Construction of Prognostic Model for Cuprotosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on TCGA Database
-
摘要:目的
构建肝细胞癌(HCC)患者铜死亡相关基因(CRGs)的预后模型。
方法基于TCGA数据库HCC患者的mRNA数据集,分析CRGs在HCC患者中的表达,对CRGs及相关基因进行GO和KEGG富集分析。Kaplan-Meier生存分析曲线评估CRGs的生存预后价值,分析其与免疫细胞浸润的相关性。单因素Cox回归分析筛选出与HCC患者生存预后显著相关的CRGs,Lasso回归和多因素Cox回归分析构建预后模型。根据风险值对患者进行分组并进行生存分析,ROC曲线评估预后模型,单因素和多因素Cox回归分析风险评分及临床因素与预后的关系。
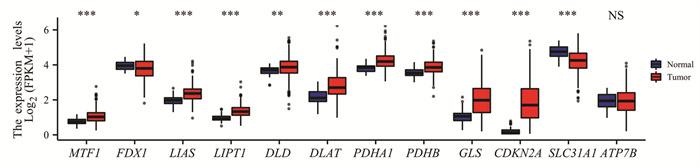
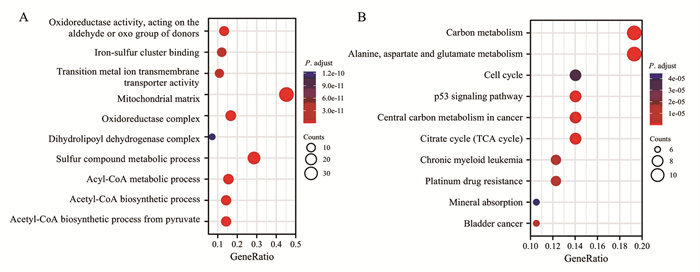
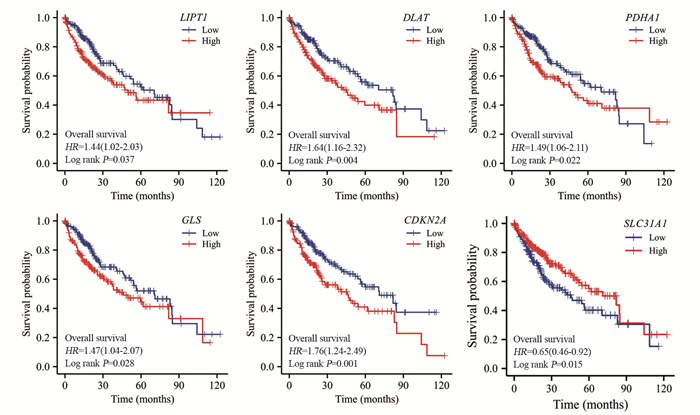
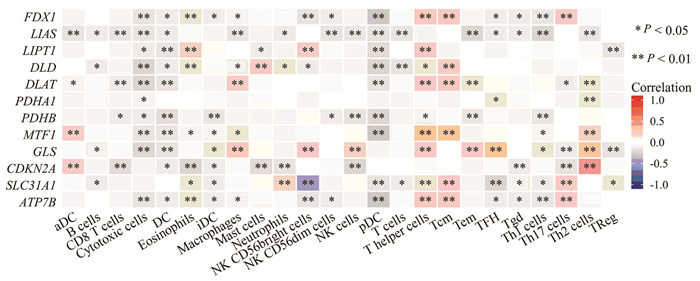
结果分析得到HCC中差异表达CRGs共11个,CRGs及其相关基因主要富集的GO条目为氧化还原酶活性,作用于供体的醛基或氧基,主要富集的KEGG信号通路为碳代谢。CRGs的表达水平与浆细胞样滤泡树突细胞、T辅助细胞等免疫细胞的浸润显著相关(P < 0.05)。筛选并构建3个CRGs的预后模型,包括CDKN2A、DLAT和LIPT1。高风险组和低风险组的生存时间存在显著差异(P < 0.001)。风险评分是预后不良的独立危险因素(P < 0.001)。
结论基于TCGA数据库数据构建CRGs的HCC患者预后模型,可为评估HCC患者的预后提供思路。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo construct a prognostic model for cuprotosis-related genes (CRGs) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
MethodsDifferential expression of CRGs in HCC was analyzed on the basis of datasets from the TCGA database. The potential mechanisms of CRGs and their related genes in HCC were explored through GO and KEGG enrichment analyses. The prognostic value of the CRGs was evaluated through Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, and the relationship between CRG expression and immune cell infiltration was investigated. CRGs significantly correlated with prognosis in patients with HCC were identified. A prognostic model was established through univariate, Lasso regression, and multivariate Cox regression analyses. The patients were divided into two groups by risk score. ROC curve was used in evaluating the prognostic model. The relationship of risk score or clinical factors with prognosis was analyzed through univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses.
ResultsA total of 11 differentially expressed CRGs in HCC were obtained. The main enriched GO item of CRGs and their related genes was oxidoreductase activity, acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donors, and the main enriched KEGG pathway was carbon metabolism. The expression of CRGs was significantly correlated with pDC, T helper cells and other immune cells (P < 0.05). Three CRGs (CDKN2A, DLAT, and LIPT1) were screened and a prognostic model was constructed. There was significant difference in overall survival between the high- and low-risk groups (P < 0.001). The risk score is an independent risk factor for poor prognosis (P < 0.001).
ConclusionThe prognostic model for CRGs in patients with HCC is constructed using TCGA database data. This model may be used in evaluating patient prognosis.
-
Key words:
- Cuprotosis /
- Hepatocellular carcinoma /
- TCGA database /
- Prognosis model
-
0 引言
晚期肺癌患者5年生存率仅5%,但若能在早期诊断并治疗,5年存活率可达57%[1-2]。因此,结合肺癌危险因素及其临床特征建立肺癌危险度预测模型对早期诊断及治疗肺癌,提高患者5年生存率具有重要意义。近年来,数据挖掘技术已经在生物医学预测模型中得到广泛应用。人工神经网络(artificial neural network, ANN)具有良好的鲁棒性、高容错性和较强的归纳能力,而C5.0算法作为决策树模型的常用算法之一,适用于分类变量和大数据集[3]。因此,该研究拟将肺癌常见危险因素与临床症状相结合,采用C5.0决策树与ANN构建肺癌危险度预测模型,并评价两模型的性能优劣,为肺癌早期筛查及临床辅助诊断提供依据和工具。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
收集2014年10月至2016年10月郑州大学第一附属医院的住院患者样本420例,其中包括肺癌患者180例,肺良性疾病患者240例。入组患者均知情同意并自愿参加。
入选标准:肺癌组:以《中华医学会肺癌临床诊疗指南(2019版)》为标准[4],经病理学或细胞学被证实为原发性肺癌患者;肺良性疾病组:由郑州大学第一附属医院诊断为肺部良性病变患者。排除标准:(1)入组前曾接受放化疗、药物治疗或手术治疗者;(2)主要脏器功能衰竭患者;(3)合并肺或其他恶性肿瘤患者;(4)妊娠或哺乳期患者;(5)不同意入组者。
1.2 观察指标
调查人员经过统一培训后,通过问卷访谈形式对患者进行调查询问获得数据资料,包括流行病学资料(疾病诊断、年龄、吸烟史、饮酒史、粉尘接触史、输血史、肺癌家族史、炎性反应史)和临床症状(咳嗽、咳痰、痰中带血、咯血、胸闷、胸痛、心慌、乏力、畏寒、发热出汗)。其中年龄根据《中华医学会肺癌临床诊疗指南(2019版)》以45岁为界限进行分组。总数据集包括18个定性变量(17个预测变量和1个因变量),因变量为诊断结果,各变量赋值见表 1。
表 1 肺癌危险度评价研究的变量赋值说明Table 1 Instructions of variables assignment in risk assessment studies of lung cancer
1.3 统计学方法
应用SPSS21.0对420例样本数据进行统计分析,对所有变量进行描述性统计分析,采用χ2检验进行差异分析,检验水准α=0.05。
使用SPSS Clementine 12.0软件建立两种数据挖掘预测模型,使用MedCalc15.10软件绘制受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic curve, ROC)曲线。将两组样本均按照7:3随机分为两部分,其中训练数据集包含302例样本,测试数据集包含118例样本。C5.0决策树模型和ANN模型的比较采用敏感度、特异性、准确度、阳性预测值(positive predictive values, PPV)、阴性预测值(positive and negative predictive values, NPV)、约登指数和ROC曲线下面积(area under ROC curve, AUC)进行评估。
2 结果
2.1 基本情况
420例患者中,肺癌患者180例(42.9%),肺良性疾病患者240例(57.1%)。肺良性疾病患者中小于45岁者(63.8%)明显多于肺癌组(36.2%),差异有统计学意义(P=0.004)。肺癌患者中吸烟、饮酒者(57.1%、55.7%)均多于肺良性疾病患者(42.9%、44.3%)。肺癌组有粉尘接触史或肺癌家族史者分别仅2例。肺良性疾病组中有6例有输血史,而肺癌组中没有。10个临床症状变量中,肺癌组中痰中带血(64.0%)及胸痛(55.3%)的比例高于肺良性疾病患者(36.0%、44.7%)。两组样本的基线特征分析结果见表 2。
表 2 肺癌组和肺良性疾病组的样本基线特征及卡方检验(n(%))Table 2 Baseline characteristics and chi-square test of lung cancer and lung benign disease groups (n(%))
2.2 输入变量的选择
两组间年龄(P=0.004)、吸烟史(P < 0.001)、饮酒史(P=0.028)、输血史(P=0.033)、炎症史(P < 0.001)、痰中带血(P=0.001)、胸痛(P=0.006)、乏力(P=0.049)和发热出汗(P < 0.001)9个因素差异有统计学意义,见表 2。此外由于既往研究提示粉尘接触史、癌症家族史、咳痰、咳嗽和咯血为肺癌的影响因素[4-5],该研究入选这14个因素作为输入变量建立风险预测模型。
2.3 危险度预测模型的构建与比较
2.3.1 两种风险预测模型的建立
经过训练,C5.0决策树风险预测模型的参数设置如下:Use partitioned data: no, Output type: Decision Tree, Group symbolic: no, Use boosting: yes, Cross-validate: no, Mode: expert, Pruning severity: 75, Minimum records per child brunch: 2, Use global pruning: yes, Window attributes: no, Use misclassification costs: no。ANN风险预测模型的参数设置如下:Use partitioned data: yes, Method: prune, Prevent overtraining sample: 50%, Set random seed: 321, Stop on: time (mins) 1 min, Optimize: memory, Continue training existing model: no; Use binary set encoding: yes, Show feedback graph: yes, Model selection: Use best network, Mode: expert。
2.3.2 两种危险度预测模型的性能比较
两种模型训练集和测试集样本的分类结果见表 3。在训练集与测试集样本中C5.0模型的准确率分别为68.54%和61.0%,ANN模型的准确率分别为69.5%和65.3%。可以看出ANN模型在训练集和预测集中准确度均高于C5.0模型。根据两个数据挖掘模型的ROC曲线中各危险因素对应的AUC评估各自变量对模型的影响大小,重要性前10位影响因素排序见表 4。由表可知,对模型影响最大的三个影响因素在ANN模型中分别是吸烟史、痰中带血与胸痛;而在C5.0模型中分别是吸烟史、胸痛与年龄。在ANN模型和C5.0模型中吸烟均为最主要的影响因素。
表 3 C5.0决策树和ANN模型的训练集和测试集样本分类结果Table 3 Classification results of training set and testing set samples by Decision tree C5.0 and ANN models 表 4 C5.0决策树模型和ANN模型中纳入变量的重要性排序Table 4 Importance ranking of variables in Decision tree C5.0 model and ANN model
表 4 C5.0决策树模型和ANN模型中纳入变量的重要性排序Table 4 Importance ranking of variables in Decision tree C5.0 model and ANN model
两种数据挖掘模型对肺癌综合预测性能的相关指标包括准确度、约登指数、敏感度、特异性、预测值和AUC。其中C5.0决策树模型的特异性和NPV高于ANN模型,ANN模型预测模型的准确度、约登指数、敏感度、PPV和AUC均高于C5.0决策树模型,见表 5。测试集中两种数据挖掘模型的ROC曲线可发现ANN模型预测性能优于C5.0决策树模型,见图 1。
表 5 两种数据挖掘模型的测试集结果比较Table 5 Comparison of testing set results between two data mining models
3 讨论
当前,肺癌的高发病率和高病死率已经造成巨大的公共卫生负担,利用肺癌的危险因素来预测肺癌危险度,对于肺癌的预防和早期筛查具有重要意义。本研究分别建立了C5.0决策树与ANN肺癌风险预测模型,比较发现,ANN模型预测性能优于C5.0决策树模型。
本研究按照0.05的显著性水平,单因素检验发现有9个变量与肺癌患病率呈相关关系:5个流行病学变量中年龄、吸烟史、饮酒史、炎性反应史与肺癌患病率呈正相关,输血史与肺癌患病率呈负相关;4个临床症状中痰中带血、胸痛与肺癌患病率正相关,乏力和发热出汗与肺癌患病率存在负相关关系。同时,本研究的两种数据挖掘模型中吸烟均为关键影响变量。既往研究表明肺癌常见于70岁以上人群且发病率和死亡率随年龄增加而升高,同时吸烟、饮酒以及慢性炎性反应均为肺癌的危险因素之一[5],而围手术期输血对肺癌预后和复发的影响当前研究仍不一致[6],这与本研究结果基本相符。有研究显示,遗传因素与职业性粉尘接触也是肺癌的危险因素之一[7],这与本研究结果不符。
决策树模型是一种由层次分类逐步构建的贪心算法,作为一种新兴的数据挖掘技术,它可以经过多次迭代演算后得到最优化的算法模型,具有较高的数据分析能力。相关研究已经将C5.0决策树模型用于利用基因表达数据和职业危险因素预测肺癌风险的模型建立[8-10]。C5.0算法作为决策树模型的常用算法之一,适用于分类变量和大数据集,已经在生物医学预测模型的建立中得到广泛应用。另外一些研究将C5.0决策树模型与其他多种研究进行比较,建立疾病风险预测模型,均得到C5.0决策树模型的预测性能最优的结果[11-12]。
ANN模型的数学结构模拟人类大脑的生物神经元学习动态,对输入变量经过训练产生一个加权组合的输出结果。ANN相比于一般统计学方法优势显著,具有良好的鲁棒性、高容错性和较强的归纳能力,可以快速识别线性模型、受阈值影响的非线性模型、分类模型、逐步线性模型,甚至偶然影响,故其可以确定潜在的预后影响因素[13]。已有研究将ANN应用于肺癌风险评估相关模型的构建[3, 14]。该研究结果同样显示ANN模型在准确度、敏感度、约登指数、阳性预测值、ROC曲线下面积均优于决策树模型[15-16],这与相关研究结果一致。因此,本研究建议利用ANN模型结合人群的流行病学资料和临床症状判别肺癌高危人群,为肺癌的早期诊断早期治疗提供参考依据[17]。
本研究仍然存在一定的局限性:一方面,纳入的样本量较少,如果能收集更大样本量和多中心样本资料,样本数据将具有更好的代表性,模型将具有更优异的性能;另一方面,纳入的变量种类有限,而与肺癌相关的危险因素众多且对肺癌存在交互作用,如果能纳入环境因素、职业因素、遗传因素、行为生活方式等多种研究变量,模型将更为准确可靠。因此,我们建议未来的研究应涵盖更大的样本量,纳入更为丰富的研究变量进行综合分析,同时将ANN模型应用于肺癌高危人群中筛查验证。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.作者贡献:雷青松:数据整理和分析、文献收集、撰写论文李麟:数据下载、设计实验、论文审阅 -
表 1 与肝癌预后相关的铜死亡相关基因的多因素Cox回归分析
Table 1 Multivariate Cox regression analysis for cuprotosis-related genes associated with prognosis of HCC

表 2 临床资料与危险评分的多因素Cox回归分析
Table 2 Multivariate Cox regression analysis of clinical data and risk score

-
[1] Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
[2] Moriguchi M, Aramaki T, Nishiofuku H, et al. Sorafenib versus hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy as initial treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with advanced portal vein tumor thrombosis[J]. Liver Cancer, 2017, 6(4): 275-286. doi: 10.1159/000473887
[3] Yang JD, Hainaut P, Gores GJ, et al. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 16(10): 589-604. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0186-y
[4] Yu M, Ren L, Zheng M, et al. Delayed Diagnosis of Wilson's disease report from 179 newly diagnosed cases in China[J]. Front Neurol, 2022, 13: 884840. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.884840
[5] Guo Y, Xia W, Peng X, et al. Almost misdiagnosed Menkes disease: A case report[J]. Heliyon, 2022, 8(4): e09268. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09268
[6] 李圣豪, 石新丽. 原发性肝癌中PD-L1表达的调控机制[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2021, 48(11): 1052-1058. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2021.21.0397 Li SH, Shi XL. Regulatory mechanism of PD-L1 expression in primary liver cancer[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2021, 48(11): 1052-1058. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2021.21.0397
[7] 黄乾荣, 张玲. 原发性肝癌治疗研究新进展[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2016, 32(14): 2275-2278. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2016.14.008 Huang QR, Zhang L. Advances in the treatment of primary liver cancer[J]. Shi Yong Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2016, 32(14): 2275-2278. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2016.14.008
[8] Li Y. Copper homeostasis: Emerging target for cancer treatment[J]. IUBMB Life, 2020, 72(9): 1900-1908. doi: 10.1002/iub.2341
[9] Shanbhag VC, Gudekar N, Jasmer K, et al. Copper metabolism as a unique vulnerability in cancer[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res, 2021, 1868(2): 118893. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118893
[10] Ge EJ, Bush AI, Casini A, et al. Connecting copper and cancer: from transition metal signalling to metalloplasia[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2022, 22(2): 102-113. doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00417-2
[11] Tawari PE, Wang Z, Najlah M, et al. The cytotoxic mechanisms of disulfiram and copper(ii) in cancer cells[J]. Toxicol Res (Camb), 2015, 4(6): 1439-1442. doi: 10.1039/c5tx00210a
[12] Li Y, Wang LH, Zhang HT, et al. Disulfiram combined with copper inhibits metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma through the NF-κB and TGF-β pathways[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22(1): 439-451. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13334
[13] Nirmala JG, Lopus M. Cell death mechanisms in eukaryotes[J]. Cell Biol Toxicol, 2020, 36(2): 145-164. doi: 10.1007/s10565-019-09496-2
[14] Tsvetkov P, Coy S, Petrova B, et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins[J]. Science, 2022, 375(6586): 1254-1261. doi: 10.1126/science.abf0529
[15] Gao W, Huang Z, Duan J, et al. Elesclomol induces copperdependent ferroptosis in colorectal cancer cells via degradation of ATP7A[J]. Mol Oncol, 2021, 15(12): 3527-3544. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13079
[16] Skrott Z, Mistrik M, Andersen KK, et al. Alcohol-abuse drug disulfiram targets cancer via p97 segregase adaptor NPL4[J]. Nature, 2017, 552(7684): 194-199. doi: 10.1038/nature25016
[17] Tsvetkov P, Detappe A, Cai K, et al. Mitochondrial metabolism promotes adaptation to proteotoxic stress[J]. Nat Chem Biol, 2019, 15(7): 681-689. doi: 10.1038/s41589-019-0291-9
[18] Soma S, Latimer AJ, Chun H, et al. Elesclomol restores mitochondrial function in genetic models of copper deficiency[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2018, 115(32): 8161-8166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1806296115
[19] 孙明明, 乔亚亚, 李垒垒, 等. 二氢硫辛酰转乙酰基酶通过乙酰化磷酸葡糖酸脱氢酶促进核酸合成[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2021, 37(3): 339-346. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWHZ202103009.htm Sun MM, Qiao YY, Li LL, et al. Dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase promotes nucleic acid synthesis by controlling phosphogluconate dehydrogenase acetylation[J]. Zhongguo Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Fen Zi Sheng Wu Xue Bao, 2021, 37(3): 339-346. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWHZ202103009.htm
[20] Sun J, Li J, Guo Z, et al. Overexpression of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase E1α Subunit Inhibits Warburg Effect and Induces Cell Apoptosis Through Mitochondria-Mediated Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma[J]. Oncol Res, 2019, 27(4): 407-414. doi: 10.3727/096504018X15180451872087
[21] 曹俊, 柏斗胜, 金圣杰, 等. 谷氨酰胺酶1介导主穹隆蛋白表达调控肝内胆管癌细胞对5-氟尿嘧啶化疗敏感性的研究[J]. 中华普通外科杂志, 2019, 28(3): 248-252. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11117-1020051370.htm Cao J, Bai DS, Jin SJ, et al. Glutamine 1 regulates the chemosensitivity of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells to 5-FU by targeting major vault protein[J]. Zhonghua Pu Tong Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2019, 28(3): 248-252. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11117-1020051370.htm
[22] Lv H, Liu X, Zeng X, et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Cuproptosis-Related Genes in Immune Infiltration and Prognosis in Melanoma[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 930041. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.930041
[23] Arnoff TE, El-Deiry WS. MDM2/MDM4 amplification and CDKN2A deletion in metastatic melanoma and glioblastoma multiforme may have implications for targeted therapeutics and immunotherapy[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2022, 12(5): 2102-2117.
[24] Lee DY, Kim EH. Therapeutic Effects of Amino Acids in Liver Diseases: Current Studies and Future Perspectives[J]. J Cancer Prev, 2019, 24(2): 72-78. doi: 10.15430/JCP.2019.24.2.72
[25] An J, Ha EM. Extracellular vesicles derived from Lactobacillus plantarum restore chemosensitivity through the PDK2-mediated glucose metabolic pathway in 5-FU-resistant colorectal cancer cells[J]. J Microbiol, 2022, 60(7): 735-745. doi: 10.1007/s12275-022-2201-1
[26] 尤晓昕, 张丹, 李尔广. 氨基酸代谢重编程在肿瘤发生发展及免疫治疗中的作用[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报, 2021, 43(9): 1846-1852. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBZZ202109016.htm You XX, Zhang D, Li EG. Amino acid metabolic reprogramming in tumorigenesis and development and its role in immunotherapy[J]. Zhongguo Xi Bao Sheng Wu Xue Xue Bao, 2021, 43(9): 1846-1852. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBZZ202109016.htm
[27] Hirschfield GM, Gershwin ME. The immunobiology and pathophysiology of primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2013, 8: 303-330. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-020712-164014
[28] Edwards DN, Ngwa VM, Raybuck AL, et al. Selective glutamine metabolism inhibition in tumor cells improves antitumor T lymphocyte activity in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. J Clin Invest, 2021, 131(4): e140100. doi: 10.1172/JCI140100
[29] Wang J, Peng C, Dai W, et al. Exploring Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Its Associations With Molecular Characteristics in Melanoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 821578. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.821578
[30] Liu H, Jia S, Guo K, et al. INK4 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors as potential prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Biosci Rep, 2022, 42(7): BSR20221082. doi: 10.1042/BSR20221082
[31] Luo JP, Wang J, Huang JH. CDKN2A is a prognostic biomarker and correlated with immune infiltrates in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Biosci Rep, 2021, 41(10): BSR20211103. doi: 10.1042/BSR20211103
[32] Zhang C, Feng S, Tu Z, et al. Sarcomatoid hepatocellular carcinoma: From clinical features to cancer genome[J]. Cancer Med, 2021, 10(18): 6227-6238. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4162
[33] Boerner T, Drill E, Pak LM, et al. Genetic Determinants of Outcome in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 74(3): 1429-1444. doi: 10.1002/hep.31829
[34] 王婷, 李春晓, 南鹏, 等. 基于多数据库分析代谢相关基因DLAT在结直肠癌中的表达及其临床意义[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2019, 44(4): 311-317. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFJY201904008.htm Wang T, Li CX, Nan P, et al. Analysis of metabolic associated gene DLAT expression in colorectal cancer based on multi-database and its clinical significance[J]. Jiefangjun Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2019, 44(4): 311-317. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFJY201904008.htm
[35] Goh WQ, Ow GS, Kuznetsov VA, et al. DLAT subunit of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is upregulated in gastric cancerimplications in cancer therapy[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2015, 7(6): 1140-1151.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 黄普超,原慧洁,张桂芳. 基于数据挖掘技术的肺癌危险度预测模型的构建. 实用预防医学. 2022(11): 1390-1394 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: