Efficacy and Safety of Anlotinib Combined with PD-1 Blockades for Patients with Advanced Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
-
摘要:目的
探讨安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂后线治疗晚期上皮性卵巢癌患者的疗效和安全性。
方法回顾性分析33例经标准二线或三线治疗失败的晚期上皮性卵巢癌患者资料,所有患者均接受安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂治疗,收集治疗期间疗效及安全性数据。
结果客观缓解率为36.4%(95%CI: 20.4%~54.9%),疾病控制率为81.8%(95%CI: 64.5%~93.0%)。中位无进展生存期和总生存期分别为7.6月(95%CI: 3.1~12.1月)和19.6月(95%CI: 15.1~24.1月)。常见的治疗相关不良反应为疲劳(66.7%)、恶心和呕吐(54.5%)、高血压(48.5%)和腹泻(39.4%)。Cox回归分析显示:ECOG PS评分和FIGO分期是影响安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂治疗晚期上皮性卵巢癌无进展生存期的独立影响因素。
结论安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂后线治疗晚期上皮性卵巢癌初步表现出较好的疗效,不良反应可耐受。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the efficacy and safety of anlotinib combined with PD-1 blockades for patients with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC).
MethodsA retrospective study was performed, enrolling 33 patients with advanced EOC who failed standard systematic therapy. All patients were administered with anlotinib combined with PD-1 blockades. The efficacy and safety profile were determined during treatment.
ResultsThe objective response rate of the 33 patients was 36.4% (95%CI: 20.4%-54.9%) and the disease control rate of the patients was 81.8% (95%CI: 64.5%-90.0%). The median PFS and OS of the 33-patient cohort were 7.6 months (95%CI: 3.1-12.1) and 19.6 months (95%CI: 15.1-24.1), respectively. The most common treatment-related adverse reactions were fatigue (66.7%), nausea and vomiting (54.5%), hypertension (48.5%), and diarrhea (39.4%). Furthermore, multivariate Cox regression analysis indicated that ECOG performance status and FIGO stage were independent factors for predicting the PFS of the combination regimen for patients with advanced EOC.
ConclusionAnlotinib combined with PD-1 blockades preliminarily exhibit satisfactory efficacy and tolerable safety profile for patients with advanced EOC.
-
Key words:
- Epithelial ovarian cancer /
- Anlotinib /
- PD-1 blockade /
- Efficacy /
- Adverse effect
-
0 引言
上皮性卵巢癌患者预后较差,5年生存率不足30%[1-2]。目前,手术联合化疗及靶向治疗是临床常用治疗方案,但是大部分患者仍会出现复发,尤其是铂类耐药复发,这也是影响上皮性卵巢癌患者预后的重要因素[3-4]。迫切需要探索晚期上皮性卵巢癌安全有效的后线治疗方案。帕唑帕尼、索拉非尼和安罗替尼等多靶点酪氨酸激酶抑制剂对既往治疗的上皮性卵巢癌患者显示出初步疗效[5-6],然而,多数患者最终会产生获得性耐药。免疫系统在卵巢癌预后中发挥重要作用,提示肿瘤内T细胞与卵巢癌患者接受传统治疗后中位无进展生存期延长呈正相关[7]。研究显示,PD-L1和PD-L2表达增加与卵巢癌的总生存期较差相关[8],证实了PD-1/PD-L1免疫检查点信号通路是影响上皮性卵巢癌免疫逃逸机制的假设。Keynote-100和Checkmate研究显示:PD-1抑制剂对于晚期上皮性卵巢癌显示出初步疗效,但是整体客观缓解率仍然较低(< 15%)[9-10],因此,本研究回顾性分析接受安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂后线治疗的33例晚期上皮性卵巢癌患者的疗效及安全性,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
收集2018年8月—2021年6月安阳市肿瘤医院收治的33例经标准治疗失败的晚期上皮性卵巢癌患者资料。纳入标准:经组织学诊断为上皮性卵巢癌、输卵管癌或腹膜癌;国际妇产科联合会(FIGO)分期标准为Ⅲ或Ⅳ期;年龄≥18岁;东部肿瘤协作组(ECOG)体力状态(PS)评分0~2分;既往二线或三线以上标准治疗失败的患者(并根据患者一线接受含铂方案治疗情况分为铂敏感型或者铂耐药型。铂敏感型:指发现肿瘤复发时间与一线末次化疗时间之间的间隔≥6个月;铂耐药型:指发现肿瘤复发时间与一线末次化疗时间之间的间隔 < 6个月或者肿瘤在一线治疗过程中进展);患者接受安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂。排除标准:既往接受过安罗替尼或任何PD-1、PD-L1或CTLA-4抗体治疗的患者;患者被诊断为鳞状细胞皮肤癌或子宫颈原位癌;存在自身免疫性疾病的患者;同时患有其他癌症或严重疾病;没有疗效评价资料。所有患者均签署知情同意书,研究方案得到安阳市肿瘤医院伦理委员会审批。
1.2 治疗方法
患者均接受安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂治疗。盐酸安罗替尼胶囊12 mg或10 mg,每日一次,早餐前口服,连续用药2周,停药1周,每3周为一个治疗周期;PD-1抑制剂包括卡瑞利珠单抗、信迪利单抗和帕博利珠单抗,剂量均为200 mg,第1天静脉滴注给药,每3周为一个治疗周期;治疗方案一直持续到疾病进展或出现无法耐受的不良反应。
1.3 疗效评价标准
每位患者接受安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂方案治疗后,每两周期进行一次计算机断层扫描(CT)或磁共振成像(MRI)检查,或者由医生根据临床症状进行评价。根据实体肿瘤疗效评价标准(RECIST 1.1)进行疗效评价[11],分为完全缓解(CR)、部分缓解(PR)、疾病稳定(SD)和疾病进展(PD),客观缓解率(ORR)=CR+PR,疾病控制率(DCR)=CR+PR+SD;无进展生存期(PFS)定义为首次用药至疾病进展或死亡时间;总生存期(OS)定义为首次用药至患者因任何原因死亡的时间。采用常见不良反应评价标准(CTCAE)4.03版评价药物的不良反应[12]。
1.4 统计学方法
采用IBM SPSS 25.0统计软件进行整体数据分析。PFS和OS生存曲线使用Kaplan-Meier法绘制。Log rank检验计算基线亚组间的PFS差异,并对PFS多变量因素进行Cox回归分析,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 临床资料
共纳入符合标准的晚期上皮性卵巢癌患者33例,基线特征见表 1。中位年龄56岁(22~73岁);5例患者接受过二线治疗,28例患者接受过三线及以上治疗;ECOG PS评分为0~1分19例(57.6%);安罗替尼初始剂量为12 mg的患者27例(81.8%);同时,PD-1抑制剂使用卡瑞利珠单抗、信迪利单抗和帕博利珠单抗的患者分别为18例、10例和5例。
表 1 33例上皮性卵巢癌患者的一般资料Table 1 Baseline characteristics of 33 patients with EOC
2.2 近期疗效
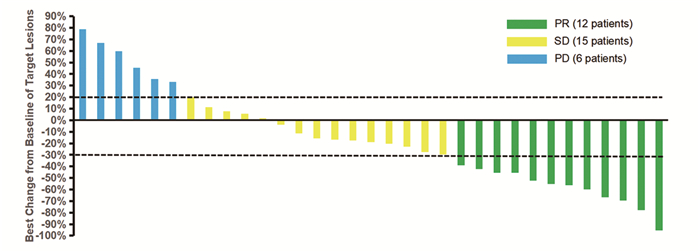
在33例可评估患者中,PR 12例,SD 15例,PD 6例,ORR为36.4%(95%CI: 20.4%~54.9%),DCR为81.8%(95%CI: 64.5%~93.0%)。33例可评估患者的最佳疗效瀑布图见图 1。
2.3 远期疗效
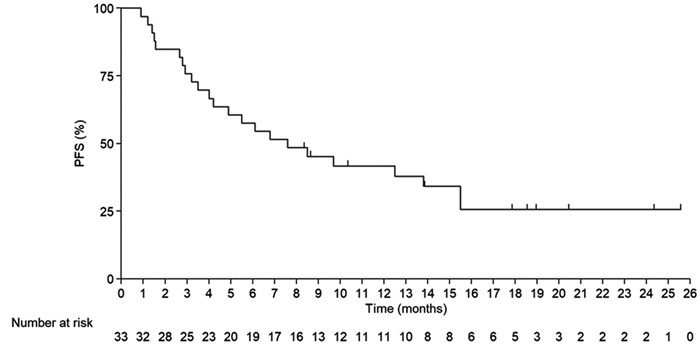
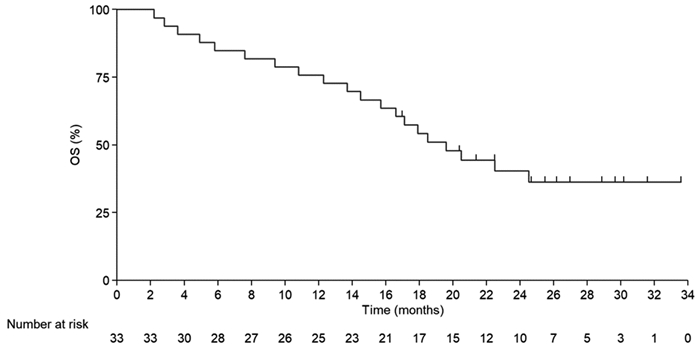
截至2021年9月30日,本研究随访时间0.9~33.5月,中位随访时间17.5月。33例上皮性卵巢癌患者的中位PFS为7.6月(95%CI: 3.1~12.1月),6个月和12个月PFS率分别为57.6%(95%CI: 39.1%~72.3%)和41.8%(95%CI: 24.8%~57.9%)。中位OS为19.6月(95%CI: 15.1~24.1月),12个月和24个月的OS率分别为75.8%(95%CI: 57.3%~87.1%)和40.4%(95%CI: 23.3%~56.9%),见图 2~3。
2.4 无进展生存期的影响因素分析
2.4.1 单因素分析
本研究根据基线特征进行了单因素分析,ECOG PS评分0~1分患者的中位PFS显著优于评分2分患者(P=0.027),FIGO分期Ⅲ期患者显著优于Ⅳ期患者(P=0.016),同时,铂敏感型患者显著优于铂耐药型患者(P=0.046)。此外,接受三种PD-1抑制剂的患者PFS并无显著性差异(P=0.572),见表 2。表明ECOG PS评分、FIGO分期和一线铂类药物敏感度与PFS显著相关。
表 2 根据基线特征对33例上皮性卵巢癌患者的PFS单因素分析Table 2 Univariate analysis for PFS of 33 patients with EOC according to baseline characteristics
2.4.2 多因素分析
多变量Cox回归分析结果显示:ECOG PS评分(HR=0.66, P=0.041)和FIGO分期(HR=0.57, P=0.026)均为PFS的独立影响因素。然而,一线铂类药物敏感度对PFS的影响并不显著(HR=1.44, P=0.069),见表 3。
表 3 根据基线特征对PFS进行多变量Cox回归分析Table 3 Multivariate Cox regression analysis for PFS according to baseline characteristics
2.5 不良反应
33例上皮性卵巢癌患者中有30例(90.9%)出现治疗相关不良反应(TRARs)。12例(36.4%)患者出现3级及以上TRARs,治疗期间未出现5级不良反应。常见的TRARs为疲劳、恶心和呕吐、高血压、腹泻、皮疹、疼痛、手足综合征、体重减轻、肝毒性、反应性皮肤毛细血管内皮增生(RCCEP)、蛋白尿、肺炎和出血。3级及以上TRARs为恶心和呕吐(15.2%)、高血压(15.2%)、疲劳(9.1%)、腹泻(6.1%)、手足综合征(6.1%)、皮疹(3.0%)和蛋白尿(3.0%),见表 4。
表 4 33例接受安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂治疗的上皮性卵巢癌患者不良反应Table 4 Adverse reactions in 33 patients with EOC treated with anlotinib and PD-1 blockades
3 讨论
多数上皮性卵巢癌患者一线治疗有效,但是大部分患者会复发并最终发展为化疗耐药,尤其是铂耐药。然而,非铂类单一药物方案有效率仅为10%~30%[13],不能满足临床需求。研究表明,血管生成在上皮性卵巢癌的增殖转移过程中发挥着重要作用。在上皮性卵巢癌患者的一线和后续联合治疗中,除了贝伐珠单抗表现出优异的临床结果外,抗血管生成TKI药物也在三线治疗中表现出初步疗效,阿帕替尼和舒尼替尼单药后线治疗均显示出不错的疗效和安全性。同时,近年来PD-1/PD-L1抑制剂等免疫药物对接受过标准治疗的上皮性卵巢癌患者也表现出潜在的疗效和安全性。Keynote-100和Checkmate研究显示:帕博利珠单抗和纳武利尤单抗单药治疗晚期上皮性卵巢癌显示出初步疗效,不过整体客观缓解率仍然较低(< 15%)[9-10]。因此,对于晚期上皮性卵巢癌患者新的联合治疗方案的探索就显得尤为重要。
本研究共纳入33例经标准治疗失败晚期上皮性卵巢癌患者,均接受了安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂方案治疗。总体结果显示:33例患者的ORR为36.4%,DCR为81.8%,中位PFS为7.6个月,显示出良好的疗效和生存获益。Cui等[14]开展了一项针对铂耐药复发上皮性卵巢癌患者使用安罗替尼为基础治疗的回顾性研究,共纳入38例患者,结果显示,17例患者接受安罗替尼单药治疗的ORR为23.5%。此外,Keynote-028研究[15]共纳入26例PD-L1阳性的晚期转移性卵巢癌患者,接受帕博利珠单抗单药治疗,ORR为11.5%。同时Checkmate研究[10]共纳入20例铂耐药复发的上皮性卵巢癌患者,纳武利尤单抗单药治疗的ORR为15%。本研究中安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂相较于其他单药治疗疗效获得明显提升,两种药物表现出潜在的协同抗肿瘤作用,这与阿特珠单抗联合贝伐珠单抗联合治疗肝细胞癌中的结论一致[16]。
Liu等[17]开展了一项纳武利尤单抗联合贝伐珠单抗治疗复发性卵巢癌患者的Ⅱ期临床试验,纳入38例复发性上皮性卵巢癌患者,结果显示:ORR为28.9%,DCR为55.3%,中位PFS为9.4月。该研究中的ORR和DCR均低于本研究,可能是因为安罗替尼不同于贝伐珠单抗,安罗替尼作为一种多靶点TKI药物,具有抗血管生成和抑制肿瘤细胞增殖转移的双重作用[18]。该研究中的PFS要长于本研究(中位PFS:9.4月vs. 7.6月),可能是由于两项研究患者基线情况不同,Liu等研究中的大多数患者只接受过一线全身化疗,而本研究中的患者是标准二线或三线治疗后失败的患者,还有ECOG PS评分比例的差异,本研究中ECOG PS评分2分的患者占42.4%,远高于Liu等研究中的0。此外,本研究针对PFS的多变量Cox回归分析表明,ECOG PS状态和FIGO分期是PFS的独立影响因素,这与之前的研究结论一致[19-20]。同时,在本研究中一线铂类药物敏感度对PFS的影响未发现具有显著统计学差异,但是具有边缘的统计学意义,这可能是研究样本量较少造成的。
本研究OS分析结果显示,中位OS略长于Keynote-028试验(19.6月vs. 13.8月)和安罗替尼在上皮性卵巢癌患者中的回顾性研究(19.6月vs. 16.5月)[14-15]。推测原因可能是自2018年以来另一种免疫疗法和PARP抑制剂(奥拉帕尼和尼拉帕尼)获批并应用于临床。据了解,PARP抑制剂对晚期上皮性卵巢癌患者后线治疗显示出初步临床获益[21]。因此,在患者使用安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂方案进展后,仍有另一种PD-L1抑制剂和PARP抑制剂可供患者使用,从而使患者持续获得生存获益。
安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂的总体不良反应是可耐受和可控的,这与最近报告的安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂治疗晚期实体瘤患者中的安全性数据一致[22]。需要注意的是,3~4级TRARs发生率为37.5%,高于纳武利尤单抗和贝伐珠单抗治疗的复发性卵巢癌患者(≥3级TRARs为23.7%)。尽管如此,对于上皮性卵巢癌患者,安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂不良反应仍是可耐受的。此外,联合方案中常见的TRARs是高血压、手足综合征、蛋白尿和出血,这可归因于安罗替尼的治疗,并且与之前安罗替尼在治疗上皮性卵巢癌患者中的安全性数据一致[14]。另外,使用PD-1抑制剂治疗引起的免疫相关不良反应,如皮疹、RCCEP和肺炎的发生率相对较低。值得注意的是,RCCEP为18例接受卡瑞利珠单抗治疗患者的特定不良反应,因此,接受卡瑞利珠单抗患者实际的RCCEP发生率为22.2%,明显低于卡瑞利珠单抗单药治疗其他癌症的发生率(约60%)。这种差异可归因于联合安罗替尼在降低卡瑞利珠单抗治疗期间RCCEP发生率方面所发挥的作用[23]。因此,安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂方案的总体不良反应耐受性良好。
综上,安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂后线治疗晚期上皮性卵巢癌显示出一定的疗效,耐受性良好,可作为晚期上皮性卵巢癌标准治疗失败后的一种选择,但仍需进行随机对照研究进一步证实其疗效及安全性。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.作者贡献:金惠敏:课题构思、资料收集及论文撰写林丽红、赵振:资料收集及数据统计分析宫喜双:课题构思指导及论文指导 -
表 1 33例上皮性卵巢癌患者的一般资料
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of 33 patients with EOC

表 2 根据基线特征对33例上皮性卵巢癌患者的PFS单因素分析
Table 2 Univariate analysis for PFS of 33 patients with EOC according to baseline characteristics

表 3 根据基线特征对PFS进行多变量Cox回归分析
Table 3 Multivariate Cox regression analysis for PFS according to baseline characteristics

表 4 33例接受安罗替尼联合PD-1抑制剂治疗的上皮性卵巢癌患者不良反应
Table 4 Adverse reactions in 33 patients with EOC treated with anlotinib and PD-1 blockades

-
[1] Rong Y, Li L. Early clearance of serum HE4 and CA125 in predicting platinum sensitivity and prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer[J]. J Ovarian Res, 2021, 14(1): 2. doi: 10.1186/s13048-020-00759-9
[2] 谭芳春, 李力. 卵巢癌分子分型及其临床应用的研究进展[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2018, 45(2): 106-109. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2018.17.0771 Tan FC, Li L. Research progress on molecular typing of ovarian cancer and its clinical application[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2018, 45(2): 106-109. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2018.17.0771
[3] Champer M, Huang Y, Hou JY, et al. Adherence to treatment recommendations and outcomes for women with ovarian cancer at first recurrence[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2018, 148(1): 19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.11.008
[4] Oronsky B, Ray CM, Spira AI, et al. A brief review of the management of platinum-resistant-platinum-refractory ovarian cancer[J]. Med Oncol, 2017, 34(6): 103. doi: 10.1007/s12032-017-0960-z
[5] Singh N, Badrun D, Ghatage P. State of the art and up-and-coming angiogenesis inhibitors for ovarian cancer[J]. Expert Opin Pharmacother, 2020, 21(13): 1579-1590. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1775813
[6] Ni J, Cheng X, Chen J, et al. Anlotinib as Exploratory Therapy for Platinum-Resistant OvarianCancer: A Retrospective Study on Efficacy and Safety[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2020, 13: 9857-9863. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S268613
[7] Zhang L, Conejo-Garcia JR, Katsaros D, et al. Intratumoral T cells, recurrence, and survival in epithelial ovarian cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2003, 348(3): 203-213. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa020177
[8] Hwang WT, Adams SF, Tahirovic E, et al. Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating T cells in ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2012, 124(2): 192-198. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.09.039
[9] Matulonis UA, Shapira-Frommer R, Santin AD, et al. Antitumor activity and safety of pembrolizumab in patients with advanced recurrent ovarian cancer: results from the phaseⅡ KEYNOTE-100 study[J]. Ann Oncol, 2019, 30(7): 1080-1087. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz135
[10] Hamanishi J, Mandai M, Ikeda T, et al. Safety and Antitumor Activity of Anti-PD-1 Antibody, Nivolumab, in Patients With Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2015, 33(34): 4015-4022. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.62.3397
[11] Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1)[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2009, 45(2): 228-247. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
[12] Miller TP, Fisher BT, Getz KD, et al. Unintended consequences of evolution of the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events[J]. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 2019, 66(7): e27747. doi: 10.1002/pbc.27747
[13] Harries M, Gore M. PartⅠ: chemotherapy for epithelial ovarian cancer-treatment at first diagnosis[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2002, 3(9): 529-536. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(02)00846-X
[14] Cui Q, Hu Y, Ma D, et al. A Retrospective Observational Study of Anlotinib in Patients with Platinum-Resistant or Platinum-Refractory Epithelial Ovarian Cancer[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2021, 15: 339-347. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S286529
[15] Varga A, Piha-Paul S, Ott PA, et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with programmed death ligand 1-positive advanced ovarian cancer: Analysis of KEYNOTE-028[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2019, 152(2): 243-250. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2018.11.017
[16] Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 382(20): 1894-1905. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1915745
[17] Liu JF, Herold C, Gray KP, et al. Assessment of Combined Nivolumab and Bevacizumab in Relapsed Ovarian Cancer: A Phase 2 Clinical Trial[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2019, 5(12): 1731-1738. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.3343
[18] Xie C, Wan X, Quan H, et al. Preclinical characterization of anlotinib, a highly potent and selective vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 inhibitor[J]. Cancer Sci, 2018, 109(4): 1207-1219. doi: 10.1111/cas.13536
[19] Rades D, Motisi L, Veninga T, et al. Predictors of Outcomes and a Scoring System for Estimating Survival in Patients Treated With Radiotherapy for Metastatic Spinal Cord Compression From Small-Cell Lung Cancer[J]. Clin Lung Cancer, 2019, 20(4): 322-329. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2019.04.005
[20] Yan Z, Gu YY, Hu XD, et al. Clinical outcomes and safety of apatinib monotherapy in the treatment of patients with advanced epithelial ovarian carcinoma who progressed after standard regimens and the analysis of the VEGFR2 polymorphism[J]. Oncol Lett, 2020, 20(3): 3035-3045. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11857
[21] Domchek SM, Aghajanian C, Shapira-Frommer R, et al. Efficacy and safety of olaparib monotherapy in germline BRCA1/2 mutation carriers with advanced ovarian cancer and three or more lines of prior therapy[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2016, 140(2): 199-203. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2015.12.020
[22] Yuan M, Zhu Z, Mao W, et al. Anlotinib Combined With Anti-PD-1 Antibodies Therapy in Patients With Advanced Refractory Solid Tumors: A Single-Center, Observational, Prospective Study[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 683502. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.683502
[23] Jiang FE, Zhang HJ, Yu CY, et al. Efficacy and safety of regorafenib or fruquintinib plus camrelizumab in patients with microsatellite stable and/or proficient mismatch repair metastatic colorectal cancer: an observational pilot study[J]. Neoplasma, 2021, 68(4): 861-866. doi: 10.4149/neo_2021_201228N1415
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 王芳,张慧芳. 酪氨酸激酶抑制剂在晚期卵巢癌治疗中的作用进展. 医师在线. 2025(01): 91-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘树雨,王丽霞,姚秀玲,李燕. 阿替利珠单抗联合化疗治疗卵巢癌的效果及对肿瘤标志物、短期预后的影响. 中国妇产科临床杂志. 2024(01): 28-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 蒋艳,黎雪梅,邹吴春,任丽,何春,阳袁莉. 血清可溶性CD276与晚期高级别浆液性卵巢癌预后及肿瘤免疫浸润相关性分析. 实用医院临床杂志. 2024(01): 123-127 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 彭晓燕. 聚腺苷二磷酸核糖聚合酶抑制剂在中晚期上皮性卵巢癌维持治疗中的应用效果. 中外医药研究. 2024(25): 54-56 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李成彪,顾刚寿. 安罗替尼三线治疗晚期卵巢癌的疗效. 中华全科医学. 2023(07): 1150-1152 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李成彪,顾刚寿. 安罗替尼治疗晚期卵巢癌的疗效分析. 癌症进展. 2023(13): 1420-1423 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 李慧芬. 外周血CD4~+PD-1~+Tcells及CD4~+T淋巴细胞ATP含量与复发性卵巢癌疗效的相关性分析. 实用妇科内分泌电子杂志. 2023(27): 24-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: