Effect of Lymph Node Metastasis on Prognosis of Small Cell Lung Cancer with M1a Disease: A Study Based on SEER database
-
摘要:目的
探讨淋巴结转移对M1a期小细胞肺癌(SCLC)患者生存的影响。
方法回顾性分析SEER数据库中2004—2015年7027例M1a期SCLC患者病例资料,采用Kaplan-Meier法及Log rank检验比较不同N分期亚组患者总体生存率(OS),Cox比例风险模型评估N分期是否为影响预后的独立危险因素。
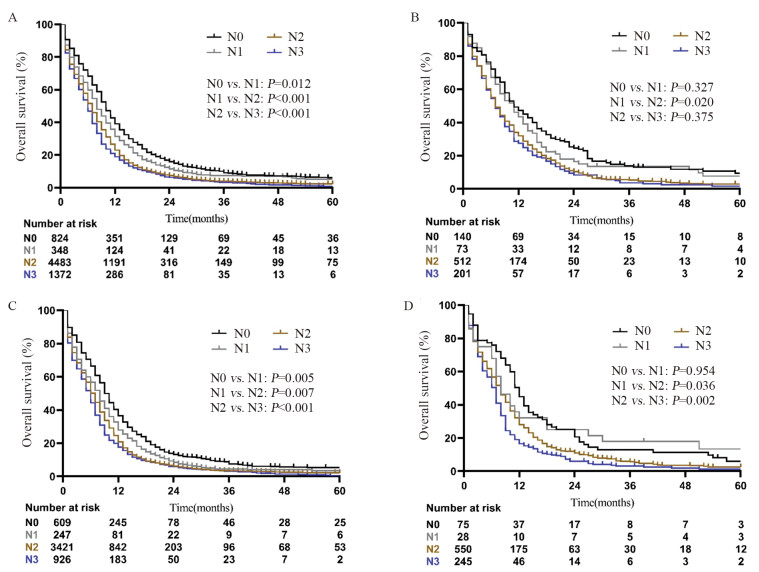
结果全组中位OS为7月。在所有M1a患者中,无淋巴结转移(N0)患者的OS最好,其次是N1患者,而N2和N3患者的预后最差(P < 0.001)。亚组分析也显示对侧肺结节组、恶性胸腔积液组和恶性心包积液组也存在随N分期升高OS递减的趋势。多因素分析显示淋巴结转移是M1a期SCLC患者的独立预后因素,在M1a不同亚群中也观察到相同的结果。
结论淋巴结转移能够影响M1a期SCLC患者生存,增加额外的预后信息,建议在下一版本的TNM分期系统中进一步完善N描述符。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the impact of lymph node metastasis on the survival of SCLC patients with M1a disease.
MethodsWe retrospectively analyzed the medical records of 7027 SCLC patients with M1a disease from 2004 to 2015 in SEER database. The Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test were used to estimate the OS in all N stage subgroups. Cox proportional hazard model was used to assess whether N stage was an independent risk factor for prognosis.
ResultsThe median OS of all patients was 7 months. Among all M1a patients, the patients without lymph node involvement (N0) had the best OS, followed by N1 stage patients; N2 and N3 stage patients had the worst OS (P < 0.001). Similarly, this trend was observed when M1a disease was subdivided into contralateral pulmonary nodules, malignant pleural effusion and malignant pericardial effusion. Multivariate analysis showed that lymph node metastasis was an independent prognostic factor for SCLC patients with M1a disease, and this result was also noticed in all subgroups of M1a disease.
ConclusionLymph node metastasis may affect the survival of SCLC patients with M1a disease, adding prognostic information. And it is recommended to further improve the N descriptor in the next version of TNM staging system.
-
Key words:
- Small cell lung cancer /
- N stage /
- M1a stage /
- SEER database /
- Prognosis
-
0 引言
宫颈癌是全球范围内最常见的女性恶性肿瘤之一,仅次于乳腺癌、肺癌及结直肠癌,也是导致女性恶性肿瘤死亡的4大原因之一,2020年全球约有60.4万新发病例和34.2万死亡病例[1]。有研究发现宫颈癌新辅助化疗(neoadjuvant chemotherapy, NACT)有效与否是影响无病生存率(disease-free survival, DFS)和生存率的一个重要因素,并对患者的预后生存具有一定的预测价值[2]。约20%的宫颈癌患者因对化疗药物不敏感而导致NACT失败、病情进展和预后不佳[3]。因此如何预测NACT的疗效、筛选出对化疗不敏感的患者以便及时更改或调整治疗方案来改善患者的预后生存情况具有重要的临床价值。有研究报道生物标志物对预测NACT的疗效具有一定临床价值[4],其中黏附分子CD44糖蛋白可变剪接产生的CD44v6的表达与宫颈癌、前列腺癌、结直肠癌、胰腺癌及食管癌的肿瘤进展、转移和化疗耐药性相关[5-6]。而EGFR是上皮生长因子(epidermal growth factor, EGF)细胞增殖和信号转导的受体,可能通过TF/FⅦa/PAR2信号通路影响化疗药物的疗效[7]。本研究通过SP法检测宫颈癌患者接受NACT前肿瘤组织中的CD44v6、EGFR的表达,结合患者临床资料进行分析,探讨CD44v6、EGFR对宫颈癌NACT疗效的临床预测价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
选择2015年11月—2017年11月经贵州医科大学附属肿瘤医院病理确诊为Ⅱ~Ⅲ期患宫颈癌患者53例,所有患者均接受了2周期紫杉醇+铂类的NACT,均为我科“生物标志物预测宫颈癌放化疗敏感的可行性探索及其与预后相关性研究(注册号ChiCTR-ONN-16008893)及紫杉醇联合洛铂或顺铂新辅助化疗序贯同步放化疗治疗局部晚期宫颈癌随机临床研究(注册号ChiCTR-IIR-17011559)”入组患者。本研究获我院伦理委员会批准,患者或近亲属均签署知情同意书。
1.2 纳入及排除标准
纳入标准:(1)经两名以上妇产科副主任医师妇科检查及FIGO分期为Ⅱ~Ⅲ期、且有可测量的肿瘤病灶;(2)入组前均未行放疗、化疗及手术治疗;(3)卡氏评分≥70分;(4)年龄25~75岁;(5)骨髓造血功能正常(WBC > 4.0×109/L,PLT≥100×109/L,Hb > 70g/L);(6)肝功能:谷丙转氨酶(ALAT)、谷草转氨酶(AST) < 正常值上限(ULN)的1.5倍;总胆红质 < 1.5×ULN;肾功能:血清肌酐 < 1.5×ULN;(7)无重要器官的功能障碍,无严重的合并症,如高血压、糖尿病、冠心病和精神病史;(8)能理解本研究并已签署知情同意书。
排除标准:(1)严重肺部或心脏疾病病史、活动性的全身感染、滥用药物或酒精成瘾;(2)肌酐清除率 < 30 ml/min;(3)同时接受本研究以外的慢性系统性免疫治疗或者激素治疗;(4)妊娠(经血清或者尿β-HCG检验证实)或者泌乳期间;(5)因各种原因未按要求完成化疗方案,如紫杉醇过敏、有严重化疗反应;(6)有体格或精神疾患,无法完全或充分理解本研究可能存在的并发症,或无民事行为能力或者限制民事行为能力。
1.3 试剂及仪器
石蜡、甲醛、二甲苯、无水乙醇、H2O2(上海国药集团);广谱二抗、DAB浓缩型试剂盒(上海长岛生物技术有限公司);苏木素(上海如吉生物科技发展有限公司);中性树脂(北京索莱宝科技有限公司);CD44v6、EGFR(无锡傲瑞东源生物科技有限公司);PBS溶液(贵州医科大学附属肿瘤医院病理科配置);正置显微镜、显微图像分析系统(日本NIKON公司);移液器(美国吉尔森P型移液器公司);恒温烘箱(上海恒一科学仪器有限公司);石蜡切片机、摊片机(湖北徕克公司)。
1.4 化疗方案
紫杉醇175 mg/m2;顺铂60~80 mg/m2(洛铂30 mg/m2),静脉滴注,d1,d21,21天为一周期,共2周期。
1.5 疗效评价
近期疗效:2周期NACT结束后,根据实体瘤疗效标准(RECIST)评价疗效分为:完全缓解(CR)、部分缓解(PR)、病变进展(PD)、病变稳定(SD)。完全缓解和部分缓解为临床有效,定义化疗敏感;稳定和进展为无效,定义为化疗不敏感。
1.6 免疫组织化学检测CD44v6和EGFR的表达
NACT前行宫颈癌组织活检,采用SP法检测肿瘤组织中CD44v6、EGFR的表达,检测过程中,具体准备及操作步骤严格按照SP试剂盒操作说明:(1)取石蜡包埋组织切片,脱蜡水化后,切片,置于载玻片上,烘干48 h后待用;(2)抗原热修复;(3)灭活内源性过氧化物酶;(4)封闭;(5)加入一抗孵育(即用型,无需稀释);(6)加入二抗孵育;(7)滴加DAB试剂显色;(8)苏木精复染;(9)将染色后的病理切片置于显微镜下观察,CD44v6定位于细胞膜,EGFR定位于细胞膜/细胞质。由病理科专科医生独立阅片,对照HE染色确定肿瘤细胞区域,于显微镜下观察,每例观察两张切片,每张切片在10×40倍镜下随机选择5个视野,每个视野计数100个细胞,共计数500个细胞。算出每个视野下阳性细胞所占百分比,将10个视野所得阳性细胞所占百分比取平均值为最终CD44v6、EGFR的表达值。
1.7 诊断效力及预测价值的评估
根据CD44v6、EGFR所对应的ROC曲线下面积(area under curve, AUC)来评价预测价值:AUC为0.5~0.7,表示预测价值较低;AUC为0.7~0.9,表示预测价值中等;AUC为0.9~1.0,表示预测价值较高。Cut-off值为约登指数最大时所对应的CD44v6、EGFR表达值。根据ROC曲线所计算得出Cut-off值,将表达值大于或等于CD44v6、EGFR的Cut-off值的患者记为高表达组,小于CD44v6、EGFR的Cut-off值的患者记为低表达组。
1.8 统计学方法
采用SPSS22.0软件进行统计分析,计数资料以率(%)表示,符合正态分布的计量资料采用(x±s)表示,不符合正态分布的计量资料采用中位数(四分位数间距)表示,计数资料采用χ2检验,符合正态分布的计量资料采用t检验,不符合正态分布资料采用非参数检验。采用ROC曲线分析CD44v6、EGFR对NACT疗效的预测价值。ROC行两指标联合预测的计算方法是将CD44v6和EGFR联合预测的检验变量采用Logistic回归得出综合值(即真实概率值),状态变量仍然为金标准(疗效)不变。采用Pearson相关性检验进行相关性分析。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 患者临床基线资料
53例NACT的患者中,敏感组(CR+PR)为38例,不敏感组(SD+PD)为15例,其中,NACT方案(紫杉醇+铂类)、绝经状态、FIGO分期、病理类型、肿瘤是否侵犯阴道、年龄与NACT疗效之间差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),肿瘤大小、肿瘤是否侵犯宫旁与NACT疗效之间差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),见表 1。
表 1 53例宫颈癌患者基线资料表(n(%))Table 1 Baseline characteristics of 53 cervical cancer patients (n(%))
2.2 CD44v6与EGFR在宫颈癌组织中的表达情况
CD44v6阳性主要定位于肿瘤细胞的胞膜,以出现完整的棕黄色着色为阳性着色。EGFR主要着色于肿瘤细胞的胞膜或胞质,以肿瘤细胞膜上或胞质中出现完整的棕褐色着色为阳性着色,见图 1。
![]() 图 1 免疫组织化学检测CD44v6和EGFR的表达A: CD44v6 expression in cervical cancer tissue (10×10); B: CD44v6 expression in cervical cancer tissue (10×20); C: EGFR expression in cervical cancer tissue (10×10); D: Expression of EGFR in cervical cancer tissue (10×20)Figure 1 Expression of CD44v6 and EGFR detected by immunohistochemical method
图 1 免疫组织化学检测CD44v6和EGFR的表达A: CD44v6 expression in cervical cancer tissue (10×10); B: CD44v6 expression in cervical cancer tissue (10×20); C: EGFR expression in cervical cancer tissue (10×10); D: Expression of EGFR in cervical cancer tissue (10×20)Figure 1 Expression of CD44v6 and EGFR detected by immunohistochemical method在53例患者中,CD44v6、EGFR表达的平均值分别为75.75%、63.36%,中位值皆为80.00%,CD44v6表达为0~100%,EGFR表达为0~90.00%。
2.3 CD44v6、EGFR的表达与宫颈癌患者临床特征的关系
53例宫颈癌患者中,肿瘤侵犯宫旁的患者较未侵犯宫旁的患者CD44v6表达升高(P < 0.05)。肿瘤直径≥4 cm的患者EGFR表达值高于 < 4 cm的患者(P < 0.05),见表 2。
表 2 CD44v6、EGFR的表达与53例宫颈癌患者临床特征的关系Table 2 Correlation of CD44v6 and EGFR expression with clinical features of 53 cervical cancer patients
2.4 CD44v6、EGFR的表达与NACT敏感度的关系
敏感组CD44v6的表达值显著低于不敏感组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);CD44v6的表达在疗效为CR、PR、SD的患者中差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);EGFR在NACT敏感组与不敏感组间及疗效为CR、PR、SD的患者中表达差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),见表 3。
表 3 CD44v6、EGFR的表达与NACT敏感度的关系Table 3 Correlation of CD44v6 and EGFR expression with sensitivity of NACT
2.5 CD44v6、EGFR的表达对NACT疗效的预测价值
ROC曲线分析结果显示,CD44v6的表达对NACT的疗效有中等预测价值(AUC=0.740, P < 0.05),其敏感度为66.70%,特异性为68.40%,Cut-off值为87.50;EGFR的表达对宫颈癌NACT的疗效无明显的预测价值(AUC=0.449, P > 0.05),CD44v6联合EGFR对NACT的疗效无预测价值(AUC=0.224, P < 0.05),见图 2,表 4。
表 4 CD44v6、EGFR对NACT疗效的预测价值Table 4 Predictive value of CD44v6 and EGFR $[0[]0]n the efficacy of NACT
2.6 CD44v6、EGFR的表达与NACT疗效的关系
结果显示,在NACT中,CD44v6的表达高低与化疗敏感度及疗效有关,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);在NACT中,CD44v6低表达组患者的CR率高于高表达组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),见表 5。
表 5 CD44v6、EGFR的表达与NACT疗效的关系Table 5 Correlation of CD44v6 and EGFR expression with efficacy of NACT
2.7 CD44v6与EGFR的相关性
宫颈癌患者肿瘤组织中CD44v6与EGFR表达呈正相关关系,相关系数为0.34,P < 0.05,见图 3。
3 讨论
目前,全球每年宫颈癌的新发病例约50万,占所有癌症新发病例的5%,其中80%以上在发展中国家。有研究[8]显示早期宫颈癌对NACT的反应是一个重要的预后因素并有助于决定下一步局部治疗方案,即放疗或手术。在一项纳入了490例宫颈癌患者的荟萃分析中指出,NACT的短期疗效与DFS显著相关,并且有效者的生存率明显高于无效者[2]。同时,另一项研究显示,对NACT的反应,包括临床反应和病理反应,与局部晚期宫颈癌(locally advanced cervical cancer, LACC)患者的预后具有相关性[9]。虽然有较多的研究为NACT提供了有力的证据,但因部分患者对NACT的疗效欠佳,进而耽误或延长治疗时间,降低生活质量甚至限制后续治疗方式的选择,从而致使NACT在临床实际应用中受到一定的限制,因此,临床上迫切地需要可以预测NACT疗效的方法以,便筛选出这部分不敏感的患者。目前,除了传统的以鳞状细胞癌抗原(squamous cell carcinoma antigen, SccAg)、癌抗原125(cancerantigen125, CA125)、癌胚抗原(carcinoembryonic antigen, CEA)作为宫颈癌的肿瘤标志物外,又新发现了几种可预测抗肿瘤治疗反应的生物标志物,如CD44v6、EGFR分子靶点及预测辐射敏感度的环氧合酶2(COX-2)、抑癌基因CHFR、DNA解旋酶WRN、缺氧诱导因子1α亚基(HIF-1α)等。
CD44作为肿瘤干细胞(CSCs)的表面标志物,其表达影响着肿瘤启动、自我更新、转移和化疗耐药性等关键的CSC相关特性[10-13]。其中含有外显子v6的CD44v6异构体主要参与异质性黏附,是肿瘤发生和转移的促进因素,表达CD44v6的肿瘤细胞更易发生脉管浸润、淋巴结转移及远处转移[10, 14-15]。Hara等[16]通过CD44v6的表达与食管鳞癌化疗疗效分析得出,与CD44v6低表达组的患者相比,CD44v6高表达组的pT/pN分期更晚,对NACT的疗效更差(应答率为53.5% vs. 77.8%,P=0.025)。在一项关于CD44v6表达与胃癌预后的meta分析显示,CD44v6的表达与远处转移、淋巴浸润、TNM分期及胃癌的进展呈正相关,且CD44v6过表达的患者预后较差[17]。
同样,CD44v6与宫颈癌的预后及NACT的疗效也具有一定的相关性,Ayhan等[18]通过对88例宫颈癌患者的研究发现,CD44v6高表达与肿瘤细胞的扩散转移及预后密切相关。Costa等[6]通过对21例Ⅰb和Ⅱa期宫颈癌患者的研究指出,CD44v6低表达是预测患者对NACT敏感度的重要指标,可作为制定治疗方案的一个参考因素,如果化疗前CD44v6表达较高,预示着宫颈癌患者对以铂类为基础的化疗不敏感,应及时更改治疗方案。在本研究中,敏感组CD44v6的表达值显著低于不敏感组,且CD44v6的表达在疗效为CR、PR、SD的患者中存在显著的差异(P < 0.05),这与Pereira等[19]提出的CD44v6阳性的细胞对顺铂的敏感度较CD44v6阴性低的结果相一致。因此,宫颈癌患者NACT的疗效与CD44v6的表达可能具有密切的关系,CD44v6高表达患者在选择以铂类为主的NACT时应更加慎重。同时CD44v6对宫颈癌以铂类为基础的NACT疗效预测的ROC曲线分析结果表示,CD44v6对预测宫颈癌NACT的疗效有重要的价值(AUC=0.740, P < 0.05),这提示CD44v6表达对预测宫颈癌NACT疗效有临床意义。但是,目前CD44v6与NACT的疗效相关联的具体作用机制尚不十分清楚,Safa等[20]指出,CD44v6通过与透明质酸、淋巴系统及循环系统之间的特殊作用获得增强细胞浸润、转移及侵袭的能力,CD44v6阳性细胞可能更易与ECM牢固结合,利于浸润转移,这可能是CD44v6导致这类肿瘤细胞对化疗药物的敏感度降低以及化疗疗效降低的原因。
表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR)是一种跨膜酪氨酸激酶受体蛋白,是原癌基因C-erbB-1的表达产物。EGFR在宫颈组织中的表达水平可能与肿瘤的发生、发展、浸润和转移密切相关,可能作为宫颈癌恶性程度判断和预后的重要指标[21]。本研究中,EGFR的表达与宫颈癌肿瘤大小相关(P < 0.05),EGFR表达越高,宫颈癌肿块越大,这与陈永发等[22]提出的宫颈癌肿块 > 4 cm时EGFR阳性表达率高于肿块≤4 cm相符。同时,Hugo等[7]指出侵袭性越强的宫颈癌CASKI细胞系中EGFR的表达水平越高,故EGFR可能通过这种高侵袭性来促进铂类化疗耐药,从而影响化疗疗效。因此,EGFR的表达可能会影响化疗疗效,但本研究中EGFR对预测NACT的疗效无显著影响,可能是由于本研究样本量少所致。单一指标预测价值可能较为局限,双指标联合预测可能会提高预测效能,提高特异度和灵敏度。目前已有研究报道CD44v6、EGFR在肺鳞癌及宫颈癌中的阳性表达率具有一定相关性,联合检测CD44v6、EGFR表达可作为宫颈癌早期诊断、转移潜能和预后的判断性指标[23],这与本研究中CD44v6与EGFR的表达具有正相关性一致。但本研究中联合检测并未提高预测价值,这可能与样本量少有关。因此,EGFR和CD44v6可能通过协同作用影响宫颈癌对紫杉醇+铂类NACT的疗效。
初治时肿瘤大小、肿瘤侵犯范围及盆腔淋巴结转移是影响宫颈癌患者疗效的重要因素[24],这与本研究中肿瘤未侵犯宫旁的患者NACT的疗效优于肿瘤侵及宫旁的结果一致。但本研究中肿瘤直径越大的患者NACT疗效越好,与部分研究的结果不同。其中邹婷婷等[4]研究发现,肿瘤直径是影响宫颈癌患者NACT疗效的影响因素,且肿瘤直径≥5 cm的患者疗效相对差,但该研究还指出,全身炎性反应指标(中性粒细胞-淋巴细胞比、单核细胞-淋巴细胞比)、盆腔淋巴结转移及宫颈肌层浸润的发生率等均可影响化疗疗效。我们分析造成本研究结果与其他研究结果不完全一致的原因有以下几点:首先,本研究未将淋巴结转移、全身炎性反应指标等因素纳入分析;其次,本研究病例数偏少,影响统计学结果;第三,目前更多的研究强调肿瘤大小与患者生存预后的关系,对于肿瘤大小与NACT疗效的研究相对较少。但是,值得注意的是肿瘤的化疗敏感度与肿瘤细胞的生长分数即肿瘤细胞群体中处于增殖阶段(S期+G2期)的细胞比例相关,生长分数越大,肿瘤生长越迅速,目前大多数抗癌药物是针对处于分裂期的细胞,因此,生长分数高的肿瘤对于化学治疗特别敏感[25]。大肿块(直径 > 4 cm)的肿瘤处于分裂期的细胞可能更多,这可能是促使肿瘤直径 > 4 cm的宫颈癌患者从NACT中获益更多的原因之一。因此,目前仍需进一步证实NACT疗效与肿瘤大小的关系。
综上,本研究通过检测53例宫颈癌患者肿瘤组织中的CD44v6与EGFR的表达,分析CD44v6与EGFR表达对NACT疗效的预测价值,初步得出结论,肿瘤组织中CD44v6的表达可能对预测NACT疗效有一定的价值,CD44v6越高,NACT的疗效越低,且CD44v6在不同分期的宫颈癌中存在表达差异。EGFR的表达可能与宫颈癌的大小有关,EGFR与CD44v6的表达具有正相关关系,因此,EGFR与CD44v6联合检测可能作为宫颈癌患者化疗前预测疗效的一项指标,从而指导临床用药,提高患者生存质量及预后,但仍需扩大样本量进一步证实。本结果对明确CD44v6对NACT疗效的预测价值有积极意义,同时将有助于制定更加有效的个体化治疗方案,提升患者疗效。但是,由于本研究的病例数较少,未来可在获取更大样本数的前提下,进行更深入的研究分析,以期为宫颈癌患者的个体化和综合治疗做出客观有益的指导。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.作者贡献:阳昊:查阅文献、提取数据、统计分析、论文撰写梅同华:把握研究方向、论文指导及修改 -
表 1 7 027例M1a期小细胞肺癌患者临床特征(n(%))
Table 1 Clinical characteristics of 7027 SCLC patients with M1a disease (n(%))

表 2 影响M1a期SCLC患者OS的单因素和多因素分析
Table 2 Univariate and multivariate survival analyses of OS in SCLC patients with M1a Disease

表 3 Cox比例风险回归模型分析对侧肺结节、恶性胸腔积液和恶性心包积液患者的OS
Table 3 Cox proportional hazards regression model analysis of OS in patients with contralateral lung nodules, malignant pleural effusion and malignant pericardial effusion

-
[1] Rudin CM, Brambilla E, Faivre-Finn C, et al. Small-cell lung cancer[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2021, 7(1): 3. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-00235-0
[2] Hiddinga BI, Raskin J, Janssens A, et al. Recent developments in the treatment of small cell lung cancer[J]. Eur Respir Rev, 2021, 30(161): 210079. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0079-2021
[3] Poirier JT, George J, Owonikoko TK, et al. New Approaches to SCLC Therapy: From the Laboratory to the Clinic[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2020, 15(4): 520-540. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2020.01.016
[4] Nicholson AG, Chansky K, Crowley J, et al. The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for the Revision of the Clinical and Pathologic Staging of Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Forthcoming Eighth Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2016, 11(3): 300-311. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2015.10.008
[5] Lin X, Xiao Z, Hu Y, et al. Combining 18F-FDG PET/CT and Serum Lactate Dehydrogenase for Prognostic Evaluation of Small Cell Lung Cancer[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 592768. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.592768
[6] Dingemans AC, Früh M, Ardizzoni A, et al. Small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up[J]. Ann Oncol, 2021, 32(7): 839-853. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.03.207
[7] 张文珏, 朱慧, 周宗玫, 等. TNM分期在局限期小细胞肺癌预后评估中的价值[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2015, 37(12): 917-922. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2015.12.008 Zhang WJ, Zhu H, Zhou ZM, et al. Prognostic value of AJCC TNM Staging 7th edition in limited-stage small cell lung cancer: validation in 437 patients[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2015, 37(12): 917-922. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2015.12.008
[8] Goldstraw P, Chansky K, Crowley J, et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for Revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Eighth) Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2016, 11(1): 39-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2015.09.009
[9] Vallières E, Shepherd FA, Crowley J, et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals regarding the relevance of TNM in the pathologic staging of small cell lung cancer in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2009, 4(9): 1049-1059. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181b27799
[10] Dai C, Ren Y, Xie D, et al. Does Lymph Node Metastasis Have a Negative Prognostic Impact in Patients with NSCLC and M1a Disease?[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2016, 11(10): 1745-1754. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.06.030
[11] Rami-Porta R, Asamura H, Travis WD, et al. Lung cancer - major changes in the American Joint Committee on Cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2017, 67(2): 138-155. doi: 10.3322/caac.21390
[12] Asamura H, Chansky K, Crowley J, et al. The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for the Revision of the N Descriptors in the Forthcoming 8th Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2015, 10(12): 1675-1684. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000678
[13] Iida T, Shiba M, Yoshino I, et al. Surgical Intervention for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Pleural Carcinomatosis: Results From the Japanese Lung Cancer Registry in 2004[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2015, 10(7): 1076-1082. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000554
[14] Ryu JS, Lim JH, Lee JM, et al. Minimal Pleural Effusion in Small Cell Lung Cancer: Proportion, Mechanisms, and Prognostic Effect[J]. Radiology, 2016, 278(2): 593-600. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015142388
[15] Kato R, Hayashi H, Chiba Y, et al. Prognostic Impact of Minimal Pericardial Effusion in Patients With Advanced Non-small-cell Lung Cancer[J]. Clin Lung Cancer, 2017, 18(6): e449-e455. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2017.05.011
[16] Morris ZS, Cannon DM, Morris BA, et al. Impact of a Contralateral Tumor Nodule on Survival in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2015, 10(11): 1608-1615. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000655
[17] Ignatius Ou SH, Zell JA. The applicability of the proposed IASLC staging revisions to small cell lung cancer (SCLC) with comparison to the current UICC 6th TNM Edition[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2009, 4(3): 300-310. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318194a355
[18] Girard N, Ostrovnaya I, Lau C, et al. Genomic and mutational profiling to assess clonal relationships between multiple non-small cell lung cancers[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2009, 15(16): 5184-5190. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0594
[19] 王继凡, 张特, 丁翰林, 等. 同时性多原发肺癌与肺内转移鉴别方法研究进展[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2021, 24(5): 365-371. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FAIZ202105009.htm Wang JF, Zhang T, Ding HL, et al. Research Progress in Distinguishing Methods of Simultaneous Multiple Primary Lung Cancer and Intrapulmonary Metastasis[J]. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi, 2021, 24(5): 365-371. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FAIZ202105009.htm
[20] Zou J, Guo S, Xiong MT, et al. Ageing as key factor for distant metastasis patterns and prognosis in patients with extensive-stage Small Cell Lung Cancer[J]. J Cancer, 2021, 12(6): 1575-1582. doi: 10.7150/jca.49681
[21] Huang LL, Hu XS, Wang Y, et al. Survival and pretreatment prognostic factors for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: A comprehensive analysis of 358 patients[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2021, 12(13): 1943-1951. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13977
[22] Lim JH, Ryu JS, Kim JH, et al. Gender as an independent prognostic factor in small-cell lung cancer: Inha Lung Cancer Cohort study using propensity score matching[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(12): e0208492. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208492
[23] Zhou K, Shi H, Chen R, et al. Association of Race, Socioeconomic Factors, and Treatment Characteristics With Overall Survival in Patients With Limited-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2021, 4(1): e2032276. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.32276
[24] Shan Q, Shi J, Wang X, et al. A new nomogram and risk classification system for predicting survival in small cell lung cancer patients diagnosed with brain metastasis: a large population-based study[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 640. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08384-5
[25] Daly ME, Ismaila N, Decker RH, et al. Radiation Therapy for Small-Cell Lung Cancer: ASCO Guideline Endorsement of an ASTRO Guideline[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2021, 39(8): 931-939. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.03364
[26] Sheikh S, Dey A, Datta S, et al. Role of radiation in extensive stage small cell lung cancer: a National Cancer Database registry analysis[J]. Future Oncol, 2021, 17(21): 2713-2724. doi: 10.2217/fon-2020-1095
[27] Lee JS, Kim S, Sung SY, et al. Treatment Outcomes of 9, 994 Patients With Extensive-Disease Small-Cell Lung Cancer From a Retrospective Nationwide Population-Based Cohort in the Korean HIRA Database[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 546672. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.546672
[28] Noronha V, Ravind R, Patil VM, et al. The role of chemotherapy in patients with small cell lung cancer and poor performance status[J]. Acta Oncol, 2020, 59(12): 1520-1527. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2020.1819562
-
期刊类型引用(23)
1. 叶明石. 曲妥珠单抗联合DC方案治疗HER2阳性乳腺癌的临床效果. 临床合理用药. 2025(03): 113-115 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘兆捷,党安建,郭静. 含曲妥珠单抗化疗方案联合参芪扶正注射液治疗HER2阳性乳腺癌的效果. 临床医学. 2025(01): 105-107 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 朱媛媛,葛琴,钱生勇,施海芹. 曲妥珠单抗和帕妥珠单抗联合TEC新辅助治疗中晚期HER-2阳性乳腺癌对保乳成功率的影响. 中国现代医学杂志. 2025(04): 17-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王剑平,冯娟娟,王飞,裴雅玲. 帕妥珠单抗治疗HER-2阳性转移性乳腺癌无进展生存期的临床研究. 医学理论与实践. 2025(04): 606-608 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 杨柳,崔红海. 帕妥珠单抗应用于HER-2阳性转移性乳腺癌无进展生存期患者的效果观察. 实用中西医结合临床. 2025(02): 13-15+31 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 叶泽霖,郑金珠,冯杰鑫,吴雄. 曲妥珠单抗与帕妥珠单抗双靶治疗在人表皮生长因子受体-2阳性乳腺癌新辅助治疗中的应用效果. 中国医药指南. 2024(01): 100-103 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 齐艳姝,傅鉴乾,黄如意. 曲妥珠单抗联合帕妥珠单抗靶向治疗HER2阳性乳腺癌患者临床疗效研究. 罕少疾病杂志. 2024(01): 75-76 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 杨文青,王静,王丽,郑璐璐. HER2阳性乳腺癌患者行帕妥珠单抗靶向治疗过程中应用预见性护理的效果. 中国药物滥用防治杂志. 2024(02): 358-361 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 郭玛丽,林丽平,丁晓芬,樊燕丹. 吡咯替尼联合化疗在人表皮生长因子受体-2阳性晚期乳腺癌一线及一线以上治疗中的应用效果. 中国当代医药. 2024(07): 114-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 王丽君,辛岗,胡崇珠,李雪. THP方案新辅助治疗HER-2阳性乳腺癌的真实世界研究. 菏泽医学专科学校学报. 2024(02): 20-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 周冰,王琴宇,周瑶,李文伟,周志兵,许志宏. 帕妥珠单抗靶向治疗联合化疗对HER-2阳性乳腺癌患者血清肿瘤标志物及生活质量的影响. 中国卫生工程学. 2024(03): 417-418+421 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 蒋海英. 曲妥珠单抗与帕妥珠单抗双靶向联合化疗在人表皮生长因子受体2阳性乳腺癌中的应用效果. 现代养生. 2024(13): 982-984 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 徐东宏,吴向东,张世博,杜永涛,胡崇珠,王恩庆. TCbHP方案新辅助治疗人表皮生长因子受体2阳性乳腺癌的效果和安全性. 肿瘤研究与临床. 2024(08): 590-593 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 董正宇. 帕妥珠单抗治疗HER2阳性乳腺癌的效果及安全性. 中国医学创新. 2024(26): 32-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 张宇,宋军,宋波. 曲妥珠单抗联合新辅助化疗在乳腺癌患者中的应用效果. 中国民康医学. 2024(19): 82-84+88 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 张培培. 曲妥珠单抗联合帕妥珠单抗治疗HER2阳性乳腺癌患者的效果观察. 交通医学. 2024(06): 580-582+585 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 张隆,王晓倩,范莉莉. 贝伐单抗联合化疗方案治疗晚期HER2阴性乳腺癌对细胞因子水平的影响. 深圳中西医结合杂志. 2024(22): 81-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 岳瑞雪,胡崇珠,郝鑫,杨进强,韩猛,崔国忠,王建军,张志生,孔凡庭,张维,何文博,李现桥,周新平. 曲妥珠单抗和帕妥珠单抗联合不同化疗方案新辅助治疗HER-2阳性乳腺癌真实世界疗效及安全性观察. 中国肿瘤临床. 2023(05): 248-254 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 张能英,陈保林,吕俊远,曾峰,方小玉,邓小玲,程晓明,李涛浪. 曲妥珠单抗生物类似药联合帕妥珠单抗新辅助治疗HER-2阳性乳腺癌的疗效和安全性. 遵义医科大学学报. 2023(07): 665-672 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 胡米,刘歆春. 曲妥珠单抗靶向治疗联合新辅助化疗治疗HER-2阳性乳腺癌的疗效. 临床合理用药. 2023(36): 23-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 孟瑶,张敬,任毅,赵长啸. 帕妥珠单抗辅助化疗治疗HER-2阳性晚期乳腺癌的效果及对血管内皮因子水平的影响. 中国卫生工程学. 2023(06): 823-825 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 王金悦,吕桂香,高旭. 部分常见单克隆抗体药物在抗肿瘤治疗中的应用及研究进展. 生命的化学. 2022(05): 950-960 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 麻丽珍,潘静进. TAC新辅助化疗方案治疗HER-2阳性乳腺癌的疗效. 吉林医学. 2022(10): 2632-2634 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)



 下载:
下载: