Effects of Chemoradiotherapy Versus Chemotherapy Alone on Survival of Patients with Primary Mediastinal Large B-cell Lymphoma
-
摘要:目的
探讨原发纵隔大B细胞淋巴瘤(PMBCL)的预后影响因素,分析利妥昔单抗时代前后接受放化疗与单纯化疗对患者预后的影响。
方法从SEER数据库中提取2001—2015年间确诊的PMBCL患者, SEER Stat软件计算PMBCL的发病率,Kaplan-Meier法和Cox回归模型分析各临床变量对预后的影响。
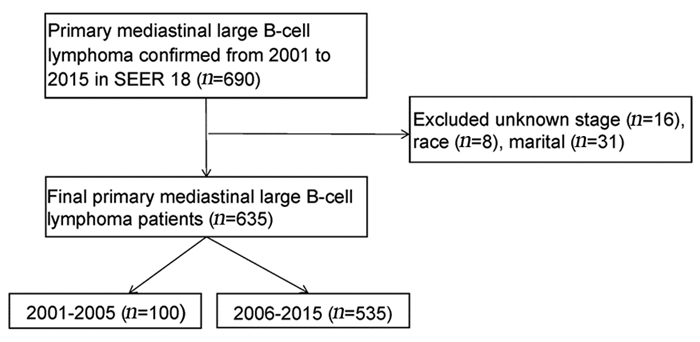
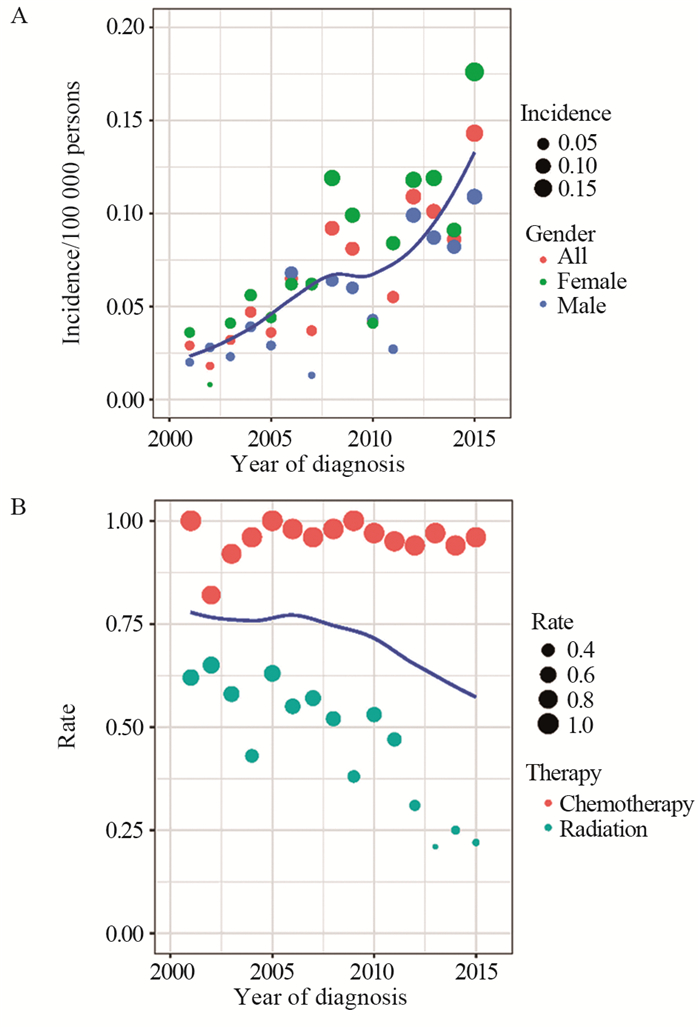
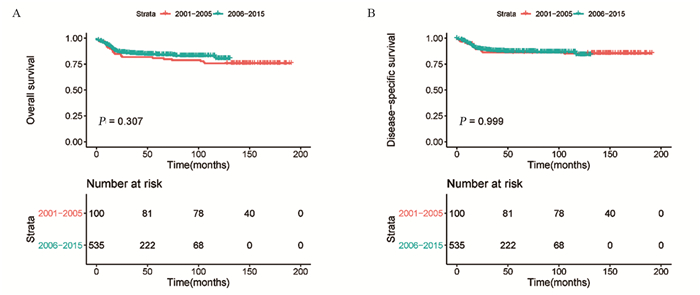
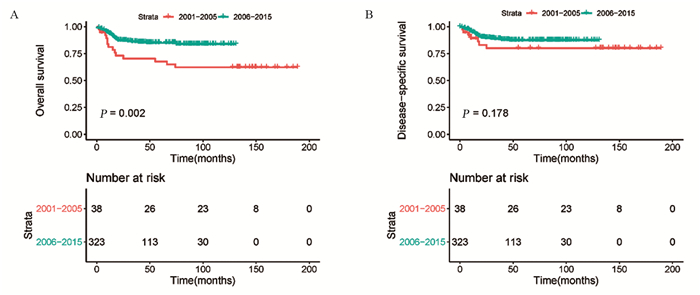
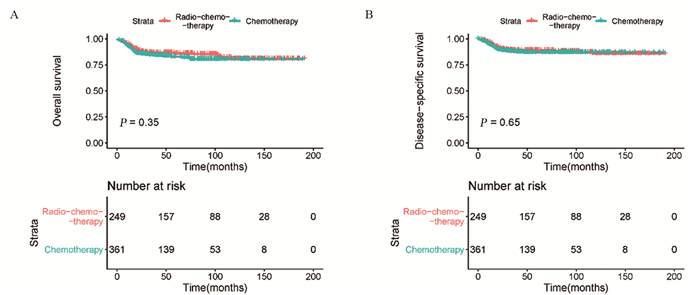
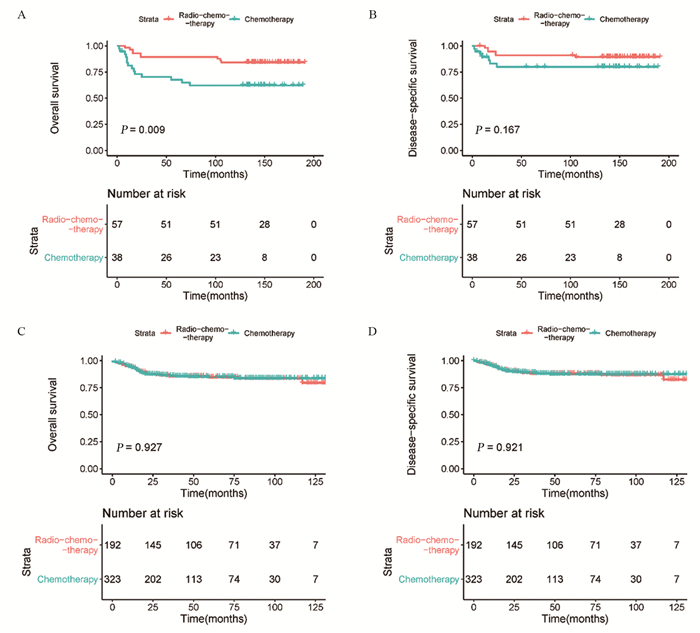
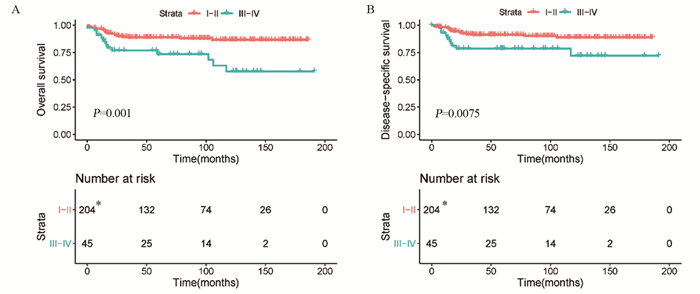
结果排除信息不完整的患者外,共纳入635例PMBCL患者。多因素Cox回归分析结果显示,年龄、分期、化疗是OS和DSS的独立预后因素。Kaplan-Meier生存分析显示,2006—2015年接受单纯化疗患者的OS明显优于2001—2005年的患者(χ2=10.002, P=0.002)。2001—2005年接受化疗联合放疗患者的OS优于接受单纯化疗的患者,两组患者的DSS未见明显差异。2006—2015年接受放化疗联合治疗患者的OS和DSS与接受单纯化疗患者无明显差异。
结论利妥昔单抗的应用改善了原发纵隔大B细胞淋巴瘤患者的长期生存,2006—2015年中接受放化疗的患者与接受单纯化疗的患者预后相当。
-
关键词:
- 原发纵隔大B细胞淋巴瘤 /
- 放化疗 /
- 化疗 /
- 监测、流行病学和结果数据库 /
- 生存分析
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the prognostic factors of primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL) and the effects of chemoradiotherapy versus chemotherapy alone on patients' prognosis before and after rituximab era.
MethodsWe extracted the data of PMBCL patients diagnosed from 2001 to 2015 from SEER database. SEER Stat software was used to calculate the incidence rate. Kaplan-Meier method and Cox regression model were used to analyze the impact of various clinical variables on prognosis.
ResultsWe included 635 patients with PMBCL. Multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that age, stage and chemotherapy were independent prognostic factors. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that OS of the patients receiving chemotherapy only in 2006-2015 was significantly better than that in 2001-2005 (χ2=10.002, P=0.002). The patients who received chemoradiotherapy had better OS than those who received chemotherapy alone from 2001 to 2005. The OS and DSS of patients receiving chemoradiotherapy were not significantly different from those of chemotherapy alone from 2006 to 2015.
ConclusionThe application of rituximab improves the long-term survival of PMBCL patients. The prognosis of patients who received chemoradiotherapy is comparable to that of chemotherapy alone from 2006 to 2015.
-
0 引言
对于高危、难治或复发性急性髓系白血病(acute myeloid leukemia, AML)患者来说,异基因造血干细胞移植(allo-HSCT)可能是唯一具有治愈潜力的治疗选择[1]。尽管人类白细胞抗原(human leukocyte antigen, HLA)匹配同胞全相合供者(matched sibling donor, MSD)allo-HSCT是首选,但仅有约30%患者能够找到合适供者[2]。对于缺乏HLA匹配的患者,绝大多数都可以找到单倍体相合供者,并且单倍体相合造血干细胞移植(Haplo-HSCT)已成为广泛接受的替代方案[3]。研究表明,与MSD-HSCT相比,Haplo-HSCT能够取得相似的临床疗效[4-6]。然而,单纯外周血造血干细胞(peripheral blood stem cell, PBSC)作为移植物行Haplo-HSCT对高危及难治/复发AML患者的疗效仍不清楚。因此,本研究评估我中心以高剂量非体外去T细胞PBSC作为移植物,行Haplo-HSCT治疗高危及难治/复发AML患者的临床疗效,并与同一时期实施MSD-HSCT的结果进行比较。
1 资料与方法
1.1 病例资料
回顾性分析2010年1月至2020年6月在新疆医科大学第一附属医院血液病中心进行造血干细胞移植的成人高危及难治/复发AML患者(≥18岁)资料。患者的诊断依据为2016版WHO造血和淋巴组织肿瘤的分型诊断标准[7],高危定义如下:伴有预后差的染色体核型或分子遗传学标志;高白细胞计数 > 50×109/L;前驱血液病史;合并中枢神经系统白血病(central nervous system leukemia, CNSL)。难治、复发AML的诊断标准依据中华医学会血液学分会制定的诊断标准[8]。所有供者、患者均签署知情同意书。
1.2 造血干细胞动员与采集
移植物均为非体外去T细胞PBSC,采用重组人粒细胞集落刺激因子(rhG-CSF)7~10 μg/(kg.d)皮下注射动员PBSC,于动员的第5、6天采集,体重过低的供者于动员第4~6天采集(供受者体重差 < 10 kg)或提前冻存干细胞(供受者体重差≥10 kg)。
1.3 预处理方案
试验分为两组:Haplo-HSCT组采用阿糖胞苷(Ara-C)+白消安(Bu)+环磷酰胺(Cy)+抗胸腺细胞球蛋白(ATG)[9],MSD-HSCT组采用ABu/Cy或者ABu/Cy+ATG或者Bu/Cy+ATG方案。两组患者均采用清髓性预处理方案。
1.4 移植物抗宿主病(GVHD)预处理方案
两组患者均采用环孢素(CsA)或他克莫司(Tac)+甲氨蝶呤(MTX)+霉酚酸酯(MMF)作为基础预防方案:CsA:移植前5天至移植后30天2.5 mg/(kg.d)静脉滴注,30天后改为(4~5)mg/(kg.d)口服,或者Tac 0.02 mg/(kg.d)静脉滴注,移植30天后改为0.1 mg/(kg.d)口服,根据血药浓度调整;MTX:移植后第1天15 mg/(m2.d)静脉滴注,移植后第3天、第6天改为10 mg/(m2.d)静脉滴注;MMF:移植前1天至移植后100天1.0 g/d口服;地塞米松(Glu):移植后1天至移植后15天5 mg/d静脉滴注,之后逐渐减量,MSD组在移植后30天停用,Haplo-HSCT组用至移植后100天。Haplo-HSCT组在上述基础上加用抗CD25单克隆抗体(舒莱)移植当天及移植后第2天12 mg/m2静脉滴注。
1.5 评估标准及指标
动态监测血常规,连续3天中性粒细胞计数绝对值(ANC)≥0.5×109/L为粒系植入时间;不输注血小板情况下血小板计数(PLT)连续7天≥20×109/L为巨核系植入时间。GVHD分级及诊断根据西雅图国际标准进行评分及分级。总生存(OS)为移植后至任何原因导致的死亡时间或随访截止时间。无病生存(DFS)为移植后至随访截止或者复发/死亡时间。
1.6 随访
随访资料来自电话随访、住院/门诊病历。随访截至2021年12月30日。
1.7 统计学方法
采用SPSS25.0和GraphPad Prism 5.0软件进行数据分析。计数和计量资料用频率和中位数等进行描述统计。组间资料比较采用卡方检验或t检验。急性和慢性GVHD、DFS以及OS等采用Kaplan-Meier进行描述和分析。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 患者基本临床特征
本研究共纳入98例患者,其中Haplo-HSCT组62例,MSD-HSCT组36例。两组中位年龄、预处理方案、MNC及CD34+细胞输注剂量差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05),其他临床指标差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05),见表 1。
表 1 98例高危及难治/复发急性髓系白血病患者的临床特征Table 1 Clinical characteristics of 98 patients with high-risk and refractory/relapsed acute myeloid leukemia
2.2 造血重建
本研究中共有4例患者植入失败,均发生在Haplo-HSCT组,两组植入率比较差异无统计学意义(93.5% vs. 100%, P=0.120)。Haplo-HSCT组、MSD-HSCT组中性粒细胞恢复中位时间分别为16(10~21)d和15.5(11~18)d(P=0.452),血小板恢复中位时间分别为15(13~20)d和16(13~22)d(P=0.231),差异均无统计学意义。
2.3 GVHD发生情况
100天内Haplo-HSCT组、MSD-HSCT组Ⅱ~Ⅳ度急性移植物抗宿主病(acute graft- versus-host disease, aGVHD)的发生率分别为27.89%(95%CI: 15.76~40.02)和17.19%(95%CI: 4.65~29.73),两组比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.246),见图 1A。Haplo-HSCT组、MSD-HSCT组Ⅲ~Ⅳ度aGVHD的发生率分别为10.96%(95%CI: 2.60~19.11)和3.45%(95%CI: 0~10.19),两组比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.154),见图 1B。
Haplo-HSCT组、MSD-HSCT组慢性移植物抗宿主病(chronic graft- versus-host disease, cGVHD)的3年累积发生率分别为46.31%(95%CI: 31.86~60.76)和35.16%(95%CI: 18.13~52.19),两组相比差异无统计学意义(P=0.433),见图 1C。Haplo-HSCT组、MSD-HSCT组广泛型cGVHD的3年累积发生率分别为9.15%(95%CI: 1.43~16.87)和20.24%(95%CI: 3.29~37.19),两组比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.473),见图 1D。
2.4 复发情况
随访期间,Haplo-HSCT组有10例患者复发,其中2例为髓外复发,复发部位分别为淋巴结和中枢神经系统,余8例为骨髓复发。MSD-HSCT组有14例患者复发,其中3例为髓外复发,复发部位分别为腮腺、肝脏和中枢神经系统,余11例为骨髓复发。两组患者3年累积复发率分别为16.2%(95%CI: 5.42~26.98)和41.1%(95%CI: 23.66~58.54),两组相比差异有统计学意义(P=0.036),见图 2A。两组患者3年非复发死亡率(NRM)分别为16.61%(95%CI: 7.18~26.04)和21.71%(95%CI: 3.13~40.29),两组相比差异无统计学意义(P=0.689),见图 2B。
2.5 移植后并发症
本研究中主要并发症为移植后感染,多为细菌和(或)真菌感染,两组相比差异无统计学意义(P=0.129)。28例患者发生出血性膀胱炎,其中Haplo-HSCT组22例、MSD-HSCT组6例,两组相比差异无统计学意义(P=0.063)。两组患者发生间质性肺炎、带状疱疹和CMV血症的差异均无统计学意义,见表 2。
表 2 高危及难治/复发的AML患者移植后并发症Table 2 Post-transplantation complications in patients with high-risk and refractory/relapsed acute myeloid leukemia
2.6 生存分析及影响生存的因素
本研究中位随访时间为27(2~119)月。Haplo-HSCT组有17例患者死亡,5人死于复发,8人死于感染,3人死于植入失败,1人死于呼吸循环衰竭。MSD-HSCT组有17例患者死亡,其中9人死于复发,4人死于感染,4人死于脑出血。Haplo-HSCT组、MSD-HSCT组3年DFS率分别为66.98(95%CI: 53.87~80.09)和41.8%(95%CI: 24.1~59.5),两组相比差异无统计学意义(P=0.140),见图 3A。Haplo-HSCT组、MSD-HSCT组3年OS率分别为73.37%(95%CI 61.55~85.19)和51.41%(95%CI: 33.59~69.23),两组相比差异无统计学意义(P=0.105),见图 3B。对可能影响患者预后的因素如患者年龄、供者年龄、供-受者性别匹配、是否发生aGVHD、是否发生cGVHD、输注MNC剂量、输注CD34+细胞剂量等进行多因素Cox回归分析,未发现影响患者生存的独立危险因素,见表 3。
表 3 98例患者DFS和OS影响因素的多因素分析Table 3 Multivariate analysis of risk factors related to DFS and OS of 98 patients
3 讨论
AML是成人最常见的恶性血液病,尽管目前对初诊患者诱导化疗后完全缓解(CR)率可达60%~80%,但对高危以及复发/难治AML患者的疗效仍欠佳[10]。Allo-HSCT是AML患者的最佳潜在治疗方法,尤其是细胞遗传学不良且单独化疗预后非常差的患者[11]。因此,选择合适的移植方式对患者的治疗策略至关重要。
最近,Haplo-HSCT的数量逐渐增加,并取得了不错的效果。越来越多的研究表明,对于AML患者接受Haplo-HSCT与MSD-HSCT疗效相当[12-14]。然而,对于Haplo-HSCT在治疗复发/难治性AML中是否存在与MSD-HSCT同等的疗效,目前相关报道较少。来自欧洲血液和骨髓移植学会(EBMT)的一项研究表明,在中度或高风险细胞遗传学首次完全缓解的AML患者中,Haplo-HSCT与MSD-HSCT的疗效相似[11]。本研究中也取得了类似结果,Haplo-HSCT与MSD-HSCT在植入、GVHD、DFS及OS方面的差异无统计学意义。然而,最近一项研究通过比较Haplo-HSCT与MSD在复发/难治性AML患者的预后发现Haplo-HSCT后OS、DFS较低,NRM较高,导致患者预后较差[15]。不同研究中心取得不同的结果可能与患者类型及移植体系有关。
Haplo-HSCT因供受体之间的HLA差异引起双向免疫屏障,导致发生原发性移植失败的倾向更高。本研究中,Haplo-HSCT组均输注高剂量非体外去T细胞PBSC作为移植物,以克服免疫屏障,促进持续稳定的植入。但是随着输注剂量的增加,GVHD的发生风险也随之增加。我们在经典的GVHD预防方案中添加了抗CD25单克隆抗体(舒莱)及短程低剂量的糖皮质激素以加强GVHD预防。由此,形成本血液病中心独特的移植体系-高剂量非体外去T细胞PBSC作为移植物联合强化的GVHD预防方案。抗CD25单克隆抗体能够抑制同种抗原诱导的T细胞增殖以及抗原特异性细胞毒性T细胞的生成,降低GVHD的发生[16]。Chang等[17]研究表明低剂量糖皮质激素能够显著降低aGVHD的发生率,并在不增加感染的情况下减少不良事件的发生。本研究结果表明,两组间GVHD的发生率比较差异无统计学意义,但是Haplo-HSCT广泛型cGVHD发生率有降低的趋势(9.15% vs. 20.24%, P=0.473),考虑可能与我们强化的GVHD预防方案有关。两组患者移植后并发症的比较未发现显著性差异,提示强化的GVHD预防方案并未增加感染的风险。
近年来,越来越多的研究显示Haplo-HSCT治疗恶性血液病较MSD-HSCT具有更强的移植物抗白血病(GVL)作用。Yu等[18]通过前瞻性多中心的研究表明,Haplo-HSCT治疗首次完全缓解的高风险AML与MSD-HSCT相比复发率更低,提示Haplo-HSCT可能存在更强的GVL效应。本研究中也得到了一致结果,Haplo-HSCT组3年累积复发率显著低于MSD-HSCT组。Guo等[19]通过动物模型发现Haplo-HSCT存在更强GVL作用,是因为自然杀伤(NK)细胞凋亡减少和细胞毒性细胞因子分泌增加。此外,从理论上来看,Haplo-HSCT存在更强GVL效应可通过降低NRM从而提高存活率[20]。本研究中两组的生存情况并无差异,多因素分析也并未发现影响患者预后的危险因素,这可能与样本量较少有关。
总之,本研究初步表明对高危以及复发/难治AML患者接受Haplo-HSCT与MSD-HSCT疗效相似,且haplo-HSCT的复发率更低,可能存在更强的GVL效应。但本研究为回顾性研究且病例数较少,后期仍需要进行前瞻性大样本研究进一步证实此结论。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.作者贡献:范冰杰:研究设计、统计分析、论文撰写常宇:文献查阅、统计分析柳喜洋:数据汇总、文献查阅张明智、张蕾:论文指导与修改 -
表 1 原发纵隔大B细胞淋巴瘤患者的临床特征
Table 1 Clinical characteristics of 635 primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma patients

表 2 利妥昔单抗时代前后原发纵隔大B细胞淋巴瘤患者的临床特征差异(n(%))
Table 2 Differences in baseline characteristics of primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma patients before and after rituximab era (n(%))

表 3 原发纵隔大B细胞淋巴瘤患者的总生存和疾病特异性生存的单因素Cox回归分析
Table 3 Univariate Cox regression analysis of overall survival(OS) and disease-specific survival(DSS) of patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma

表 4 原发纵隔大B细胞淋巴瘤患者的总生存和疾病特异性生存的多因素Cox回归分析
Table 4 Multivariable Cox regression analysis of overall survival and disease-specific survival of patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma

-
[1] Mottok A, Wright G, Rosenwald A, et al. Molecular classification of primary mediastinallarge B-cell lymphoma using routinely available tissue specimens[J]. Blood, 2018, 132(22): 2401-2405. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-05-851154
[2] Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms[J]. Blood, 2016, 127(20): 2375-2390. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-01-643569
[3] Ahmed Z, Afridi SS, Shahid Z, et al. Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma: A2021Updateon Genetics, Diagnosis, and Novel Therapeutics[J]. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk, 2021, 21(11): e865-e875. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2021.06.012
[4] Martelli M, Ferreri A, Di Rocco A, et al. Primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2017, 113: 318-327. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.01.009
[5] Zhou H, Xu-Monette ZY, Xiao L, et al. Prognostic factors, therapeutic approaches, and distinct immunobiologic features in patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma on long-term follow-up[J]. Blood Cancer J, 2020, 10(5): 49. doi: 10.1038/s41408-020-0312-7
[6] Dunleavy K, Pittaluga S, Maeda LS, et al. Dose-adjusted EPOCH-rituximab therapy in primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2013, 368(15): 1408-1416. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1214561
[7] Wilson WH, Jung SH, Porcu P, et al. A Cancer and Leukemia Group B multi-center study of DA-EPOCH-rituximab in untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with analysis of outcome by molecular subtype[J]. Haematologica, 2012, 97(5): 758-765. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2011.056531
[8] Dunleavy K, Wilson WH. Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma and mediastinal gray zone lymphoma: do they require a unique therapeutic approach?[J]. Blood, 2015, 125(1): 33-39. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-05-575092
[9] Goldschmidt N, Kleinstern G, Orevi M, et al. Favorable outcome of primary mediastinallarge B-cell lymphoma patients treated with sequential RCHOP-RICE regimen without radiotherapy[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2016, 77(5): 1053-1060. doi: 10.1007/s00280-016-3024-8
[10] Bhakta N, Liu Q, Yeo F, et al. Cumulative burden of cardiovascular morbidity in paediatric, adolescent, and young adult survivors of Hodgkin's lymphoma: an analysis from the St Jude Lifetime Cohort Study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2016, 17(9): 1325-1334. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30215-7
[11] Hamlin PA, Satram-Hoang S, Reyes C, et al. Treatment patterns and comparative effectiveness in elderly diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients: a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results-medicare analysis[J]. Oncologist, 2014, 19(12): 1249-1257. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0113
[12] Neelapu SS, Locke FL, Bartlett NL, et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377(26): 2531-2544. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1707447
[13] Locke FL, Ghobadi A, Jacobson CA, et al. Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): a single-arm, multicentre, phase 1-2 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2019, 20(1): 31-42. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30864-7
[14] Vardhana S, Hamlin PA, Yang J, et al. Outcomes of Relapsed and Refractory Primary Mediastinal (Thymic) Large B Cell Lymphoma Treated with Second-Line Therapy and Intent to Transplant[J]. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant, 2018, 24(10): 2133-2138. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.06.009
[15] Giri S, Bhatt VR, Pathak R, et al. Role of radiation therapy in primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma in rituximab era: A US population-based analysis[J]. Am J Hematol, 2015, 90(11): 1052-1054. doi: 10.1002/ajh.24172
[16] Vassilakopoulos TP, Pangalis GA, Katsigiannis A, et al. Rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone with or without radiotherapy in primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma: the emerging standard of care[J]. Oncologist, 2012, 17(2): 239-249. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2011-0275
[17] Filippi AR, Piva C, Giunta F, et al. Radiation therapy in primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma with positron emission tomography positivity after rituximab chemotherapy[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2013, 87(2): 311-316. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.05.053
[18] Messmer M, Tsai HL, Varadhan R, et al. R-CHOP without radiation in frontline management of primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma[J]. Leuk Lymphoma, 2019, 60(5): 1261-1265. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2018.1519812
[19] Hayden AR, Tonseth P, Lee DG, et al. Outcome of primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma using R-CHOP: impact of a PET-adapted approach[J]. Blood, 2020, 136(24): 2803-2811. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019004296
[20] Vassilakopoulos TP, Papageorgiou SG, Angelopoulou MK, et al. Positron emission tomography after response to rituximab-CHOP in primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma: impact on outcomes and radiotherapy strategies[J]. Ann Hematol, 2021, 100(9): 2279-2292. doi: 10.1007/s00277-021-04421-2
[21] Armand P, Rodig S, Melnichenko V, et al. Pembrolizumab in Relapsed or Refractory Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2019, 37(34): 3291-3299. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.01389
[22] Zinzani PL, Santoro A, Gritti G, et al. Nivolumab Combined With Brentuximab Vedotin for Relapsed/Refractory Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Efficacy and Safety From the Phase Ⅱ CheckMate 436 Study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2019, 37(33): 3081-3089. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.01492
[23] Hatic H, Sampat D, Goyal G. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in lymphoma: challenges and opportunities[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2021, 9(12): 1037. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-6833
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: