Mutation Genes in Common Tumors of Digestive System and Druggability of New Targets
-
摘要:目的
通过对消化系统常见肿瘤的突变基因进行分析,建立抗肿瘤药物新靶点的成药性评估方法。
方法搜集Integrative Onco Genomics数据库中5种消化系统常见肿瘤(食管癌、胃癌、结直肠癌、肝癌以及胰腺癌)的突变基因数据,从中筛选出各肿瘤中突变率较高的基因,通过canSAR数据库对这些基因或其编码的蛋白进行成药性评估,找到可用于抗肿瘤新药开发的潜在靶点。
结果本研究搜集了5种肿瘤共计35个队列,5445个肿瘤样品。选择每个肿瘤突变率排名前10的基因进一步分析,使用canSAR数据库对未公开研究的突变基因或其编码的蛋白质进行成药性分析,共筛选到17个可成药的潜在药物治疗靶点。
结论本研究建立了一种基于突变基因或其编码蛋白的靶点成药性评估方法,该方法的运用能够为寻找新的抗肿瘤药物治疗靶点提供参考,节省新药开发中靶点筛选的成本与时间。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo establish a druggability evaluation method for new targets of anti-tumor drugs by analyzing the mutation genes of common tumors in the digestive system.
MethodsWe collected the mutant gene data of the five common tumors of the digestive system (esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, liver cancer and pancreatic cancer) in the Integrative Onco Genomics database, and screened out the genes with higher mutation rates in each tumor. We evaluated the druggability of these genes or their encoded proteins, and discovered the potential targets for the new anti-tumor drugs.
ResultsA total of five tumors, 35 cohorts and 5445 tumor samples were collected in this study. The top 10 mutation genes were selected for further analysis. The canSAR database was used to analyze the druggability of unpublished mutant genes or their encoded proteins, and a total of 17 potential therapeutic drug targets were screened out.
ConclusionA method for evaluating druggability of targets based on mutant genes or their encoded protein is established in this study. The application of this method can provide a reference for discovering new anti-tumor therapeutic target, saving the cost and time of target screening in new drug development.
-
Key words:
- Digestive system tumors /
- Driver genes /
- Mutant genes /
- Targets /
- Druggability /
- New drugs
-
0 引言
近年来随着基因组学技术的快速发展,我们可以全面描述患者和健康者基因组之间的差异。肿瘤的主要特征之一是基因突变引起的细胞生长异常和失控,这些突变被称为“驱动器”。肿瘤研究的主要目标之一就是发现不同肿瘤中的驱动基因,为开发新的抗肿瘤靶向治疗药物以及寻找治疗反应或预后的生物标志物奠定坚实的基础。已有多项权威文献对肿瘤的驱动基因进行了系统性分析[1-2]。为了能够鉴定尽可能多的驱动肿瘤发生的突变基因,西班牙巴塞罗那生物医学研究所的科学家们对66个癌种,221个队列的28 076个肿瘤样本进行了突变基因的生物信息学分析,形成了庞大的Integrative Onco Genomics数据库(https://www.intogen.org/search),以帮助研究者更好地获取这些突变基因的相关信息[3]。
2020年美国流行病学数据显示,食管癌、胃癌、结直肠癌、肝癌及胰腺癌是发病率及死亡率均排名前五的消化系统肿瘤。预计的新发患者人数占所有消化系统肿瘤新发人数的88.2%,死亡人数占所有消化系统肿瘤死亡人数的93.9%[4]。然而,针对晚期无法手术的消化系统肿瘤,至今仍然缺乏有效的治疗药物。根据2020年CSCO临床诊疗指南推荐,食管癌、胃癌、结直肠癌以及胰腺癌的药物治疗仍然是以氟尿嘧啶、铂类、紫杉类等化疗药物为主。鉴于消化系统肿瘤治疗药物未满足临床需求的现状,本文搜集Integrative Onco Genomics数据库中上述5种消化系统肿瘤的突变基因,对各肿瘤中突变基因进行系统分析,以突变基因为切入点,结合多个数据库对突变基因及其编码的蛋白质作为新药开发靶点的可行性进行评估,为常见消化系统肿瘤的治疗药物开发提供新的生物信息学证据。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
检索Integrative Onco Genomics数据库建库至2021年6月7日有关食管癌、胃癌、结直肠癌、肝癌及胰腺癌的突变基因数据。食管癌共7个队列,945个样本。胃癌共5个队列,707个样本。结直肠癌共7个队列,1281个样本。肝癌共9个队列,1 616个样本。胰腺癌共7个队列,896个样本,见表 1。
表 1 5种消化系统常见肿瘤的队列数、样本数及突变基因数Table 1 Number of cohorts, samples and mutant genes of five common tumors of digestive system
1.2 分析方法
1.2.1 Venn分析
利用在线Venn分析工具(http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/),对5个癌种中排名前10的突变基因进行Venn分析。
1.2.2 以突变基因为靶点的新药研究现状分析
利用Cortellis数据库(https://access.cortellis.cn/login?app=cortellis)对需要分析的基因进行检索,检索范围为建库至2021年6月17日的数据,检索关键词为基因对应的蛋白简称或全称。对分类项为“Drugs”中的数据进行分析,剔除其中“Highest Status”为“Discontinued”以及“No Development Reported”的数据,对剩余数据的“Highest Status”以及“Technologies”进行统计。“Highest Status”中研究状态为“Pre-clinical”以及“Discovery”统一为临床前研究,“Technologies”中的抗体药物、融合蛋白、细胞治疗等非传统小分子治疗方式统一为生物治疗。
1.2.3 靶点成药性分析
利用英国癌症研究所开发的canSAR数据库(https://cansarblack.icr.ac.uk/)对基因编码的蛋白进行靶点成药性分析。利用数据库的蛋白注释工具,对蛋白的亚细胞分布、可成药3D结构数目、活性小分子数量进行批量分析。同时,对每个基因进行检索,统计每个基因的癌症相关指数、可与配体结合的结构域数量、基于化学的评分以及抗体药物成药性。本研究为评估蛋白的抗癌药物靶点成药潜力,设置了以下标准:(1)癌症相关评分 > 70;(2)可成药3D结构数目≥1;(3)可与配体结合的结构域数量或活性小分子数量≥1;(4)基于化学的评分 > 70;(5)抗体成药性为Y。若被评估蛋白同时满足(1)、(2)~(4)中的任意二项或(5)即被认为具有较大的成药潜力。
2 结果
2.1 消化系统常见肿瘤突变基因分析
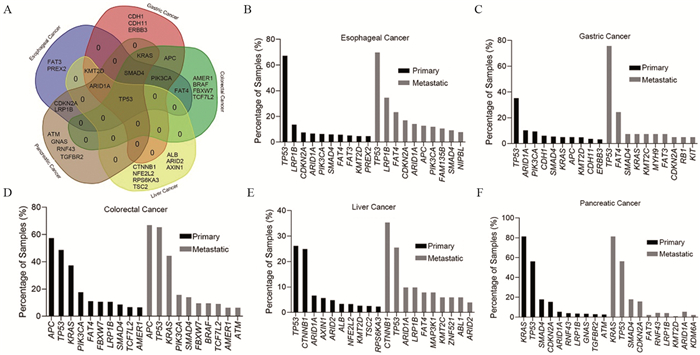
对上述5种肿瘤的突变基因进行分析,按照突变基因占所有样本的百分比进行排序,每种肿瘤选择排名前10的突变基因进行Venn分析。结果显示,TP53在5种肿瘤中均为常见的突变基因,ARID1A及SMAD的突变在4种肿瘤中有重叠,KMT2D、KRAS及PIK3CA的突变在3种肿瘤中有重叠,APC、FAT4、CDKN2A及LRP1B的突变在2种肿瘤中有重叠,见图 1A。为研究原位与转移性肿瘤中突变基因的差别,分别统计了5种肿瘤中原位及转移性肿瘤中排名前10的突变基因。结果显示,APC、FAM135B以及NIPBL的基因突变在转移性食管癌中更为常见,见图 1B。在胃癌以及肝癌中,原位与转移性肿瘤中常见的基因突变差异较大,仅有TP53、SMAD4、KRAS三个基因(胃癌)及TP53、CTNNB1、ARID1A、ARID2四个基因(肝癌)的突变在原位及转移性肿瘤中重叠,见图 1C、1E。与胃癌及肝癌相反,结直肠癌及胰腺癌中两种亚型的常见基因突变较为相似,大部分基因的突变在原位及转移性肿瘤中保持一致,见图 1D、1F。
![]() 图 1 5种消化系统常见肿瘤的基因突变情况分析Figure 1 Gene mutations in five common tumors of digestive systemA: Venn analysis of the top 10 mutations in esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, liver cancer and pancreatic cancer; the top 10 mutant genes in situ and metastatic esophageal cancer(B), gastric cancer(C), colorectal cancer(D), liver cancer(E) and pancreatic cancer (F).
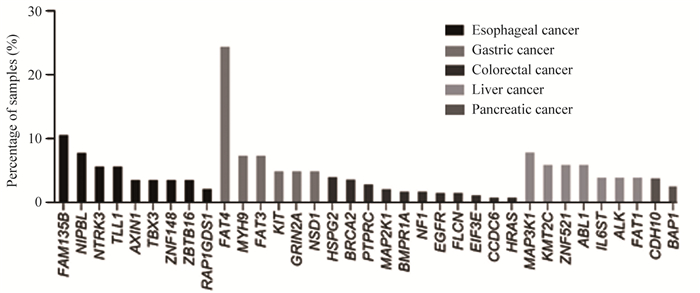
图 1 5种消化系统常见肿瘤的基因突变情况分析Figure 1 Gene mutations in five common tumors of digestive systemA: Venn analysis of the top 10 mutations in esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, liver cancer and pancreatic cancer; the top 10 mutant genes in situ and metastatic esophageal cancer(B), gastric cancer(C), colorectal cancer(D), liver cancer(E) and pancreatic cancer (F).通过对原位及转移性肿瘤中所有检测到的突变基因进行分析。结果显示,有部分突变的基因仅在转移性肿瘤中被检测到,如食管癌中的FAM135B、NIPBL、NTRK3及TLL1;胃癌中的FAT4、MYH9及FAT3;结直肠癌中的HSPG2、BRCA2及PTPRC;肝癌中的MAP3K1、KMT2C、ZNF521及ABL1;胰腺癌中的CDH10及BAP1,见图 2。
2.2 以突变基因编码的蛋白为靶点的新药研究现状
以上在各肿瘤中突变频率较高的基因及仅在转移性肿瘤中检测到的突变基因与肿瘤的发生发展密切相关,它们自身及其编码的蛋白都有可能作为抗肿瘤新药开发的靶点。本研究中,我们重点关注这些突变基因编码的蛋白。通过对上述62个突变基因(5种肿瘤中突变发生率排名前10的基因)编码的蛋白进行数据检索及分析,共筛选到了22个突变基因编码的蛋白,见表 2。截至我们检索数据的日期,至少有一项以这些蛋白为靶点的新药研究正在开展。仅在转移性肿瘤中检测到的35个突变基因中,有10个突变基因编码的蛋白正在作为抗肿瘤药物的靶点进行开发,见表 2。在靶向药物的类型中,依然是小分子占多数,然而在一些研究较为成熟的靶点(如TP53、KRAS、EGFR、KIT及ERBB3等),生物治疗的数量正在迅速攀升,生物药的开发已然成为抗肿瘤新药开发中不可或缺的一部分。
表 2 以22个突变基因编码的蛋白为靶点的新药研究概况Table 2 Overview of new drug research targeting proteins encoded by 22 mutant genes
2.3 新靶点的成药性评估
在62个突变基因编码的蛋白中,前面已筛选了22个作为新药靶点进行开发的蛋白,因此我们利用canSAR数据库对剩余的40个蛋白进行抗癌药物靶点成药性分析,结果显示:筛选出17个基因编码的蛋白具备作为抗癌药物开发的潜在靶点,分别为HRAS、TGFBR2、RPS6KA3、SMAD4、BMPR1A、NF1、IL6ST、KMT2C、EIF3E、NSD1、MYH9、HSPG2、KMT2D、MAP3K1、GNAS、RNF43及TSC2。其中,HRAS、BMPR1A、NF1、EIF3E以及HSPG2基因的突变仅在转移性结直肠癌中被检测到;IL6ST、KMT2C、MAP3K1基因的突变仅在转移性肝癌中被检测到;NSD1基因的突变仅在转移性胃癌中被检测到。在筛选到的17个基因编码的蛋白中,有12个蛋白仅可作为小分子抗癌药物的潜在靶点,有5个蛋白由于在细胞膜上有分布,因此可同时作为小分子及大分子抗癌药物的潜在靶点,见表 3。
表 3 40个突变基因编码蛋白的成药性分析Table 3 Druggability assessment of proteins encoded by 40 mutant genes
为了进一步分析以上17个蛋白的突变或表达水平与消化道肿瘤的相关性,利用canSAR数据库对17个蛋白与31个肿瘤的相关性评分进行排名(突变及表达水平),除了GNAS基因编码的蛋白未检索到相关肿瘤类型,其余16个基因检索到的评分排名见表 4。除HRAS以及RPS6KA3外,其余基因的突变都与胃癌的发生有明显的相关性(排名前10位,下同),相反,这些基因编码的蛋白表达与胃癌的发生并没有显示出明显的相关性。因此,如选择这些蛋白作为胃癌治疗的靶点时,应重点关注这些蛋白编码基因的突变。在结直肠癌中,9个基因的突变与结直肠癌的发生有明显相关性,14个蛋白的表达水平与结直肠癌的发生相关。在肝癌中,5个基因(RPS6KA3、BMPR1A、IL6ST、KMT2D以及TSC2)的突变及3个基因编码的蛋白(SMAD4、BMPR1A、MYH9)表达与肝癌的发生明显相关。在16个基因中,仅TGFBR2、SMAD4以及BMPR1A的基因突变与胰腺癌的发生显著相关,然而这些基因编码的蛋白表达与胰腺癌之间的相关性较弱。此外,根据Integrative Onco Genomics数据库显示,这16个突变基因中,HRAS、IL6ST、EIF3E、NSD1以及MYH9的作用方式为癌基因的激活。剩余的基因中,除了HSPG2的作用方式尚不确定,其余基因的作用方式均为失去抑癌基因的功能,见表 4。
表 4 胃癌、结直肠癌、肝癌及胰腺癌中16个突变基因的突变与表达评分在31种肿瘤类型中的排名情况Table 4 Ranking of mutation and expression scores of 16 mutant genes in gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, liver cancer and pancreatic cancer among 31 tumor types
为了进一步验证数据库预测的基因突变或表达水平与肿瘤之间的关系,我们检索了表 4中16个突变基因与胃癌、结直肠癌、肝癌以及胰腺癌的相关性研究。结果显示,有相当一部分MS/ES排名靠前基因的突变或表达水平与肿瘤之间的关系在研究中得到证实。以上数据表明,数据库预测的基因突变或表达水平的排名与肿瘤的相关性准确性较高,具有较强的参考价值。
3 讨论
众所周知,基因突变与肿瘤发生之间的关系密切,越来越多的研究找到了与肿瘤相关的关键突变基因,使得它们成为抗肿瘤治疗的潜在靶点。有研究通过对数百名不同类型肿瘤患者的RNA测序数据的深入分析,找到了SF3B1的基因突变在白血病、骨髓增生异常综合征、黑色素瘤、乳腺癌等多种肿瘤发生中的作用[24]。此外,尽管肿瘤是一种高度异质性的疾病,不同肿瘤之间的突变仍然存在相似性。研究者们在对乳腺癌样本的全基因组测序研究中发现了一种可能与肺癌发生密切相关的PTPRH基因的突变[25]。因此,肿瘤中的突变基因是寻找抗肿瘤药物治疗靶点的重要途径之一。
流行病学统计显示,中国人群中胃癌、食管癌、肝癌、结直肠癌以及胰腺癌的发病率及死亡率均非常高[26]。然而,针对这一系列肿瘤的治疗手段迄今仍然非常有限。根据2020年CSCO临床诊疗指南推荐,除了原发性肝癌外,另外4种消化系统常见肿瘤的药物治疗仍然是以氟尿嘧啶、铂类、紫杉类等化疗药物为主。获批用于以上4种肿瘤的靶向治疗药物仅有靶向HER2的曲妥珠单抗、靶向BRAF的达拉非尼、靶向MEK的曲美替尼、靶向VEGFR的贝伐珠单抗、雷莫芦单抗、阿帕替尼以及基于PD-1/PD-L1的免疫疗法。因此,在药物治疗方面,消化系统肿瘤是未满足临床需求的大适应证,开发新的药物治疗方法任重道远。
本研究对五种常见消化系统肿瘤排名前10的突变基因Venn分析结果显示,消化系统各常见肿瘤间具有一定的同质性。此外,在胃癌以及肝癌中,原位与转移性肿瘤中基因突变的差异较大。相反,在食管癌、结直肠癌以及胰腺癌中,原位与转移性肿瘤中的基因突变则较为相似。由于转移性肿瘤异质性强、恶性程度高、患者预后差,在转移性肿瘤中特异的基因突变相对原位肿瘤更具生物学意义,具备成为肿瘤转移的生物标志物及抗肿瘤药物靶点的潜力。
如何从众多突变的基因中找到治疗性药物开发的目标是一项极具挑战性的工作,寻找有效的、高效的、系统的筛选方法至关重要。英国癌症研究所开发的canSAR数据库汇集了生物、化学及药理等多个学科的数据,能够从生物学、化学、空间结构等多个维度来综合评估基因的成药性[27]。由于目前已上市的或正在研究的靶向药物靶点多是蛋白质,因此,本研究的主要目标是这些突变基因编码的蛋白质。基于canSAR数据库中的亚细胞分布、癌症相关评分、可成药3D结构数目(小分子)、可与配体结合的结构域数量(小分子)、活性小分子数量、基于化学的评分以及抗体药物成药性评估等多个参数对40个突变基因编码的蛋白质进行抗癌药物靶点成药性分析,最终筛选到17个具备作为抗癌药物开发潜在靶点的突变基因编码的蛋白。在最终筛选到的17个基因中,SMAD4、BMPR1A以及IL6ST的基因突变评分至少在3种消化系统肿瘤中的排名较为靠前。以这三个基因为例,查阅以它们为靶点的抗肿瘤药物研发进展。以SMAD4为靶点的两个抗肿瘤治疗专利均作用于SMAD4的基因水平,以基因调节剂或激活剂发挥作用,治疗形式均为生物治疗。IL6ST基因编码的蛋白为IL-6Rβ(CD130),共找到6篇作用于该蛋白的生物治疗专利文章,然而这些专利的适应证多为免疫相关疾病。由于其与多种消化系统肿瘤之间密切联系,开展其在肿瘤适应证中的生物学验证极具意义。未找到以BMPR1A为靶点的抗肿瘤治疗专利或研究,其或许可作为消化系统肿瘤的新治疗靶点。
综上所述,本研究从消化系统5种常见肿瘤的突变基因为切入点,通过canSAR数据库对未有研究的突变基因或其编码的蛋白进行成药性分析,找到能够用于后续抗肿瘤新药开发的潜在靶点。该方法适用于基于差异表达基因/蛋白数据集的成药性分析。然而该方法也存在一些不足,比如针对突变基因编码的蛋白质的成药性分析,该蛋白为野生型蛋白,不能完全代表突变基因的功能。此外,对于成药性分析的参数设置较为主观,这个问题还需要将参数调整后的分析结果多方验证才能够形成较为成熟的方案,有待后续工作来实现。尽管存在一定的不足,在肿瘤治疗严重未满足临床需求的现状下,该方法的运用能够为寻找新的抗肿瘤药物治疗靶点提供较为坚实的科学基础,为新药的研究者们减少潜在靶点的筛选成本与时间。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.作者贡献:季晓君:课题设计、数据分析及文章撰写苗雷、唐莹:部分数据的搜集及文章审阅马昌友:指导数据分析周秋华:文章审阅吴舰、徐丹:文章思路设计及审阅 -
表 1 5种消化系统常见肿瘤的队列数、样本数及突变基因数
Table 1 Number of cohorts, samples and mutant genes of five common tumors of digestive system

表 2 以22个突变基因编码的蛋白为靶点的新药研究概况
Table 2 Overview of new drug research targeting proteins encoded by 22 mutant genes

表 3 40个突变基因编码蛋白的成药性分析
Table 3 Druggability assessment of proteins encoded by 40 mutant genes

表 4 胃癌、结直肠癌、肝癌及胰腺癌中16个突变基因的突变与表达评分在31种肿瘤类型中的排名情况
Table 4 Ranking of mutation and expression scores of 16 mutant genes in gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, liver cancer and pancreatic cancer among 31 tumor types

-
[1] Dietlein F, Weghorn D, Taylor-Weiner A, et al. Identification of cancer driver genes based on nucleotide context[J]. Nat Genet, 2020, 52(2): 208-218. doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0572-y
[2] Bailey MH, Tokheim C, Porta-Pardo E, et al. Comprehensive Characterization of Cancer Driver Genes and Mutations[J]. Cell, 2018, 173(2): 371-385. e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.060
[3] Martínez-Jiménez F, Muiños F, Sentis I, et al. A compendium of mutational cancer driver genes[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2020, 20(10): 555-572. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-0290-x
[4] Siegel RL, Miller K D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(1): 7-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21590
[5] Nadauld L D, Garcia S, Natsoulis G, et al. Metastatic tumor evolution and organoid modeling implicate TGFBR2 as a cancer driver in diffuse gastric cancer[J]. Genome Biol, 2014, 15(8): 428. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0428-9
[6] Ogino S, Kawasaki T, Ogawa A, et al. TGFBR2 mutation is correlated with CpG island methylator phenotype in microsatellite instability-high colorectal cancer[J]. Hum Pathol, 2007, 38(4): 614-620. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2006.10.005
[7] Xiangming C, Natsugoe S, Takao S, et al. Preserved Smad4 expression in the transforming growth factor beta signaling pathway is a favorable prognostic factor in patients with advanced gastric cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2001, 7(2): 277-282.
[8] Mei Z, Shao YW, Lin P, et al. SMAD4 and NF1 mutations as potential biomarkers for poor prognosis to cetuximab-based therapy in Chinese metastatic colorectal cancer patients[J]. BMC Cancer, 2018, 18(1): 479. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4298-5
[9] Mehrvarz Sarshekeh A, Advani S, Overman MJ, et al. Association of SMAD4 mutation with patient demographics, tumor characteristics, and clinical outcomes in colorectal cancer[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(3): e0173345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173345
[10] Mizuno T, Cloyd JM, Vicente D, et al. SMAD4 gene mutation predicts poor prognosis in patients undergoing resection for colorectal liver metastases[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2018, 44(5): 684-692. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2018.02.247
[11] Blackford A, Serrano OK, Wolfgang CL, et al. SMAD4 gene mutations are associated with poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2009, 15(14): 4674-4679. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0227
[12] Wang S, Ma G, Zhu H, et al. miR-107 regulates tumor progression by targeting NF1 in gastric cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 36531. doi: 10.1038/srep36531
[13] Georgiou A, Stewart A, Cunningham D, et al. Inactivation of NF1 Promotes Resistance to EGFR Inhibition in KRAS/NRAS/BRAFV600-Wild-Type Colorectal Cancer[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2020, 18(6): 835-846. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-19-1201
[14] Chen J, Liu H, Chen J, et al. PLXNC1 Enhances Carcinogenesis Through Transcriptional Activation of IL6ST in Gastric Cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 33. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00033
[15] Rebouissou S, Amessou M, Couchy G, et al. Frequent in-frame somatic deletions activate gp130 in inflammatory hepatocellular tumours[J]. Nature, 2009, 457(7226): 200-204. doi: 10.1038/nature07475
[16] Cho SJ, Yoon C, Lee JH, et al. KMT2C Mutations in Diffuse-Type Gastric Adenocarcinoma Promote Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 24(24): 6556-6569. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1679
[17] Liu K, Wang JF, Zhan Y, et al. Prognosis model of colorectal cancer patients based on NOTCH3, KMT2C, and CREBBP mutations[J]. J Gastrointest Oncol, 2021, 12(1): 79-88. doi: 10.21037/jgo-21-28
[18] Li Z, Lin S, Jiang T, et al. Overexpression of eIF3e is correlated with colon tumor development and poor prognosis[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2014, 7(10): 6462-6474.
[19] Li B, Han Y. NSD1 stimulated survival and migration of gastric cancer cells through WNT10B[J]. J Mens Health, 2021, 17(3): 139-144.
[20] Ye G, Yang Q, Lei X, et al. Nuclear MYH9-induced CTNNB1 transcription, targeted by staurosporin, promotes gastric cancer cell anoikis resistance and metastasis[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(17): 7545-7560. doi: 10.7150/thno.46001
[21] Wang B, Qi X, Liu J, et al. MYH9 Promotes Growth and Metastasis via Activation of MAPK/AKT Signaling in Colorectal Cancer[J]. J Cancer, 2019, 10(4): 874-884. doi: 10.7150/jca.27635
[22] Neumeyer V, Vieth M, Gerhard M, et al. Mutated Rnf43 Aggravates Helicobacter Pylori-Induced Gastric Pathology[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2019, 11(3): 372. doi: 10.3390/cancers11030372
[23] Eto T, Miyake K, Nosho K, et al. Impact of loss-of-function mutations at the RNF43 locus on colorectal cancer development and progression[J]. J Pathol, 2018, 245(4): 445-455. doi: 10.1002/path.5098
[24] Inoue D, Chew GL, Liu B, et al. Spliceosomal disruption of the non-canonical BAF complex in cancer[J]. Nature, 2019, 574(7778): 432-436. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1646-9
[25] Rennhack JP, To B, Swiatnicki M, et al. Integrated analyses of murine breast cancer models reveal critical parallels with human disease[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 3261. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11236-3
[26] Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(2): 115-132. doi: 10.3322/caac.21338
[27] Patel MN, Halling-Brown MD, Tym JE, et al. Objective assessment of cancer genes for drug discovery[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2013, 12(1): 35-50. doi: 10.1038/nrd3913
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 金传娄,刘倩,韩玥,谢小芬,张霞霞,梁娜. 抑癌基因nm23和WWOX在肿瘤发生发展中的作用研究进展. 四川医学. 2023(03): 303-306 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: