Efficacy of Different Pharmacological Interventions for Cervical High-risk HPV Infection: Bayesian Network Meta-analysis
-
摘要:目的
基于贝叶斯网状Meta分析方法比较临床常见干预方式治疗宫颈高危型HPV感染的疗效。
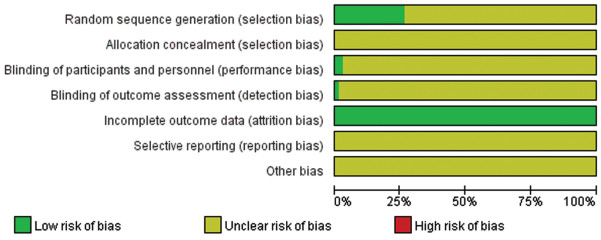
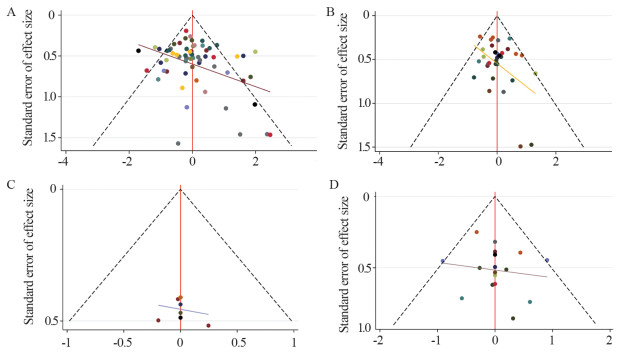
方法检索PubMed、中国生物医学文献数据库等中英文数据库收录的从建库以来至2021年7月31日临床常见干预方式治疗宫颈高危型HPV感染的随机对照试验。按照纳入和排除标准筛选文献,Cochrane系统评价策略评价纳入文献的质量,RevMan5.3和Stata16.0软件进行Meta分析。
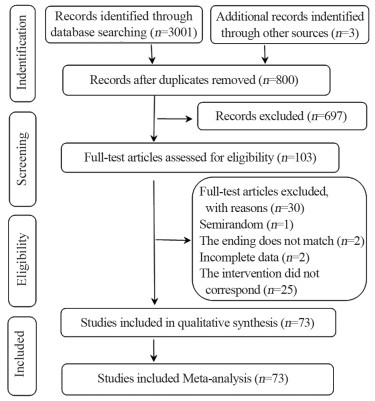
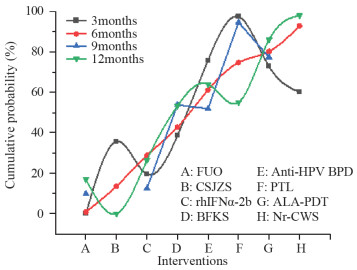
结果纳入73篇RCTs,3 642例患者,涉及8种干预方式。网状Meta分析结果显示,治疗后3个月转阴率排序为PTL > Anti-HPV BPD > ALA-PDT > Nr-CWS > BFKS > CSJZS > rhIFNα-2b > FUO;治疗后6个月转阴率排序为Nr-CWS > ALA-PDT > PTL > Anti-HPV BPD > BFKS > rhIFN > FUO > CSJZS;治疗后9个月转阴率排序为PTL > ALA-PDT > BFKS > Anti-HPV BPD > rhIFNα-2b > FUO;治疗后12个月转阴率排序为Nr-CWS > ALA-PDT > Anti-HPV BPD > PTL > BFKS > rhIFNα-2b > FUO > CSJZS。
结论就HPV转阴率而言,Nr-CWS和PTL具有较好的疗效,是目前较为理想的方案,但仍需今后高质量研究予以证实。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo compare the efficacy of common clinical interventions in the treatment of cervical high-risk (HR) HPV infection based on Bayesian network meta-analysis.
MethodsRandomized controlled trials (RCTs) about common clinical interventions for cervical HR-HPV infection were searched in PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, The Cochrane Library, CBM, CNKI, Wanfang Data, and VIP databases from inception to July 31, 2021 using specific inclusion and exclusion criteria. The quality of the included studies was evaluated in accordance with the Cochrane systematic review manual. Meta-analysis was performed with Stata16 and RevMan5.3 software.
ResultsSeventy-three RCTs were included, involving 3642 patients and eight treatment methods. Network meta-analysis showed that in the three months after treatment, the negative conversion rate was in the order: PTL > anti-HPV BPD > ALA-PDT > Nr-CWS > BFKS > CSJZS > rhIFNα-2b > FUO. In the six months after treatment, the negative conversion rate was in the order: Nr-CWS > ALA-PDT > PTL > anti-HPV BPD > BFKS > rhIFNα-2b > FUO > CSJZS. In the nine months after treatment, the negative conversion rate was in the order: PTL > ALA-PDT > BFKS > anti-HPV BPD > rhIFNα-2b > FUO. IN the 12 months after treatment, the negative conversion rate was in the order: Nr-CWS > ALA-PDT > anti-HPV BPD > PTL > BFKS > rhIFNα-2b > FUO > CSJZS.
ConclusionIn terms of HPV negative conversion rate, Nr-CWS and PTL are more effective and currently ideal compared with the other treatments. Owing to the quality of the evidence, the above conclusions must be confirmed by future high-quality studies.
-
Key words:
- Human papillomavirus /
- HPV /
- High-risk /
- Network meta-analysis
-
0 引言
NIMA激酶[1],是在丝状真菌-构巢曲霉中发现的一种苏氨酸/丝氨酸激酶,通过对纺锤体极的作用调节细胞周期。NEK(NIMA-related kinase)家族是在高等真核生物中发现的类似NIMA激酶的蛋白激酶家族,共有11个(NEK1~11)成员,其中NEK2是和NIMA同源性最高的一个成员[2]。NEK2在有丝分裂过程中也发挥重要的作用,具有调控中心体、纺锤体、染色体等功能,能推动细胞周期的正常进行。
NEK2的功能异常会造成中心体过度复制,纺锤体形成异常,染色体分离失误等有丝分裂障碍,从而产生非整倍体性或染色体不稳定性细胞,这些都是恶性肿瘤中最常见的现象,因此认为NEK2的功能异常可能与肿瘤的发生发展之间有一定的关系。本文拟对目前NEK2与肿瘤发生,以及NEK2在肿瘤治疗中的潜在作用作一综述。
1 NEK2结构、定位及表达情况
NEK2蛋白有3个剪接异构体,三者在结构上具有较高的同源性,氨基末端都是典型的丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶区域,只在羧基末端存在一定的差异,见图 1。NEK2A在细胞核和细胞质中均有分布,NEK2B主要聚集在细胞质,而NEK2C只存在于细胞核[3]。研究发现NEK2在整个细胞周期中的表达量是不断变化的,在G1期不活跃,在S期和G2期增长,G2期达到高峰,主要在S期和G2期发挥作用[4]。
![]() 图 1 NEK2蛋白分子结构Figure 1 NEK2 protein structureThree splice variants of NEK2 had been described: NEK2A, NEK2B and NEK2C. The domain structures of these three proteins were shown relatively high homology, mainly including the relative positions of catalytic domain(KINASE), leucine zipper(LZ), coiled coil(CC), splice site, protein phosphatase-1(PP1) binding site, KEN-box, D-box, centrosome and microtubule localization, nucleolar localization. Numbers above and below the structures indicated amino acid positions
图 1 NEK2蛋白分子结构Figure 1 NEK2 protein structureThree splice variants of NEK2 had been described: NEK2A, NEK2B and NEK2C. The domain structures of these three proteins were shown relatively high homology, mainly including the relative positions of catalytic domain(KINASE), leucine zipper(LZ), coiled coil(CC), splice site, protein phosphatase-1(PP1) binding site, KEN-box, D-box, centrosome and microtubule localization, nucleolar localization. Numbers above and below the structures indicated amino acid positions2 NEK2的细胞周期调控机制
NEK2在细胞周期的调控过程中起着重要的作用,首先NEK2可以促进微管成核,形成正确的中心体,并维持中心体的稳定性。该功能主要通过与有丝分裂激酶(polo-like kinase 1,PLK1)的协同作用,加速γ-微管蛋白聚集,促进微管晶核的形成。研究发现在NEK2缺失的果蝇S2细胞内,中心粒极失去与γ-微管蛋白的结合能力,微管成核受到抑制,不能形成功能正常的中心体[5]。NEK2还可以通过作用于其互作蛋白(NEK2-interacting protein, NIP2)来调控微管的形态和功能,维持中心体的稳定性,避免中心体破裂[6]。
随着分裂的进行,在G2/M期NEK2可以作用于跨膜受体蛋白(dishevelled, DVL)促进Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的活化,继而调节中心体链接蛋白(centrosome-associated protein 1, C-Nap1)和小根蛋白的降解来调节亲代和子代中心粒之间的内聚力,启动中心粒的分离形成两级纺锤体,牵引染色体移向两极,使染色体均匀分布到两个子细胞中[7]。为使染色体精确分离,NEK2和癌症高表达蛋白1(high expression in cancer 1, Hec1)相互作用,召集有丝分裂阻滞缺陷蛋白1、2(mitotic arrest deficient 1, 2,Mad1, 2)复合物结合到动粒上,激活纺锤体检查点的APC-Cdc20途径调控染色体的精准分离,促进有丝分裂的精确进行[8]。
3 NEK2在人类肿瘤中的表达与作用
3.1 NEK2可能参与人类肿瘤发生发展过程
肿瘤的形成是遗传和环境等因素共同作用的结果,是一个涉及到多基因、多通路和多分子作用的过程。现代分子生物学的不断发展使肿瘤的研究已经深入到基因和分子水平,很多研究发现染色体的非整倍性和不稳定性是肿瘤细胞中最常见的特征。
NEK2可以通过调控中心体的分离和纺锤体的形成使染色体精确的分离到两个子细胞中。因此,NEK2的异常表达将会对该过程造成损害,导致细胞分裂异常,在细胞中表现为不成熟的中心体过早分离,纺锤体形成异常,中心体过度复制及染色体分离异常等,这些异常都可以导致染色体的非整倍性和不稳定性。因此,有学者提出NEK2的异常表达可能是细胞恶化形成肿瘤细胞的重要推动力,与肿瘤的发生发展之间存在着一定的联系[9]。
恶性肿瘤中NEK2表达增高的现象最早是在尤文氏瘤衍生细胞系中进行mRNA微点阵分析时发现的[10]。随后的研究发现,NEK2 mRNA和蛋白表达水平在人类多数癌症中都存在增高的现象。对Oncomine癌基因芯片数据库中几种人类常见的癌症进行分析,发现肿瘤组织较正常组织的NEK2 mRNA表达均明显增高,且两者之间的差异有统计学意义,见表 1。蛋白免疫印迹结果也显示在三种前列腺癌细胞中NEK2表达远远高于前列腺正常细胞[11];免疫组织化学结果显示40例肝癌患者的肿瘤组织中NEK2蛋白表达水平明显高于癌旁组织[12];有更多的研究显示,NEK2在人类多种癌症,包括非小细胞型肺癌[13-14]、骨髓瘤[9]、卵巢癌[15]、乳腺癌[16-17]、前列腺癌[11]、结肠直肠癌[18]、恶性外周神经鞘瘤[19]、肾细胞癌[16]、胰腺导管腺癌[20]等组织或细胞中的表达量比正常的组织或细胞的表达量增高。因此可以认为,NEK2在人类多数肿瘤中表达增高是一种普遍存在的现象。结合NEK2的异常表达会造成染色体不稳定性和非整倍体性这些在肿瘤细胞中最常见的现象,我们初步认为,NEK2高表达可能是促使肿瘤发生发展的一个重要因素。
表 1 NEK2 mRNA在人类不同肿瘤中的表达Table 1 NEK2 mRNA expression in different human cancers
3.2 NEK2可能是一种新型的肿瘤标志物
肺癌是世界范围内死亡率很高的癌症,5年生存率只有16%,严重威胁人类的健康,寻找一种特异性强的肿瘤标志物是提高患者生存率的有效措施。Zhong等[13]对270份非小细胞型肺癌组织进行分析发现,NEK2的表达情况和已知的两种细胞增殖标志物MCM7和Ki67相类似,能够指示肿瘤细胞的增殖程度。统计学分析显示,NEK2表达量可以预示非小细胞型肺癌的分期程度、淋巴结转移能力,表达量越高则恶性程度越高。同时NEK2还可以作为一个预后标志,预测患者的5年生存率,两者间呈负相关,表达量高的患者总生存时间明显降低。另有研究得到了类似的结果,NEK2表达量高的前列腺癌患者肿瘤格里森分级高、侵袭转移能力强;在前列腺癌患者中,NEK2表达量升高的患者前列腺特异性抗原PSA(PSA是前列腺癌复发的一个标志)表达量越高,则患者复发的时间越短,两者间的关系存在统计学意义[11]。因此,NEK2可能是一个重要的肿瘤标志物,其表达量可以预示肿瘤增殖和预后情况,并指导医生做出更合适的临床决策,进而提高肿瘤的治疗效果。
3.3 NEK2可能是一个未来肿瘤治疗的靶点
NEK2在人类多种癌症中的高表达现象,提示NEK2可以作为靶标对肿瘤进行分子治疗的可能性。Zeng等[11]通过在裸小鼠皮下注射前列腺癌细胞团建立的肿瘤模型发现,NEK2失活组裸小鼠形成的肿瘤尺寸明显小于对照组;Kokuryo等[21]也发现,抑制NEK2的表达可以抑制裸鼠皮下异种移植胰腺癌肿瘤模型的生长,延长腹膜内胰腺癌肿瘤异种移植模型裸鼠的生存时间,通过门静脉系统注射NEK2 siRNA可以有效阻止胰腺癌细胞的肝转移。细胞水平实验进一步验证了这一猜想,与正常的肝癌细胞HepG2相比,通过siRNA转染技术沉默NEK2表达的HepG2细胞有丝分裂周期受到影响,G1期发生了明显的阻滞,细胞周期不能正常进行,肿瘤细胞的生长受抑制,迁移能力和侵袭能力也受到抑制;在诱导凋亡实验中发现,消耗内生性的NEK2可以显著提高细胞凋亡的基础水平[9, 22]。在更多人类肿瘤的相关实验中也发现了下调NEK2的表达能够抑制肿瘤增殖,促进凋亡的现象。
NEK2在分子水平调控肿瘤细胞凋亡水平的有力证据是由Naro等[3]给出的,他们提出,NEK2是丝氨酸/精氨酸蛋白特异性激酶1(serine/arginine protein-specific kinase 1, SRPK1)的剪接因子激酶,能够激活丝氨酸/精氨酸富集剪接因子1(serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 1, SRSF1),SRSF1是位于细胞核内的一种原癌蛋白,通过影响PI3K-Akt-mTOR、Ras-MNK-MAPK及Wnt-β-catenin信号通路中相关基因的剪接方式发挥致癌作用。例如激活的SRSF1能够选择性剪接B淋巴细胞瘤-2(B-cell lymphoma-2, Bcl-2)基因家族的Bcl-x,提高抑制细胞凋亡剪接变体Bcl-xL的表达,抑制促进细胞凋亡的剪接变体Bcl-xS的表达,从而下调细胞的凋亡水平。在肿瘤细胞中高表达的NEK2会过量激活SRSF1,从而抑制细胞的凋亡能力,促进肿瘤细胞的生长。这些体内外实验的结果均证明了NEK2可能是今后肿瘤治疗的潜在作用靶点。
Oncotarget杂志报道的一种新型分子复合物MBM-5,可以干扰NEK2对细胞周期的调控作用,造成染色体分离失误,使细胞阻滞于G2期,从而引发细胞的凋亡。MBM-5通过干扰NEK2功能能够抑制白血病、胃癌、结肠癌、前列腺癌、乳腺癌、肝癌等多种肿瘤细胞的增殖能力,对胃肠道肿瘤细胞的抑制作用更明显,并能够高效地抑制胃肠道癌细胞的异种移植瘤生长[23]。该研究显示了以NEK2为分子靶标进行肿瘤治疗的可能性。
美国加利福尼亚大学的医学研究室发现的一种小分子抑制剂INH(inhibitor for NEK2 and hec1 binding)可以直接和癌症高表达蛋白1(highly expressed in cancer 1, Hec1)结合,阻止NEK2对Hec1 S165位点的磷酸化,诱导NEK2降解和Hec1失活,造成染色体分离失误,从而引起有丝分裂障碍,最终导致细胞死亡。在小鼠乳腺癌移植瘤模型部位注射INHs,能显著地抑制肿瘤生长并且没有明显的细胞毒副作用。因此这种INH的派生复合物有可能在今后被应用于肿瘤的临床治疗。
4 小结
从目前的研究看来,NEK2作为一种重要的细胞周期蛋白,具有调控中心体的组装与分离、纺锤体的形成,染色体的精确分离等功能。因其在人类多种肿瘤中高表达的现象,引起了越来越多的关注,NEK2功能异常造成的染色体不稳定性可能是肿瘤发生发展的重要驱动力。同时,NEK2还可能成为肿瘤分化程度和预后检测的重要标志物,并且是癌症治疗的一个重要的潜在靶目标。对NEK2功能和机制的继续深入研究,将为NEK2在肿瘤临床的应用提供重要的依据。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。作者贡献:罗 喜:文献检索、统计分析、论文写作黄紫薇:文献检索及质量评估范孝盈、李晓娟:文献筛选、数据收集与统计张伶俐:方向指导、论文审校 -
表 1 随访3个月HPV转阴率的网状Meta分析结果
Table 1 Network meta-analysis of negative conversion rate in three months after treatment

表 2 随访6个月HPV转阴率的网状Meta分析结果
Table 2 Network meta-analysis of negative conversion rate in six months after treatment

表 3 随访9个月HPV转阴率的网状Meta分析结果
Table 3 Network meta-analysis of negative conversion rate in nine months after treatment

表 4 随访12个月HPV转阴率的网状Meta分析结果
Table 4 Network meta-analysis of negative conversion rate in 12 months after treatment

表 5 宫颈高危型HPV转阴率的累计排序概率表
Table 5 Cumulative probability ranking of negative conversion rate of cervical HR-HPV infection

-
[1] US Preventive Services Task Force, Curry SJ, Krist AH, et al. Screening for Cervical Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement[J]. JAMA, 2018, 320(7): 674-686. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.10897
[2] Huh WK, Ault KA, Chelmow D, et al. Use of primary high-risk human papillomavirus testing for cervical cancer screening: interim clinical guidance[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2015, 136(2): 178-182. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2014.12.022
[3] Salazar KL, Duhon DJ, Olsen R, et al. A review of the FDA-approved molecular testing platforms for human papillomavirus[J]. J Am Soc Cytopathol, 2019, 8(5): 284-292. doi: 10.1016/j.jasc.2019.06.001
[4] 中华预防医学会疫苗与免疫分会. 子宫颈癌等人乳头瘤病毒相关疾病免疫预防专家共识[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2019, 53(8): 761-803. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FKLC202001002.htm Vaccine and Immunization Branch, Chinese Preventive Medicine Association. Expert consensus on immunological prevention of human papillomavirus-related diseases[J]. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2019, 53(8): 761-803. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FKLC202001002.htm
[5] Kombe Kombe AJ, Li B, Zahid A, et al. Epidemiology and Burden of Human Papillomavirus and Related Diseases, Molecular Pathogenesis, and Vaccine Evaluation[J]. Front Public Health, 2021, 8: 552028. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.552028
[6] 郑荣寿, 张思维, 孙可欣, 等. 2016年中国恶性肿瘤流行情况分析[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2023, 45(3): 212-220. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20220922-00647 Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Sun KX, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2016[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2023, 45(3): 212-220. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20220922-00647
[7] Landy R, Sasieni PD, Mathews C, et al. Impact of screening on cervical cancer incidence: A population-based case-control study in the United States[J]. Int J Cancer, 2020, 147(3): 887-896. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32826
[8] Xia C, Hu S, Xu X, et al. Projections up to 2100 and a budget optimisation strategy towards cervical cancer elimination in China: a modelling study[J]. Lancet Public Health, 2019, 4(9): e462-e472. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(19)30162-8
[9] Hu S, Xu X, Zhang Y, et al. A nationwide post-marketing survey of knowledge, attitude and practice toward human papillomavirus vaccine in general population: Implications for vaccine roll-out in mainland China[J]. Vaccine, 2021, 39(1): 35-44. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.11.029
[10] Li Y, Xu C. Human Papillomavirus-Related Cancers[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2017, 1018: 23-34.
[11] Beckmann MW, Stuebs FA, Vordermark D, et al. The Diagnosis, Treatment, and Aftercare of Cervical Carcinoma[J]. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 2021, 118(47): 806-812.
[12] de Sanjosé S, Brotons M, Pavón MA. The natural history of human Papillomavirus infection[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol, 2018, 47: 2-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2017.08.015
[13] Qingqing B, Jie Z, Songben Q, et al. Cervicovaginal microbiota dysbiosis correlates with HPV persistent infection[J]. Microb Pathog, 2021, 152: 104617. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104617
[14] Perea SE, López-Ocejo O, García-Milian R, et al. Interferon-alpha elicits downregulation of human papillomavirus 18 mRNA in HeLa cells by selective repression of endogenous viral transcription[J]. J Interferon Cytokine Res, 1995, 15(6): 495-501. doi: 10.1089/jir.1995.15.495
[15] 刘莲慧, 秦文敏, 张莹雪, 等. 派特灵治疗高危型人乳头瘤病毒(HR-HPV)感染疗效的Meta分析[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(22): 6928-6938. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.22.019 Liu LH, Qin WM, Zhang YX, et al. Meta-analysis on effect of Paiteling on high-risk HPV infection[J]. Zhong Cao Yao, 2021, 52(22): 6928-6938. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.22.019
[16] Tao P, Zheng W, Meng X, et al. Effect of paiteling on human papillomavirus infection of the cervix[J]. Mol Clin Oncol, 2017, 7(6): 957-964.
[17] 刘运华, 赵宗江, 张新雪, 等. 派特灵对HeLa细胞增殖迁移能力及PI3K/Akt信号转导通路的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2020, 26(17): 56-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSFX202017008.htm Liu YH, Zhao ZJ, Zhang XX, et al. Effect of Paiteling on HeLa Cell Proliferation and Metastasis Ability and PI3K/Akt Signal Transduction Pathway[J]. Zhongguo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi, 2020, 26(17): 56-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSFX202017008.htm
[18] 杨涛, 张萌萌, 刘运华, 等. 派特灵对Ect1/E6E7细胞增殖迁移能力及Wnt/β-catenin通路的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2020, 35(12): 6330-6336. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY202012112.htm Yang T, Zhang MM, Liu YH, et al. Effects of Paiteling on proliferation and migration of Ect1/E6E7 cells and its effects on Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi, 2020, 35(12): 6330-6336. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY202012112.htm
[19] Tao Y, Wang G, Zhai J, et al. Functional modulation of CD8+ T cell by approved novel immune enhancer: Nocardia rubra Cell-Wall Skeletons (Nr-CWS)[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020, 78: 106023. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106023
[20] 赵健, 詹少兵, 李雪倩, 等. Nr-CWS对TC-1细胞致瘤作用的影响及抗女性下生殖道人乳头状瘤病毒感染的研究[J]. 中华实验和临床病毒学杂志, 2007, 21(4): 340-342. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSB200704015.htm Zhao J, Zhan SB, Li XQ, et al. Effect of Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton (Nr-CWS) on oncogenicity of TC-1 cells and anti-human papillomavirus effect of Nr-CWS in lower genital tract of women[J]. Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi, 2007, 21(4): 340-342. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSB200704015.htm




 下载:
下载: