Cordycepin Attenuates Immune Function Injury in A Rat Model of Lung Cancer After Radiotherapy by Inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 Pathway
-
摘要:目的
探讨虫草素通过JAK2/STAT3信号通路对肺癌大鼠放射性治疗免疫功能损伤的抑制作用。
方法50只大鼠建立荷瘤模型,另设正常组(10只)。建模成功大鼠随机分为模型组、放疗组、虫草素组、激动剂组和激动剂+虫草素组,每组10只。比较各组大鼠瘤重、肿瘤体积、抑瘤率、IL-6、TNF-α、脾指数、胸腺指数、T淋巴细胞亚群数量、JAK2、p-JAK2、STAT3和p-STAT3蛋白表达水平。
结果与正常组比较,模型组IL-6、TNF-α、CD8+、p-JAK2、p-STAT3升高,脾指数、胸腺指数、CD4+、CD4+/CD8+降低(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,放疗组瘤重、肿瘤体积、脾指数、胸腺指数、CD4+、CD4+/CD8+降低,IL-6、TNF-α、CD8+、p-JAK2和p-STAT3升高(P < 0.05);与放疗组比较,虫草素组瘤重、肿瘤体积、IL-6、TNF-α、CD8+、p-JAK2、p-STAT3降低,抑瘤率、脾指数、胸腺指数、CD4+、CD4+/CD8+升高,激动剂组瘤重、肿瘤体积、IL-6、TNF-α、CD8+、p-JAK2、p-STAT3升高,抑瘤率、脾指数、胸腺指数、CD4+、CD4+/CD8+降低(P < 0.05);与激动剂+虫草素组比较,虫草素组瘤重、肿瘤体积、IL-6、TNF-α、CD8+、p-JAK2、p-STAT3降低,抑瘤率、脾指数、胸腺指数、CD4+、CD4+/CD8+升高,激动剂组瘤重、肿瘤体积、IL-6、TNF-α、CD8+、p-JAK2、p-STAT3升高,抑瘤率、脾指数、胸腺指数、CD4+、CD4+/CD8+降低(P < 0.05)。
结论虫草素可有效抑制肺癌大鼠放射性治疗免疫功能损伤,其机制可能通过抑制JAK2/STAT3信号通路蛋白表达发挥调控作用。
-
关键词:
- 虫草素 /
- 放疗 /
- 免疫功能 /
- JAK2/STAT3
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the inhibitory effect of cordycepin on immune function injury in lung cancer rats after radiation therapy through JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway.
MethodsFifty rats were used to establish tumor-bearing model and other 10 rats were taken as normal group. After successful modeling, the rats were randomly divided into model group, radiotherapy group, cordycepin group, agonist group and agonist+cordycepin group (10 rats in each group). We compared tumor weight, tumor volume, tumor inhibition rate, IL-6, TNF-α, spleen index and thymus index, the number of T lymphocyte subsets, JAK2, p-JAK2, STAT3 and p-STAT3 protein expression levels among all groups.
ResultsCompared with normal group, IL-6, TNF-α, CD8+, p-JAK2 and p-STAT3 in model group were increased, while spleen index, thymus index, CD4+ and CD4+/CD8+ were decreased (P < 0.05). Compared with model group, tumor weight, tumor volume, spleen index, thymus index, CD4+ and CD4+/CD8+ were decreased in radiotherapy group, while IL-6, TNF-α, CD8+, p-JAK2 and p-STAT3 were increased (P < 0.05). Compared with radiotherapy group, tumor weight, tumor volume, IL-6, TNF-α, CD8+, p-JAK2 and p-STAT3 were decreased in cordycepin group, while tumor inhibition rate, spleen index thymus index, CD4+ and CD4+/CD8+ were increased; tumor weight, tumor volume, IL-6, TNF-α, CD8+, p-JAK2 and p-STAT3 protein expression were increased in agonist group, while tumor inhibition rate, spleen index, thymus index, CD4+ and CD4+/CD8+ were decreased (P < 0.05). Compared with agonist+cordycepin group, tumor weight, tumor volume, IL-6, TNF-α, CD8+, p-JAK2 and p-STAT3 were decreased in cordycepin group, while tumor inhibition rate, spleen index, thymus index, CD4+ and CD4+/CD8+ were increased; tumor weight, tumor volume, IL-6, TNF-α, CD8+, p-JAK2 and p-STAT3 were increased in agonist group, while tumor inhibition rate, spleen index, thymus index, CD4+ and CD4+/CD8+ were decreased (P < 0.05).
ConclusionCordycepin can effectively inhibit the immune function injury in lung cancer rats after radiation therapy, and may play a regulatory role by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 signal pathway.
-
Key words:
- Cordycepin /
- Radiation therapy /
- Immune function /
- JAK2/STAT3
-
0 引言
晚期肺癌患者5年生存率仅5%,但若能在早期诊断并治疗,5年存活率可达57%[1-2]。因此,结合肺癌危险因素及其临床特征建立肺癌危险度预测模型对早期诊断及治疗肺癌,提高患者5年生存率具有重要意义。近年来,数据挖掘技术已经在生物医学预测模型中得到广泛应用。人工神经网络(artificial neural network, ANN)具有良好的鲁棒性、高容错性和较强的归纳能力,而C5.0算法作为决策树模型的常用算法之一,适用于分类变量和大数据集[3]。因此,该研究拟将肺癌常见危险因素与临床症状相结合,采用C5.0决策树与ANN构建肺癌危险度预测模型,并评价两模型的性能优劣,为肺癌早期筛查及临床辅助诊断提供依据和工具。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
收集2014年10月至2016年10月郑州大学第一附属医院的住院患者样本420例,其中包括肺癌患者180例,肺良性疾病患者240例。入组患者均知情同意并自愿参加。
入选标准:肺癌组:以《中华医学会肺癌临床诊疗指南(2019版)》为标准[4],经病理学或细胞学被证实为原发性肺癌患者;肺良性疾病组:由郑州大学第一附属医院诊断为肺部良性病变患者。排除标准:(1)入组前曾接受放化疗、药物治疗或手术治疗者;(2)主要脏器功能衰竭患者;(3)合并肺或其他恶性肿瘤患者;(4)妊娠或哺乳期患者;(5)不同意入组者。
1.2 观察指标
调查人员经过统一培训后,通过问卷访谈形式对患者进行调查询问获得数据资料,包括流行病学资料(疾病诊断、年龄、吸烟史、饮酒史、粉尘接触史、输血史、肺癌家族史、炎性反应史)和临床症状(咳嗽、咳痰、痰中带血、咯血、胸闷、胸痛、心慌、乏力、畏寒、发热出汗)。其中年龄根据《中华医学会肺癌临床诊疗指南(2019版)》以45岁为界限进行分组。总数据集包括18个定性变量(17个预测变量和1个因变量),因变量为诊断结果,各变量赋值见表 1。
表 1 肺癌危险度评价研究的变量赋值说明Table 1 Instructions of variables assignment in risk assessment studies of lung cancer
1.3 统计学方法
应用SPSS21.0对420例样本数据进行统计分析,对所有变量进行描述性统计分析,采用χ2检验进行差异分析,检验水准α=0.05。
使用SPSS Clementine 12.0软件建立两种数据挖掘预测模型,使用MedCalc15.10软件绘制受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic curve, ROC)曲线。将两组样本均按照7:3随机分为两部分,其中训练数据集包含302例样本,测试数据集包含118例样本。C5.0决策树模型和ANN模型的比较采用敏感度、特异性、准确度、阳性预测值(positive predictive values, PPV)、阴性预测值(positive and negative predictive values, NPV)、约登指数和ROC曲线下面积(area under ROC curve, AUC)进行评估。
2 结果
2.1 基本情况
420例患者中,肺癌患者180例(42.9%),肺良性疾病患者240例(57.1%)。肺良性疾病患者中小于45岁者(63.8%)明显多于肺癌组(36.2%),差异有统计学意义(P=0.004)。肺癌患者中吸烟、饮酒者(57.1%、55.7%)均多于肺良性疾病患者(42.9%、44.3%)。肺癌组有粉尘接触史或肺癌家族史者分别仅2例。肺良性疾病组中有6例有输血史,而肺癌组中没有。10个临床症状变量中,肺癌组中痰中带血(64.0%)及胸痛(55.3%)的比例高于肺良性疾病患者(36.0%、44.7%)。两组样本的基线特征分析结果见表 2。
表 2 肺癌组和肺良性疾病组的样本基线特征及卡方检验(n(%))Table 2 Baseline characteristics and chi-square test of lung cancer and lung benign disease groups (n(%))
2.2 输入变量的选择
两组间年龄(P=0.004)、吸烟史(P < 0.001)、饮酒史(P=0.028)、输血史(P=0.033)、炎症史(P < 0.001)、痰中带血(P=0.001)、胸痛(P=0.006)、乏力(P=0.049)和发热出汗(P < 0.001)9个因素差异有统计学意义,见表 2。此外由于既往研究提示粉尘接触史、癌症家族史、咳痰、咳嗽和咯血为肺癌的影响因素[4-5],该研究入选这14个因素作为输入变量建立风险预测模型。
2.3 危险度预测模型的构建与比较
2.3.1 两种风险预测模型的建立
经过训练,C5.0决策树风险预测模型的参数设置如下:Use partitioned data: no, Output type: Decision Tree, Group symbolic: no, Use boosting: yes, Cross-validate: no, Mode: expert, Pruning severity: 75, Minimum records per child brunch: 2, Use global pruning: yes, Window attributes: no, Use misclassification costs: no。ANN风险预测模型的参数设置如下:Use partitioned data: yes, Method: prune, Prevent overtraining sample: 50%, Set random seed: 321, Stop on: time (mins) 1 min, Optimize: memory, Continue training existing model: no; Use binary set encoding: yes, Show feedback graph: yes, Model selection: Use best network, Mode: expert。
2.3.2 两种危险度预测模型的性能比较
两种模型训练集和测试集样本的分类结果见表 3。在训练集与测试集样本中C5.0模型的准确率分别为68.54%和61.0%,ANN模型的准确率分别为69.5%和65.3%。可以看出ANN模型在训练集和预测集中准确度均高于C5.0模型。根据两个数据挖掘模型的ROC曲线中各危险因素对应的AUC评估各自变量对模型的影响大小,重要性前10位影响因素排序见表 4。由表可知,对模型影响最大的三个影响因素在ANN模型中分别是吸烟史、痰中带血与胸痛;而在C5.0模型中分别是吸烟史、胸痛与年龄。在ANN模型和C5.0模型中吸烟均为最主要的影响因素。
表 3 C5.0决策树和ANN模型的训练集和测试集样本分类结果Table 3 Classification results of training set and testing set samples by Decision tree C5.0 and ANN models 表 4 C5.0决策树模型和ANN模型中纳入变量的重要性排序Table 4 Importance ranking of variables in Decision tree C5.0 model and ANN model
表 4 C5.0决策树模型和ANN模型中纳入变量的重要性排序Table 4 Importance ranking of variables in Decision tree C5.0 model and ANN model
两种数据挖掘模型对肺癌综合预测性能的相关指标包括准确度、约登指数、敏感度、特异性、预测值和AUC。其中C5.0决策树模型的特异性和NPV高于ANN模型,ANN模型预测模型的准确度、约登指数、敏感度、PPV和AUC均高于C5.0决策树模型,见表 5。测试集中两种数据挖掘模型的ROC曲线可发现ANN模型预测性能优于C5.0决策树模型,见图 1。
表 5 两种数据挖掘模型的测试集结果比较Table 5 Comparison of testing set results between two data mining models
3 讨论
当前,肺癌的高发病率和高病死率已经造成巨大的公共卫生负担,利用肺癌的危险因素来预测肺癌危险度,对于肺癌的预防和早期筛查具有重要意义。本研究分别建立了C5.0决策树与ANN肺癌风险预测模型,比较发现,ANN模型预测性能优于C5.0决策树模型。
本研究按照0.05的显著性水平,单因素检验发现有9个变量与肺癌患病率呈相关关系:5个流行病学变量中年龄、吸烟史、饮酒史、炎性反应史与肺癌患病率呈正相关,输血史与肺癌患病率呈负相关;4个临床症状中痰中带血、胸痛与肺癌患病率正相关,乏力和发热出汗与肺癌患病率存在负相关关系。同时,本研究的两种数据挖掘模型中吸烟均为关键影响变量。既往研究表明肺癌常见于70岁以上人群且发病率和死亡率随年龄增加而升高,同时吸烟、饮酒以及慢性炎性反应均为肺癌的危险因素之一[5],而围手术期输血对肺癌预后和复发的影响当前研究仍不一致[6],这与本研究结果基本相符。有研究显示,遗传因素与职业性粉尘接触也是肺癌的危险因素之一[7],这与本研究结果不符。
决策树模型是一种由层次分类逐步构建的贪心算法,作为一种新兴的数据挖掘技术,它可以经过多次迭代演算后得到最优化的算法模型,具有较高的数据分析能力。相关研究已经将C5.0决策树模型用于利用基因表达数据和职业危险因素预测肺癌风险的模型建立[8-10]。C5.0算法作为决策树模型的常用算法之一,适用于分类变量和大数据集,已经在生物医学预测模型的建立中得到广泛应用。另外一些研究将C5.0决策树模型与其他多种研究进行比较,建立疾病风险预测模型,均得到C5.0决策树模型的预测性能最优的结果[11-12]。
ANN模型的数学结构模拟人类大脑的生物神经元学习动态,对输入变量经过训练产生一个加权组合的输出结果。ANN相比于一般统计学方法优势显著,具有良好的鲁棒性、高容错性和较强的归纳能力,可以快速识别线性模型、受阈值影响的非线性模型、分类模型、逐步线性模型,甚至偶然影响,故其可以确定潜在的预后影响因素[13]。已有研究将ANN应用于肺癌风险评估相关模型的构建[3, 14]。该研究结果同样显示ANN模型在准确度、敏感度、约登指数、阳性预测值、ROC曲线下面积均优于决策树模型[15-16],这与相关研究结果一致。因此,本研究建议利用ANN模型结合人群的流行病学资料和临床症状判别肺癌高危人群,为肺癌的早期诊断早期治疗提供参考依据[17]。
本研究仍然存在一定的局限性:一方面,纳入的样本量较少,如果能收集更大样本量和多中心样本资料,样本数据将具有更好的代表性,模型将具有更优异的性能;另一方面,纳入的变量种类有限,而与肺癌相关的危险因素众多且对肺癌存在交互作用,如果能纳入环境因素、职业因素、遗传因素、行为生活方式等多种研究变量,模型将更为准确可靠。因此,我们建议未来的研究应涵盖更大的样本量,纳入更为丰富的研究变量进行综合分析,同时将ANN模型应用于肺癌高危人群中筛查验证。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.作者贡献:刘建波:实验设计及论文撰写李白羽:实验实施和资料收集柯善保:论文撰写张伟:论文修订和审校 -
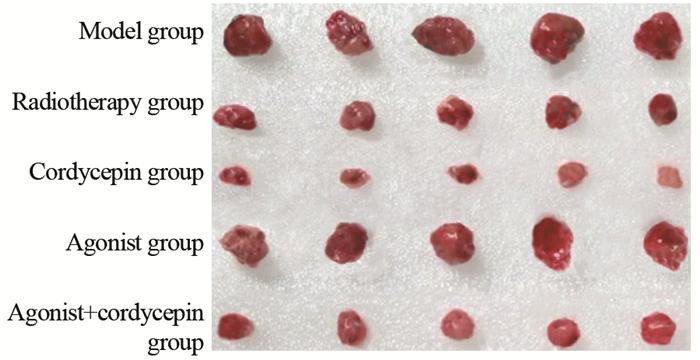
表 1 各组大鼠瘤重、肿瘤体积和抑瘤率比较(x±s)
Table 1 Comparison of tumor weight, tumor volume and tumor inhibition rate of rats among five groups (x±s)

表 2 各组大鼠血清IL-6和TNF-α水平比较(x±s)
Table 2 Comparison of IL-6 and TNF-α levels in serum of rats among all groups (x±s)

表 3 各组大鼠脾指数和胸腺指数比较(x±s)
Table 3 Comparison of spleen index and thymus index among all groups (x±s)

表 4 各组大鼠脾脏T淋巴细胞亚群数量比较(x±s)
Table 4 Comparison of T lymphocyte subsets number in spleen of rats among all groups (x±s)

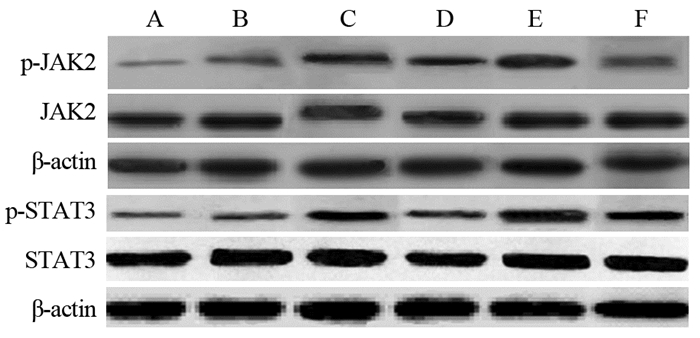
表 5 脾脏组织中JAK2、p-JAK2、STAT3和p-STAT3蛋白表达(x±s)
Table 5 Comparison of JAK2, p-JAK2, STAT3 and p-STAT3 protein levels in spleen of rats among all groups (x±s)

-
[1] 宋春洋, 祝淑钗, 沈文斌, 等. 临床Ⅲ期食管癌患者放疗前后免疫功能及外周血炎症指标对预后的影响分析[J]. 中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2020, 40(3): 189-195. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-5098.2020.03.006 Song CY, Zhu SC, Shen WB, et al. Analysis of the effects of immunity index and blood inflammatory markers pre- and post-radiotherapy on prognosis of clinical stage Ⅲ esophageal cancer patients[J]. Zhonghua Fang She Yi Xue Yu Fang Hu Za Zhi, 2020, 40(3): 189-195. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-5098.2020.03.006
[2] 王多, 鲍荣, 王芳, 等. 虫草素抗肿瘤作用分子机制研究进展[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2015, 29(4): 643-650. doi: 10.3867/j.issn.1000-3002.2015.04.018 Wang D, Bao R, Wang F, et al. progress in molecular mechanisms of anticancer action of corycepin[J]. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Yu Du Li Xue Za Zhi, 2015, 29(4): 643-650. doi: 10.3867/j.issn.1000-3002.2015.04.018
[3] Zhang Y, Zhang XX, Yuan RY, et al. Cordycepin induces apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells via the mitochondrial-mediated intrinsic pathway and suppresses tumor growth in vivo[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2018, 11: 4479-4490. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S164670
[4] Wang C, Mao ZP, Wang L, et al. Cordycepin inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in human cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Neoplasma, 2017, 64(6): 834-839. doi: 10.4149/neo_2017_604
[5] Lin YT, Liang SM, Wu YJ, et al. Cordycepin suppresses endothelial cell proliferation, migration, angiogenesis, and tumor growth by regulating focal adhesion kinase and p53[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2019, 11(2): 168. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000041694748599_3052.html
[6] 韩丹, 崔琳琳, 王莹, 等. 虫草素药理作用研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技, 2019, 40(9): 335-338, 345. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPKJ201909057.htm Han D, Cui LL, Wang Y, et al. Research Progress On Pharmacological Effects Of Cordycepin[J]. Shi Pin Gong Ye Ke Ji, 2019, 40(9): 335-338, 345. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPKJ201909057.htm
[7] Mao Y, Yang D, He J, et al. Epidemiology of lung cancer[J]. Surg Oncol Clin N Am, 2016, 25(3): 439-445. doi: 10.1016/j.soc.2016.02.001
[8] Michaelidesová A, Konířová J, Bartůněk P, et al. Effects of radiation therapy on neural stem cells[J]. Genes(Basel), 2019, 10(9): 640. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31450566
[9] Kirova Y, Tallet A, Aznar MC, et al. Radio-induced cardiotoxicity: from physiopathology and risk factors to adaptation of radiotherapy treatment planning and recommended cardiac follow-up[J]. Cancer Radiother, 2020, 24(6-7): 576-585. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2020.07.001
[10] Weichselbaum RR, Liang H, Deng L, et al. Radiotherapy and immunotherapy: a beneficial liaison?[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2017, 14(6): 365-379. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.211
[11] Woolley VC, Teakle GR, Prince G, et al. Cordycepin, a metabolite of Cordyceps militaris, reduces immune-related gene expression in insects[J]. J Invertebr Pathol, 2020, 177: 107480. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2020.107480
[12] Lei J, Wei Y, Song P, et al. Cordycepin inhibits LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2018, 818: 110-114. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.10.029
[13] Tan L, Song X, Ren Y, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of cordycepin: A review[J]. Phytother Res, 2020. Online ahead of print.
[14] 安青, 何立巍, 吴红雁, 等. 虫草素通过调节CD4+T淋巴细胞PD-1受体促进肿瘤免疫及机制研究[J]. 南京中医药大学学报, 2018, 34(5): 495-498. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJZY201805015.htm An Q, He LW, Wu HY, et al. Mechanism of cordycepin promotes tumor immunity by regulating PD-1 receptor of CD4+T lymphocytes[J]. Nanjing Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao, 2018, 34(5): 495-498. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJZY201805015.htm
[15] Zundler S, Neurath MF. Integrating immunologic signaling networks: the JAK/STAT pathway in colitis and colitis-associated cancer[J]. Vaccines(Basel), 2016, 4(1): 5. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040540984510_5b25.html
[16] Yu T, Li Z, Xu L, et al. Anti-inflammation effect of Qingchang suppository in ulcerative colitis through JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2021, 266: 113442. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113442
[17] Qing Y, Stark GR. Alternative activation of STAT1 and STAT3 in response to interferon-gamma[J]. J Biol Chem, 2004, 279(40): 41679-41685. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406413200
[18] Lei RE, Shi C, Zhang PL, et al. IL-9 promotes proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular cancer cells by activating JAK2/STAT3 pathway[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2017, 10(7): 7940-7946. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/326058664_IL-9_promotes_proliferation_and_metastasis_of_hepatocellular_cancer_cells_by_activating_JAK2STAT3_pathway
[19] Chen J, Zhang W, Xu Q, et al. Ang-(1-7) protects HUVECs from high glucose-induced injury and inflammation via inhibition of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2018, 41(5): 2865-2878. http://www.spandidos-publications.com/ijmm/41/5/2865/download
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 黄普超,原慧洁,张桂芳. 基于数据挖掘技术的肺癌危险度预测模型的构建. 实用预防医学. 2022(11): 1390-1394 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: