-
摘要:目的
探讨CENPF在非小细胞肺腺癌(LUAD)中的表达与患者临床预后的关系及其对肺腺癌细胞转移能力的影响。
方法公共数据库分析CENPF在LUAD中的表达及其与患者预后的关系。免疫组织化学染色验证CENPF LUAD在组织芯片中的表达,Kaplan-Meier分析CENPF表达与肺腺癌患者预后的关系;Cox生存风险比例回归模型分析影响患者生存的因素;卡方分析CENPF表达与患者临床病理分期及分级的关系。慢病毒敲除NCI-H2126细胞中CENPF的表达,检测细胞增殖、侵袭及迁移能力的变化。RNA-seq检测CENPF敲除后细胞mRNA表达谱改变,生物信息学分析CENPF下游信号通路及靶基因,Western blot验证下游基因表达水平变化。
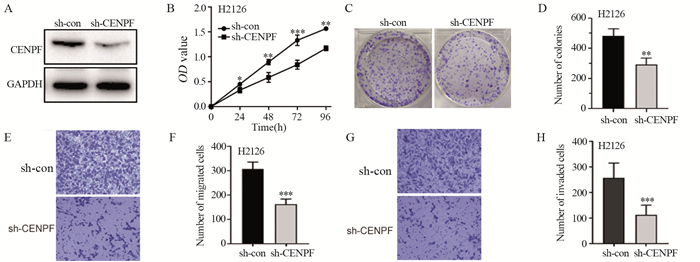
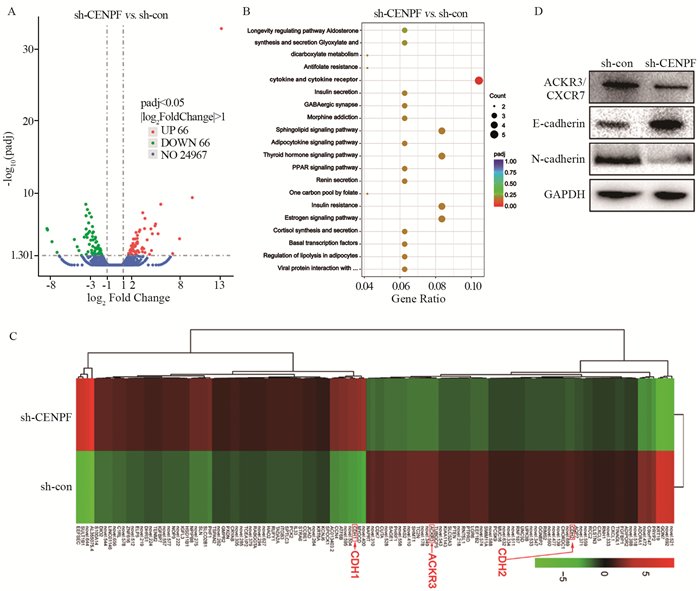
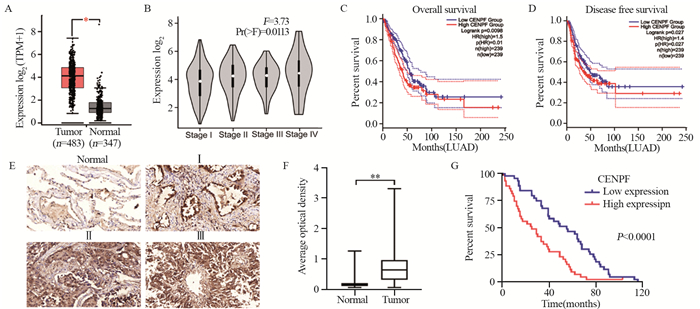
结果CENPF在LUAD肿瘤组织中显著上调(P < 0.05),与病理分期显著相关(P=0.013),表达越高患者预后越差(P=0.01, P=0.027)。敲除CENPF表达后,细胞增殖、迁移及侵袭能力均显著降低(P < 0.01);RNA-seq富集分析显示细胞趋化因子通路基因表达改变富集显著(P < 0.001);聚类差异分析则表明,ACKR3/CXCR7及CDH2/N-cadherin显著下调,CDH1/E-cadherin则显著上调;Western blot结果证实,敲除CENPF后,ACKR3/CXCR7及N-cadherin显著下调,E-cadherin则显著上调。
结论CENPF的表达与LUAD患者临床预后呈负相关,其通过ACKR3/CXCR7调控与EMT相关的N-cadherin及E-cadherin的表达促进EMT的发生。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the relationship between the expression of CENPF in NSCLC adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and the clinical prognosis of patients and its effect on the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells.
MethodsThe expression of CENPF in LUAD and its relationship with patient prognosis were analyzed by online bioinformatics. The expression of CENPF was verified by LUAD tissue microarray immunohistochemical staining. Kaplan-Meier analysis was performed to analyze the relationship between the expression of CENPF and the prognosis of patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Cox survival hazard ratio was used to analyze the factors affecting the survival of patients. Chi-square analysis was adopted to examine the relationship between CENPF expression and clinicopathological stage and grade of patients. The expression of CENPF in NCI-H2126 cells were knocked out by lentivirus, and then the proliferation, invasion, and migration abilities of the cells were detected. Changes in mRNA expression profiles after CENPF knockout were detected by RNA-seq. Bioinformatics analysis of downstream signaling pathways and the target genes of CENPF was also performed. Western blot was used to verify the target gene.
ResultsCENPF was significantly upregulated in LUAD tumor tissue (P < 0.05) and significantly correlated with pathological stage (P=0.013). The higher expression of CENPF, the worse the prognosis of patients (P=0.01, P=0.027). After the expression was CENPF of knocked out, the cell proliferation, migration, and invasion abilities significantly reduced (P < 0.01). The expression of chemokine pathway genes in cells was enriched significantly (P < 0.001). ACKR3/CXCR7 and CDH2/N-cadherin were significantly downregulated, whereas CDH1/E-cadherin was significantly upregulated. After CENPF was knocked out, ACKR3/CXCR7 and N-cadherin were significantly downregulated, whereas E-cadherin significantly increased.
ConclusionThe expression of CENPF is negatively correlated with the clinical prognosis of patients with LUAD, and it promotes the occurrence of EMT by regulating the expression levels of N-cadherin and E-cadherin related to EMT through ACKR3/CXCR7.
-
Key words:
- CENPF /
- Lung adenocar-cinoma /
- ACKR3 /
- Epithelial-mesen-chymal transition /
- CXCR7
-
0 引言
肺癌是全球范围内发病率和死亡率最高的恶性肿瘤。2017年死于肺癌的总人数超过乳腺癌、前列腺癌、结直肠癌和脑瘤的总和,预计2020年死于肺癌的人数将达到所有癌症死亡人数的22%以上[1],局部复发和远处转移是导致肺癌高病死率的主要原因。肿瘤的异质性是单次活检无法获取肿瘤全部分子信息的重要原因,也是造成肿瘤耐药性的基础,因此需要对肿瘤的分子分型进行动态评估。液体活检作为一种非侵入性的肿瘤检测方法,可持续、动态地评估肿瘤细胞的基因突变状态[3]。循环肿瘤细胞(circulating tumor cell, CTCs)、循环肿瘤DNA(circulating tumor DNA, ctDNA)、外泌体、mi-RNA、cf-DNA等是肺癌液态活检的主要检测指标[4],其中CTCs可以提供包含DNA、RNA和蛋白质等多层次的分子信息,而其他指标只能提供遗传层面的异常信息[5]。可见CTCs在肺癌的诊断、疗效评价、预后预测等方面作用显著[6]。本文讨论了CTCs的转移级联过程、检测方法,以及肺癌CTCs在临床早期筛查、预测复发转移、疗效监测评价等方面的应用,并融合入中医“正虚伏毒”理论,以期为肺癌转移转化研究提供新的思路。
1 肺癌循环肿瘤细胞
1869年,Ashworth首次提出循环肿瘤细胞的概念,CTCs是从原发肿瘤脱落进入血液的肿瘤细胞,从浸润至进入循环会发生一系列转移级联过程进而造成远处转移和定植[7]。2019年,田建辉等从一例Ⅱa期肺癌患者的血液中分离出CTCs,成功建立了永久性的人肺腺癌循环肿瘤细胞系CTC-TJH-01。CTC-TJH-01处于上皮间质转化(EMT)的中间阶段,具有干细胞表型、耐药性强和休眠的特性,在NOD-SCID小鼠上具有致瘤性和肺转移能力[8]。根据EMT的不同阶段可将CTCs亚群分为上皮-间充质型循环肿瘤细胞、上皮型循环肿瘤细胞和间充质型循环肿瘤细胞[9],不同表型的CTCs转移能力有所差异。
2 CTCs参与肿瘤转移级联过程
2.1 肿瘤细胞脱落
肿瘤细胞从原发灶脱落浸润基底膜主要有两种方式:(1)EMT介导途径。EMT是上皮细胞向间质细胞转化的关键过程,通过分泌相关转录因子(Snail、Twist、ZEB-1)、细胞外分子(TGF-β、HGF)、炎性细胞以及特定的信号转导途径(Wnt、β-catenin、NF-κB、PI3K)调节相关蛋白(上皮标志物:EpCAM、E-cadherin、CK;间质标志物:Vimentin、N-cadherin等)表达,使肿瘤细胞向间充质型转化,从而获得更强的移动性并抵抗细胞凋亡[10];(2)非EMT介导途径。肿瘤细胞通过外力和中心体增大的方式,介导肿瘤细胞被动渗入血液,以单细胞或细胞簇的形式离开原发肿瘤[11]。通过以上两种方式进入循环的CTCs可能具有不同的细胞表型,皆可引起肿瘤转移。
2.2 血液循环中的CTCs
实体肿瘤每天都有数以万计的肿瘤细胞进入血液循环,CTCs在血液循环中面临着免疫监视、血流剪切力、氧化应激等多方面的因素,只有未被免疫系统清除的CTCs才能进一步播散定植[12]。其中单个循环肿瘤细胞易被免疫细胞清除,发生失巢凋亡。而由多个循环肿瘤细胞组成的循环肿瘤细胞簇或循环肿瘤微栓(circulating tumor microemboli, CTM)能更大程度上发生免疫逃逸,具有更强的凋亡抵抗,更易发生转移[13]。血液循环中的CTCs可被血小板识别,激活血小板并诱导相关细胞因子释放和聚集,形成由血小板包被的细胞簇,从而逃避NK细胞和T细胞的杀伤作用,进而发生免疫逃逸[14]。
2.3 CTCs远处转移和定植
进入血液循环的CTCs可以锚定在内皮细胞的表面,通过受体-配体结合的方式使CTC发生外渗,进而产生远处转移。不同的是,单个CTCs通过毛细血管向外迁移,而CTC簇可逆性地重组为单排链,再横向穿过毛细血管[15]。CTCs表面的整联蛋白通过与内皮细胞表面的黏附分子1(ICAM1)或血管细胞黏附分子1(VCAM1)结合,为CTCs突破血管壁细胞外基质提供动力。CTCs产生的趋化因子配体取决于各自受体的表达,进而决定远处的归巢器官[16]。CTCs还可调节肿瘤微环境中相关抑制性免疫细胞以支持自身增殖和存活。
3 肺癌循环肿瘤细胞检测
CTCs的富集和分离主要有两种方式:其一,基于CTCs独特的物理特性,通过过滤或密度梯度离心等方式获取,被称为“非标记依赖法”;其二,基于CTCs经历的EMT过程,表达特异性细胞表面蛋白,可通过免疫磁珠分选、抗体特异性结合等方式获得,被称为“标记依赖法”,最常用的细胞表面标志物是上皮细胞黏附分子(EpCAM)、细胞角蛋白(CK)等。目前常用的基于物理方法的CTCs检测系统主要有:ISET、MetaCell、CellSieve、Parsortix、OncoQuick、VitaAssay等;基于标记依赖的CTCs检测仪器主要有:CellSearch、MagSweeper、MACS、EPISPOT、CellCollector等[17]。然而,不同系统的CTCs检出效率有差异,如Tamminga等比较了CellSearch和ISET对肺癌CTCs的检出率,发现CellSearch的检出率为69%,而ISET的检出率为88%,表明ISET更适合于肺癌患者的CTCs检测[18]。
研究者正在对检测系统进行优化研究,研发出多种不同原理的CTCs检测方法和新型检测仪器,以提高肺癌CTCs的检出率:(1)微流控装置。Wang等设计的集成微流控装置对肺癌CTCs的平均回收率达到92.5%,纯度达到94%[19];(2)芯片法。Yan等则使用集成多功能电化学芯片将CTCs的捕获效率控制在8%~100%[20];(3)免疫磁珠分离法。通常采用上皮细胞黏附分子(EpCAM)作为主要标志物,将与磁性微粒结合的EpCAM抗体加入外周血中,通过免疫磁珠分离富集CTCs[21];(4)纳米技术。核酸适配体修饰的PEG-PLGA-纳米纤维(PPN)微流控系统,可识别肺癌患者中罕见的CTC亚型并进行优化,显著提高对多克隆源性肿瘤细胞的捕获效率[22];(5)新型肺癌CTCs检测仪器。光流式细胞仪(OFCM)集成了多级微流控芯片和四色荧光检测系统,可以完成自动肺癌CTCs分离,进行3D聚焦和单细胞表型分析[23]。
4 肺癌循环肿瘤细胞的临床应用
4.1 早期筛查
肺癌患者在癌症发展早期基本处于无症状阶段,多数患者明确诊断时已至中晚期,已发生转移,错失治疗的最佳时机。肺癌的早期筛查主要通过低剂量计算机断层扫描(LDCT)实现,然而LDCT具有高假阳性,令患有非恶性结节的患者面临不必要的活检相关风险[24]。Duan等使用CellCollector检测了44名肺结节患者和20例健康志愿者外周血中的CTCs,在志愿者外周血中未检测到CTCs。通过病理学诊断结果对比后发现,肺结节患者外周血中CTCs阳性率为52.94%,其诊断特异性为90%,CellCollector系统检测CTCs可有效区分良恶性结节,用于肺癌早期筛查[25]。Li等采用阴性富集-荧光原位杂交(NE-FISH)方法检测肺癌患者及健康志愿者外周血中CTCs水平,发现肺癌患者的CTCs数量明显高于志愿者或患有良性肺疾病的患者,将CTCs与血清肿瘤标志物联合检测可提高早期肺癌患者的诊断敏感度[26]。
4.2 预后及复发转移预测
肺癌的预后与分期密切相关。大量研究表明,检测肺癌患者手术、放化疗前后血液中的CTCs数量和亚群可预测预后,指导进一步的治疗。Wang等发现放射治疗后NSCLC患者外周血中PD-L1+CTC亚群比例升高,预示着治疗反应与预后不良[27]。Tamminga等研究发现晚期NSCLC患者体内CTCs的存在与酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(TKI)或化疗反应率低、无进展生存期(PFS)和总生存期(OS)短相关[28]。复发转移是导致肺癌患者死亡、生存期短和生活质量低的主要原因。患者术后伴有原发灶切除和淋巴结清扫,短期内无法评估和发现复发转移等情况。有研究发现,手术可以导致肺癌患者术后CTCs数目减少,但术后1天与3天的CTCs数目出现早期反弹现象,且与几月后的复发有关[29]。Chinniah等对48例接受放化疗的局部晚期非小细胞肺癌(LA-NSCLC)患者的CTCs进行纵向监测发现,在患者外周血中检测到CTCs早于放射影像学证据显示疾病复发[30]。
4.3 化疗及免疫靶向治疗的疗效监测与评价
由于肿瘤细胞的异质性,存在基因突变(如ALK重排、EGFR突变等)的患者易发生耐药突变,此时需要进行重复的基因检测。通过对捕获的CTCs进行单细胞测序可以检测到EGFR、MET、ALK和ROS1等基因的分子变化以及PD-L1的表达,鉴定肺癌患者免疫靶向治疗后的耐药性突变,其动态变化有助于实时疗效监测及个性化治疗方案的选择[31]。Guibert等研究发现,NSCLC患者外周血中分离的CTCs表面PD-L1阳性率(83%)高于癌组织(41%),且在使用PD-L1抑制剂治疗的患者中,治疗前PD-L1+CTCs与预后不良相关[32]。
5 创新肺癌亚临床研究思路,提出并验证“正虚伏毒”学说
早期肺癌术后患者影像学评估无可见病灶,临床评估为治愈,但是其外周循环和器官组织中还存有CTCs或休眠的肿瘤细胞,患者实际上处于肺癌转移的亚临床状态,这将成为日后复发转移发生的根源。针对该阶段病理特征,田建辉传承《道德经》“有生于无”和《黄帝内经》重视“正气”思想,融合现代肿瘤学和免疫学进展,提出“正虚伏毒”学说并系统验证,“正虚”主要免疫衰老和免疫逃逸为主的免疫抑制内环境,“伏毒”指高危人群或术后患者体内存在的肿瘤干细胞、循环肿瘤细胞和休眠肿瘤细胞等,“伏毒”具有“毒自内生,深伏血道,内藏脏腑,流注全身,伺机为患,正盛则伏而不出,正虚则出而为病”的特点。认为肺癌术后患者存在伏毒是绝对事件,而最终是否发生复发转移与机体的免疫状态密切相关,免疫功能紊乱可以表现为免疫监视和免疫清除能力下降(正虚),促使潜伏在患者循环系统或者脏器内的CTCs(伏毒)、休眠肿瘤细胞和微小转移灶等发生免疫逃逸,最终导致复发与转移的发生[33]。该学说为肺癌复发转移的研究提供了启发和探索。
课题组前期采用阴性富集和阳性富集(微流控芯片结合免疫磁珠分离技术)研究发现肺癌患者外周血中CTC计数与临床分期之间存在负相关性,早期患者外周血中具有较高数目的CTCs。同时研究发现免疫负调控细胞Tregs和MDSCs的比例与肺癌患者的临床分期呈正相关[34]。提示在局部脏器中免疫抑制微环境的形成可能是促进CTCs定植后存活、增殖形成转移灶的原因之一,目前正在进一步研究。此外,田建辉课题组围绕前期建立的肺癌循环肿瘤细胞系(CTC-TJH-01),证实其具有干细胞表型、休眠、免疫逃逸特征,体内研究证实其致瘤性和肺转移特征,目前发现CTCs形成细胞簇后较单个CTCs具有更强的转移能力;而调控NK细胞功能可抑制CTCs肺转移的发生等现象,从而构建了肺癌转移的体内外研究平台,促进肺癌转移转化研究效率的提高[35]。
6 小结与展望
复发转移是导致早期肺癌术后患者死亡的主要因素,也是制约肺癌整体防控效率提高的关键,但是目前仍缺乏成熟的亚临床阶段发病学理论,而循环肿瘤细胞的研究丰富了对该阶段的认识。2018版CSCO《原发性肺癌诊疗指南》肯定了肺癌术后循环肿瘤细胞检测在预测复发中的价值,并逐渐进入临床研究。然而现阶段肺癌CTCs的研究仍局限于检测技术的开发与完善,由于CTCs检测技术具有多样性,而应用不同原理研发的检测系统灵敏度存在差异,导致临床上尚缺乏统一的检测方法和判定标准;另外由于不同CTCs亚群的转移能力也有所区别,仅以CTCs数目预测转移仍存在争议;CTCs最终是否转移与其所处环境因素密切相关,如CTCs与自然杀伤细胞、巨噬细胞等固有免疫细胞;T、B淋巴细胞等适应性免疫细胞以及血小板等存在复杂的作用机制,有待进一步研究探索[36]。因此,通过精准鉴定转移潜能强的CTCs亚群,进而与免疫、凝血功能状态结合构建肺癌转移风险模型是促进临床推广的关键。充分发挥中医学认知疾病的系统性优势,融合现代科学精华不断创新肺癌转移理论和研究体系,将促进突破制约转移疗效提高的瓶颈,推动肺癌整体防控效率的提高。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.作者贡献:顾彤、姜瑜珩:实验实施及数据整理、论文撰写丁姝、陈炜:数据分析罗超:实验设计和文章审核于伟勇、陈小飞:研究设计、数据审核、文稿撰写及修改 -
表 1 Cox生存风险比例分析与患者死亡相关因素
Table 1 Cox survival hazard ratio analysis of major factors associated with patient death

表 2 CENPF表达与临床病理因素之间的关联
Table 2 Association between CENPF expression and clinicopathological factors

-
[1] Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
[2] Zeng H, Chen W, Zheng R, He J, et al. Changing cancer survival in China during 2003-15: a pooled analysis of 17 population-based cancer registries[J]. Lancet Glob Health, 2018, 6(5): e555-e567. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30127-X
[3] 程颖. 晚期非小细胞肺癌免疫治疗的研究进展[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2021, 48(8): 745-750. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2021.21.0472 Cheng Y. Research progress of immunotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2021, 48(8): 745-750. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2021.21.0472
[4] 肖佳龙, 郑莹. 全球肺癌的流行及预防进展[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2020, 30(10): 721-725. doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2020.10.001 Xiao JL, Zheng Y. The global prevalence and prevention of lung cancer[J]. Zhongguo Ai Zheng Za Zhi, 2020, 30(10): 721-725. doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2020.10.001
[5] Zou PA, Yang ZX, Wang X, et al. Upregulation of CENPF is linked to aggressive features of osteosarcoma[J]. Oncol Lett, 2021, 22(3): 648-652. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12909
[6] Aytes A, Mitrofanova A, Lefebvre C, et al. Cross-species regulatory network analysis identifies a synergistic interaction between FOXM1 and CENPF that drives prostate cancer malignancy[J]. Cancer Cell, 2014, 25(5): 638-651. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.03.017
[7] Lin SC, Kao CY, Lee HJ, et al. Dysregulation of miRNAs-COUP-TFⅡ-FOXM1-CENPF axis contributes to the metastasis of prostate cancer[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 11418. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11418
[8] Liao GB, Li XZ, Zeng S, et al. Regulation of the master regulator FOXM1 in cancer[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2018, 16(1): 57. doi: 10.1186/s12964-018-0266-6
[9] Nakagawa K, Nadal E, Garon EB, et al. RELAY Subgroup Analyses by EGFR Ex19del and Ex21L858R Mutations for Ramucirumab Plus Erlotinib in Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2021, 27(19): 5258-5271. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0273
[10] Berto A, Doye V. Regulation of Cenp-F localization to nuclear pores and kinetochores[J]. Cell Cycle, 2018, 17(17): 2122-2133. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1520569
[11] Manalo A, Schroer AK, Fenix AM, et al. Loss of CENP-F Results in Dilated Cardiomyopathy with Severe Disruption of Cardiac Myocyte Architecture[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 7546. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25774-1
[12] Auckland P, Roscioli E, Coker HLE, et al. CENP-F stabilizes kinetochore-microtubule attachments and limits dynein stripping of corona cargoes[J]. J Cell Biol, 2020, 219(5): e201905018. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201905018
[13] Berto A, Yu J, Morchoisne-Bolhy S, et al. Disentangling the molecular determinants for Cenp-F localization to nuclear pores and kinetochores[J]. EMBO Rep, 2018, 19(5): e44742.
[14] Shi J, Zhang P, Liu L, et al. Weighted gene coexpression network analysis identifies a new biomarker of CENPF for prediction disease prognosis and progression in nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer[J]. Mol Genet Genomic Med, 2019, 7(11): e982.
[15] Chen EB, Qin X, Peng K, et al. HnRNPR-CCNB1/CENPF axis contributes to gastric cancer proliferation and metastasis[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2019, 11(18): 7473-7491.
[16] Parol-Kulczyk M, Gzil A, Ligmanowska J, et al. Prognostic significance of SDF-1 chemokine and its receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7 involved in EMT of prostate cancer[J]. Cytokine, 2022, 150: 155778. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155778
[17] Shahid M, Kim M, Lee MY, et al. Downregulation of CENPF Remodels Prostate Cancer Cells and Alters Cellular Metabolism[J]. Proteomics, 2019, 19(11): e1900038. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201900038
[18] Shahid M, Lee MY, Piplani H, et al. Centromere protein F (CENPF), a microtubule binding protein, modulates cancer metabolism by regulating pyruvate kinase M2 phosphorylation signaling[J]. Cell Cycle, 2018, 17(24): 2802-2818. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1557496
[19] 申雪芳, 花晴, 王敬, 等. 上皮-间质转化诱导转录因子在肺癌诊断和预后预测中的作用[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2020, 30(4): 284-292. Shen XF, Hua Q, Wang J, et al. EMT-TFs are predictors in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis[J]. Zhongguo Ai Zheng Za Zhi, 2020, 30(4): 284-292.
[20] Choi S, Yu J, Kim W, et al. N-cadherin mediates the migration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells toward breast tumor cells[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(14): 6786-6799. doi: 10.7150/thno.59703



 下载:
下载: