度的苦龙胆酯苷处理热消融不全HepG2细胞24 h后CD133的表达
Table 2 CD133 expressionin the models of insufficient thermal ablation HepG2 cells after treatment with different concentrations of amarogentin

表 3 苦龙胆酯苷对热消融不全HepG2细胞增殖、凋亡及相关分子的影响
Table 3 Effects of amarogentin on proliferation, apoptosis, and related molecules of insufficient thermal ablation HepG2 cells

-
[1] Donne R, Lujambio A. The Liver Cancer Immune Microenvironment: Therapeutic Implications for Hepatocellular Carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2022, 77(5): 1773-1796.
[2] Huang AC, Dodge JL, Yao FY, et al. National Experience on Waitlist Outcomes for Down-staging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: High Dropout Rate in "All-Comers"[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 21(6): 1581-1589. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.08.023
[3] Deng Q, He M, Fu C, et al. Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2022, 39(1): 1052-1063. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2022.2059581
[4] Zhu S, Wu Y, Zhang X, et al. Targeting N7-Methylguanosine tRNA modification blocks hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis after insufficient radiofrequency ablation[J]. Mol Ther, 2023, 31(6): 1596-1614. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.08.004
[5] Zou YW, Ren ZG, Sun Y, et al. The latest research progress on minimally invasive treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2023, 22(1): 54-63. doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2022.08.004
[6] Chen L, Zhang W, Sun T, et al. Effect of Transarterial Chemoembolization Plus Percutaneous Ethanol Injection or Radiofrequency Ablation for Liver Tumors[J]. J Hepatocell Carcinoma, 2022, 9: 783-797. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S370486
[7] Dong S, Li Z, Kong J, et al. Arsenic trioxide inhibits angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma after insufficient radiofrequency ablation via blocking paracrine angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2[J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2022, 39(1): 888-896. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2022.2093995
[8] Guo Y, Ren Y, Dong X, et al. An Overview of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Insufficient Radiofrequency Ablation[J]. J Hepatocell Carcinoma, 2022, 9: 343-355. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S358539
[9] Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Wang J, et al. Amarogentin Inhibits Liver Cancer Cell Angiogenesis after Insufficient Radiofrequency Ablation via Affecting Stemness and the p53-Dependent VEGFA/Dll4/Notch1 Pathway[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 5391058.
[10] Wang S, Liu J, Wu H, et al. All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) inhibits insufficient radiofrequency ablation (IRFA)-induced enrichment of tumor-initiating cells in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chin J Cancer Res, 2021, 33(6): 694-707. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2021.06.06
[11] Zhang X, Zheng Q, Yue X, et al. ZNF498 promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis by suppressing p53-mediated apoptosis and ferroptosis via the attenuation of p53 Ser46 phosphorylation[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 41(1): 79. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02288-3
[12] Xiao Y, Chen J, Zhou H, et al. Combining p53 mRNA nanotherapy with immune checkpoint blockade reprograms the immune microenvironment for effective cancer therapy[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 758. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28279-8
[13] Delman M, Avcı ST, Akçok İ, et al. Antiproliferative activity of (R)-4'-methylklavuzon on hepatocellular carcinoma cells and EpCAM+/CD133+ cancer stem cells via SIRT1 and Exportin-1 (CRM1) inhibition[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2019, 180: 224-237. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.07.024
[14] Pustovalova M, Blokhina T, Alhaddad L, et al. CD44+ and CD133+ Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells Exhibit DNA Damage Response Pathways and Dormant Polyploid Giant Cancer Cell Enrichment Relating to Their p53 Status[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(9): 4922. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094922
[15] Choi HY, Siddique HR, Zheng M, et al. p53 destabilizing protein skews asymmetric division and enhances NOTCH activation to direct self-renewal of TICs[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 3084. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16616-8
[16] Machida K. Cell fate, metabolic reprogramming and lncRNA of tumor-initiating stem-like cells induced by alcohol[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2020, 323: 109055. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109055
[17] Song B, Zhou W. Amarogentin has protective effects against sepsis-induced brain injury via modulating the AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB pathway[J]. Brain Res Bull, 2022, 189: 44-56. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.08.018
[18] Pal D, Sur S, Roy R, et al. Hypomethylation of LIMD1 and P16 by downregulation of DNMT1 results in restriction of liver carcinogenesis by amarogentin treatment[J]. J Biosci, 2021, 46: 53. doi: 10.1007/s12038-021-00176-0
[19] Sur S, Pal D, Banerjee K, et al. Amarogentin regulates self renewal pathways to restrict liver carcinogenesis in experimental mouse model[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2016, 55(7): 1138-1149. doi: 10.1002/mc.22356
[20] Ma H, Li Z, Yuan J, et al. Extrapolating Prognostic Factors of Primary Curative Resection to Postresection Recurrences Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatable by Radiofrequency Ablation[J]. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2021, 2021: 8878417.
[21] Chen X, Huang Y, Chen H, et al. Augmented EPR effect post IRFA to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of arsenic loaded ZIF-8 nanoparticles on residual HCC progression[J]. J Nanobiotechnology, 2022, 20(1): 34. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01161-3
[22] Wang F, Xu C, Li G, et al. Incomplete radiofrequency ablation induced chemoresistance by up-regulating heat shock protein 70 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2021, 409(2): 112910. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112910
[23] Tong Y, Yang H, Xu X, et al. Effect of a hypoxic microenvironment after radiofrequency ablation on residual hepatocellular cell migration and invasion[J]. Cancer Sci, 2017, 108(4): 753-762. doi: 10.1111/cas.13191
[24] Zaimoku R, Miyashita T, Tajima H, et al. Monitoring of Heat Shock Response and Phenotypic Changes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Heat Treatment[J]. Anticancer Res, 2019, 39(10): 5393-5401. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13733
[25] Pal D, Sur S, Mandal S, et al. Prevention of liver carcinogenesis by amarogentin through modulation of G1/S cell cycle check point and induction of apoptosis[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2012, 33(12): 2424-2431. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs276
[26] Pal D, Sur S, Roy R, et al. Epigallocatechin gallate in combination with eugenol or amarogentin shows synergistic chemotherapeutic potential in cervical cancer cell line[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 234(1): 825-836.
[27] Park EK, Lee JC, Park JW, et al. Transcriptional repression of cancer stem cell marker CD133 by tumor suppressor p53[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2015, 6(11): e1964. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.313
[28] Xu Y, Xu Z, Li Q, et al. Mutated p53 Promotes the Symmetric Self-Renewal of Cisplatin-Resistant Lung Cancer Stem-Like Cells and Inhibits the Recruitment of Macrophages[J]. J Immunol Res, 2019, 2019: 7478538.
[29] Feldman DE, Chen C, Punj V, et al. The TBC1D15 oncoprotein controls stem cell self-renewal through destabilization of the Numb-p53 complex[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2): e57312. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057312
[30] Machida K, Feldman DE, Tsukamoto H. TLR4-dependent tumor-initiating stem cell-like cells (TICs) in alcohol-associated hepatocellular carcinogenesis[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2015, 815: 131-144.
[31] Espinosa-Sánchez A, Suárez-Martínez E, Sánchez-Díaz L, et al. Therapeutic Targeting of Signaling Pathways Related to Cancer Stemness[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 1533.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 陈泽玲,刘慧. 逆向法定位穿刺点在蝶翼针植入输液港中的应用. 中国当代医药. 2024(08): 175-178+182 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 连蕊,张军军,韩敏,李琳,汪京萍. 国内外完全植入式输液港研究可视化对比分析. 军事护理. 2024(07): 68-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 吴娇,祝中荣,吴晓霞,肖娜,黄晓波. 床旁超声引导下锁骨下静脉输液港置管术在恶性肿瘤患者中的应用效果. 癌症进展. 2024(24): 2704-2707 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: