α-Hederin Regulates SREBP1/FASN Pathway and Inhibits Malignant Phenotype of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
-
摘要:目的
探讨α-常春藤皂苷对非小细胞肺癌细胞增殖和侵袭的调控作用及其相关分子机制。
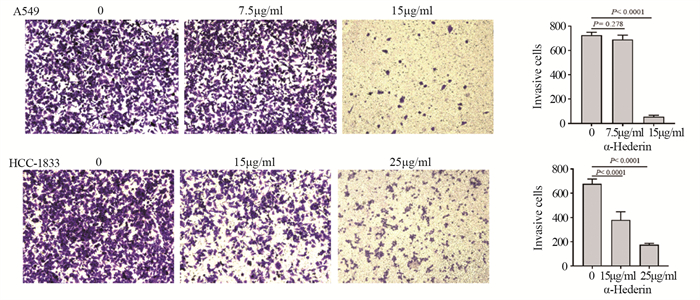
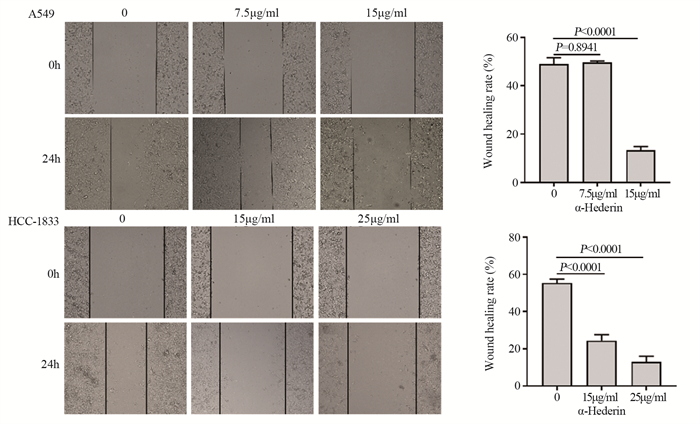
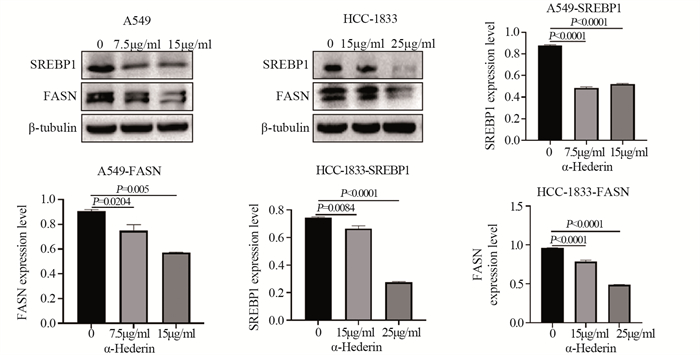
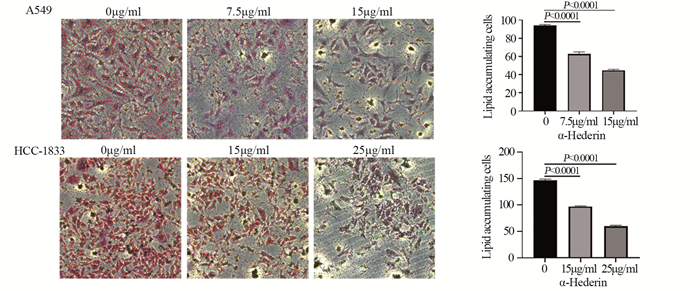
方法采用梯度浓度α-常春藤皂苷分别处理A549和HCC-1833细胞24和48 h后, CCK8法检测细胞活力值(OD450nm)并计算半数抑制浓度(IC50)。根据IC50值将A549细胞和HCC-1833细胞分为空白对照组和α-常春藤皂苷组。EdU试剂盒检测细胞增殖, 流式细胞术检测细胞周期和细胞凋亡率, Transwell检测细胞迁移率, 划痕实验检测细胞侵袭率, Western blot检测SREBP1和FASN蛋白表达水平, 油红O染色检测细胞脂质积累。
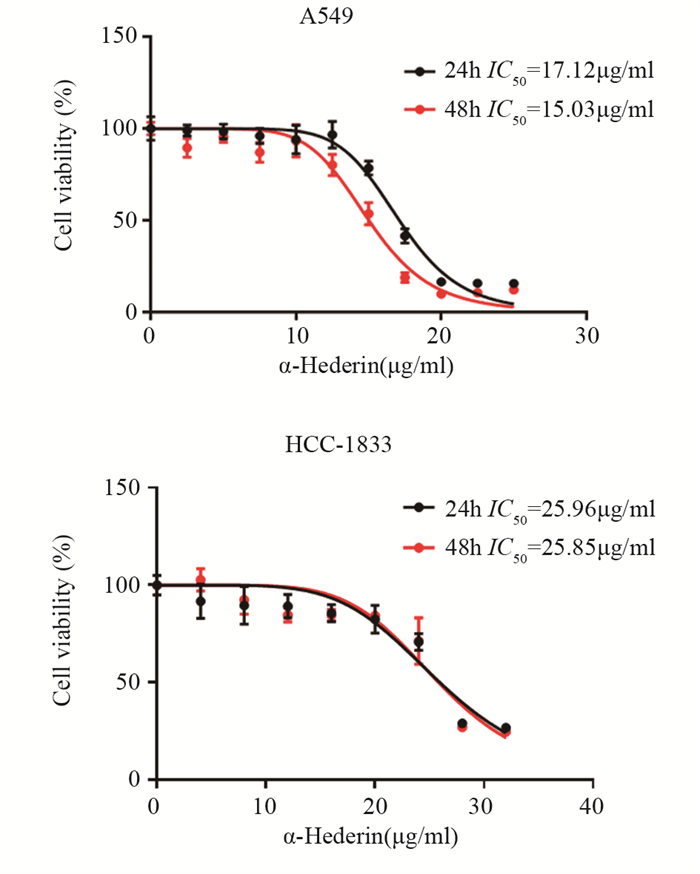
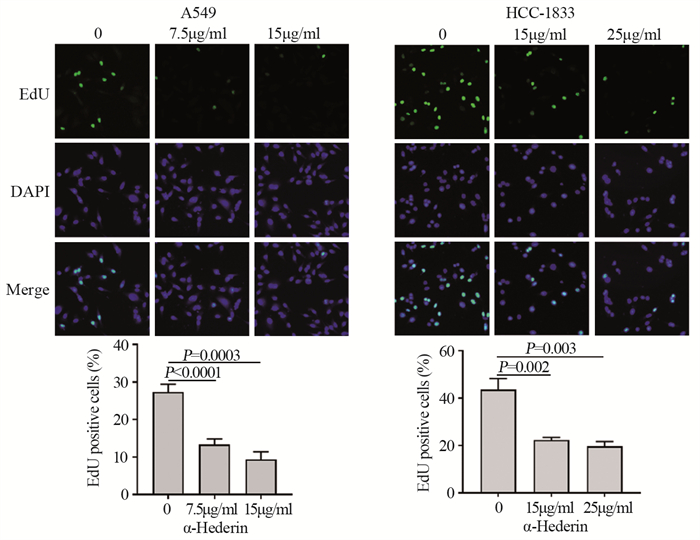
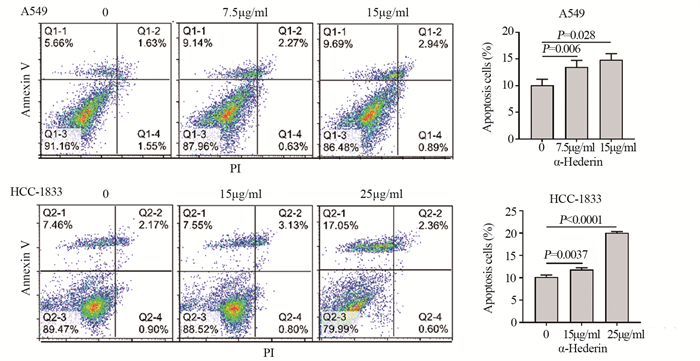
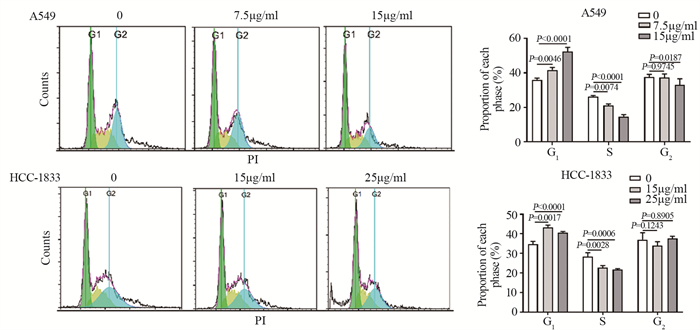
结果肺癌细胞的存活率随α-常春藤皂苷的浓度升高显著降低, 48 h对应的A549细胞和HCC-1833细胞的IC50分别为15 μg/ml和25 μg/ml。与对照组相比, α-常春藤皂苷处理后, 细胞的增殖、迁移被显著抑制, 细胞阻滞于G1/S期, 细胞凋亡率增加, SREBP1和FASN的蛋白表达和细胞脂质积累都显著降低。
结论α-常春藤皂苷可抑制NSCLC细胞增殖、迁移, 诱导细胞凋亡, 使细胞阻滞于G1/S期, 通过下调SREBP1和FASN的表达, 减少细胞脂质积累, 阻碍非小细胞肺癌恶性进程。
-
关键词:
- α-常春藤皂苷 /
- 非小细胞肺癌 /
- 固醇调节元件结合蛋白-1 /
- 脂肪合成酶 /
- 脂质积累
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the regulative effect of α-Hederin on the proliferation and invasion of NSCLC and investigate its related molecular mechanism.
MethodsAfter A549 and HCC-1833 cells were treated with a concentration gradient of α-Hederin for 24 and 48 h, the OD450nm was detected by using CCK8 assays, and the IC50 was calculated.The A549 and HCC-1833 cells were divided into the blank control and α-Hederin groups in accordance with IC50 values.Cell proliferation was detected by EdU assays, and cell cycle transformation and cell apoptosis were detected by flow cytometry.Cell mobility was detected by using Transwell and scratch assays.SREBP1 and FASN protein expression levels were detected through Western blot analysis, and cell lipid accumulation was detected via oil red O staining.
ResultsThe survival rate of lung cancer cells decreased significantly with the increase of α-Hederin concentration, and the IC50 values of A549 and HCC-1833 cells at 48 h were 15 and 25 μg/ml, respectively.Compared with the blank control group, cells proliferation and migration were significantly inhibited, cells were blocked in the G1/S phase, the apoptosis rate increased, and the protein expression and lipid accumulation of SREBP1/FASN significantly reduced after α-Hederin treatment.
Conclusionα-Hederin can inhibit the proliferation and migration, G1/S phase transition and induce the apoptosis of NSCLC cells and hinder the malignant progression of NSCLC by downregulating the expression of SREBP1 and FASN and reducing the accumulation of cell lipids.
-
Key words:
- α-Hederin /
- NSCLC /
- SREBP1 /
- FASN /
- Lipid accumulation
-
0 引言
多形性胶质母细胞瘤(glioblastoma multiforme, GBM)是成人最常见的恶性原发性脑肿瘤之一。目前主要治疗手段包括手术切除联合放疗,但疗效不佳,中位生存期仅12~15月[1]。通过手术获得的肿瘤组织的组织学检查是目前确定性诊断的必要条件。尽管神经系统影像学检查可以提供GBM诊断价值,但对与GBM具有相似的影像学特征的其他脑病变诊断价值不大。因此,在组织学结果不确定或手术禁忌的情况下,筛选GBM分子标志物将为其诊断提供一定帮助。目前已经发现一些GBM中潜在的生物标志物,如PTEN[2]、IDH1[3]、TP53[4]。
本研究利用生物信息学方法对基因芯片GSE7696进行分析来获得差异表达基因(differentially expressed genes, DEGs),并对差异基因进行聚类分析和功能富集分析,同时构建蛋白互作(protein-protein interaction, PPI)网络来筛选核心基因,最后通过TCGA肿瘤数据库GBM全基因组表达谱数据,对核心基因的表达水平进行验证,以提供GBM更多可能的潜在诊断和治疗的分子靶标。
1 材料与方法
1.1 芯片数据
从GEO(gene expression omnibus, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/)中下载编号为GSE7696[5]的基因芯片,该芯片共有84例样本,包括4例正常脑组织样本(对照组)和80例GBM组织样本(实验组),比较实验组和对照组之间基因表达谱的差异情况。该芯片的平台信息:GPL570(HG-U133 Plus 2.0,Affymetrix Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Array)。芯片的探针注释信息来自Affymetrix公司,包含54 675条探针信息。芯片表达谱分析方法利用R软件(https://www.r-project.org/)。
1.2 样本的预处理及聚类分析
从GEO数据库下载原始CEL文件,利用R软件读取原始文件后,使用Affy包中的RMA算法标准化数据后得到基因的表达矩阵,计算样本之间的Pearson相关系数,对所有样本进行聚类分析,剔除离群样本。
1.3 差异表达基因分析
将预处理后得到的基因表达矩阵文件用R软件读入,利用R软件中limma包[6]对80例GBM组织样本和4例正常脑组织样本进行差异表达分析,并且应用贝叶斯检验方法进行多重检验校正。差异基因筛选标准为P < 0.05,基因表达值倍数变化(fold change, FC)≥2或≤-2。
1.4 GO功能注释、KEGG信号富集以及通路网络构建
采用DAVID在线分析平台[7](https://david.ncifcrf.gov/)对差异基因在基因本体(gene ontology, GO)中注释其参与的生物学过程(biological process, BP),并进行京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes, KEGG)通路分析。采用Cytoscape软件对富集到的所有信号通路进行网络构建。
1.5 蛋白互作网络构建及核心蛋白筛选
利用String蛋白互作数据库[8](the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes, STRING, http://string-db.org/)分析GBM组织和正常脑组织差异基因之间的蛋白互作关系,构建蛋白质互作网络,以综合评分(combination score)大于0.4为阈值条件。将STRING中所得蛋白互作网络数据导入Cytoscape软件[9],运用其网络分析(network analyzer)插件计算节点的边(Degree, 即互作连线的数量)筛选网络中心节点(Hub Node)。中心节点对应的蛋白质为具有重要生理调节功能的核心蛋白质(基因)[10]。
1.6 核心蛋白(基因)的验证
利用TCGA肿瘤数据库(The Cancer Genome Atlas Database, https://cancergenome.nih.gov/)获取169例GBM样本和5例正常脑组织样本全基因组表达谱数据,对PPI网络的核心基因进行进一步验证。
1.7 统计学方法
采用SPSS19.0统计软件。两组比较采用t检验,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 样本聚类分析
Pearson相关分析结果显示80例GBM组织样本和4例正常脑组织样本聚类良好,无离群样本,84例样本均可用于下一步分析,见图 1。
2.2 差异表达基因
以P < 0.05,基因表达值倍数变化≥2或≤-2为筛选条件。GBM组织和正常脑组织DEGs一共2 142个,其中上调基因968个,下调基因1 174个,见图 2。差异基因基本能够区分肿瘤组织样本和正常组织样本。
2.3 差异表达基因生物学功能注释
GO功能注释显示,GBM中差异表达基因富集到的生物学过程(biological process, BP)中富集度最高的20条,见图 3A。其中与GBM密切相关程度最高的3个生物学过程是突触传递(synaptic transmission)、有丝分裂细胞周期(mitotic cell cycle)、细胞分裂(cell division)。图 3A中每一条横柱代表一个生物学过程,横柱的长度代表富集到的差异基因数目,颜色越红表示P值越小,越具有统计学意义,下同。
2.4 差异表达基因KEGG信号通路及信号通路网络(pathway network)
利用DAVID在线富集工具将差异基因进行KEGG信号通路富集,图 3B显示富集度最高的20条通路。其中在GBM中明显富集且研究较多的3条信号通路有细胞周期(cell cycle)、MAPK信号通路(MAPK signaling pathway)以及PI3K-Akt信号通路(PI3K-Akt signaling pathway)。信号通路网络图(图 3C)显示MAPK信号通路、凋亡(apoptosis)、细胞周期以及P53信号通路(P53 signaling pathway)在通路网络中处于核心地位,说明他们在GBM的发生发展中起到极其重要的作用。图 3C中点的大小代表degree值,点越大代表通路越核心;颜色反映了通路中差异表达基因的情况,红色代表差异基因全部上调,蓝色代表下调,黄色代表既有上调又有下调。带箭头的实线表示两个信号通路之间的上下游关系,箭头起始端为上游的信号通路,箭头指向端为下游的信号通路。
2.5 通过Cytoscape软件构建的蛋白互作网络
网络分析显示,根据每个基因的节点数目排序,节点数目最多的基因,代表在整个PPI网络中所起的作用越大,即最相关的核心基因,有CDK1、KIF2C、BIRC5、CDC20、KIF11、CENPA、KIF20A、TOP2A、NDC80等9个核心基因,见图 4。这9个核心基因中全部在GBM中表达升高,差异有统计学意义,见表 1。
表 1 GBM基因芯片数据GSE7696中9个核心基因表达情况Table 1 Detailed information of the nine hub genes in GSE7696 gene chip
2.6 核心基因TCGA肿瘤数据库验证
从TCGA肿瘤数据库获取169例GBM样本和5例正常脑组织样本全基因组表达谱数据,比较这9个核心基因在GBM和正常组织中的转录水平,相对于正常组织,9个基因在GBM样本中表达明显升高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001),见图 5(略)。
3 讨论
目前基因芯片在疾病的诊断,特别是肿瘤和正常组织对比、肿瘤组织来源的鉴别等方面具有重要作用。它可用于肿瘤基因表达检测,寻找新基因,为寻找肿瘤的分子靶标提供了一个重要手段。
本研究从GEO芯片数据库获取了美国Affymatrix公司全基因组表达谱芯片,包括80例GBM组织和4例正常的脑组织样本,进行深入分析,以Fold Change绝对值≥2和差异显著性指标P < 0.05为条件,我们获得差异表达基因的数目为2 142个,其中上调968个,下调1 174个。这一结果提示在GBM发生发展的过程中,多种肿瘤相关的基因表达异常或者肿瘤抑制基因表达失活,说明GBM是由多个分子生物学调节异常共同导致。
为了探究这些调节异常基因在GBM中所起的生物学作用,我们将获得的2 142个差异基因进行GO功能注释,结果发现这些基因群主要参与细胞周期、细胞增殖、信号转导以及小分子物质代谢过程,由此说明这些生物学过程的调节异常是导致GBM发生发展的重要因素。同时,为了探究这些基因群所参与的信号通路过程,我们将差异基因进行了KEGG信号通路富集分析,同样发现细胞周期的异常调节在GBM中占有重要地位,其他明显富集到的信号通路有PI3K-AKT信号通路,肿瘤相关信号通路、钙离子信号通路以及MAPK信号通路。对富集到的信号通路进行网络分析后发现,MAPK信号通路处于通路网络的核心,由此说明GBM的发生与该信号通路密切相关。MAPK又称丝裂原活化蛋白激酶,是信号从细胞表面转导到细胞核内部的重要传递者,许多肿瘤的发生和发展都与MAPK信号通路的异常调节有关[11]。以上结果对于研究GBM的生物学发生过程具有很好的提示作用,有待进一步验证。
在9个核心基因中,与细胞周期调节有关的有CDK1和CDC20。CDK1又称细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶1,是一种高度保守的蛋白质,起到丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶的作用,是细胞周期调控的关键参与者。CDK1的过度表达与多种肿瘤细胞的增殖密切相关[12]。CDC20又称细胞分裂周期蛋白20,通过与其他几种蛋白质相互作用从而在细胞周期的多个点上起到调节作用[13]。
与细胞分裂有关的基因有KIF2C、KIF11、CENPA、KIF20A、TOP2A、NDC80。KIF2C属于驱动蛋白样蛋白家族的成员,该家族的大多数蛋白质是微管依赖的分子马达,在细胞分裂期间运输细胞器中的细胞器并移动染色体。最新的研究表明,沉默KIF11可以导致染色体的不稳定从而促进肿瘤的发生[14]。CENPA是修饰的核小体或核小体样结构的组成部分,其含有靶向着丝粒所需的组蛋白H3相关蛋白结构域,在细胞的有丝分裂中发挥重要作用,研究表明CENPA是乳腺癌潜在的预后生物标志物,其表达增加与乳腺癌的不良预后有关[15]。KIF20A过表达与宫颈癌患者进展和不良预后有关[16],并且,研究发现KIF20A在神经胶质瘤组织中高表达并且提示预后不良[17]。TOP2A基因编码DNA拓扑异构酶,是一种控制和改变转录过程中DNA拓扑状态的酶,在乳腺癌[18]、神经母细胞瘤[19]、肺癌[20]等肿瘤中高表达,并且促进肿瘤细胞的增殖和迁移。NDC80在细胞有丝分裂的过程中主要参与染色体的正确分离的调控,有研究发现过表达NDC80后能够明显促进结肠癌细胞的增殖和迁移[21]。
BIRC5又称survivin蛋白或者存活蛋白,凋亡抑制剂家族的成员。survivin蛋白抑制半胱天冬酶活性的作用,从而负性调控导致凋亡。抑制survivin蛋白导致细胞凋亡增加和肿瘤生长减少[22]。数据表明survivin蛋白可能作为癌症治疗的新靶标。最近研究发现survivin蛋白的核表达是GBM患者预后不良的一个因素,survivin蛋白亚细胞定位可以帮助预测用标准方案治疗的GBM患者的总生存期[23]。
综上,应用基因表达谱芯片可以筛选GBM相关基因及信号通路,是否是GBM特异的敏感基因需要更多病例验证以及细胞实验的进一步研究,希望从中能筛选出有助于GBM早期诊断和治疗的分子标志物或基因治疗靶点。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。作者贡献:常毓真:实验实施,论文撰写和修改杨浩:实验构思,方法设计,数据分析、整理,论文审阅和修改黄钢:实验指导,论文修改,基金项目支持 -
-
[1] 许健, 詹月萍, 蒋元烨, 等. α-常春藤皂苷的抗肿瘤药理作用研究进展[J]. 实用肿瘤学杂志, 2019, 33(6): 553-556. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZL201906018.htm Xu J, Zhan YP, Jiang YY, et al. Advance in anti-tumor pharmacological action of α-hederin[J]. Shi Yong Zhong Liu Xue Za Zhi, 2019, 33(6): 553-556. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZL201906018.htm
[2] 李金秋. RACK1通过Akt/mTOR/SREBP1介导脂肪酸合成影响宫颈癌细胞增殖和凋亡的研究[D]. 新疆医科大学, 2022. Li JQ. Study on the effect of RACK1 on proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells through Akt/mTOR/SREBP1-mediated fatty acid synthesis[D]. Xinjiang Medical University, 2022.
[3] 薛乃铭, 柴梦钰, 杨万山, 等. 白花前胡乙素通过SREBP1c/FASN信号通路抑制卵巢癌SKOV-3细胞增殖的作用[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2021, 41(13): 2773-2777. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2021.13.026 Xue NM, Chai MY, Yang WS, et al. Inhibitory effect of praeruptorin B on SK-OV-3 cell proliferation in ovarian cancer by SREBP-1c/FASN signaling pathway[J]. Zhongguo Lao Nian Xue Za Zhi, 2021, 41(13): 2773-2777. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2021.13.026
[4] 吴静, 彭丞, 胡学谦, 等. 非小细胞肺癌的中西医治疗研究进展[J]. 中国现代医生, 2022, 60(26): 123-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDYS202226021.htm Wu J, Pang C, Hu XQ, et al. Research progress in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer with traditional Chinese and western medicine[J]. Zhongguo Xian Dai Yi Sheng, 2022, 60(26): 123-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDYS202226021.htm
[5] Wu Y, Wang D, Lou Y, et al. Regulatory mechanism of α-hederin upon cisplatin sensibility in NSCLC at safe dose by destroying GSS/GSH/GPX2 axis-mediated glutathione oxidation-reduction system[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2022, 150: 112927. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112927
[6] 方聪. α-常春藤皂苷通过干预非小细胞肺癌有氧糖酵解而抑制肿瘤生长的实验研究[D]. 江西中医药大学, 2019. Fang C. The Study on Inhibition of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Growth by Interfering with Aerobic Glycolysis of α-Hederin[D]. Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019.
[7] Fang C, Liu Y, Chen L, et al. α-Hederin inhibits the growth of lung cancer A549 cells in vitro and in vivo by decreasing SIRT6 dependent glycolysis[J]. Pharmaceutical Biol, 2021, 59(1): 11-20. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1862250
[8] 张夜航, 卢文丽, 彭佩克, 等. α-常春藤皂苷协同雷公藤红素对SMMC7721肝癌细胞增殖和周期的影响[J]. 中成药, 2022, 44(4): 1099-1106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2022.04.011 Zhang YH, Lu WL, Peng PK, et al. Synergistic effects of α-Hederin and celastrol on proliferation and cell cycle of SMMC7721 hepatoma cells[J]. Zhong Cheng Yao, 2022, 44(4): 1099-1106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2022.04.011
[9] Chen T, Sun D, Wang Q, et al. α-Hederin Inhibits the Proliferation of HepatocellularCarcinoma Cells Hippo-Yes-Associated Protein Signaling Pathway[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 839603. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.839603
[10] Li J, Wu D, Zhang J, et al. Mitochondrial pathway mediated by reactive oxygen species involvement in α-hederin-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2018, 24(17): 1901-1910. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1901
[11] 李娇, 马静静, 胡雪, 等. α-常春藤皂苷通过活性氧—线粒体途径促进食管癌细胞凋亡的研究[J]. 疑难病杂志, 2018, 17(9): 932-935, 939. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6450.2018.09.016 Li J, Ma JJ, Hu X, et al. The study of α-Hederin induces the apoptpsis of esophageal carcinoma cells via the mitochodrial pathway mediated by reactive oxygen species[J]. Yi Nan Bing Za Zhi, 2018, 17(9): 932-935, 939. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6450.2018.09.016
[12] Wang J, Wu D, Zang J, et al. α-Hederin Induces Apoptosis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma via an Oxidative and Mitochondrial-Dependent Pathway[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2019, 64(12): 3528-3538. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05689-1
[13] 刘颖慧. α-常春藤皂苷调控人胃癌耐药细胞增殖和凋亡机制研究[D]. 武汉大学, 2020. Liu YH. Effect of α-Hederin on the apoptosis and growth inhibition of cisplatin-resistant Gastric Cancer Cells[D]. Wuhan University, 2020.
[14] Deng H, Ma J, Liu Y, et al. Combining α-Hederin with cisplatin increases the apoptosis of gastric cancer in vivo and in vitro via mitochondrial related apoptosis pathway[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 120: 109477. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109477
[15] Wang J, Deng H, Zhang J, et al. α-Hederin induces the apoptosis of gastric cancer cells accompanied by glutathione decrement and reactive oxygen species generation via activating mitochondrial dependent pathway[J]. Phytothery Res, 2020, 34(3): 601-611. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6548
[16] 王国娟, 余文燕, 郭红飞, 等. α-常春藤皂苷抗结肠癌增殖作用研究[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2017, 33(4): 41-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYL201704012.htm Wang GJ, Yu WY, Guo HF, et al. Research of anti-proliferative effect of α-hederin on colon cancer[J]. Zhong Yao Yao Li Yu Lin Chuang, 2017, 33(4): 41-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYL201704012.htm
[17] 张步鑫, 赵献敏, 成琼, 等. α-常春藤皂苷对黑色素瘤B16细胞增殖和凋亡的影响及机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2018, 24(12): 81-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSFX201812014.htm Zhang BX, Zhao XM, Cheng Q, et al. Effect of α-Hederin on Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis in Melanoma B16Cells and Its Mechanism[J]. Zhongguo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi, 2018, 24(12): 81-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSFX201812014.htm
[18] 许健. α-常春藤皂苷通过抑制Bcl2表达克服乏氧介导的结肠癌耐药的机制研究[D]. 上海中医药大学, 2020. Xu J. Study on the mechanism of α-Hederin overcoming hypoxia-mediated drug resistance in colon cancer by inhibiting Bcl2 expression[D]. Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020.
[19] Sun D, Shen W, Zhang F, et al. α-Hederin inhibits interleukin 6-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition associated with disruption of JAK2/STAT3 signaling in colon cancer cells[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 101: 107-114. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.062
[20] Sun J, Feng Y, Wang Y, et al. α-hederin induces autophagic cell death in colorectal cancer cells through reactive oxygen species dependent AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway activation[J]. Int J Oncol, 2019, 54(5): 1601-1612.
[21] 贺肖梦, 郑燕. 脂质代谢与肺癌相关性及其潜在治疗靶点[J]. 浙江中西医结合杂志, 2021, 31(6): 583-585. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJZH202106026.htm He XM, Zheng Y. Relationship between lipid metabolism and lung cancer and its potential therapeutic targets[J]. Zhejiang Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi, 2021, 31(6): 583-585. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJZH202106026.htm
[22] 胡超帆. 非小细胞肺癌患者组织中PD-L1和FASN表达关系及其临床意义[D]. 郑州大学, 2019. Hu CF. Expression relationship of PD-L1 and FASN in non-small cell lung cancer patients and its clinical significance[D]. Zhengzhou University, 2019.
[23] 秦新新, 邱竞, 吕雪莲, 等. miR-17通过调节脂肪酸代谢抑制非小细胞肺癌A549细胞的生长和转移[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2020, 55(7): 1057-1063. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YIKE202007014.htm Qin XX, Qiu J, Lv XL, et al. miR-17 inhibits the growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells by regulating fatty acid metabolism[J]. Anhui Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao, 2020, 55(7): 1057-1063. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YIKE202007014.htm
[24] 冯晓异, 何朋伦, 赵梓铭, 等. 从CRTC2/SREBP1调节探讨三七总皂苷改善非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠脂质代谢的作用[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2022, 37(2): 1107-1112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY202202122.htm Feng XY, He PL, Zhao ZM, et al. Effects of Panax notoginseng spaponins on the lipid metabolism of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease rat via regulating expression of CRTC2 and SREBP1[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi, 2022, 37(2): 1107-1112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY202202122.htm
[25] 罗婷婷, 杨仁国, 贺微微. 甲基莲心碱通过活化HepG-2细胞中的AMPK并介导ACC/CPT1A和SREBP1/FAS通路改善棕榈酸诱导的脂质积累[J]. 中药材, 2021, 44(7): 1754-1758. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYCA202107037.htm Luo TT, Yang RG, He WW. Neferine improves palmitic acid induced lipid accumulation by activating AMPK in HepG-2 cells and mediating ACC/CPT1A and SREBP1/FAS pathways[J]. Zhong Yao Cai, 2021, 44(7): 1754-1758. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYCA202107037.htm
[26] 马漪, 谢琼. 苦参碱对结肠癌肝转移小鼠SCAP/SREBP1信号通路的调节作用研究[J]. 天津中医药, 2022, 39(3): 386-391. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJZY202203019.htm Ma Y, Xie Q. Regulation of Matrine on SCAP/SREBP1 Signal Pathway in Mice with Liver Metastasis of Colon Cancer[J]. Tianjin Zhong Yi Yao, 2022, 39(3): 386-391. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJZY202203019.htm
[27] 朴颖, 金翔宇, 周东梅, 等. 丁香酚通过AMPK及SREBP1途径改善非酒精性脂肪肝的机制[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2022, 37(2): 1102-1106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY202202121.htm Pu Y, Jin XY, Zhou DM, et al. Mechanism of eugenol improving nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through AMPK and SREBP1 pathways[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi, 2022, 37(2): 1102-1106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY202202121.htm
[28] 王帅, 王凤荣. 姜黄素对泡沫细胞胆固醇流出及SREBP1、ABCA1表达的影响[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2020, 31(7): 1580-1583. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZGY202007013.htm Wang S, Wang FR. Effects of curcumin on cholesterol efflux and expression of SREBP1 and ABCA1 in foam cells[J]. Shizhen Guo Yi Guo Yao, 2020, 31(7): 1580-1583. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZGY202007013.htm
[29] Wang Q, Tian N, Zhang W, et al. Fatty Acid Synthase Mutations Predict Favorable Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Outcome and Response in Melanoma and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients[J]. Cancers, 2022, 14(22): 5638.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 安俊达,李玉双. 基于超声图像评估甲状腺和乳腺病变的通用计算方法. 燕山大学学报. 2024(01): 86-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 杨茜雯,宋博,高婷婷,薛无瑕,李立坤,纪永章. 2021—2022年某三甲医院体检人群重要异常结果分布特征分析. 健康体检与管理. 2024(02): 174-177+202 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨倩倩,夏源,张云飞,杨桂云,郭文佳,张秀华. 基于列线图的女性乳腺癌患者再发第二原发性甲状腺癌风险预测模型的构建和验证. 中国医药导报. 2024(24): 117-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 阙厦丹,陈敦雁. 乳腺良性肿瘤和恶性肿瘤与自身免疫性甲状腺疾病的关系. 慢性病学杂志. 2023(05): 755-757 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王婷. 中西医结合治疗乳腺癌术后甲状腺结节的临床疗效. 世界复合医学. 2022(04): 109-111+116 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: