Application of 18F-FDG PET-CT Simulation Localization in Radiotherapy of Recurrent Abdominal and Pelvic Tumors
-
摘要:目的
探讨18F-FDG PET-CT模拟定位在复发腹盆腔肿瘤放疗中的临床价值。
方法采用18F-FDG PET-CT对38例治疗后复发的腹盆腔肿瘤患者进行模拟定位, 分别根据CT影像及18F-FDG PET-CT拟定全身治疗方案及放疗靶区勾画, 对比二者差异。
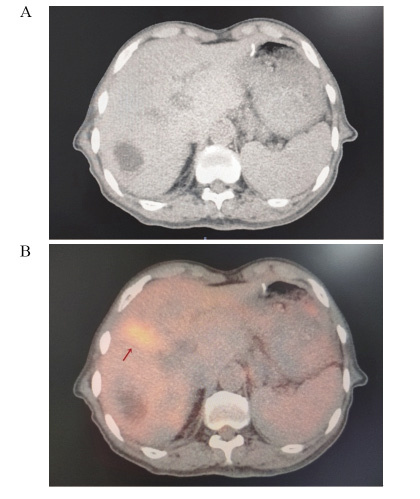
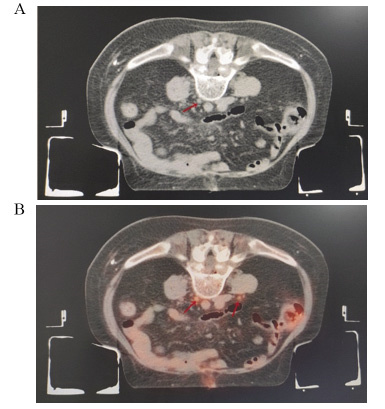
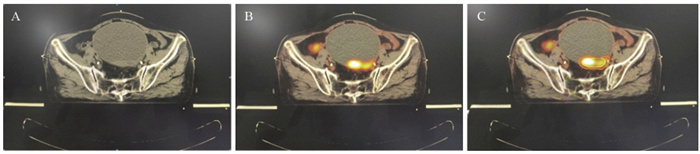
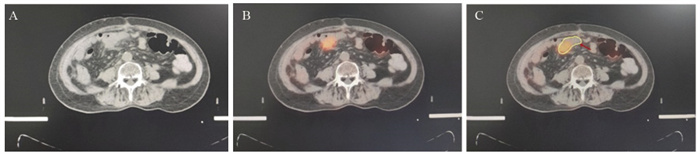
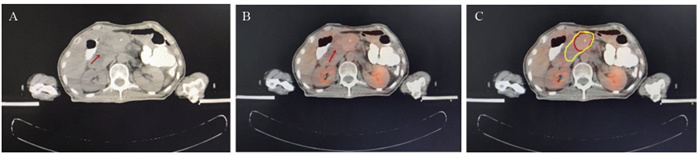
结果在38例患者中, 21.1%(8/38)发现了盆腹腔外远处转移, 改变了治疗方案。34例(89.5%)放射治疗靶区发生了改变。GTVPET-CT的均值为118.14 cm3, GTVCT的均值为148.53 cm3(P=0.044)。
结论18F-FDG PET-CT模拟定位对于复发盆腹腔肿瘤患者, 完善了肿瘤再分期, 改变了部分患者治疗方案, 更加精确放射治疗靶区。
-
关键词:
- 腹盆腔肿瘤 /
- 18F-FDGPET-CT模拟定位 /
- 放射治疗
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the clinical application value of 18F-FDG PET-CT simulation localization in radiotherapy of recurrent abdominal and pelvic tumors.
Methods18F-FDG PET-CT was used to simulate positioning 38 patients with abdominal and pelvic tumors who relapsed after treatment.Based on both CT images and 18F-FDG PRT-CT, we drew up a systemic treatment plan and outlined the radiotherapy target area, and then compared the differences between the two methods.
ResultsIn 38 patients, 21.1%(3/8) of patients were found to have distal metastases outside the pelvic and abdominal cavity, and changed the systemic treatment plan.The radiotherapy target was altered in 34(89.5%) patients.The mean value of GTVPET-CT was 118.14cm3and the mean value of GTVCT was 148.53cm3(P=0.044).
ConclusionFor patients with recurrent abdominal and pelvic tumors, 18F-FDG PET-CT simulation localization treatment improves tumor re-staging, changes the integrated therapy for some patients, and makes the target area of radiotherapy more accurate.
-
0 引言
反义寡核苷酸技术(antisense oligonucleotides, ASOs)又称反义技术,是指一种利用一段人工合成或表达的能与RNA或DNA互补结合的寡核苷酸链,抑制目的基因表达的技术[1-2],也可用于干扰肿瘤细胞中特定基因的表达,从而探讨肿瘤发生的机制和开发基因的治疗策略。近来研究显示,微小RNA-21(miR-21)与包括结直肠癌在内的多种肿瘤的发生密切相关[3-8],可能是肿瘤基因治疗的潜在新靶标[9-10]。我们在前期研究中发现,通过ASOs可显著下调人结肠癌SW620细胞中miR-21的表达,并抑制肿瘤的生长[11]。本研究中进一步利用人结肠癌HCT116细胞建立人结肠癌裸鼠实验动物模型,观察ASOs下调miR-21的效果及对人结肠癌细胞体内生长的效应,为开发基于ASOs技术的人结肠癌基因治疗策略提供实验基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验动物、细胞株和主要试剂
12只雌性BALB/c裸鼠,4~5周龄,体质量11~14 g左右,购自北京维通利华实验动物技术有限公司[实验动物许可证编号:SCXK(京)2011-0011],于遵义医学院SPF级免疫学实验室人工饲养。人结肠癌HCT116细胞株购自中国生命科学院,重组质粒p-miR-21-ASOs和对照质粒p-Cont均由本实验室保存。McCoy's 5A培养基、磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)均购自北京索莱宝科技有限公司,优质胎牛血清购自美国Gibco公司,100×三抗(青霉素-链霉素-两性霉素B)购自上海第四制药股份有限公司;SYBR Premix Ex Taq,Premix Ex Taq Version2.0以及RNAisoTM Plus均购自北京宝日医生物技术有限公司;miR-21探针试剂盒购自美国ABI公司;RevertAidTM First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit反转录合成试剂盒购自美国Fermentas公司;总RNA提取试剂盒购自北京天根科技有限公司,0.5%Triton-X-100(聚乙二醇辛基苯基醚)购自北京索莱宝科技有限公司;APC标记的兔抗小鼠Ki-67单克隆抗体、DAPI染液均购自美国ThermoFisher公司;兔抗p-Akt、Akt一抗以及兔抗ERK1/2、p-ERK1/2一抗、HRP标记的羊抗兔二抗均购自英国Abcam公司;全蛋白提取试剂盒购自江苏凯基生物公司;ECL显色液、RIPA裂解液、PVDF膜购自中国联科生物技术公司。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 细胞培养
按如下条件培养人结肠癌HCT116细胞株:人结肠癌HCT116细胞株在10%优质胎牛血清、100 u/ml青霉素、100 μg/ml链霉素、0.25 μg/ml两性霉素B及11.9 g/L McCoy's 5A细胞培养液中培养,将人结肠癌HCT116细胞株置于37℃、5%CO2的条件下培养,待HCT116细胞处于对数生长期时,使用0.25%胰蛋白酶37℃消化2 min,离心收集细胞,使用PBS重复清洗3次,计算细胞总数,利用PBS调整HCT116细胞密度为4.5×107个/毫升备用。
1.2.2 建立人结肠癌裸鼠皮下移植瘤模型
4~5周龄裸鼠购回后先于本实验室SPF级环境下观察并饲养5~7 d。5~7 d天后小鼠饮食精神状况良好,随后接种100 μl密度为4.5×107个/毫升的人结肠癌HCT116细胞于裸鼠右侧腋窝外侧中部皮下,荷瘤后继续饲养并随时观察注射部位有无红肿溃烂、裸鼠的饮食、精神情况以及每只裸鼠荷瘤成功后的成瘤时间。接种后5~7 d出现肉眼可见的肿瘤包块时,即为荷瘤裸鼠模型构建成功。将实验荷瘤小鼠随机分为实验组(p-miR-21-ASOs组)和对照组(p-Cont组),每组6只,随后每隔4 d分别向两组荷瘤小鼠的肿瘤组织中注射100 μg p-Cont质粒和p-miR-21-ASOs质粒,共注射4次,并每隔3 d测量一次裸鼠皮下肿瘤体积。
1.2.3 观察荷瘤裸鼠体内肿瘤生长情况
观察方法同前期工作[11]。
1.2.4 免疫组织荧光法检测肿瘤组织中Ki-67蛋白的表达
从-80℃超低温冰箱取出用75%冰乙醇固定好的冰冻组织切片,室温(15℃~25℃)平衡10 min,PBS缓冲液漂洗3次,每次5 min;山羊血清封闭液封闭1.5 h,PBS漂洗3次,每次10 min;加0.5%Triton-X-100,冰上破膜2 min,PBS漂洗3次,每次10 min;吸弃封闭液,滴加APC标记的兔抗小鼠单克隆Ki-67抗体后置于湿盒内,4℃冰箱避光过夜孵育,次日,取出冰冻切片肿瘤组织用PBS缓冲液漂洗3次,每次10 min;滴加DAPI染液,染色3 min,PBS漂洗3次,每次10 min;滴加含有DAPI染液的封片剂,封片并固定24 h后观察;激光共聚焦显微镜观察细胞染色情况,拍片。
1.2.5 实时荧光定量PCR检测肿瘤组织中miR-21和肿瘤生长相关因子的表达
肿瘤组织中miR-21、细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶(cyclin- dependent kinase, CDK)表达的检测同前期工作[11]。
1.2.6 Western blot检测Akt、ERK1/2、磷酸化Akt、磷酸化ERK1/2蛋白的表达
蛋白样品的制备及BCA法定量蛋白的检测同前期工作[11]。Western blot检测相关信号通路的变化:(1)电泳:分离胶10%,积层胶5%,80 V跑积层胶,120 V跑分离胶;(2)上样:第一泳道Marker,其余泳道加提取的总蛋白;(3)转膜:PVD膜,36 V,180 min电转;(4)洗膜:用TBS或者PBS洗膜;5 min一次;(5)封闭:用含5%脱脂奶粉的TBST或者PBST封闭1 h;(6)加一抗:加入相关目的蛋白的一抗(稀释比例均为1:2 000),4℃过夜;(7)洗膜:次日用TBST或者PBST洗膜,10 min三次;(8)加二抗:加入HRP标记的相关目的蛋白的二抗(稀释比例均为1:2 000),室温孵育1 h;(9)用PBST洗膜,10 min×3次;(10)用发光试剂(ECl)对膜进行处理,于发光仪上进行蛋白曝光检测。
1.3 统计学方法
实验数据使用GraphPad Prism 5软件进行统计学分析。本研究中各实验数据均独立重复3次,结果以(x±s)表示。其中组间比较采用t检验或单因素方差分析,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 p-miR-21-ASOs重组质粒注射后各组裸鼠荷瘤模型中肿瘤的生长变化
结果显示,与p-Cont组相比,p-miR-21-ASOs组皮下肿瘤生长显著延缓,且肿瘤组织的体积、大小、重量都明显减小,差异有统计学意义,见图 1。
2.2 肿瘤组织病理学改变
HE染色显示:p-Cont组肿瘤细胞形态不一,细胞核深染且核呈多形性,核质比加大;而p-miR-21-ASOs组则可见肿瘤组织大面积坏死,见图 2。
2.3 p-miR-21-ASOs重组质粒注射后肿瘤组织中miR-21成熟体的表达
结果显示:与p-Cont组相比,p-miR-21-ASOs组肿瘤组织中miR-21的表达水平显著下调,且差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),见图 3。
2.4 免疫荧光技术检测肿瘤组织中细胞的增殖
免疫荧光共聚焦观察发现:相比于p-Cont组,p-miR-21-ASOs组肿瘤组织中Ki-67的表达水平明显减少(P < 0.01),见图 4。
2.5 p-miR-21-ASOs重组质粒注射后周期蛋白依赖性激酶的表达
结果显示:与p-Cont组相比,p-miR-21-ASOs组肿瘤细胞生长周期相关的周期蛋白依赖性激酶CDK2、CDK3、CDK4以及CDK6的表达水平均明显下调,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05, P < 0.001),见图 5。
2.6 Western blot检测肿瘤组织中相关信号通路的表达
结果显示:与p-Cont组相比,p-miR-21-ASOs组中p-ERK1/2,p-Akt的蛋白表达水平明显降低(P < 0.05, P < 0.01),见图 6。
3 讨论
近来的研究发现,ASOs技术可广泛用于多种临床疾病发生机制探讨和治疗策略开发[12-18]。对于肿瘤基因治疗来说,利用ASOs技术干预特定基因表达来影响肿瘤生长方面的研究也取得了重要进展[19-20]。我们在新近工作中也发现利用真核载体过表达ASOs干预miR-21表达可显著抑制人结肠癌SW620细胞的体内生长[11]。本研究中,我们进一步发现,真核载体过表达ASOs也可有效抑制人结肠癌HCT116细胞中miR-21的表达,同时肿瘤细胞体内生长受到抑制。范钰等[21]用ASOs下调人喉癌Hep-2细胞中miR-21的表达,发现肿瘤细胞的生长、侵袭能力明显减弱。吴子晏等[22]研究发现ASOs干预miR-21联合顺铂在体内、外能显著抑制人骨肉瘤MG-63细胞生长,并促进细胞凋亡,显示了一定的治疗效应。这些研究结果提示,利用ASOs技术干预miR-21表达可能是一种能有效影响特定肿瘤生长的手段,为后续开发基于ASOs的人结肠癌基因治疗策略提供了重要工作基础。
研究显示,miR-21可通过对多种靶分子和信号途径传递的调节来调控人结肠癌的生长[23-28]。在前期工作中,我们也发现ASOs下调miR-21表达后,肿瘤细胞生长相关信号途径Akt和ERK1/2明显改变,与其靶分子PTEN的表达变化有关[4, 10]。本研究进一步发现ASOs下调miR-21表达后,肿瘤组织存在坏死,肿瘤细胞的增殖能力明显减弱,同时,肿瘤组织中p-Akt和p-ERK1/2等蛋白的表达水平均明显下调,进一步提示了miR-21对Akt和ERK1/2等信号途径的调控作用。现已知,细胞内CDKs家族分子的表达改变与肿瘤细胞生长相关。本研究也发现肿瘤细胞内CDKs家族成员表达水平显著减低。鉴于已有的研究表明,肿瘤细胞生长相关信号途径Akt和ERK1/2与细胞内CDKs家族成员表达间存在密切联系[29-31]。因此,推测ASOs干预miR-21表达后对人结肠癌细胞体内生长的抑制效应机制,包括肿瘤组织坏死的变化,与Akt和ERK1/2等信号途径传递改变,进而影响CDKs家族分子的表达有关。然而,鉴于不同实验条件的差异性,ASOs下调miR-21后抑制人结肠癌细胞体内生长的确切分子机制仍有待后续研究阐明。
总之,本研究发现ASOs可显著下调人结肠癌动物模型中肿瘤组织miR-21的表达,同时肿瘤体内生长受到明显抑制,该效应与Akt和ERK1/2等信号途径传递变化有关,为后续深入探讨miR-21调控肿瘤生长的分子机制,以及开发基于ASOs技术的人结肠癌基因治疗策略提供前期实验基础。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.作者贡献:金龙:病例收集、论文撰写、统计分析徐大蒙、周园园:图像采集、放疗模拟定位于娇:靶区勾画、论文修改 -
表 1 38例复发腹盆腔肿瘤基本临床特征
Table 1 Basic characteristics of 38 recurrent abdominal and pelvic tumors patients

-
[1] Halperin EC, Wazer DE, Perez CA, et al. Perez and Brady' s principles and practice of radiation oncology[M]. 6th ed. Waltham: Wolters Kluwer Health, 2013: 1521-1522.
[2] Wen X, Qiu H, Shao Z, et al. Pulsed low-dose rate radiotherapy has an improved therapeutic effect on abdominal and pelvic malignancies[J]. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B, 2021, 22(9): 774-781. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2000793
[3] Cliffe H, Patel C, Prestwich R, et al. Radiotherapy response evaluation using FDG PET-CT- established and emerging applications[J]. Br J Radiol, 2016, 90(1071): 20160764.
[4] Kumagai T, Rahman F, Smith A. The microbiome and radiation induced-bowel injury: evidence for potential mechanistic role in disease pathogenesis[J]. Nutrients, 2018, 10(10): 1405. doi: 10.3390/nu10101405
[5] Mercieca S, Belderbos JSA, van Herk M. Challenges in the target volume definition of lung cancer radiotherapy[J]. Transl Lung Cancer Res, 2021, 10(4): 1983-1998. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-627
[6] Church J. The Role of PET-CT in Radiation Therapy Planning[J]. Radiol Technol, 2018, 89(4): 399-401.
[7] 朱苏雨, 胡炳强. PET-CT用于肿瘤精确放疗靶区勾画的困惑[J]. 国际放射医学核医学杂志, 2007, 31(4): 217-221. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4114.2007.04.008 [Zhu SY, Hu BQ. The dilemma of the target delineation with PET-CT in the radiotherapy planning for malignant tumors[J]. Guo Ji Fang She Yi Xue He Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2007, 31(4): 217-221. ] doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4114.2007.04.008
[8] 朱苏雨, 席许平, 胡炳强. PET/CT用于肿瘤放疗计划靶区勾画的相关问题[J]. 中国肿瘤, 2010, 19(8): 494-499. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHLU201008003.htm [Zhu SY, Xi XP, Hu BQ. Issues on target delineation for radiation with PET/CT[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Liu, 2010, 19(8): 494-499. ] https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHLU201008003.htm
[9] Hanaoka K, Okumura M, Monzen H. PET/CT Simulation for Radiation Therapy Planning[J]. Igaku Butsuri, 2018, 38(2): 85-88.
[10] Kruser TJ, Bradley KA, Bentzen SM, et al. The impact of hybrid PET-CT scan on overall oncologic management, with a focus on radiotherapy planning: a prospective, blinded study[J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2009, 8(2): 149-158. doi: 10.1177/153303460900800208
[11] 石景真, 李奉祥, 李建彬, 等. 诊断PET-CT用于食管癌原发肿瘤大体肿瘤体积勾画的比较研究[J]. 中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2020, 40(4): 290-295. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10422-1020136018.htm [Shi JZ, Li FX, Li JB, et al. Comparison of the gross target volume based on diagnostic PET/CT for primary esophageal cancer[J]. Zhonghua Fang She Yi Xue Yu Fang Hu Za Zhi, 2020, 40(4): 290-295. ] https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10422-1020136018.htm
[12] 张英杰, 李建彬. PET-CT应用于非小细胞肺癌放疗计划的研究进展[J]. 中华放射肿瘤学杂志, 2019, 28(11): 876-879. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4221.2019.11.017 [Zhang YJ, Li JB. Research progress on PET-CT in radiotherapy planning for non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Zhonghua Fang She Zhong Liu Xue Za Zhi, 2019, 28(11): 876-879. ] doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4221.2019.11.017
[13] Akin EA, Qazi ZN, Osman M, et al. Clinical impact of FDG PET/CT in alimentary tract malignancies: an updated review[J]. Abdom Radiol(NY), 2020, 45(4): 1018-1035. doi: 10.1007/s00261-020-02447-0
[14] 胡晓燕, 李蕾, 倪茵, 等. 18F-FDG PET/CT诊断肝细胞癌及肝内胆管细胞癌[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2018, 34(9): 1372-1376. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXX201809033.htm [Hu XY, Li L, Ni Y, et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT in diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ying Xiang Ji Shu, 2018, 34(9): 1372-1376. ] https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXX201809033.htm
[15] Monteil J, Le BrunLy V, Cachin F, et al. Comparison of 18FDG-PET/CT and conventional follow-up methods in colorectal cancer: A randomised prospective study[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2021, 53(2): 231-237. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2020.10.012
[16] 陈兰兰, 郝珊瑚, 张国旭, 等. PET/CT显像在妇科恶性肿瘤术后复发及转移中的临床应用价值[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2019, 27(4): 657-660. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2019.04.029 [Chen LL, Hao SH, Zhang GX, et al. Clinical value of PET/CT imaging in the recurrence and metastasis of gynecologic malignant tumors postoperatively[J]. Xian Dai Zhong Liu Yi Xue, 2019, 27(4): 657-660. ] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2019.04.029
[17] 胡鹏程, 石洪成, 顾宇参, 等. 18F-FDGPET/CT与增强CT诊断腹部肿瘤腹腔转移的对比研究[J]. 中华核医学与分子影像杂志, 2013, 33(3): 228-229. [Hu PC, Shi HC, Gu YS, et al. Comparative study of 18F-FDG PET/CT and enhanced CT in diagnosis of abdominal tumor metastasis[J]. Zhonghua He Yi Xue Yu Fen Zi Ying Xiang Za Zhi, 2013, 33(3): 228-229. ]
[18] 黄世明, 吴思雨, 孙永锋, 等. 不同影像诊断方法对卵巢癌腹膜转移诊断价值的系统评价[J]. 中华介入放射学电子杂志, 2021, 9(2): 177-182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHJR202102011.htm [Huang SM, Wu SY, Sun YF, et al. Meta-analysis of the diagnostic value of different imaging methods for peritoneal metastasis of ovarian cancer[J]. Zhonghua Jie Ru Fang She Xue Dian Zi Za Zhi, 2021, 9(2): 177-182. ] https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHJR202102011.htm
[19] Calles-Sastre L, Mucientes-Rasilla J, San-Frutos Llorente LM, et al. Prognostic significance of metabolic tumor volume and total lesion glycolysis in patients with advanced cervical carcinoma[J]. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol(Engl ED), 2019, 38(1): 17-21. .
[20] Takagi H, Sasagawa T, Shibata T, et al. Association between 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-PET/CT and histological grade of uterine endometrial carcinoma[J]. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol, 2018, 57(2): 283-288. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2018.02.018
[21] Ashamalla H, Rafla S, Parikh K, et al. The contribution of integrated PET/CT to the evolving definition of treatment volumes in radiation treatment planning in lung cancer[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2005, 63(4): 1016-1023. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.04.021
[22] Lin S, Han B, Yu L, et al. Comparison of PET-CT images with the histopathological picture of a resectable primary tumor for delineating GTV in nonsmall cell lung cancer[J]. Nucl Med Commun, 2011, 32(6): 479-85. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0b013e32834508d2
[23] 王天禄, 宋颖秋, 党军, 等. PET/CT对合并肺不张非小细胞肺癌治疗方案制定和放疗靶区勾画的影响[J]. 中华核医学与分子影像杂志, 2012, 32(2): 115-118. [Wang TL, Song YQ, Dang J, et al. Impact of PET/CT on the treatment planning and target volume delineation of radiotherapy in the patients with non-small-cell lung cancer complicated by atelectasis[J]. Zhonghua He Yi Xue Yu Fen Zi Ying Xiang Za Zhi, 2012, 32(2): 115-118. ]
[24] 张红娇, 姜杰, 黄伟. 功能影像辅助伴肺不张肺癌放疗靶区勾画的研究进展[J]. 国际肿瘤学杂志, 2022, 49(1): 51-55. [Zhang HJ, Jiang J, Huang W. Research progress of functional imaging-assisted radiotherapy target delineation of lung cancer with atelectasis[J]. Guo Ji Zhong Liu Xue Za Zhi, 2022, 49(1): 51-55. ]
[25] 陈韦翔, 张余琴, 张煜. PET/CT图像分割技术在NSCLC患者放疗中的应用[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2021, 19(6): 55-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTMR202106018.htm [Chen WX, Zhang YQ, Zhang Y. Application of PET/CT Image Segmentation Technology in Radiotherapy of NSCLC Patients[J]. Zhongguo CT He MRI Za Zhi, 2021, 19(6): 55-57. ] https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CTMR202106018.htm




 下载:
下载: