-
摘要:目的
探讨cfDNA在胰腺癌中的诊断价值。
方法选取467例胰腺癌患者和129例健康对照受试者,采用QuantiDNA Direct cfDNA Test(DiaCarta)试剂盒检测cfDNA浓度。采用Mann-Whitney U检验比较不同组间cfDNA浓度差异,卡方检验分析cfDNA与胰腺癌病理资料的关系。ROC曲线评估诊断效能。
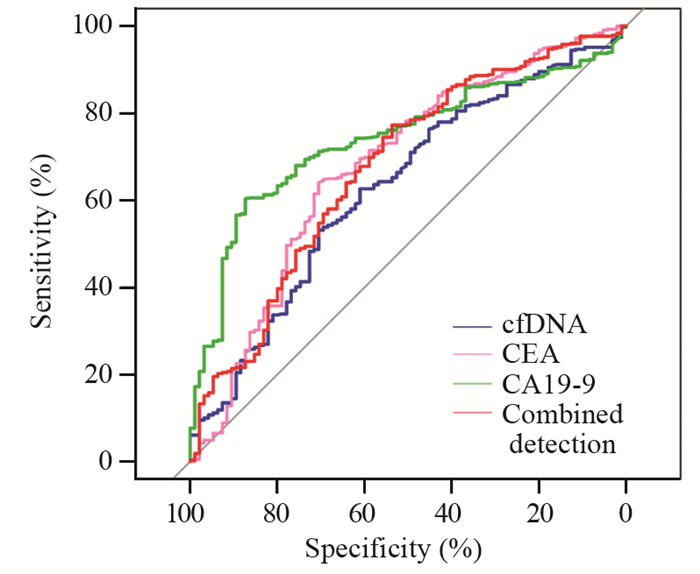
结果胰腺癌患者cfDNA水平显著高于健康对照组(20.85 vs. 15.15 ng/ml, P=0.0027)。cfDNA在胰腺癌中的阳性率高于健康对照组(77.73% vs. 59.68%)。cfDNA、CEA和CA19-9作为诊断标志物的敏感度分别为62.65%、64.04%和60.32%,特异性分别为61.05%、70.53%和87.37%。cfDNA联合检测CEA和CA19-9敏感度为77.26%,特异性为53.58%。cfDNA、CEA、CA19-9和联合检测曲线下面积分别为0.62、0.67、0.74和0.67。
结论cfDNA在胰腺癌患者中水平升高,可作为胰腺癌潜在的辅助诊断标志物。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the diagnostic value of cfDNA in pancreatic cancer.
MethodsA total of 467 patients with pancreatic cancer and 129 healthy controls were enrolled. cfDNA concentration was detected using the QuantiDNA Direct cfDNA Test (DiaCarta) kit. Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare cfDNA concentration between different groups, and Chi-square test was used to analyze the relationship between cfDNA and pathological data of pancreatic cancer. Diagnostic efficacy was evaluated by ROC analysis.
ResultsThe cfDNA level of patients with pancreatic cancer was significantly higher than that of healthy controls (20.85 vs. 15.15 ng/ml, P=0.0027). The positive rate of cfDNA in pancreatic cancer was higher than that in healthy controls (77.73% vs. 59.68%). The sensitivity levels of cfDNA, CEA, and CA19-9 as diagnostic markers were 62.65%, 64.04%, and 60.32%, and their specificity levels were 61.05%, 70.53%, and 87.37%, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of the combined detection were 77.26% and 53.58% respectively. The areas under the curve of cfDNA, CEA, CA199, and combined detection were 0.62, 0.67, 0.74, and 0.67, respectively.
ConclusioncfDNA is elevated in patients with pancreatic cancer and may serve as an effective marker for its diagnosis.
-
Key words:
- Pancreatic cancer /
- cfDNA /
- CEA /
- CA19-9 /
- Diagnosis
-
0 引言
胰腺癌(pancreatic cancer, PC)是一种常见的恶性实体肿瘤,其发病率和死亡率持续升高[1-3]。手术是胰腺癌最重要的治疗手段。由于症状不典型和缺乏有效的筛查工具,许多患者在诊断时已发展到不可切除的状态,据统计只有20%的病例可以切除病灶[4]。此外,即使在治愈性手术后,复发率也很高,且长期生存率比其他癌症短[5-6]。因此探索胰腺癌诊断和预后相关标志物对于改善胰腺癌患者预后意义重大。
液体活检利用外周循环血液代替组织标本进行检测,可提供肿瘤辅助诊断和治疗相关信息,成为近年来的研究热点。作为液体活检之一的游离DNA(cell-free DNA, cfDNA)是一类由坏死或者凋亡细胞产生的存在于体液中的DNA,在肿瘤中可由肿瘤细胞释放到血液中,因此cfDNA越来越多地引起肿瘤研究者关注[7-11]。研究显示cfDNA Stat3在乳腺癌中升高,并与肿瘤体积相关,cfDNA还可作为非小细胞肺癌患者预后的生物标志物和疗效预测指标[12-13]。此外,cfDNA检测在分析肿瘤衍生突变、肿瘤突变负担、微卫星不稳定性、突变特征和体细胞突变来源等方面提供许多信息[14]。目前有关cfDNA在胰腺癌中的应用价值探讨较少,因此本课题拟研究血浆cfDNA检测在胰腺癌中的临床价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1 资料
选取江苏省肿瘤医院2018年1月—2021年12月收治的胰腺癌患者467例以及129例健康体检者(健康对照组),其中男332例,女264例,年龄17~86岁,中位年龄62岁(53~69岁)。纳入标准:均经病理确诊为胰腺癌;均无除胰腺癌外其他恶性肿瘤;均知情同意并自愿参与本次研究;术前未行任何抗肿瘤药物治疗。排除标准:有既往肿瘤病史;有严重心、肝、肾等功能不全。收集的胰腺癌患者病理资料包括年龄、性别、肿瘤TNM分期(参照美国癌症联合委员会胰腺癌第八版分期标准)、血清CEA和CA19-9。本研究通过江苏省肿瘤医院伦理委员会批准。
1.2 方法
抽取受试者2 ml静脉全血,EDTA-K2抗凝,1 900 g离心15 min后获得血浆。使用帝基(南京)生物科技有限公司生产的QuantiDNA Direct cfDNA Test(DiaCarta)试剂盒检测cfDNA浓度,主要过程如下:在90 μl PBS中加入10 μl血浆,95℃加热10 min,然后放置冰上5 min,DNA标准品采用相同处理。配置74 μl裂解液、1 μl封闭液、4 μl人类Alu探针、捕获磁珠和0.1 μl蛋白酶K作为每孔的工作液,然后进行杂交,采用Luminex MAGPIX®仪器读取结果,操作步骤详见试剂说明书。cfDNA的Cut off值为12 ng/ml。使用Roche e 601电化学发光仪检测患者血清CEA和CA19-9水平。
1.3 统计学方法
采用Spass16.0统计软件进行数据处理。数据经正态性分布检验,偏态分布的数据采用中位数和25%~75%百分位形式显示,组间数据比较采用Mann-Whitney U检验。cfDNA与胰腺癌病理资料的关系采用卡方检验。绘制ROC曲线评估相关指标作为标志位的效能。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 cfDNA在胰腺癌和健康对照组中的水平
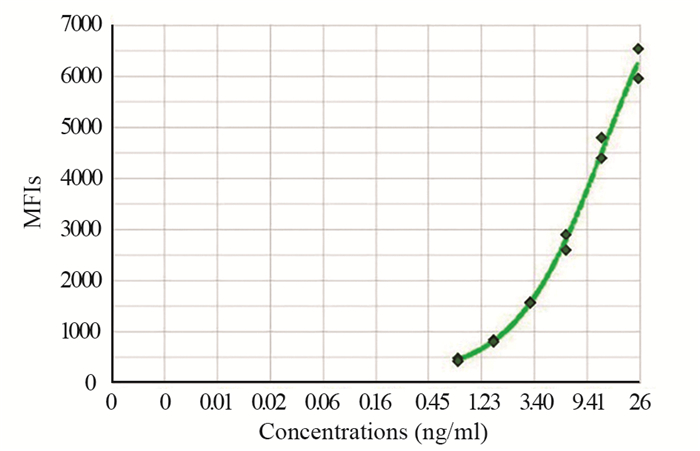
采用cfDNA检测试剂盒,建立cfDNA浓度标准曲线,见图 1。统计分析467例胰腺癌患者和129例健康对照组血浆cfDNA含量,两组均不呈正态分布,健康对照组cfDNA中位数15.15(9.65~32.48)ng/ml,胰腺癌cfDNA中位数20.85(12.9~35.96)ng/ml,差异有统计学意义(P=0.0027, Mann-Whitney U=24932)。cfDNA在胰腺癌中的阳性率为77.73%(363/467),高于健康对照组中的阳性率59.68%(77/129)。
2.2 cfDNA与胰腺癌患者病理资料的关系
分析47例病理资料完整的胰腺癌手术患者cfDNA水平和患者性别、年龄、TNM、CEA和CA19-9等病理资料关系,发现cfDNA水平与这些因素不同分组间无显著相关性,见表 1。
表 1 cfDNA与胰腺癌病理资料的关系Table 1 Relationship between cfDNA and clinicopathologic features of patients with pancreatic cancer
2.3 cfDNA作为胰腺癌诊断标志物的临床价值
cfDNA、CEA和CA19-9作为诊断标志物的敏感度分别为62.65%、64.04%和60.32%,特异性分别为61.05%、70.53%和87.37%,见表 2。cfDNA联合检测CEA和CA19-9敏感度为77.26%,特异性为53.58%。cfDNA、CEA、CA19-9和联合检测曲线下面积分别为0.62、0.67、0.74和0.67。cfDNA作为肿瘤标志物的敏感度高于CA19-9,但是特异性低于CA19-9,此三项指标联合检测敏感度得到显著提高,见图 2。
表 2 cfDNA、CEA和CA19-9作为胰腺癌诊断标志物的效能Table 2 Performance of cfDNA, CEA, and CA19-9 as pancreatic cancer biomarkers
3 讨论
胰腺癌恶性程度高,目前缺乏可靠的早期筛查方法,5年生存率仅为9%[15-16]。因此,在临床治疗中,迫切需要找到影响胰腺癌预后的生物标志物,便于对患者的预后进行评估,并通过对患者的个体化治疗来改善预后。但目前对于胰腺癌临床上缺乏特异性的生物标志物[17],常用的主要血清标志物是CEA和CA19-9,然而,它们的敏感度不够理想[18]。
近年来血浆cfDNA检测作为一种新的液态活检方法逐渐成为研究热点。肿瘤发生过程中更高的坏死和凋亡率与cfDNA浓度增加有关[19]。癌症患者cfDNA携带了肿瘤发生相关的遗传改变信息,例如DNA含量、DNA完整性、杂合性缺失及癌基因和抑癌基因的突变等,这些改变与癌症的发展、进展和对治疗的抵抗有关,为临床诊断和治疗提供了有用信息[19-22]。据报道,cfDNA片段的大小对晚期胰腺癌患者具有预后价值,较短的cfDNA片段与较差的预后有关[23]。既往研究证实突变体K-RAS可作为胰腺癌的关键驱动基因,一项对正在接受手术/化疗的晚期胰腺癌患者的研究发现突变循环K-RAS水平降低,证实了该化疗方案的有效性,循环K-RAS DNA状态的改变可以提供预测治疗反应的关键信息[24]。何建新等采用实时荧光定量PCR方法检测发现40例胰腺癌患者血浆cfDNA水平高于健康对照组[25],本研究采用SuperbDNATM技术检测596例样本,得出结果与何建新等的相符,胰腺癌患者的血浆cfDNA水平高于健康对照组。此外,结果显示cfDNA与胰腺癌病理资料之间无显著相关性,虽然cfDNA在16例胰腺癌远端转移组和31例非转移组之间差异无统计学意义,但发现5例远端转移的患者cfDNA水平较转移前显著升高。由于观察的例数过少,是否具有统计学意义还有待验证,未来需要扩大病例数进一步论证cfDNA与胰腺癌转移的关系。
CA19-9是一种低聚糖肿瘤相关抗原,在胰腺癌患者血清中升高,大量研究表明其在胰腺癌筛查、诊断、预后和疗效评估方面具有重要作用[26]。虽然CA19-9被认为是胰腺癌的早期诊断标志物,但也有报道其存在一些不足,包括诊断的敏感度和特异性较差,不能满足临床需求[27]。CEA主要用于结肠癌的诊断和疗效监测,并在约60%的胰腺癌患者血清中升高,但关于CEA在胰腺癌中的临床价值讨论较少。据报道其诊断胰腺癌的敏感度仅为30%左右,并存在非特异性结肠炎和重度吸烟等干扰因素。然而,对于诊断为胰腺癌的患者,CEA可用于评估治疗的有效性和复发监测[28]。值得注意的是,在转移性和局部进展性胰腺癌中,CEA被认为是比CA19-9更好的预测生物标志物,但在生存和早期复发方面,它的预测价值不是很理想[29]。这些肿瘤标志物单独应用时诊断效能不高,一般推荐联合检测。本研究发现CA19-9在诊断胰腺癌方面具有较高的特异性,但是敏感度不高,联合应用CA19-9、CEA和cfDNA后,敏感度显著提高。此外,到三个指标联合检测后特异性相比单个指标的特异性有所降低,这可能与采用不同的Cut off值有关。我们认为仅通过监测cfDNA浓度得到的信息有限,需要深入挖掘这些DNA突变或者DNA片段完整性等相关信息,才能充分发挥cfDNA在胰腺癌诊断和治疗监测方面的价值。
综上,肿瘤患者的cfDNA以一种液态活检形式在肿瘤诊断和治疗方面具有无创、采样方便可动态监测等特点。本研究发现cfDNA在胰腺癌患者中水平高于健康对照组,联合检测cfDNA和常规标志物可一定程度地改善胰腺癌的诊断效能。cfDNA在胰腺癌中的临床生物学价值需要更多的研究来挖掘,为胰腺癌的诊断和治疗提供更好的标志物指标。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.作者贡献:徐亦君:实验研究、数据分析和论文撰写竺明晨:实验设计、论文修改和基金来源 -
表 1 cfDNA与胰腺癌病理资料的关系
Table 1 Relationship between cfDNA and clinicopathologic features of patients with pancreatic cancer

表 2 cfDNA、CEA和CA19-9作为胰腺癌诊断标志物的效能
Table 2 Performance of cfDNA, CEA, and CA19-9 as pancreatic cancer biomarkers

-
[1] Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
[2] Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, et al. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States[J]. Cancer Res, 2014, 74(11): 2913-2921. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0155
[3] 杨欢, 王晓坤, 范金虎. 中国胰腺癌流行病学、危险因素及筛查现况[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2021, 48(10): 909-915. http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/abstract/abstract9900.shtml Yang H, Wang XK, Fan JH. Present Status of Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Screening of Pancreatic Cancer in China[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2021, 48(10): 909-915. http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/abstract/abstract9900.shtml
[4] Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012[J]. Int J Cancer, 2015, 136(5): E359-386. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29210
[5] Park W, Chawla A, O'Reilly EM. Pancreatic Cancer: A Review[J]. JAMA, 2021, 326(9): 851-862. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.13027
[6] Sánchez-Ramírez D, Medrano-Guzmán R, Candanedo-González F, et al. High expression of both desmoplastic stroma and epithelial to mesenchymal transition markers associate with shorter survival in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Eur J Histochem, 2022, 66(1): 3360.
[7] Cisneros-Villanueva M, Hidalgo-Pérez L, Rios-Romero M, et al. Cell-free DNA analysis in current cancer clinical trials: a review[J]. Br J Cancer, 2022, 126(3): 391-400. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01696-0
[8] Barney R, Stalker K, Lutes A, et al. Assessment of seminal cell-free DNA as a potential contaminate in studies of human sperm DNA methylation[J]. Andrology, 2022, 10(4): 702-709. doi: 10.1111/andr.13163
[9] Reddy T, Esmail A, Chang JC, et al. Utility of Cell-Free DNA Detection in Transplant Oncology[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2022, 14(3): 743. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030743
[10] Callesen LB, Sørensen BS, Pallisgaard N, et al. Total cell-free DNA measurement in metastatic colorectal cancer with a fast and easy direct fluorescent assay[J]. Mol Clin Oncol, 2022, 16(3): 64. doi: 10.3892/mco.2022.2497
[11] Zhao H, Zhang H, Xu W, et al. A Sight of the Diagnostic Value of Aberrant Cell-Free DNA Methylation in Lung Cancer[J]. Dis Markers, 2022, 2022: 9619357.
[12] Wang YF, Wang XJ, Lu Z, et al. Overexpression of Stat3 increases circulating cfDNA in breast cancer[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2021, 187(1): 69-80. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06142-6
[13] Zhou X, Li C, Zhang Z, et al. Kinetics of plasma cfDNA predicts clinical response in non-small cell lung cancer patients[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 7633. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85797-z
[14] Razavi P, Li BT, Brown DN, et al. High-intensity sequencing reveals the sources of plasma circulating cell-free DNA variants[J]. Nat Med, 2019, 25(12): 1928-1937. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0652-7
[15] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(1): 7-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21590
[16] McGuigan A, Kelly P, Turkington RC, et al. Pancreatic cancer: A review of clinical diagnosis, epidemiology, treatment and outcomes[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2018, 24(43): 4846-4861. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i43.4846
[17] Zhang L, Sanagapalli S, Stoita A. Challenges in diagnosis of pancreatic cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2018, 24(19): 2047-2060. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i19.2047
[18] Zhu H, Li T, Du Y, et al. Pancreatic cancer: challenges and opportunities[J]. BMC Med, 2018, 16(1): 214. doi: 10.1186/s12916-018-1215-3
[19] Lo YMD, Han DSC, Jiang P, et al. Epigenetics, fragmentomics, and topology of cell-free DNA in liquid biopsies[J]. Science, 2021, 372(6538): eaaw3616. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw3616
[20] Seton-Rogers S. Closing in on cfDNA-based detection and diagnosis[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2020, 20(9): 481. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-0293-7
[21] Zhitnyuk YV, Koval AP, Alferov AA, et al. Deep cfDNA fragment end profiling enables cancer detection[J]. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21(1): 26. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01491-8
[22] Nakamura Y, Okamoto W, Kato T, et al. Circulating tumor DNA-guided treatment with pertuzumab plus trastuzumab for HER2-amplified metastatic colorectal cancer: a phase 2 trial[J]. Nat Med, 2021, 27(11): 1899-1903. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01553-w
[23] Lapin M, Oltedal S, Tjensvoll K, et al. Fragment size and level of cell-free DNA provide prognostic information in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer[J]. J Transl Med, 2018, 16(1): 300. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1677-2
[24] Watanabe F, Suzuki K, Tamaki S, et al. Longitudinal monitoring of KRAS-mutated circulating tumor DNA enables the prediction of prognosis and therapeutic responses in patients with pancreatic cancer[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(12): e0227366. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227366
[25] 何建新, 张金锋, 王利健, 等. 血浆游离DNA含量及完整性对胰腺癌的诊断价值研究[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2017, 27(24): 3558-3560. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWJZ201724021.htm He JX, Zhang JF, Wang LJ, et al. Diagnostic value of plasma free DNA content and integrity in pancreatic cancer[J]. Zhongguo Wei Sheng Jian Yan Za Zhi, 2017, 27(24): 3558-3560. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWJZ201724021.htm
[26] Goh SK, Gold G, Christophi C, et al. Serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a mini review for surgeons[J]. ANZ J Surg, 2017, 87(12): 987-992. doi: 10.1111/ans.14131
[27] Singh S, Tang SJ, Sreenarasimhaiah J, et al. The clinical utility and limitations of serum carbohydrate antigen (CA19-9) as a diagnostic tool for pancreatic cancer and cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2011, 56(8): 2491-2496. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-1709-8
[28] Jelski W, Mroczko B. Biochemical diagnostics of pancreatic cancer-Present and future[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2019, 498: 47-51.
[29] van Manen L, Groen JV, Putter H, et al. Elevated CEA and CA19-9 serum levels independently predict advanced pancreatic cancer at diagnosis[J]. Biomarkers, 2020, 25(2): 186-193.
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 候博,陈挺,商冠宁. 负压封闭引流技术在骨与软组织肿瘤高危切口中的应用. 中国医师进修杂志. 2023(04): 301-305 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 单静,吕苏梅,李海红,刘伟. 思维导图联合回授法健康教育模式在骨与软组织肿瘤病人胸壁输液港护理中的应用. 循证护理. 2023(13): 2381-2385 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 冯颖颖,赵思,宗园. 超声造影与MRI-DWI对良恶性软组织肿瘤的诊断效能比较. 中国医药导报. 2023(25): 160-163 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 赵玲玲,张晓娟,郭倩,陈平,贾莉. 恶性骨肿瘤患者疾病感知现状及其影响因素分析. 护理实践与研究. 2023(24): 3657-3663 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王默然,王峻,李星晨,刘浩,葛艳玲. 原发性恶性骨肉瘤术中输血影响因素的回顾性研究. 中国输血杂志. 2022(01): 35-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. Yi-Ting Zhou,Ruo-Yu Wang,Yao Zhang,Dong-Yi Li,Jian Yu. Local hyperthermia combined with chemotherapy for the treatment of multiple recurrences of undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma: A case report. World Journal of Clinical Cases. 2022(09): 2916-2922 .  必应学术
必应学术
7. 方菲,原浩,韦燕. 调强放射治疗联合安罗替尼治疗转移性四肢软组织肉瘤的临床观察. 中国现代医药杂志. 2022(06): 57-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 李善武,叶永杰,王志强,银毅,孙官军. 高强度聚焦超声治疗恶性骨肿瘤的研究进展. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版). 2021(02): 231-234 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 徐婉琳,李柳宁. 李柳宁教授从虚痰瘀论治软组织肉瘤思想探析. 四川中医. 2021(10): 1-4 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 孙全球,夏国仁,詹守山,姜世峰,付宇,储彬,段瑾. 3D可视化技术在骨与软组织肿瘤个体化精准治疗中的临床应用及探索. 中国基层医药. 2021(12): 1861-1865 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 吴昕,刘家明,宋宏海,杨起坤,应辉,刘志礼. 抑制Aurora激酶B的表达可促进骨肉瘤143B细胞凋亡. 南方医科大学学报. 2020(09): 1273-1279 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 祝开忠,王挺锐,陈焕雄,陈涛,钟贞浩. 骨肉瘤中O-GlcNAc糖基转移酶的表达及其对增殖和顺铂敏感性的影响. 中国癌症杂志. 2020(09): 682-688 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)



 下载:
下载: