Effects of Linc00460 on Aerobic Glycolysis in Breast Cancer Cells via Sponge Adsorption of miR-320a
-
摘要:目的
探讨Linc00460通过海绵吸附miR-320a对乳腺癌(BC)细胞有氧糖酵解作用的影响。
方法qRT-PCR法检测正常乳腺上皮细胞系MCF-10A及5种BC细胞系中Linc00460和miR-320a表达水平。qRT-PCR检测干扰Linc00460对miR-320a表达的影响,双荧光素酶报告基因实验检测miR-320a和Linc00460的靶向关系。将si-Linc00460和miR-320a inhibitor共转染至MDA-MB-231细胞,qRT-PCR检测细胞中miR-320a表达水平;MTT法检测细胞增殖能力;2-NBDG法检测细胞葡萄糖摄取率;比色法检测细胞上清液中乳酸含量;酶活性试剂盒检测糖酵解关键酶的活性;Western blot检测酵解途径中关键蛋白表达水平。
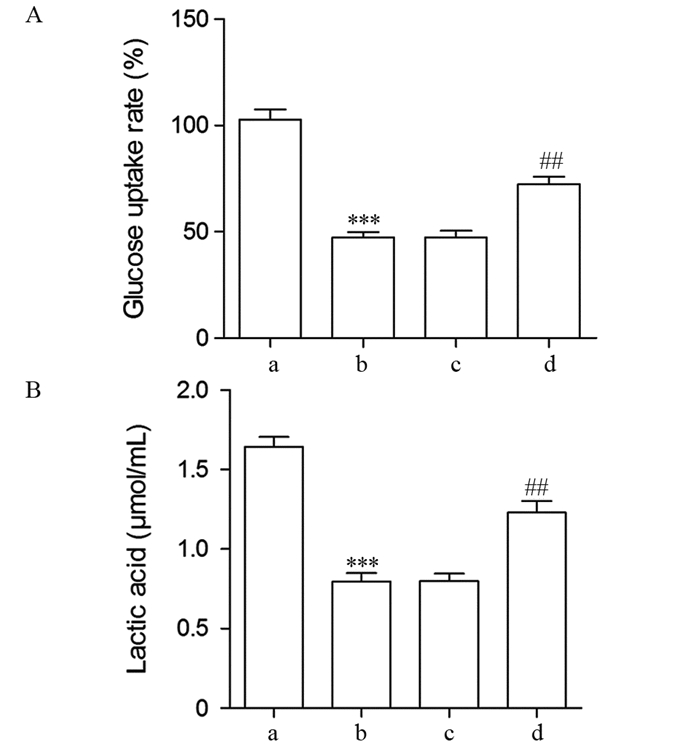
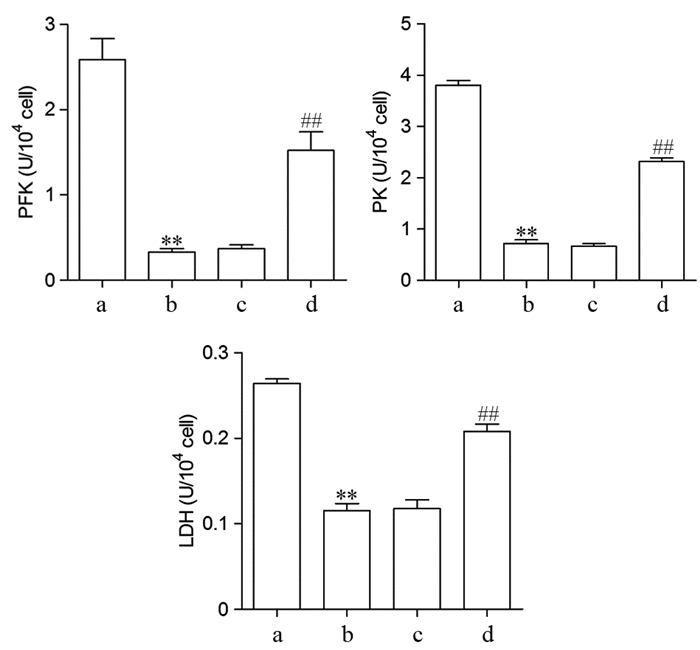
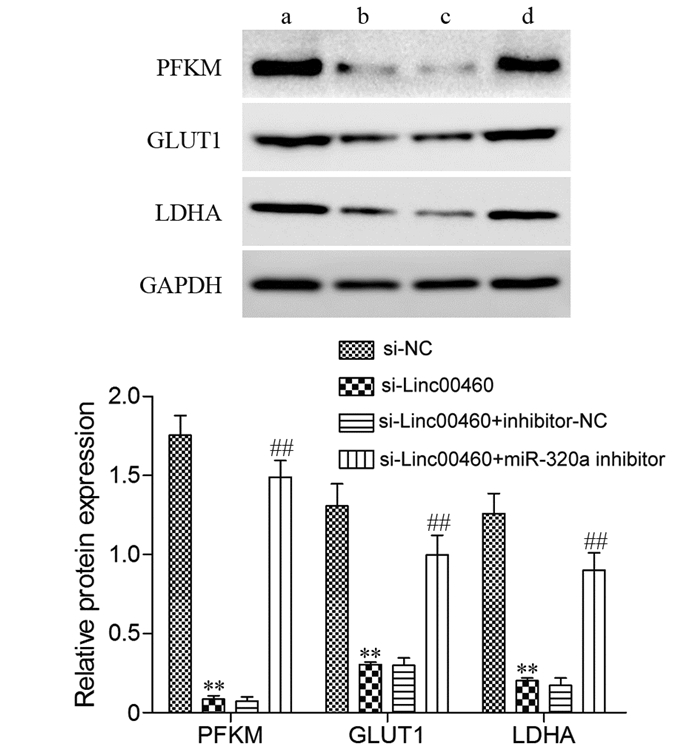
结果与MCF-10A细胞比较,5种BC细胞系中Linc00460高表达,而miR-320a低表达。干扰Linc00460后,MDA-MB-231细胞中miR-320a表达显著升高。双荧光素酶报告基因实验证实,miR-320a和Linc00460可靶向结合。干扰Linc00460表达后MDA-MB-231细胞增殖能力受到明显抑制(P=0.000),细胞葡萄糖摄取率和细胞上清液中乳酸含量降低(均P=0.000),PFK、PK和LDH酶活性受到抑制(均P=0.000),PFKM、GLUT1和LDHA蛋白表达水平下调(均P=0.000)。抑制miR-320a可明显逆转si-Linc00460对MDA-MB-231细胞增殖和糖酵解的抑制作用(均P=0.000或0.001)。
结论Linc00460可能通过海绵吸附miR-320a,上调PFKM表达,从而促进BC细胞有氧糖酵解作用。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the effect of Linc00460 on the aerobic glycolysis of breast cancer (BC) cells through sponge adsorption of miR-320a.
MethodsThe qRT-PCR method was used to detect Linc00460 and miR-320a expression levels in normal breast epithelial cell line MCF-10A and five BC cell lines. The effect of interfering Linc00460 on miR-320a expression was detected by qRT-PCR. The double luciferase reporter gene experiment was used to analyze the targeting relationship between miR-320a and Linc00460. In addition, the si-Linc00460 and miR-320a inhibitor were co-transfected into MDA-MB-231 cells, and the expression level of miR-320a in the cells was detected by qRT-PCR; cell proliferation ability was measured by the MTT method; glucose uptake rate was detected by 2-NBDG method; the content of lactic acid in the cell supernatant was detected by colorimetric method; the key enzymes of glycolysis was detected by the enzyme activity kit; and the expression levels of the key proteins in the glycolysis pathway were detected by Western blot.
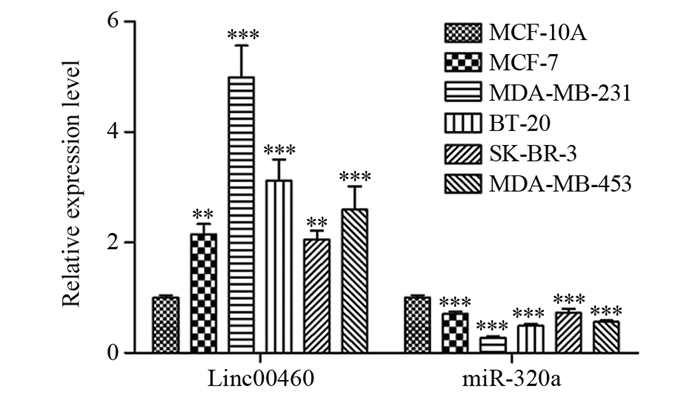
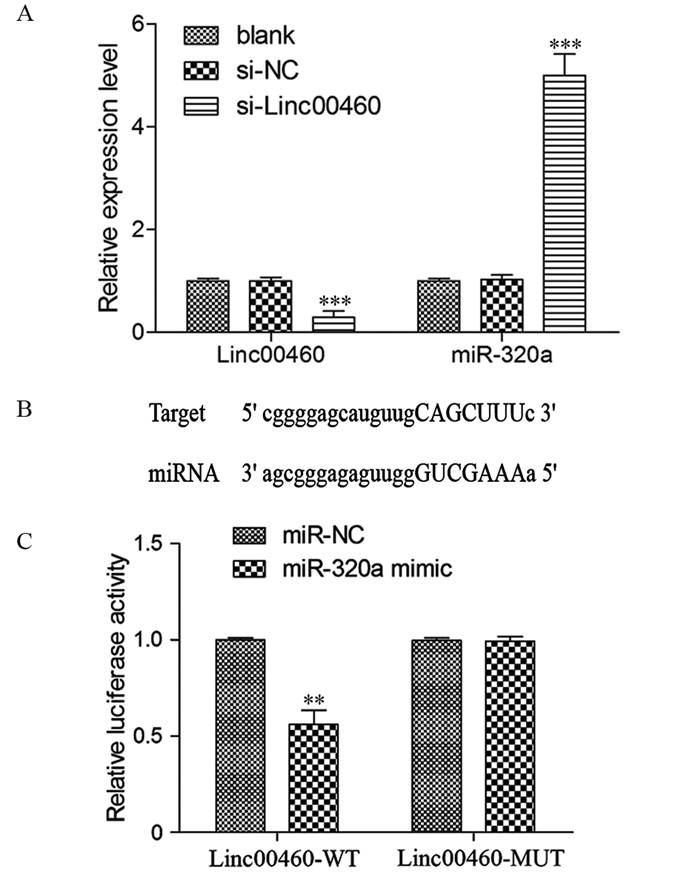
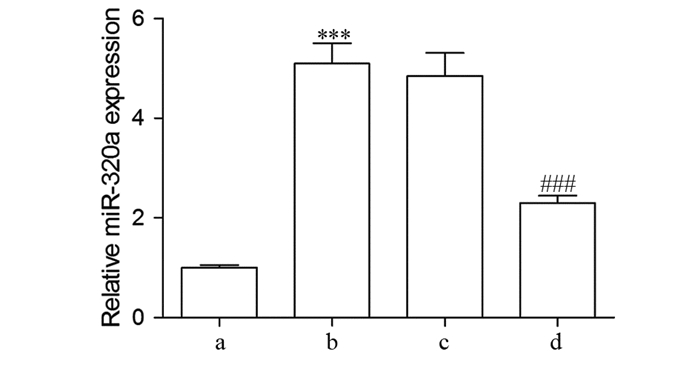
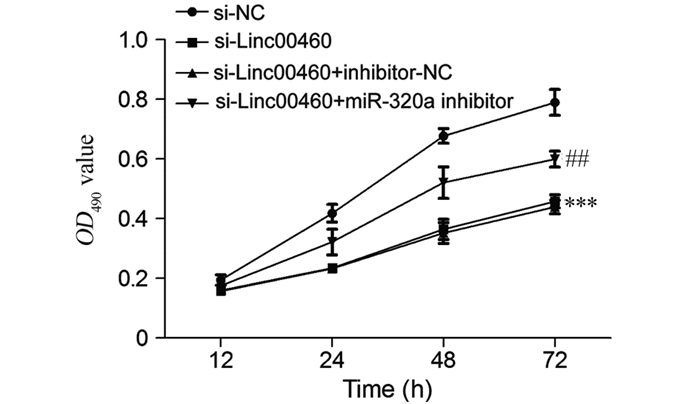
ResultsLinc00460 was highly expressed in five BC cell lines, while miR-320a was lowly expressed as compared with MCF-10A cells. The expression of miR-320a in MDA-MB-231 cells significantly increased after interfering with Linc00460. The double luciferase reporter gene experiment confirmed that miR-320a and Linc00460 could target binding. Interfering with the expression of Linc00460 could inhibit MDA-MB-231 cells proliferation (all P=0.000), reduce the rate of cellular glucose uptake and the content of lactic acid in the cell supernatant (all P=0.000), inhibit the activities of PFK, PK, and LDH enzymes (all P=0.000), and downregulate the protein expression levels of PFKM, GLUT1, and LDHA (all P=0.000). Meanwhile, inhibition of miR-320a could reverse the inhibitory effect of si-Linc00460 on the proliferation and glycolysis of MDA-MB-231 cells (all P=0.000 or 0.001).
ConclusionLinc00460 might adsorb miR-320a, consequently leading to upregulation of PFKM expression, thereby promoting aerobic glycolysis in BC cells.
-
Key words:
- Breast cancer /
- Linc00460 /
- miR-320a /
- Glycolysis /
- PFKM
-
0 引言
目前,乳腺癌严重威胁着女性的健康。在乳腺癌的转移机制中,上皮间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition, EMT)是其中一个核心的生物学进程,与乳腺癌的侵袭和转移密切相关。JMJD3又称赖氨酸去甲基化酶6B(lysine demethylase 6B, KDM6B)作为一种Lys27位点三甲基化组蛋白H3(histone H3 methylated Lys27,H3K27me3)去甲基化酶[1],其异常表达与多种肿瘤的发生、发展密切相关[2-3]。JMJD3在肿瘤中是促癌基因还是抑癌基因研究报道尚不一致,有关JMJD3在乳腺癌中的作用,以及JMJD3与上皮间质转化的相关性尚未见类似报道。本研究收集120例乳腺浸润性导管癌组织标本,采用免疫组织化学法检测JMJD3和上皮间质转化相关蛋白E-cadherin、Vimentin和N-cadherin的表达,并分析其相关性及临床病理意义,以拓展和丰富人们对乳腺癌发病机制的认识。
1 资料与方法
1.1 病例资料
收集郑州人民医院2014年1月—2015年12月间收治的120例乳腺原发浸润性导管癌及相应的癌旁病理活检标本和相关临床资料。患者术前均未接受放疗或化疗。按照2012年WHO乳腺癌组织病理分级分类法对其进行分组。所有标本均经10%的甲醛固定,石蜡包埋,并经郑州人民医院病理科确诊。
1.2 主要试剂
JMJD3一抗兔抗人多克隆抗体购自英国Abcam公司,E-cadherin、Vimentin和N-cadherin一抗兔抗人单克隆抗体(即用型)、二抗及二氨基联苯胺(DAB)均为福州迈新公司产品。
1.3 免疫组织化学染色
主要步骤如下:(1)石蜡组织切片、烤片、脱蜡并水化;(2)EDTA抗原修复;(3)兔抗人单克隆抗体一抗37℃孵育2 h;(4)二抗37℃孵育20~30 min;(5)DAB显色5~10 min;(6)脱水、透明和封片。用已知JMJD3、E-cadherin、Vimentin和N-cadherin阳性的乳腺癌组织和PBS分别代替一抗作为阳性和空白对照。
1.4 免疫组织化学结果判断
JMJD3阳性信号呈棕褐色,表达于细胞核;E-cadherin和N-cadherin阳性信号为棕黄色,表达于细胞膜;Vimentin阳性信号为棕黄色,表达于细胞质。按样本中JMJD3、E-cadherin、Vimentin及N-cadherin阳性细胞占总细胞的比例分为4个等级[4]: < 5%为阴性、5%~ < 25%为弱阳性、25%~50%为中等阳性、≥50%为强阳性。其中阴性和弱阳性判断为低表达,中等阳性和强阳性判断为高表达,阳性表达率=(中等阳性+强阳性样本量)/总样本量,免疫组织化学的判读由两位高年资病理医师采用双盲法进行。
1.5 统计学方法
采用SPSS17.0统计软件进行数据处理与统计分析,JMJD3、E-cadherin、Vimentin和N-cadherin阳性表达率和病理因素的相关性采用χ2检验,蛋白间的相关性采用Spearman相关分析,以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 乳腺浸润性导管癌中JMJD3、E-cadherin、Vimentin和N-cadherin的表达
JMJD3主要定位于细胞核,在乳腺浸润性导管癌及癌旁组织中呈棕褐色,在导管癌中的阳性表达率明显低于癌旁组织,差异有统计学意义(χ2=7.326, P=0.007),见图 1、表 1。JMJD3表达较高者,组织学分化程度高,细胞黏附性强,极性较好,JMJD3表达较低者,组织学分化程度差,细胞黏附性下降,失去极性,细胞梭形更为明显,见图 2。
表 1 乳腺癌和癌旁组织中JMJD3、E-cadherin、Vimentin及N-cadherin的阳性表达(n(%))Table 1 Expression of JMJD3, E-cadherin, Vimentin and N-cadherin in breast cancer tissues and adjacent tissues (n(%))
E-cadherin在乳腺浸润性导管癌及癌旁组织中主要定位于细胞膜,为粗细相对均匀的棕褐色颗粒,乳腺浸润性导管癌中E-cadherin阳性表达率明显低于癌旁组织,差异有统计学意义(χ2=10.256, P=0.001)。Vimentin主要表达于上皮周围的间质细胞中,在癌及癌旁组织中主要定位于细胞质,为粗细不等的棕褐色颗粒,乳腺浸润性导管癌中Vimentin阳性表达率明显高于癌旁组织,差异有统计学意义(χ2=24.033, P=0.000)。N-cadherin在癌及癌旁组织中主要定位于细胞膜,为粗细相对均匀的棕褐色颗粒,乳腺浸润性导管癌中N-cadherin阳性表达率为明显高于癌旁组织,差异有统计学意义(χ2=35.281, P=0.000),见图 1、表 1。
2.2 JMJD3、E-cadherin、Vimentin和N-cadherin与乳腺浸润性导管癌临床病理特征的关系
在乳腺浸润性导管癌中,JMJD3与肿瘤直径(χ2=9.697, P=0.008)、组织学分级(χ2=27.313, P=0.000)、淋巴结转移(χ2=12.587, P=0.000)TNM分期有关(χ2=12.385, P=0.000),与乳腺癌患者年龄和肿瘤位置均无关(均P > 0.05)。E-cadherin在高分化、中分化和低分化乳腺癌中表达率依次降低,差异具有统计学意义(χ2=14.152, P=0.001);其在淋巴结有转移组中低于无淋巴结转移组,差异有统计学意义(χ2=9.903, P=0.002);其在TNM Ⅲ期、Ⅳ期组别低于Ⅰ期、Ⅱ期组别,差异具有统计学意义(χ2=20.771, P=0.000)。E-cadherin与乳腺癌患者年龄、肿瘤位置和肿瘤直径均无关(均P > 0.05)。Vimentin在高分化、中分化和低分化乳腺癌中表达率依次升高,差异具有统计学意义(χ2=28.410, P=0.000);其在淋巴结有转移组中高于无淋巴结转移组(χ2=14.090, P=0.000),TNMⅢ期、Ⅳ期组高于Ⅰ期、Ⅱ期组(χ2=13.218, P=0.000),与年龄、肿瘤位置和肿瘤直径均无关(均P > 0.05)。N-cadherin在高分化、中分化和低分化中表达率依次升高(χ2=28.410, P=0.000);其在淋巴结有转移组中高于无淋巴结转移组(χ2=17.678, P=0.000),在TNM Ⅲ期、Ⅳ期组高于Ⅰ期、Ⅱ期组(χ2=30.035, P=0.000)。N-cadherin与乳腺癌患者年龄、肿瘤位置及肿瘤直径均无关(均P > 0.05),见表 2。
表 2 乳腺癌中JMJD3、E-cadherin、Vimentin及N-cadherin的表达与临床病理特征的关系(n(%))Table 2 Correlation of JMJD3, E-cadherin, Vimentin and N-cadherin expression with clinicopathological characteristics of breast cancer patients (n(%))
2.3 乳腺浸润性导管癌中JMJD3与E-cadherin、Vimentin和N-cadherin相关性分析
采用Spearman相关分析,结果显示JMJD3和E-cadherin表达呈正相关(r=0.204, P=0.025)。JMJD3和Vimentin表达呈负相关(r=-0.467, P=0.000)。JMJD3和N-cadherin表达呈负相关(r=-0.500, P=0.000),见表 3。
表 3 乳腺癌中JMJD3与E-cadherin, Vimentin和N-cadherin的Spearman相关性分析Table 3 Spearman correlation analysis of JMJD3 expression with E-cadherin, Vimentin and N-cadherin expression in breast cancer tissues
3 讨论
JMJD3编码基因位于人类第17号染色体上,其异常表达与肿瘤的发生发展有密切关系。Tokunaga等[5]对151例结肠癌患者的术后生存分析结果表明,JMJD3低表达者术后生存期普遍较短,且回归分析表明JMJD3的低表达是患者不良预后的独立危险因素之一。国内有研究发现JMJD3过表达对胃癌细胞的增殖具有抑制作用,对细胞凋亡具有促进作用[6]。胡贺芳等[7]研究发现JMJD3表达降低可能促进肺癌的发生发展。李彦伟等[8]发现胶质瘤细胞中JMJD3较瘤旁组织表达降低,其过表达可增强胶质瘤细胞迁移能力,该机制通过影响SNAIL基因调控区H3K27me3水平而调节胶质瘤侵袭过程[9]。
JMJD3是促癌基因还是抑癌基因研究报道尚不一致,本研究采用免疫组织化学方法发现JMJD3在乳腺浸润性导管癌组织表达率较癌旁组织低,其在组织学分化差、有淋巴结转移及较高TNM分期的组织中表达率减低,提示JMJD3在乳腺癌的浸润转移中扮演了抑癌基因的角色。此外本研究结果还显示JMJD3低表达与肿瘤直径相关,肿瘤直径的大小反映细胞增殖能力,我们推测JMJD3对乳腺癌细胞增殖具有抑制作用,这与以往其在胃癌研究报道观点一致[6]。
在乳腺癌的转移机制中,EMT是其中一个核心的生物学进程。EMT的过程中,上皮细胞标志性蛋白E-cadherin减少,而间质细胞标志性蛋白Vimentin和N-cadherin表达量上升[10-12]。E-cadherin主要分布于胚胎组织和成熟组织的上皮细胞中,除具有调节胚胎组织的发育、组织形成、参与细胞与细胞间信息传递交流等作用外,对促进细胞的黏附聚集、维持上皮形态结构完整性、极性和参与分化调节也至关重要。Vimentin主要表达于间叶组织和淋巴造血细胞,在上皮中几乎不表达,当细胞出现上皮间质转化时可有表达。N-cadherin表达于神经外胚层和中胚层来源的组织,正常上皮组织不表达或低表达。N-cadherin在上皮组织中的异位表达可以影响上皮细胞的形态和行为,诱导其向间质转化,即产生EMT。
本研究结果显示从乳腺癌旁组织到乳腺癌组织JMJD3和E-cadherin阳性率逐渐减少,而Vimentin和N-cadherin阳性率逐渐增高;同时它们均与乳腺癌分化程度、TNM分期和淋巴结转移相关,表明JMJD3和EMT相关蛋白共同参与乳腺癌的发生、发展,其可能机制是通过降低肿瘤细胞间的黏附力,使乳腺癌更容易发生浸润和转移。本研究中E-cadherin、Vimentin和N-cadherin的表达情况与以往文献报道的结果基本一致[13-14]。
通过查阅国内外文献,我们发现JMJD3表达对上皮间质转化的影响在胶质瘤细胞[15]、肝癌细胞[16-17]、肾癌细胞[18]和弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤[19]已有研究报道,其在乳腺癌中尚未见研究报道。上述研究均表明JMJD3过表达能够促进上皮间质转化过程进而促进肿瘤的浸润转移。本研究相关分析结果发现JMJD3与E-cadherin表达呈正相关,与Vimentin和N-cadherin表达呈负相关,表明JMJD3低表达可能通过下调E-cadherin及上调Vimentin和N-cadherin的表达使乳腺癌上皮细胞获得间质细胞的特性,进而促进EMT的发生。提示JMJD3阳性率较低的乳腺癌患者更易发生淋巴结转移和较差的组织学分化,而组织学分化较差的乳腺癌细胞在形态学上细胞极性消失,细胞梭形明显,黏附性下降,从形态学上表明JMJD3可能通过上皮间质转化途径参与乳腺癌的发生发展。本研究从蛋白水平对乳腺癌中JMJD3、E-cadherin和Vimentin表达进行分析,尚缺少分子生物学调节实验,还需进一步深入研究。
综上所述,乳腺浸润性导管癌中组蛋白去甲基化酶JMJD3与E-cadherin呈正相关,与Vimentin和N-cadherin呈负相关,JMJD3可能通过调节乳腺癌细胞上皮间质转化,调控乳腺癌侵袭转移,其具体机制有待后续深入研究。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.作者贡献:芮一奇:实验实施、文章撰写、经费支持邓飞:实验实施、数据采集王文文:实验设计、文章审阅、数据分析许华、李晓伟、丁永斌:实验实施、数据分析范姝琳:实验指导、统计学分析、英文摘要撰写 -
-
[1] Wang X, Gao C, Feng F, et al. Construction and analysis of competing endogenous RNA networks for breast cancer based on TCGA dataset[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 4078596.
[2] Morales MAG, Rodríguez RB, Cruz JRS, et al. Overview of new treatments with immunotherapy for breast cancer and a proposal of a combination therapy[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(23): 5686. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235686
[3] Zhu Y, Yang L, Chong QY, et al. Long noncoding RNA Linc00460 promotes breast cancer progression by regulating the miR-489-5p/FGF7/AKT axis[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2019, 11: 5983-6001. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S207084
[4] Guan J, Zhou Y, Mao F, et al. MicroRNA-320a suppresses tumor cell growth and invasion of human breast cancer by targeting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor[J]. Oncol Rep, 2018, 40(2): 849-858.
[5] Yu J, Wang JG, Zhang L, et al. MicroRNA-320a inhibits breast cancer metastasis by targeting metadherin[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(25): 38612-38625. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9572
[6] Tang H, Lee M, Sharpe O, et al. Oxidative stress-responsive microRNA-320 regulates glycolysis in diverse biological systems[J]. FASEB J, 2012, 26(11): 4710-4721. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-197467
[7] Cisneros-Villanueva M, Hidalgo-Pérez L, Cedro-Tanda A, et al. LINC00460 is a dual biomarker that acts as a predictor for increased prognosis in basal-like breast cancer and potentially regulates immunogenic and differentiation-related genes[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 628027. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.628027
[8] Li J, Huang S, Zhang Y, et al. LINC00460 enhances bladder carcinoma cell proliferation and migration by modulating miR-612/FOXK1 axis[J]. Pharmacology, 2021, 106(1-2): 79-90. doi: 10.1159/000509255
[9] Ruan T, Lu S, Xu J, et al. lncRNA LINC00460 functions as a competing endogenous RNA and regulates expression of BGN by Sponging miR-149-5p in colorectal cancer[J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2021, 20: 1533033820964238.
[10] Li F, Zhu W, Wang Z, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00460 promotes the progression of cervical cancer via regulation of the miR-361-3p/Gli1 axis[J]. Hum Cell, 2021, 34(1): 229-237. doi: 10.1007/s13577-020-00447-2
[11] Cheng J, Lou Y, Jiang K, et al. Downregulation of long non-coding RNA LINC00460 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion, and promotes apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells via modulation of the miR-320b/ARF1 axis[J]. Bioengineered, 2021, 12(1): 96-107. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2020.1863035
[12] Yang Y, Wang R, Feng L, et al. LINC00460 promotes cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via miR-320a/BGN axis[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2021, 14: 2279-2291. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S282947
[13] Zhou Y, Lin F, Wan T, et al. ZEB1 enhances Warburg effect to facilitate tumorigenesis and metastasis of HCC by transcriptionally activating PFKM[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(12): 5926-5938. doi: 10.7150/thno.56490
[14] Gao W, Huang M, Chen X, et al. The role of S-nitrosylation of PFKM in regulation of glycolysis in ovarian cancer cells[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(4): 408.
[15] Yu L, Chen X, Wang L, et al. The sweet trap in tumors: aerobic glycolysis and potential targets for therapy[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(25): 38908-38926.
[16] Feng L, Rao M, Zhou Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA 00460 (LINC00460) promotes glioma progression by negatively regulating miR-320a[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(6): 9556-9563.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 苗晓红,袁志英,李媛,韩秀青,李光. 宫颈癌组织含Jumonji结构域的蛋白2B、造血相关PBX相互作用蛋白的表达与预后关系的分析. 中国性科学. 2023(01): 60-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 徐小艳,王建君,闫琛,李川,刘微,杨金花. ALKBH5促进乳腺浸润性导管癌细胞上皮间质转化和血管生成并增强其侵袭和转移. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志. 2021(04): 355-361 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: