Transcriptomic Effects of LINC01614 on Lung Cancer A549 Cells and Relevance of Drug Resistance
-
摘要:目的
研究LINC01614在非小细胞肺癌A549细胞中的生物学作用及其耐药相关机制。
方法采用CRISPR/Cas9技术构建敲除LINC01614的A549细胞模型。对敲除LINC01614的A549细胞进行转录组测序。对转录组差异基因MCAM和ABCC3进行基因水平的验证。对MCAM进行蛋白水平的验证。检测不同浓度顺铂作用下,敲除LINC01614后的A549细胞IC50变化。检测敲除LINC01614对A549细胞迁移能力的影响。
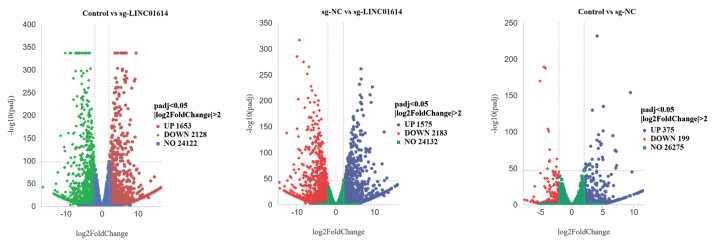
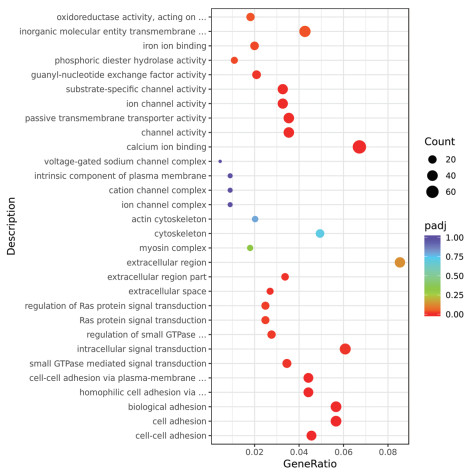
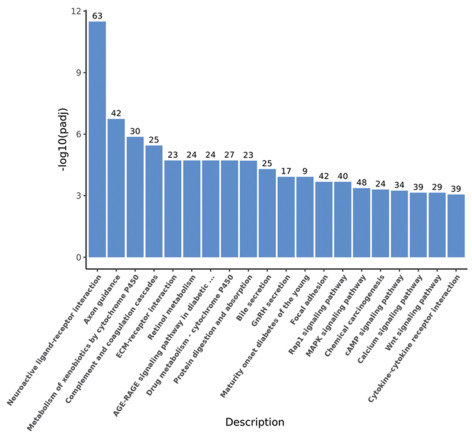
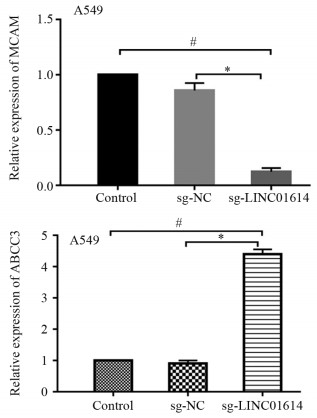
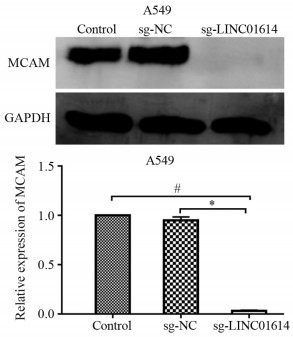
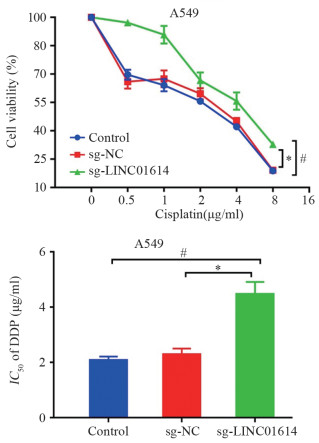
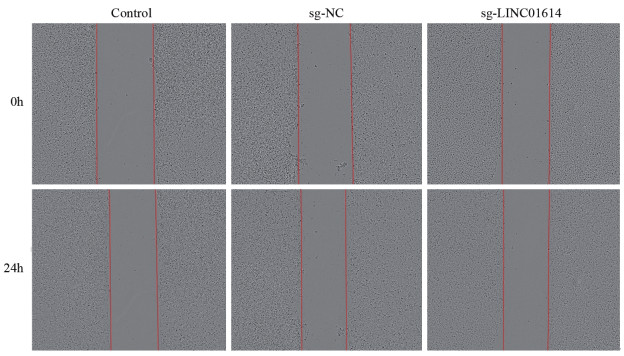
结果差异基因表达分析结果显示,敲除LINC01614后,共得到2 713个DEGs,其中上调基因1 626个,下调基因1 087个。GO分析结果显示,DEGs与细胞内信号转导、细胞黏附等有关。KEGG分析结果显示,DEGs与Wnt信号通路、TGF-β信号通路以及Rap1信号转导途径等有关。从DEGs中选择耐药相关基因ABCC3与MCAM进行验证,qRT-PCR结果显示,敲除LINC01614后,MCAM在A549细胞上的表达显著下调(P<0.05),ABCC3在A549细胞上的表达显著上调(P<0.05)。敲除LINC01614后,A549细胞中MCAM的蛋白表达量显著下降(P<0.05);A549细胞对顺铂的IC50显著上升(P<0.05);A549细胞的划痕愈合率显著降低(P<0.05)。
结论LINC01614可能与A549细胞的增殖、侵袭以及凋亡通路有关。LINC01614可能通过MCAM来发挥其自身的迁移能力以及通过ABCC3发挥对顺铂的化疗耐药性。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the biological role of LINC01614 in non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells and its drug resistance-related mechanism.
MethodsThe CRISPR/Cas9 technology was used to construct the A549 cell model with knockdown of LINC01614. Transcriptome sequencing was performed on A549 cells knocked down with LINC01614. We validated the transcriptomic differential genes MCAM and ABCC3 at the gene level and MCAM at the protein level, detected the IC50 changes of A549 cells after knockdown of LINC01614 under the effect of different concentrations of cisplatin, and detected the effect of knockdown of LINC01614 on the migration ability of A549 cells.
ResultsOf the 2 713 DEGs after knockdown of LINC01614, a total of 1 626 genes were up-regulated and 1, 087 genes were down-regulated. GO analysis showed that DEGs were associated with intracellular signaling, cell adhesion, and so on. Meanwhile, the KEGG analysis showed that DEGs were associated with the Wnt signaling pathway, TGF-β signaling pathway, and Rap1 signaling pathway. Selection of drug resistance-associated gene ABCC3 from DEGs for validation with MCAM: qRT-PCR results showed that knockdown of LINC01614 significantly down-regulated the expression of MCAM (P<0.05) and upregulated the expression of ABCC3 on A549 cells (P<0.05). After knockdown of LINC01614, the protein expression of MCAM, was significantly decreased in A549 cells (P<0.05); the IC50 of A549 cells to cisplatin was significantly increased (P<0.05); and the scratch healing rate of A549 cells was also significantly decreased (P<0.05).
ConclusionLINC01614 may be associated with the proliferation, invasion, and apoptotic pathways of A549 cells. In addition, LINC01614 may exert its migration ability through MCAM and chemoresistance to cisplatin through ABCC3.
-
Key words:
- LINC01614 /
- Non-small cell lung cancer /
- Transcriptome sequencing /
- Cisplatin /
- Drug resistance
-
0 引言
甲状腺癌作为最常见的恶性内分泌肿瘤,发病率逐年提高,2018年东亚地区的年龄标准化发病率为男性5.3/10万、女性18.1/10万[1]。超声弹性成像技术的应用可以发现微小甲状腺癌,能更好地鉴别良性结节,从而提高了甲状腺癌的检出水平[2]。甲状腺癌的治疗目前仍以手术为主。2007年Kang等[3]首次行达芬奇机器人甲状腺手术,从此微创甲状腺手术进入新的时代。甲状腺癌淋巴结转移是甲状腺癌远处转移和复发的高危因子,因此甲状腺癌手术中淋巴结的清扫显得尤为重要[4]。甲状腺癌术后并发症主要包括喉返神经的损失和甲状旁腺功能的减退,其对患者术后生活质量有明显影响。如何在彻底清扫淋巴结的同时有效保护喉返神经与甲状旁腺、预防术后肿瘤复发及并发症发生,一直是甲状腺手术的热点。因纳米碳示混悬液淋巴结染色明显,性能稳定,毒副作用小,作为一种示踪剂已广泛应用于甲状腺癌+淋巴结清扫术中,在传统开放手术及腔镜手术中的作用已有诸多报道[5-6],而在达芬奇机器人甲状腺手术中的临床应用价值未见明确报道。本研究回顾性分析纳米碳示踪剂在达芬奇甲状腺癌手术中对淋巴结的识别效果及对甲状旁腺、喉返神经的保护作用。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
将2017年9月—2019年2月于解放军联勤保障部队第940医院普外科行达芬奇甲状腺乳头状癌根治术(甲状腺全切除+双侧中央区淋巴结清扫)的60例患者纳入研究,采用随机数字表法分组,30例术中应用纳米碳示踪剂的患者纳入研究组,30例未应用纳米碳,仅行常规达芬奇甲状腺癌根治术的患者纳入对照组。纳入标准:(1)初次手术患者;(2)术前未行放化疗及免疫治疗;(3)未合并其他甲状腺病史;(4)术前检查提示肿瘤位于甲状腺包膜内,未提示颈侧淋巴结转移及未达到cN1b期;(5)肿瘤直径≤2.0 cm;(6)BMI指数≤25;(7)术前血钙及甲状旁腺水平正常;(8)术前患者发声正常,纤维电子喉镜检查见声带正常;(9)术后病理活检证实为甲状腺乳头状癌;(10)充分告知患者及家属纳米碳示踪剂的相关事宜,由患者及家属自行决定是否使用。排除标准:(1)合并严重的基础疾病;(2)未达R0切除标准;(3)因肿瘤囊内出血或其他原因行急诊手术;(4)临床病理资料不全。本研究患者均签署知情同意书,并经医院伦理会审查通过,符合《赫尔辛基宣言》。本研究使用纳米碳示踪剂(卡纳琳)购于重庆莱美制药公司。
1.2 手术及纳米碳注射方法
本研究手术由具有达芬奇手术资质的高级别医生按照2016年《机器人手术系统辅助甲状腺和甲状旁腺手术专家共识》行手术操作[7]。选择双侧乳房及右侧腋窝下为入路。将稀释后的罗哌卡因+肾上腺素注入预定径路皮下,再用分离棒沿预定径路建立手术隧道。在左右乳晕及右侧腋窝取切口依次置入12 mm(主操作孔)、10 mm(观察孔)、5 mm(辅助操作孔)Trocar,连机械臂及CO2气体,游离颈前肌、颈阔肌间隙,形成手术空间。从颈白线处切开颈前筋膜,用U型甲状腺特制拉钩拉开颈前肌,见图 1,以方便完整暴露甲状腺。研究组皮试针抽取纳米碳示踪剂0.2 ml,经皮肤刺入,斜行注入甲状腺组织,避开肿瘤进行注射,深度约0.5 cm,同时回抽以防注入血管中,在注射后用纱布压迫注射点防止纳米碳外渗使周围组织染黑,影响术野,见图 2。等待约5~10 min确定中央区淋巴结染黑后继续手术。后续操作亦遵循2016年《机器人手术系统辅助甲状腺和甲状旁腺手术专家共识》,术中原位暴露喉返神经、甲状旁腺,见图 3~4。中央区淋巴结清扫范围上下分别是舌骨下缘、胸骨上缘,两侧是颈动脉鞘内缘。
1.3 观察指标
(1)病理学检查记录Ⅵ区总淋巴结检出数、阳性淋巴结数、甲状旁腺误切数;(2)测定所有患者术前1天、术后连续2天血钙及PTH水平,术后2天内任一次血钙低于2.2 mmol/L即认定为暂时性低钙血症、任一次PTH低于15 ng/L(正常值15~65 ng/L)即认定为暂时性甲状旁腺功能减退,如出现上述情况给以补充钙剂+骨化三醇治疗,术后6月再次测定血钙及PTH水平,若仍低于正常,即认定为永久性低钙血症或永久性甲状旁腺功能减退;(3)术后行纤维电子喉镜检查声带活动情况及位置,结合患者发声质量(是否声音嘶哑、发声无力)来判断喉返神经是否受损,如喉返神经受损则给以营养神经治疗,6月后复查,如声带情况未恢复即认定为永久性喉返神经损伤。
1.4 统计学方法
所有数据均应用SPSS22.0软件进行统计描述与推断,其中服从正态或近似正态分布的计量资料以均值±标准差(x±s)表示,组间方差齐者比较采用两独立样本t检验,组间方差不齐者比较采用校正t检验;不符合正态分布的计量资料以中位数与四分位数(M(X25, X75))表示,组间比较采用Wilcoxon秩和检验;计数资料以构成比或率(%)表示,组间比较采用卡方检验或Fisher精确检验。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 一般情况
两组甲状腺癌患者在年龄、性别、BMI指数、肿瘤大小、肿瘤多灶与否、手术时长等差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),见表 1。
表 1 两组甲状腺癌患者一般资料比较Table 1 Comparison of general data of thyroid carcinoma patients between two groups
2.2 术后标本情况
研究组标本中共清扫淋巴结数目247枚,其中阳性淋巴结数目99枚;对照组标本中共清扫淋巴结数目173枚,其中阳性淋巴结数目65枚。研究组Ⅵ区总淋巴结检出率和阳性淋巴结检查率较对照组为优,差异有统计学意义(均P < 0.05),见表 2。
表 2 两组甲状腺癌患者术后标本Ⅵ区淋巴结检出与甲状旁腺误切情况Table 2 Lymph node detection and mistaken dissection of parathyroid gland in area Ⅵ of two groups
研究组总清扫的247枚淋巴结中,淋巴结染黑率为93.1%(230/247),染黑淋巴结转移率为42.2%(97/230);淋巴结未染黑率为6.9%(17/247),未染黑淋巴结转移率为11.8%(2/17),染黑淋巴结较未黑染淋巴结转移率高,差异有统计学意义(χ2=6.327, P=0.012)。
2.3 手术前后血钙及PTH水平
两组术前1天血钙及PTH水平相当,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);但研究组术后1、2天血钙及PTH水平均较对照组高,两者差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05);术后6月两组血钙及PTH水平差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),见表 3。
表 3 两组甲状腺癌患者手前、术后血钙及PTH水平(x±s)Table 3 Serum calcium and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels before and after operation in two groups(x±s)
2.4 术后并发症发生情况
术后研究组暂时性低血钙症发生率低于对照组,但差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);研究组暂时性甲状旁腺功能减退发生率低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);研究组未发生永久性低血钙症和永久性甲状旁腺功能减退,对照组发生永久性低血钙症和永久性甲状旁腺功能减退1例(为同一病患),但差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。
研究组暂时性喉返神经损伤发生率低于对照组,但差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);研究组未发生永久性喉返神经损伤,对照组发生永久性喉返神经损伤1例(3.3%),但差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),见表 4。
表 4 两组甲状腺癌患者术后并发症发生情况(n(%))Table 4 Postoperative complications in two groups (n(%))
3 讨论
3.1 纳米碳混悬液及甲状腺术式
淋巴结清扫是恶性肿瘤手术的关键环节,如何将其清扫彻底并保证安全性一直是研究的热点,淋巴结示踪剂就因此诞生。作为第三代淋巴结示踪剂,纳米碳团粒平均直径约为150 nm,可以通过毛细淋巴管的内皮间隙(平均直径120~500 nm),却不能通过毛细血管的内皮间隙(平均直径20~50 nm)。故纳米碳团粒难以进入血管却可很快进入淋巴管,之后巨噬细胞将其吞噬,使其高度集聚于淋巴结,导致淋巴结被染黑。因为其染色原理,加之其颗粒相较前两代淋巴结示踪剂更加均匀,所以染色更加迅速,染色特异性更加明显。在多项动物实验中,纳米碳示踪剂未表现出明显的毒副作用和致癌性[8-9],安全性得到进一步验证。目前,纳米碳已较为普遍的应用于胃、结肠、直肠、乳腺、甲状腺等多种肿瘤的诊治中[10-14]。
甲状腺乳头状癌是最常见的分化型甲状腺癌,手术治疗仍为首选,与后续的I131、TSH抑制治疗形成综合性个体化治疗。关于甲状腺癌手术切除范围目前国内外还未达成统一共识,但根据我国2012年《甲状腺结节和分化型甲状腺癌诊治指南》及解放军联勤保障部队第940医院的病患情况行甲状腺全/近全切者占较大多数。关于术前检查及术中探查未发现明显颈部淋巴结转移者(cN0期)是否行预防性淋巴结清扫,也尚在争论中。颈部淋巴结转移是甲状腺乳头状癌复发的独立危险因素[15],而颈部淋巴结转移多发生在中央区。有术前及术中未发现明显淋巴结转移者行预防性中央区淋巴结清扫后病理活检却证实转移的报道[16]。本研究中两组患者均行达芬奇甲状腺癌全切+中央区淋巴结清扫。作为当前最先进的内窥镜系统,达芬奇机器人可将视野放大10~15倍并产生立体感,加之机械臂可滤除术者双手抖动及关节的灵活转动,有利于术者于窄小空间进行精细稳定的操作。达芬奇机器人手术可以做到精细解剖以及清晰的视野,更容易看清甲状旁腺及喉返神经,避免对其造成牵拉、烧灼、切割等伤害以及破坏甲状旁腺血流供应,从而充分保护甲状旁腺及喉返神经[17]。那么在达芬奇甲状腺癌根治术清扫Ⅵ区淋巴结的过程中应用纳米碳示踪剂可否更好保护甲状旁腺及喉返神经?2016年《机器人手术系统辅助甲状腺和甲状旁腺手术专家共识》推荐在手术过程中应用纳米碳识别淋巴结和甲状旁腺,但未提及纳米碳对保护喉返神经是否有意义。
3.2 Ⅵ区淋巴结清扫
在本研究中,研究组总淋巴检出率及阳性淋巴结检出率均高于对照组(P < 0.05),表明使用纳米碳示踪剂对于达芬奇甲状腺手术淋巴结的清扫是有意义的。这可能与术中应用纳米碳使组织对比更加明显并使微小淋巴结染黑,手术医师可以更精确地进行淋巴结的彻底清扫同时不遗漏小的淋巴结有关,也为术后黑染的淋巴结标本提供了更好的指示,病理科医师可以找到更多淋巴结有关。在单独分析研究组的淋巴结染色情况时,笔者发现总清扫的淋巴结中有17枚淋巴结并未染黑,其中1枚甚至直径达3 mm,而且其中有两枚是转移的淋巴结。这提示使用纳米碳并不能指示所有淋巴结,而且未染黑的淋巴结中也可能有转移淋巴结,之前文献也有类似报道[18],但染黑淋巴结较未染黑淋巴结转移率高。因此,达芬奇甲状腺癌手术使用纳米碳示踪剂不意味我们可以仅清扫黑染的淋巴结,仍需行Ⅵ区常规彻底的淋巴结清扫术,纳米碳示踪剂在其中起辅助作用,而手术医师的经验、技术更为重要。
3.3 甲状旁腺与喉返神经的保护作用
如今在甲状腺手术后的并发症中,甲状旁腺损伤已取代喉返神经,成为首要关注问题。甲状腺手术后出现低钙血症和低PTH提示甲状旁腺损伤可能。甲状腺癌手术容易损伤甲状旁腺的原因如下:(1)甲状旁腺质地、颜色与脂肪、淋巴组织差异性不大;(2)甲状旁腺位置变异性较大,可以位于甲状腺包膜内外,甚至包裹于甲状腺中,而且由于甲状腺肿瘤的增大压迫,更易造成甲状旁腺位置移位;(3)甲状腺全切+淋巴结清扫的过程中如未精细解剖,容易损坏甲状旁腺滋养血管。王猛等[19]报道650例达芬奇甲状腺手术后甲状旁腺功能暂时性低下发生率为18.46%。Liu等[20]报道行500例机器人甲状腺手术后甲状旁腺暂时性和永久性低下的发病率各为18.8%及2.1%。
本研究中研究组和对照组甲状旁腺误切率各为3.3%及10.0%,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),考虑与研究样本数量较少有关,而且当手术医师经验、技术较好时,即使不使用纳米碳示踪剂也可避免误切甲状旁腺。甲状旁腺误切与血钙及PTH并不是完全相关,因为甲状旁腺损伤不只是甲状旁腺的切除,也可以是电灼、切割的伤害及甲状旁腺血供的破坏。所以两组术后1、2天血钙、PTH水平及暂时性甲状旁腺功能减退有明显统计学差异是可以解释的(P < 0.05),这也证明了使用纳米碳对保护甲状旁腺有一定作用。但两组术后暂时性低钙血症发生率差异无统计学意义,这可能与术后补钙有关。术后6月血钙、PTH水平、永久性甲状旁腺功能减低发生率差异无统计学意义,这可能有如下原因:(1)甲状旁腺损伤后绝大部分病患经或未经治疗甲状旁腺功能均能恢复,永久性甲状旁腺功能低下发生率极低;(2)本研究入组样本数量较少。
喉返神经损伤是甲状腺手术的另一常见并发症。Chen等[21]认为甲状腺癌手术中常规暴露喉返神经可有效预防喉返神经损伤。本研究中两组术中均常规原位暴露喉返神经。而两组术后暂时性喉返神经损伤各为3.3%及10.0%,研究组未发生永久性喉返神经损伤,对照组永久性喉返神经损伤3.3%,差异均无统计学意义。这与部分学者[22-23]的研究结果一致。但也有学者认为纳米碳对于甲状腺癌手术中喉返神经具有保护价值[24]。
综上所述,达芬奇甲状腺癌手术中使用纳米碳混悬液,有利于彻底清扫中央区淋巴结,同时可以减少甲状旁腺的损伤,有效保护甲状旁腺,但对于喉返神经无肯定保护作用。但本研究样本量较少,考虑今后继续积累病例资料,同时做好随访工作,在本研究的基础上对纳米碳示踪剂对于肿瘤复发及生存预后影响进行大样本量统计分析。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。作者贡献:白钰明:研究设计、实验实施和论文撰写李 金:实验实施施琳、贾永峰:查阅文献、提出修改建议刘 霞:数据分析云 芬:实验指导和论文审校 -
表 1 引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences

-
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2022, 72(1): 7-33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21708
[2] Friedlaender A, Addeo A, Russo A, et al. Targeted Therapies in Early Stage NSCLC: Hype or Hope[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(17): 6329. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176329
[3] Liu Z, Han L, Yu H, et al. LINC01619 promotes non-small cell lung cancer development via regulating PAX6 by suppressing microRNA-129-5p[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2020, 2(6): 2538-2553.
[4] Xing C, Sun SG, Yue ZQ, et al. Role of lncRNA LUCAT1 in cancer[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 134: 111158. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111158
[5] Gao Y, Shang S, Guo S, et al. Lnc2Cancer 3.0: an updated resource for experimentally supported lncRNA/circRNA cancer associations and web tools based on RNA-seq and scRNA-seq data[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2021, 49(D1): D1251-D1258. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1006
[6] Tripathi SC, Fahrmann JF, Celiktas M, et al. MCAM Mediates Chemoresistance in Small-Cell Lung Cancer via the PI3K/AKT/SOX2 Signaling Pathway[J]. Cancer Res, 2017, 77(16): 4414-4425. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2874
[7] Chandra F, Tania TF, Nurcahyanti ADR. Bixin and Fuxoxanthin Alone and in Combination with Cisplatin Regulate ABCC1 and ABCC2 Transcription in A549 Lung Cancer Cells[J]. J Pharm Bioallied Sci, 2023, 15(1): 15-20. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_50_23
[8] Zhang F, Wang J, Wang X, et al. CD146-mediated acquisition of stemness phenotype enhances tumour invasion and metastasis after EGFR-TKI resistance in lung cancer[J]. Clin Respir J, 2019, 13(1): 23-33. doi: 10.1111/crj.12976
[9] Wang Q, Li K, Li X. Knockdown of LncRNA LINC00958 Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of NSCLC Cells by MiR-204-3p/KIF2A Axis[J]. Cell Transplant, 2021, 30: 9636897211025500.
[10] Liang H, Peng J. LncRNA HOTAIR promotes proliferation, invasion and migration in NSCLC cells via the CCL22 signaling pathway[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(2): e0263997. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263997
[11] Hua Q, Mi B, Xu F, et al. Hypoxia-induced lncRNA-AC020978 promotes proliferation and glycolytic metabolism of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating PKM2/HIF-1α axis[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(11): 4762-4778. doi: 10.7150/thno.43839
[12] Geng Q, Li Z, Li X, et al. LncRNA NORAD, sponging miR-363-3p, promotes invasion and EMT by upregulating PEAK1 and activating the ERK signaling pathway in NSCLC cells[J]. J Bioenerg Biomembr, 2021, 53(3): 321-332. doi: 10.1007/s10863-021-09892-6
[13] Zhao X, Jin X, Zhang Q, et al. Silencing of the lncRNA H19 enhances sensitivity to X-ray and carbon-ions through the miR-130a-3p/WNK3 signaling axis in NSCLC cells[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2021, 21(1): 644. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02268-1
[14] 郑建洲, 白煜, 戚春建. LncRNA FENDRR通过调控ERK/MAPK影响肺鳞癌H226细胞增殖、迁移和凋亡[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2022, 49(6): 563-568. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2022.21.1193 Zheng JZ, Bai Y, Qi CJ. LncRNA FENDRR Affect Proliferation, Migration and Apoptosis of Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma H226 Cells via ERK/MAPK Signaling Pathway[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2022, 49(6): 563-568. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2022.21.1193
[15] Zhen Q, Gao LN, Wang RF, et al. LncRNA DANCR Promotes Lung Cancer by Sequestering miR-216a[J]. Cancer Control, 2018, 25(1): 1073274818769849.
[16] Deng H, Qianqian G, Ting J, et al. miR-539 enhances chemosensitivity to cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting DCLK1[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 106: 1072-1081. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.024
[17] Liu AN, Qu HJ, Yu CY, et al. Knockdown of LINC01614 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell progression by up-regulating miR-217 and down-regulating FOXP1[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22(9): 4034-4044. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13483
[18] de Waart DR, van de Wetering K, Kunne C, et al. Oral availability of cefadroxil depends on ABCC3 and ABCC4[J]. Drug Metab Dispos, 2012, 40(3): 515-521. doi: 10.1124/dmd.111.041731
[19] Ramírez-Cosmes A, Reyes-Jiménez E, Zertuche-Martínez C, et al. The implications of ABCC3 in cancer drug resistance: can we use it as a therapeutic target?[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2021, 11(9): 4127-4140.
[20] Chen J, Dang Y, Feng W, et al. SOX18 promotes gastric cancer metastasis through transactivating MCAM and CCL7[J]. Oncogene, 2020, 39(33): 5536-5552. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1378-1




 下载:
下载: