Clinicopathological Significance of Poorly Differentiated Clusters in Liver Metastatic Lesions of Colorectal Carcinoma
-
摘要:目的
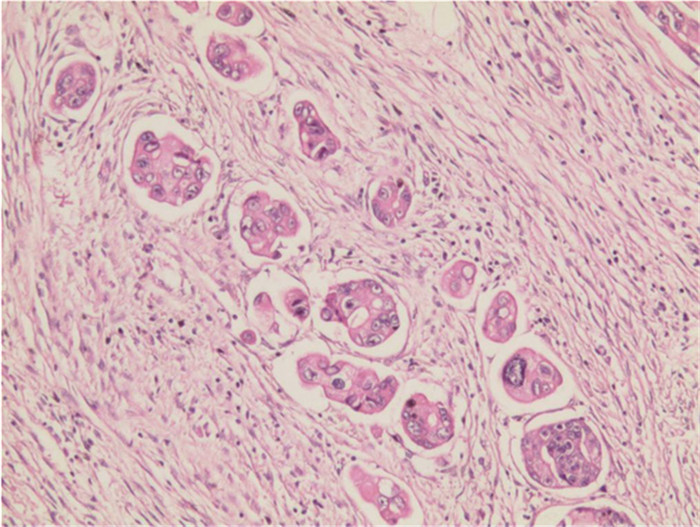
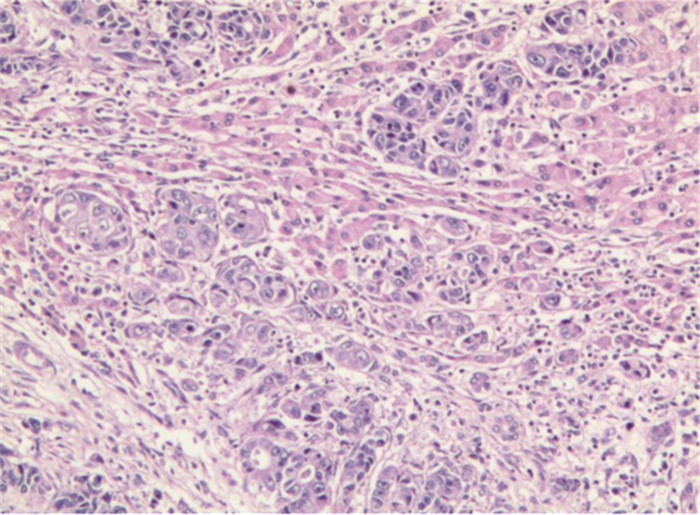
探讨肝转移灶中差分化肿瘤细胞群(PDC)的临床病理意义,分析肝转移灶与肠原发灶中PDC分级的相关性。
方法回顾性分析72例结直肠癌伴有肝转移的配对病例。同时对结肠癌原发灶和肝转移灶中PDC进行判读,分析肝转移灶中PDC分级与各临床病理参数之间的关系及原发灶与转移灶中PDC分级的相关性。PDC的判读方法采用Ueno标准。
结果72例结直肠癌肝转移灶中,PDC分级G1、G2、G3的例数分别为28、24、20。转移灶的PDC分级与转移灶的肿瘤芽、原发灶的PDC分级具有正相关,而与转移灶大小、数目、原发灶部位、级别、浸润深度、淋巴结转移情况、脉管侵犯及肿瘤芽无显著相关。
结论结直肠腺癌肝转移瘤与原发性结直肠腺癌的PDC分级存在正相关,评估原发灶PDC分级或可为肝转移风险提供参考。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the clinicopathological significance of PDC in liver metastases and analyze the correlation of PDC between liver metastases and primary lesions.
MethodsRetrospective analysis of 72 matched cases of colorectal cancer with liver metastases was performed. The PDC in primary tumor and liver metastatic lesion was interpreted synchronously, and then the relationship between PDC in liver metastasis and clinicopathological parameters was analyzed based on the correlation of PDC between primary and metastatic lesions. In addition, PDC were interpreted in accordance with Uenos' standard.
ResultsAmong the 72 cases of liver metastasis of colorectal cancer, the number of G1, G2, and G3 graded by PDC was 28, 24, and 20, respectively. The PDC in liver metastatic lesion was correlated with tumor budding in liver metastatic lesion and PDC grade of primary lesion. No significant correlation with the size and number of liver metastatic lesion, the site, WHO grade, depth of invasion, lymph node metastasis, vascular invasion or tumor budding of the primary lesion was observed.
ConclusionA positive correlation is found between liver metastasis of colorectal adenocarcinoma and PDC grade of primary tumor. Evaluating the PDC grade of primary tumor may provide a reference for the risk of liver metastasis.
-
0 引言
肿瘤是威胁人类健康的一类疾病且病程较为隐匿,往往发现时已是晚期,对治疗带来极大的困难。纳米材料在医学中的应用越来越广泛,为人类战胜肿瘤带来曙光。金属有机框架(metal-organic frameworks,MOFs)作为一类新型纳米材料,具有生物相容性好[1-4]、比表面积大等特点[5-6],与传统药物载体相比,MOFs可以负载更大的药物剂量,而且其pH敏感度强的特性使所载药物能精准、可控地在pH呈弱酸性的肿瘤部位释放,从而达到靶向治疗的效果[7-9]。研制基于MOFs的新型材料是当前肿瘤靶向治疗研究的热点之一,其优异的负载能力能够作为光动力治疗中光敏剂的有效载体[10],一些卟啉类MOFs甚至能够直接作为光敏剂使用[11]。另外MOFs负载免疫佐剂或免疫激活剂在免疫治疗的研究中也表现出一定的价值。本文主要基于MOFs及其衍生材料在肿瘤载药治疗、光动力治疗(photodynamic therapy, PDT)及免疫治疗中的应用进行综述。
1 金属有机框架的概述
MOFs是一类由金属离子或者离子簇与有机配体通过配位反应自组装形成的具有二维[12]或者三维[13]结构的材料,通过改变金属离子和有机配体的种类可以获得不同类别、不同特性的MOFs,例如类沸石咪唑骨架材料(zeolite imidazole frameworks, ZIFs)[14]、Lavoisier研究所材料(materials of insititut Lavoisier, MILs)[15]、卟啉金属有机框架材料[16]等;反应温度、时间、溶剂或金属与配体的比例等的不同,可以改变MOFs的粒径、孔径或比表面积等相关参数,例如研究者通过增大反应体系的黏度或降低反应体系的温度来减小产物MOFs的粒径[17-18],较小的纳米粒更易被肿瘤细胞摄取。Torad等[19]将反应物中的硝酸锌改为乙酸锌,合成ZIF-8的比表面积由1 530 m2/g升高至1 960 m2/g,比表面积的提升能加强药物的吸附能力。另外有机配体功能基团的存在,能够对已有MOFs进行功能化修饰,进一步改善或增加其特定功能[20],以上特点极大地扩展了MOFs的应用范围。
1.1 生物相容性
一种材料要应用在生物医学中,生物相容性是首要考虑的因素之一。为了增加MOFs的生物相容性,研究者们通常会选择一些较低毒性的有机配体与金属离子来合成MOFs粒子[21]。
Zhang等[1]将负载维拉帕米(verapamil, VER)和阿霉素(doxorubicin, DOX)的ZIF-8纳米粒注射入小鼠体内,结果显示ZIF-8载药纳米粒对正常组织、器官的溶血改变和生物毒性可忽略不计。还有研究表明,不同类型的MOFs,如MIL-125-Ti与ZIF-8,对肾脏毒性(肌酐浓度值变化)具有相似的作用。与0.9%氯化钠溶液组相比,MOFs组的小鼠肝、肾重量和体重均没有明显变化(P > 0.05),而且小鼠心脏切片显示,MOFs组心肌细胞凋亡数量没有明显增加[2]。血液生化分析结果无明显异常[3]。另外将细胞培养在含有高浓度MOFs的培养液中,细胞的活性(采用MTT法检测)也没有明显降低[4]。综上所述,优异的生物相容性为MOFs在生物医学中的广泛应用奠定了基础,另外MOFs特有的框架结构也可避免药物渗漏,这种局部应用带来的全身不良反应可忽略不计。
1.2 比表面积
一般来说,材料的比表面积越大,其吸附能力就越强。MOFs材料通常具有较大的比表面积,使MOFs材料的物理吸附能力较强,研究者将这一特性用于肿瘤治疗的研究中。如Gao等[5]合成了比表面积达到1 580 m2/g的UIO-66纳米粒,利用UIO-66作为O2的吸附载体,靶向肿瘤组织来改变肿瘤组织内的乏氧环境。随着研究的进展,MOFs材料比表面积的记录持续被刷新。Farha等[6]合成的NU-110材料的比表面积高达7 140 m2/g,这一数值远远超过介孔二氧化硅、碳纳米管等传统药物载体,且他们通过计算机模拟,得出MOFs的理论比表面积上限约14 600 m2/g。因此,较大的比表面积为MOFs材料能够成为良好负载体提供了理论依据。
1.3 pH敏感度
肿瘤组织由于代谢旺盛,其组织及细胞内pH往往呈弱酸性,因此利用这种肿瘤微环境来控制药物的可控释放,是提高药物治疗效果的有效方法之一。Wu等[7]合成的负载DOX的MOFs纳米粒释药速率呈明显的pH相关性,在pH=5.0时,72 h DOX释药率接近70%,而pH=7.4时仅约15%。研究表明,对MOFs表面进行化学修饰后,MOFs释药速率仍然能够表现出pH依赖相关性[8]。随着pH的降低,药物的释放速率和累积量均明显增加[2]。由于修饰层的保护,MOFs载药体系能使所载药物持续释放的时间延长[22],且在生理条件下,MOFs载药体系能够维持相对稳定性。
2 金属有机框架在肿瘤治疗中的应用
传统的化疗易导致较大的全身不良反应,而靶向治疗技术的发展为无法耐受传统化疗的患者带来希望。MOFs材料因其超大的比表面积与易修饰的特点使其成为药物递送的良好载体,较传统的载体具有更高的载药量。MOFs表面修饰相关配体后,能够提高对肿瘤组织的靶向性,减少药物在正常组织和器官中的富集,降低损伤。研究者们在实验中已经成功实现了以MOFs为载体的药物靶向输送[7, 23-25]。与注射相同剂量的游离药物相比,MOFs能够明显延长药物在血液中的循环时间[8]。Wu等[7]研究表明,DOX对正常组织的毒性因MOFs的包覆而降低,但其抗癌活性不受影响。也有研究表明,对MOFs进行表面修饰不仅有助于控制负载物的释放,而且能够提高MOFs体系的稳定性[20]。
2.1 药物负载
亲水性和疏水性MOFs均可用于药物的装载和输送,其中亲水性MOFs较疏水性MOFs可以更好地保持负载药物的生物活性[26]。He等[23]将阿齐沙坦(azilsartan, AZL)封装在γ-环糊精(γ-cyclodextrin, γ-CD)金属有机框架(CD-MOF)中,结果表明,AZL在大鼠体内的生物利用率提高了9.7倍,溶解性提高了340倍,认为CD-MOF可以改善疏水性AZL的溶解性使其更易被机体吸收。由此可见,MOFs具有作为其他不溶性或难溶性药物有效载体的潜力,提高这类药物在体内的利用率,降低给药剂量。Fernández-Paz等[24]制备出MIL-100纳米给药系统,通过呼吸道吸入,将负载异烟肼的MIL-100纳米粒均匀地输送到肺部终末细支气管和肺泡中,实现肺结核治疗的靶向给药,不仅为肺部肿瘤的治疗提供参考,同时也为一些慢性疾病的治疗带来新的可能性,例如糖尿病患者的胰岛素无创给药。研究发现,一些MOFs自身就可作为药物使用,如ZIF-8已经被证明具有显著的抗菌活性,研究者从细胞膜受锌离子损伤的角度解释了其抗菌机制[27]。MOFs在其他领域的抗菌效果也被证明[28]。
不同种类MOFs对同种药物分子的装载量差异较大,因此通过选择性封装或结合,能使药物分子有选择地负载到杂化相MOFs的不同结构域中,通过调节药物在MOFs中的空间分布来实现可控的负载和释放[29], 因此多种药物的同时负载也被证明是可行的。Tan等[25]将DOX和塞来昔布(celecoxib,Cel)双负载在MOFs孔隙中,用做口腔癌局部治疗的植入物,实现两种药物稳定及持续的释放,提高了对口腔癌的治疗效果,表现出优异的肿瘤杀伤能力。
Chen等[30]的研究发现,将辣根过氧化物酶(horseradish peroxidase, HRP)包裹在2D结构的MOFs材料中,MOFs中的HRP活性与游离HRP相近,他们从2D MOFs结构使酶的扩散路径缩短的角度解释了这一结果。Liao等[31]将过氧化氢酶(catalase,CAT)镶嵌到ZIF-90及ZIF-8纳米粒中,结果证实ZIFs的包覆限制了酶分子的空间,降低了其构型改变的能力,增加了CAT对复杂环境的耐受能力,即使暴露在6 mol/L尿素变性剂或80℃高温下时,仍然表现出一定的分解H2O2的活性。Huang等[32]发现,将酶固定在MOFs中可有效延长酶的寿命。也有报道表明,即使酶的尺寸稍大于MOFs的孔径,仍然可以被有效地负载[33]。综上所述,得益于MOFs的保护,生物大分子能够在更复杂的环境下维持其生物活性,而要阐述酶在MOFs中的空间方位对其催化性能的影响,则需要进一步的深入研究。
MOFs作为药物载体在细胞实验及动物实验中的研究成果瞩目,但其材料本身的不足也逐渐显现出来,大多数MOFs材料pH敏感度强,会在弱酸性条件下缓慢分解,因此在体内一些pH呈弱酸性的正常组织中MOFs也会缓慢分解,但这种不足可以通过对MOFs材料表面的修饰来改善,例如Song等[2]将适量的透明质酸(hyaluronic acid,HA)修饰在MIL-125-Ti载药纳米粒表面,不仅能够避免MIL-125-Ti分解与DOX在正常组织中的释放,而且可以与MCF-7细胞表面CD44受体结合,增加纳米粒的靶向性,降低DOX在正常组织中的积累。An等[34]使用肿瘤同源细胞膜修饰负载亚硝基谷胱甘肽(S-nitrosoglutathione,GSNO)与二氢卟吩e6(Chlorin E6,Ce6)的ZIF-8纳米粒表面,靶向肿瘤细胞,避免其在到达肿瘤部位之前分解并释放药物;MOFs独特的组成成分不可避免地会引入一些金属离子,可能会导致局部组织中金属离子浓度过高,出现金属中毒症状,这需要研究者们进一步测试MOFs在不同组织内的安全峰值浓度。
2.2 光动力治疗
光动力治疗是指光敏剂在特定波长光照条件下产生活性氧(reactive oxygen species, ROS),对肿瘤细胞产生杀伤作用的一种无创治疗方法,通常作为肿瘤治疗的补充手段。MOFs以比表面积大、生物相容性好、易修饰的特点,使其成为光敏剂的理想运输载体,一些卟啉类MOFs甚至本身就可作为光敏剂使用。如果进一步增加纳米粒的靶向性,还能使PDT的效果进一步提高[35]。
Kan等[10]将S-乙基硫醇酯单取代卟啉(TPP-SH)修饰在UIO-66表面,制成一种新型的纳米粒UIO-66-TPP-SH,在660 nm近红外(near infrared, NIR)光照条件下,DMF环境中的产氧率测试表明,UIO-66-TPP-SH组的产氧率较游离TPP-SH组更高,且修饰在MOFs表面的卟啉光毒性比装载在MOFs内部的卟啉更强。体外细胞实验结果表明,无光照条件下,细胞存活率在93%以上,而在NIR照射下细胞存活率仅为30%,PDT治疗效果显著。
但是PDT的一些缺陷限制了它的临床应用范围:PDT通常使用特殊波长的NIR照射,其对深层组织的穿透能力有限,因此目前仅被用于治疗表浅部位的肿瘤。而亟待解决的是,肿瘤内部的乏氧环境限制了ROS的产生和积累,使PDT治疗效率较低,不足以完全杀死肿瘤组织,极易导致复发。因此如何解除肿瘤组织的乏氧环境并提高PDT的治疗效果也成为研究者们的研究热点,并已取得一定突破。一些学者通过引入外部O2的方法,改善了肿瘤乏氧环境。如Gao等[5]利用UIO-66的气体吸附能力,将UIO-66作为O2的载体,把光敏剂吲哚菁绿(indocyanine green, ICG)配位在UIO-66表面,并用红细胞膜包裹防止O2释放。在808 nm NIR光照下,ICG产生ROS用作PDT,同时逐渐分解红细胞膜并释放UIO-66携带的O2,而且NIR照射带来的光热作用进一步促进O2的释放,增加肿瘤部位的O2含量,降低了肿瘤乏氧对PDT的抑制;利用肿瘤细胞内浓度较高的H2O2转化为O2也是有效改善肿瘤乏氧环境的方法之一,Lan等[11]制备了Fe3O与5, 10, 15, 20-四(对苯甲酰基)卟啉(TBP)配位构建的Fe-TBP纳米粒,将其注射进CT26结肠腺癌小鼠体内,NIR照射条件下,细胞中的H2O2逐渐被发生的类芬顿反应分解,检测到肿瘤细胞内的H2O2荧光强度降低,同时检测到ROS的产生。PDT与光热治疗(photothermal therapy, PTT)的结合也是一种提高治疗效果的有效策略,研究表明PDT/PTT联合治疗在体内与体外的治疗效果均优于单独的PDT或PTT[16, 36]。
2.3 免疫治疗
免疫治疗是指通过激活人体免疫系统来消灭肿瘤细胞的一种方法。在MOFs的帮助下,将细胞癌变坏死后产生的肿瘤相关抗原(tumor-associated antigens, TAAs)和负载的免疫激动剂或免疫佐剂等物质高效地呈递给免疫细胞,激活强烈的免疫应答,杀死肿瘤细胞。免疫治疗不仅被证明长期有效和安全,且能够减少治疗后肿瘤复发和转移的风险。
Cai等[37]选用的PCN-MOF在670 nm NIR照射下可以产生ROS,且在PCN-MOF表面修饰缺氧诱导因子信号抑制剂(ACF)与免疫佐剂胞嘧啶-磷酸-鸟嘌呤二核苷酸(CpG)后不影响ROS的产生,后续实验结果表明,ACF可阻断PDT后加重的缺氧信号,有效抑制了缺氧导致的HIF-1α信号通路激活所引起的肿瘤转移。在CpG的帮助下,肿瘤细胞坏死后产生的TAAs引发了强烈的抗肿瘤免疫应答。PCN-MOF治疗组在肿瘤部位发现更多聚集的CD8+T细胞和CD4+T细胞,产生抗肿瘤免疫应答。Zhao等[38]将MIL-88A与编码卡妥索单抗(catuma-xomab)的DNA片段(MC)混合,将MOF/MC作为简单的基因传递系统,对破坏免疫系统的肿瘤模型小鼠注射MOF/MC及T细胞,与未注射组相比,肿瘤切片显示出更强的CD3+T细胞浸润,即MOF/MC能够导向T细胞有效地聚集在肿瘤部位。Shao等[39]合成了上转换纳米粒子(upconversion nanoparticles, UCNP)为核心,包覆卟啉MOF为外壳的具有核-壳结构的纳米粒(UCS),并将替拉扎明(tirapazamine, TPZ)负载在UCS的孔隙中,在980 nm NIR照射条件下,UCS表现出明显的细胞学毒性。NIR照射后再给予PD-L1阻断治疗,观察到原发及远处转移的肿瘤均能被有效地抑制,流式细胞仪检测证实UCS组肿瘤部位CD4+ T细胞、CD8+T细胞及NK细胞占比明显高于PBS组。Miao等[40]将卵清蛋白(ovalbumin, OVA)封装在Al-MOFs内,并在其表面包覆酵母胶囊(yeast capsules, YCs),将合成后的OVA@Al-MOFs/YCs纳米粒作为免疫疫苗对小鼠进行注射,研究结果表明,OVA@Al-MOFs/YCs纳米粒能够通过肠系膜M细胞运输,随后被肠系膜淋巴结中的巨噬细胞内吞,在巨噬细胞内被包裹的OVA(抗原)和Al-MOF分解的Al离子(佐剂)释放,促进巨噬细胞的成熟,进而诱发免疫反应。这项研究有望用于口服疫苗的研制,同时为传统静脉注射药品的口服应用奠定一定的基础。
采用MOFs材料诱导的免疫治疗在实验中表现出明显的抗肿瘤效果,另外作为免疫佐剂,MOFs材料同样能够有效激活受体的免疫反应,增强药物在机体复杂环境的耐受性,特别是保护蛋白质类药物,避免其在到达特定位置前失去活性。基于MOFs材料的免疫治疗作为近年来研究热点之一,虽然已经取得了一些可观的成果,但总体而言仍然处于起步阶段,还存在一些待解决的问题。例如,如何选择合适的MOFs材料,以及不同种类、不同粒径的MOFs对免疫治疗效果的影响等。如何通过选择MOFs以实现高效的免疫治疗,依然需要大量的实验去研究。
3 小结与展望
研究者们尝试使用不同的金属离子与有机配体合成MOFs材料,因此,时至今日仍然不断有新的MOFs材料诞生。良好的生物相容性是MOFs材料在生物医学领域的应用基础,较大的比表面积能够吸附较多的药物分子以达到载药效果,而其较强的pH敏感度则能够实现药物的可控释放。MOFs的多活性位点可以修饰不同的官能团,使MOFs可以获得多变的靶向性,不仅可以实现对特定物质的识别,还可特异识别病变靶组织、靶器官。近年来,MOFs材料在生物医学领域的研究取得了较大进展,但与其他药物载体材料相比,仍处于起步阶段,还有很多问题需要解决,如一些MOFs材料,特别是卟啉MOFs材料的合成成本仍然较高,目前的研究仅限于在实验室中的少量合成,需要进一步降低生产成本后才能广泛应用于临床实验;MOFs材料不论在载药的合成过程中,还是储存或对其进行修饰时,都不可避免地造成部分药物损失,变相提高了制造成本;多数MOFs的化学稳定性较差;MOFs的孔径限制一些大分子蛋白质及DNA片段的运载;长期应用导致机体金属离子过量。而且,目前国内外已报道出的研究都仅限于细胞、动物实验阶段,尚没有MOFs材料被实际用于临床治疗之中。
因此,可以探索更多种类MOFs材料在生物医学中应用的可行性;通过改变MOFs合成的条件,进一步调整MOFs的相关参数,使材料更适合生物医学研究;探索不同组织对MOFs材料的安全峰值浓度,并研究长期摄入MOFs可能对机体造成的影响,这些实验数据的积累都能为MOFs材料早日应用于临床治疗打下坚实基础。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.作者贡献:彭辉:课题设计及论文撰写张志发:统计分析伍颖君、朱贤强:结果判读张潇涵:资料收集秦海丽:病理制片 -
表 1 结直肠腺癌肝转移灶中PDC和肝转移灶、肠癌原发灶病理参数的相关性
Table 1 Correlation between PDC in liver metastases of colorectal adenocarcinoma and pathological parameters of liver metastases and primary colorectal cancer

-
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2022, 72(1): 7-33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21708
[2] Watanabe T, Muro K, Hashiguchi Y, et al. Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon and Rectum (JSCCR guidelines) 2016 for the treatment of colorectal cancer[J]. Int J Clin Oncol, 2018, 23(1): 1-34. doi: 10.1007/s10147-017-1101-6
[3] Ueno H, Kajiwara Y, Shimazaki H, et al. New criteria for histologic grading of colorectal cancer[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2012, 36(2): 193-201. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318235edee
[4] 彭辉, 张志发, 朱贤强, 等. 结直肠腺癌差分化细胞群与临床病理学参数的相关性研究[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2021, 31(9): 817-821. Peng H, Zhang ZF, Zhu XQ, et al. A study of correlation between poorly differentiated clusters and clinicopathological parameters in colorectal adenocarcinoma[J]. Zhongguo Ai Zheng Za Zhi, 2021, 31(9): 817-821.
[5] Slik K, Blom S, Turkki R, et al. Combined epithelial marker analysis of tumour budding in stageⅡcolorectal cancer[J]. J Pathol Clin Res, 2019, 5(1): 63-78. doi: 10.1002/cjp2.119
[6] Shivji S, Conner JR, Barresi V, et al. Poorly differentiated clusters in colorectal cancer: a current review and implications for future practice[J]. Histopathology, 2020, 77(3): 351-368. doi: 10.1111/his.14128
[7] Kinoshita O, Kishimoto M, Murayama Y, et al. The number of metastatic lymph nodes exhibiting poorly differentiated clusters predicts survival in patients with pStage Ⅲ colorectal cancer[J]. Int J Colorectal Dis, 2016, 31(2): 283-290. doi: 10.1007/s00384-015-2393-5
[8] Backes Y, Elias SG, Groen JN, et al. Histologic factors associated with need for surgery in patients with pedunculated T1 colorectal carcinomas[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 154(6): 1647-1659. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.023



 下载:
下载: