Clinical Characteristics and Prognostic Influence Factors of Patients with AIDS-related Malignant Tumor
-
摘要:目的
分析艾滋病病毒(HIV)感染者/艾滋病(AIDS)合并恶性肿瘤患者的临床特点及生存预后情况。
方法回顾性分析354例艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤患者资料,采用Log-rank检验进行单因素分析,采用Cox比例风险回归模型进行多因素分析。
结果患者平均年龄54.10±12.96岁,男女比例2.1:1,艾滋病合并淋巴瘤的患者最多(28.25%);1、3、5年生存率分别为78.48%、62.13%、55.31%。单因素分析显示不同恶性肿瘤类型、年龄、性别、医保类型、确诊合并艾滋病后住院次数、平均住院天数、是否放疗、有无遵医嘱离院等患者的预后差异均有统计学意义;多因素分析显示性别、入院次数、平均住院天数、自费比例以及有无遵医嘱离院是影响患者生存预后的独立危险因素。
结论艾滋病容易合并淋巴瘤、肺癌、宫颈癌。患者在医院接受抗肿瘤疗程不足。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo analyze the clinical characteristics and survival prognosis of patients with AIDS-related malignant tumor.
MethodsWe retrospectively analyzed the data of 354 patients with AIDS-related malignant tumor. Univariate analysis was conducted by Log rank test and multivariate analysis was conducted by Cox proportional risk regression model.
ResultsThe average age of the patients was 54.10±12.96 years old. The ratio of male to female patients was 2.1:1. The number of patients with AIDS complicated with lymphoma was the most, accounting for 28.25%. The 1-, 3- and 5-year survival rates were 78.48%, 62.13% and 55.31%, respectively. Univariate analysis showed that there were statistical differences in prognosis of patients with different types of malignant tumor, age, gender, medical insurance type, number of admissions after diagnosis of AIDS, average length of stay, radiotherapy or not, leaving hospital according to medical advice. Multivariate analysis showed that gender, number of admissions after diagnosis of AIDS, average length of stay, proportion of out-of-pocket and leaving hospital according to medical advice were independent risk factors affecting the survival and prognosis of patients.
ConclusionAIDS is easily complicated with lymphoma, lung cancer and cervical cancer. The patients received insufficient anti-tumor courses in hospital.
-
Key words:
- HIV /
- Malignant tumor /
- Clinical features /
- Survival /
- Prognosis
-
0 引言
艾滋病病毒(human immunodeficiency virus, HIV)会降低人体的免疫功能,增加人体患各种恶性肿瘤的风险[1],特别是引入联合抗反转录病毒疗法之后,艾滋病(acquired immune deficiency syndrome, AIDS)患者/HIV感染者的病程不断延长,而恶性肿瘤也逐渐成为此类患者死亡的重要病因之一[2]。近年来,我国HIV/AIDS患者人数在不断增加,HIV/AIDS合并恶性肿瘤(简称:艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤)的人数也随之增加[3-4]。我国对于艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤的规范性诊断和治疗工作开展较晚[5],加之临床上重治疗、轻随访,对于该类患者的大样本生存预后的研究报道较少。因此,本研究旨在更好地了解此类患者的临床特点,探讨患者生存预后情况及其影响因素,为进一步诊治提供参考依据。
1 资料与方法
1.1 资料
回顾性分析2013年1月1日—2020年12月31日在重庆大学附属肿瘤医院住院的354例艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤患者资料。所有患者HIV抗体检测均为阳性,均经病理确诊为恶性肿瘤,疾病编码以医院当年病案室专职编码员填写的ICD编码为依据。纳入标准:(1)首次确诊艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤患者;(2)年龄≥18岁;(3)住院治疗患者。排除标准:(1)非HIV或非恶性肿瘤患者;(2)门诊诊疗患者;(3)重复入院患者。本研究符合《赫尔辛基宣言》的要求,研究数据库已做隐私保密处理。
1.2 方法
收集患者的人口学特征(包括年龄、性别、职业、婚姻状况等)、医保信息(包括医疗保险类型、自费比例等)、住院治疗(包括确诊艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤后的住院治疗次数、平均住院天数、直接医疗总花费、是否接受手术/放疗/化疗、有无遵医嘱离院等)以及随访等预后相关信息。多因素分析采用Cox回归模型,利用条件向前法筛选变量,确定α=0.20,分类变量以哑变量的形式纳入模型,参照组为每个变量的第一个亚组,其他变量直接纳入模型进行分析。
1.3 统计学方法
采用R4.0.2,(https://www.r-project.org)统计软件进行统计分析,正态计量资料采用均数±标准差(x±s),计数资料采用绝对数(%)表示;采用Kaplan-Meier法计算平均生存时间、生存率并绘制生存曲线;单因素分析采用Log rank检验进行生存分析;多因素分析采用Cox比例风险回归模型进行分析;P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 患者临床特征
患者平均年龄54.10±12.96岁(23~87岁);男女患者比例为2.1:1;所有患者中,合并淋巴瘤的患者最多,其次是肺癌和宫颈癌;从医保类型分布情况来看,城镇居民医保的患者最多。治疗数据显示:大部分患者只在医院接受一次住院治疗,确诊后在院的直接医疗费用在3万以上的有151例,占42.66%;分别接受过手术、放疗、化疗的患者占30%左右;27.97%的患者有过未遵医嘱出院的行为,见表 1。
表 1 艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤患者的临床特征Table 1 Clinical characteristics of patients with AIDS-related malignant tumor
2.2 患者生存情况
随访数据显示,54例(占15.25%)患者失访,104例(占29.38%)患者死亡,所有研究对象的平均生存时间为58.42月(95%CI: 53.11~63.73),1、3、5年观察生存率分别为78.48%、62.13%、55.31%。
单因素分析结果显示:不同恶性肿瘤类型、年龄、性别、医疗保险类型、确诊合并HIV后的住院次数、平均住院天数、直接总医疗费用、自费比例、是否放疗、有无遵医嘱离院患者的预后差异均有统计学差异,见表 2。
表 2 艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤患者预后的单因素分析Table 2 Survival of patients with AIDS-related malignant tumor: univariate analysis
2.3 影响艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤患者预后的多因素分析
多因素分析结果显示,性别、入院次数、平均住院天数、自费比例以及有无遵医嘱离院是影响患者生存预后的独立危险因素。可以认为男性患者发生死亡的风险是女性2.02倍;住院次数1次的发生死亡的风险是2次及以上的1.70倍,平均住院天数在8天及以上的患者发生死亡的风险是住院天数≤4天的2.91倍,自费比例≤40%的患者发生死亡的风险是 > 40%患者的1.52倍,遵医嘱离院的患者发生死亡的风险是未遵医嘱离院患者的2.38倍,见表 3。
表 3 影响艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤患者预后的多因素分析Table 3 Multivariate analysis of prognosis of patients with AIDS-related malignant tumor
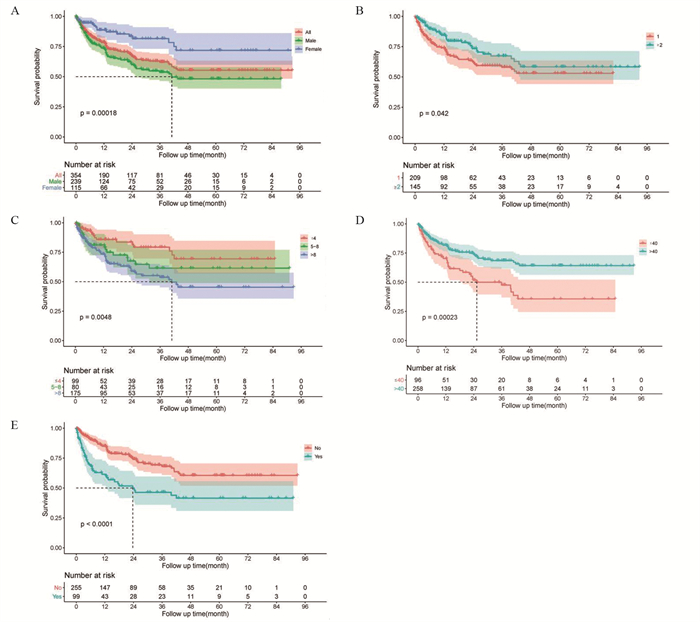
将多因素分析有统计学差异的变量逐个绘制生存曲线图,结果显示女性患者生存预后好于男性,2次及以上的患者生存预后好于只有1次入院记录的患者,平均住院日在8天以上患者生存预后最差,自费比例 > 40%的患者生存预后逊于≤40%的患者,遵医嘱离院的患者生存预后好于未遵医嘱离院的患者,见图 1。
![]() 图 1 不同患者的Kaplan-Meier生存曲线A: survival of all and different gender patients; B: survival of patients with different admissions; C: survival of patients with different length of stay; D: survival of patients with different proportion of out-ofpocket; E: survival of patients leaving hospital according to medical advice.Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier survival curves of different groups of patients
图 1 不同患者的Kaplan-Meier生存曲线A: survival of all and different gender patients; B: survival of patients with different admissions; C: survival of patients with different length of stay; D: survival of patients with different proportion of out-ofpocket; E: survival of patients leaving hospital according to medical advice.Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier survival curves of different groups of patients3 讨论
随着我国艾滋病防控工作的进一步推进以及检测覆盖面的扩大,每年新诊断的艾滋病患者人数也在不断增加。据估计,2018年我国艾滋病新发感染人数为8万,而现存活人数达到125万,且未来几年将持续增加[6-7]。随着医疗技术的进步,艾滋病患者的生命周期会不断延长,艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤的人数也会不断增加,本次研究数据也证实了该趋势。目前国内对于艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤患者的治疗情况以及该类型患者的预后情况的研究报道不多,因此,本研究利用重庆大学附属肿瘤医院的电子病历信息系统以及随访系统,纳入HIV合并肿瘤真实世界最大病例数,回顾性地研究该类型患者的临床特点及生存预后情况。研究病例数据量较大,随访时间较长,能在一定程度上反映真实情况,为该类型患者防治工作的进一步开展提供有效依据。
艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤可以分为艾滋病相关肿瘤和非艾滋病相关肿瘤,其中艾滋病相关肿瘤主要包括卡波西肉瘤、非霍奇金淋巴瘤及浸润性宫颈癌三种级别,非艾滋病相关肿瘤主要包括肺癌、肝癌、肛门癌、皮肤癌、结直肠癌以及霍奇金淋巴瘤等[8-9]。本研究结果显示患者以艾滋病相关肿瘤为主,与国内其他研究结论一致[10-12]。具体以合并淋巴瘤最多(占28.25%),其次是肺癌(占14.97%)和宫颈癌(占14.12%),这与国内外其他研究报道有所区别[13-15],可能与不同地区的恶性肿瘤疾病构成及流行趋势不同有关,比如有些肿瘤在某些地区高发,有的医院收治的患者多,艾滋病合并该类肿瘤的患者也会相应增加。实际调查中也发现部分科室不太愿意收治艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤的患者,具体表现在门诊中发现该类患者就不收入住院治疗或者是入院发现后要求患者转院治疗。
本研究显示患者年龄以46岁及以上患者居多,性别以男性为主,与国内外研究一致[16-17],这也与恶性肿瘤发病特点一致[18]。建议临床上要加强对中老年患者艾滋病病史的询问和HIV抗体筛查。59.04%的患者只有一次入院治疗的记录、平均住院日≤4天以及直接医疗花费在1万元及以下等数据提示该类患者接受专业的抗肿瘤治疗不足。建议医院加强院感管理,设置专有病房,减少暴露风险,同时也要加强对患者的宣教和保护患者的利益。
本研究结果显示总体患者的5年观察生存率为55.31%,与国内其他研究报道的恶性肿瘤5年生存率基本一致[19]。而单艾滋病患者及时接受抗病毒治疗能够有效控制病情,5年生存率能达到98%左右[20-21]。提示艾滋病病毒只要经过系统治疗,不会影响患者抗肿瘤治疗的疗效,但具体还需要做进一步的研究来论证。多因素分析显示男性患者死亡风险高于女性,这与其他研究报道男性HIV患者死亡率高于女性结论一致[16]。可能与不同性别的患者接受抗病毒或抗肿瘤治疗的依从性或者与两性间的生活习惯不同等有关,需要进一步论证。住院次数及平均住院天数也是影响患者生存预后的因素。肿瘤患者需要定期复查,有些治疗比如放疗、化疗也是周期性的,患者需要重复住院。患者出院应该听从医嘱,如果患者没有定期住院治疗或者住院天数不够,以及患者没有遵从医嘱自行出院,可以认为患者接受治疗不足或者是治疗依从性不好,进而影响患者的预后。自费比例 > 40%的患者预后要好于≤40%的患者,提示要加大医保的投入,提高患者医疗保险比例。另外,由于本次研究对象为艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤患者的特殊人群,患者诊疗行为及预后会受到社会、经济以及医疗技术发展等多方因素影响,而本研究为单中心回顾性研究,因此建议后期联合传染病医院以及疾控中心等机构开展多中心研究。
综上所述,艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤患者的生存预后影响因素较多。只要接受系统的抗艾滋病病毒治疗,艾滋病病毒对恶性肿瘤的生存预后影响较小。因此,建议加强对患者的宣教,早发现、早系统治疗。同时也建议医院开展抗艾滋病和抗肿瘤双重治疗,做好院感防护,提高患者的生存质量。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.作者贡献:雷海科、李小升:组织随访、数据统计、文章撰写李杰平、刘俊、肖春燕:文章审阅及修改王颖、张维、刘耀、吴永忠::组织实施、文章审阅及修改 -
表 1 艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤患者的临床特征
Table 1 Clinical characteristics of patients with AIDS-related malignant tumor

表 2 艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤患者预后的单因素分析
Table 2 Survival of patients with AIDS-related malignant tumor: univariate analysis

表 3 影响艾滋病合并恶性肿瘤患者预后的多因素分析
Table 3 Multivariate analysis of prognosis of patients with AIDS-related malignant tumor

-
[1] Trickey A, May MT, Gill MJ, et al. Cause-specific mortality after diagnosis of cancer among HIV-positive patients: A collaborative analysis of cohort studies[J]. Int J Cancer, 2020, 146(11): 3134-3146. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32895
[2] Sellier P, Hamet G, Brun A, et al. COREVIH Ile-de-France-Est research group. Mortality of People Living with HIV in Paris Area from 2011 to 2015[J]. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses, 2020, 36(5): 373-380. doi: 10.1089/aid.2019.0143
[3] Qiao YC, Xu Y, Jiang DX, et al. Epidemiological analyses of regional and age differences of HIV/AIDS prevalence in China, 2004-2016[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2019, 81: 215-220. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2019.02.016
[4] 王丽艳, 秦倩倩, 丁正伟, 等. 中国艾滋病全国疫情数据分析[J]. 中国艾滋病性病, 2017, 23(4): 330-333. [Wang LY, Qian QQ, Ding ZW, et al. Current situation of AIDS epidemic in China[J]. Zhongguo Ai Zi Bing Xing Bing, 2017, 23(4): 330-333. ]
[5] Ji Y, Lu H. Malignancies in HIV-Infected and AIDS Patients[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2017, 1018: 167-179.
[6] 吕繁, 陈方方. 艾滋病疫情估计及结果解读要点[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2019, 40(10): 1191-1196. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2019.10.004 [Lyu F, Chen FF. National HIV/AIDS epidemic estimation and interpretation in China[J]. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi, 2019, 40(10): 1191-1196. ] doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2019.10.004
[7] Li Z, Morano JP, Khoshnood K, et al. HIV-related stigma among people living with HIV/AIDS in rural Central China[J]. BMC Health Serv Res, 2018, 18(1): 453. doi: 10.1186/s12913-018-3245-0
[8] Vangipuram R, Tyring SK. AIDS-Associated Malignancies[J]. Cancer Treat Res, 2019, 177: 1-21.
[9] Costiniuk CT, Jenabian MA. Cannabinoids and inflammation: implications for people living with HIV[J]. AIDS, 2019, 33(15): 2273-2288. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002345
[10] 黄曦悦, 石明巧, 苟瑜, 等. 64例HIV/AIDS患者合并肿瘤临床特征分析[J]. 四川医学, 2018, 39(7): 743-747. [Huang XY, Shi MQ, Gou Y, et al. Analysis of the clinical features of 64 cases of HIV/AIDS patients with tumor[J]. Sichuan Yi Xue, 2018, 39(7): 743-747. ]
[11] 王红羚, 张天勇. 肿瘤患者HIV74例感染情况分析[J]. 重庆医学, 2012, 41(31): 3302-3304. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2012.31.024 [Wang HL, Zhang TY. Survey of HIV infection in 74 tumor patients[J]. Chongqing Yi Xue, 2012, 41(31): 3302-3304. ] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2012.31.024
[12] 张珂, 熊英, 吴立春, 等. 肿瘤患者中HIV感染状况的初步调查分析[J]. 肿瘤预防与治疗, 2011, 24(2): 83-85. [Zhang K, Xiong Y, Wu LC, et al. Investigation of HIV Infection Status in Cancer Patients[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yu Zhi Liao, 2011, 24(2): 83-85. ]
[13] Robbins HA, Shiels MS, Pfeiffer RM, et al. Epidemiologic contributions to recent cancer trends among HIV-infected people in the United States[J]. AIDS, 2014, 28(6): 881-890. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000163
[14] 中国疾病预防控制中心, 性病艾滋病预防控制中心, 性病控制中心. 2016年12月全国艾滋病性病疫情[J]. 中国艾滋病性病, 2017, 23(2): 93. [NCAIDS, NCSTD, China CDC. Update on the AIDS/STD epidemic in China in December, 2016[J]. Zhongguo Ai Zi Bing Xing Bing, 2017, 23(2): 93. ]
[15] 王袁, 张树敬, 蔡黎霞, 等. 肿瘤专科医院就诊患者HIV感染情况分析[J]. 中国皮肤性病学杂志, 2017, 31(4): 410-411, 418. [Wang Y, Zhang SJ, Cai NX, et al. Prevalence and Analysis of HIV Infection in Tumor Patients in Cancer Hospital[J]. Zhongguo Pi Fu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi, 2017, 31(4): 410-411, 418. ]
[16] 倪明健, 陈学玲, 马媛媛, 等. 新疆维吾尔自治区艾滋病抗病毒治疗者不同性别死亡率及其影响因素分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2015, 36(9): 971-975. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2015.09.014 [Ni MJ, Chen XL, Ma YY, et al. Sex specific mortality in HIV/AIDS patients receiving antiretroviral therapy and risk factors in Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region[J]. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi, 2015, 36(9): 971-975. ] doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2015.09.014
[17] Antiretroviral Therapy Cohort Collaboration. Survival of HIV-positive patients starting antiretroviral therapy between 1996 and 2013: a collaborative analysis of cohort studies[J]. Lancet HIV, 2017, 4(8): e349-e356. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(17)30066-8
[18] 国家癌症中心. 2019中国肿瘤登记年报[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2021: 75. [National Cancer Center. Chinese cancer registry annual report 2019[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2021: 75. ]
[19] 雷海科, 李小升, 赵玉兰, 等. 2011-2018年重庆多中心恶性肿瘤出院患者生存分析[J]. 中国肿瘤, 2020, 29(3): 192-198. [Lei HK, Li XS, Zhao YL, et al. Survival of Discharged Malignant Tumor Patients from Multi-centers in Chongqing from 2011 to 2018[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Liu, 2020, 29(3): 192-198. ]
[20] 胡俊华, 胡艳秋, 许红霞, 等. 佳木斯市艾滋病抗病毒治疗患者生存率及影响因素分析[J]. 中国现代医生, 2021, 59(19): 10-13. [Hu JH, Hu YQ, Xu HX, et al. Analysis of survival rate and influencing factors of AIDS patients treated with antiviral therapy in Jiamusi City[J]. Zhongguo Xian Dai Yi Sheng, 2021, 59(19): 10-13. ]
[21] 郑武, 赵丁源, 张薇, 等. 湖北省2008-2018年艾滋病抗病毒治疗患者生存及影响因素分析[J]. 中国热带医学, 2020, 20(5): 417-422. [Zheng W, Zhao DY, Zhang W, et al. Survival time and influence factors of HAART in Hubei, 2008-2018[J]. Zhongguo Re Dai Yi Xue, 2020, 20(5): 417-422. ]
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 张莎,唐立,闵海燕,段月勋,张娅玲,张月华,陈石芬,樊珊珊,罗佳. HIV/AIDS合并肿瘤患者生命质量状况及影响因素. 中国艾滋病性病. 2024(01): 34-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 高敏. 3例艾滋病合并膀胱癌患者行手术治疗后的护理经验. 医学理论与实践. 2024(06): 1036-1037 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 亓露,李新新,郭巧丽,闫鹏,张岩红. HIV阳性女性感染高危型人乳头瘤病毒的调查分析. 临床医学. 2024(04): 54-56 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王宁,李刚,李丹,龚胜,袁晔,周君,陈朝琼,姚晓军. 食管癌合并HIV感染/AIDS患者临床特征及淋巴结转移的危险因素分析. 肿瘤预防与治疗. 2024(04): 328-334 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张媛媛,朱浩智,许南松,余金吨,邓创忠,黄丽华. 肿瘤专科医院2022年就诊患者常见传染病感染状况分析. 中山大学学报(医学科学版). 2024(04): 666-672 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李新新,亓露. 艾滋病合并宫颈病变患者细胞免疫状态及其高危型HPV感染率研究. 罕少疾病杂志. 2024(09): 137-138 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 李丹,姚晓军. 食管癌合并HIV/AIDS的流行病学特征与诊治进展. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志. 2024(11): 1684-1689 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: