Relation Between CD8+T Lymphocyte Infiltration and Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Triple-negative Breast Cancer
-
摘要:目的
探讨三阴性乳腺癌组织CD8+T淋巴细胞浸润(CD8+Tils)的特点与患者预后的关系。
方法回顾性分析术前行新辅助化疗的126例三阴性乳腺癌患者的临床病理资料,采用免疫组织化学法分析CD8+Tils与临床病理特征的关系;Kaplan-Meier法绘制生存曲线,Cox风险比例回归模型分析患者无病生存时间(DFS)的预后影响因素。
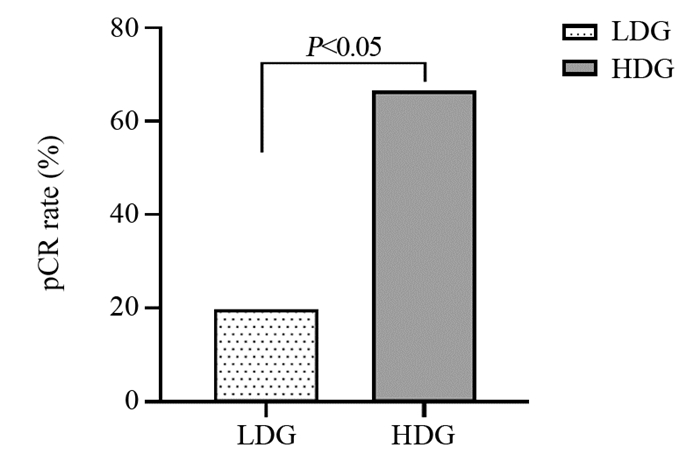
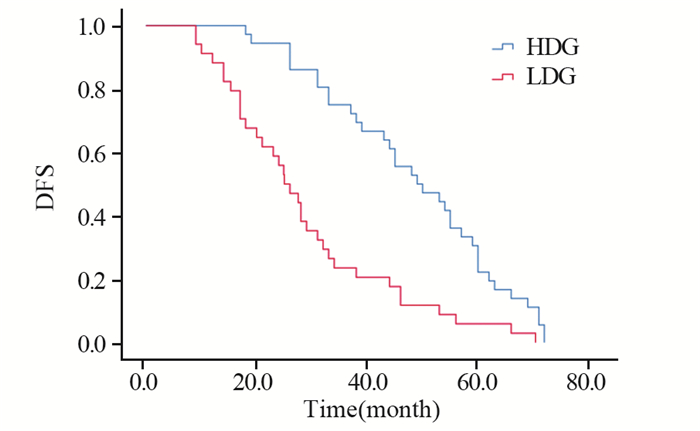
结果高密度CD8+Tils浸润与年龄 < 60岁、病理高分级、临床高分期显著相关(P < 0.05)。CD8+Tils高密度浸润患者术后pCR率较低密度组高(66.7% vs. 19.8%, P=0.000)。高密度组中位DFS显著长于CD8+Tils低密度组(49 vs. 25月, P < 0.05)。多因素分析显示病理高分级、肿瘤直径 > 2 cm、淋巴结转移、脉管侵犯、CD8+Tils低密度浸润均为预后不良影响因素(P < 0.05),CD8+Tils为独立预后因素。
结论CD8+Tils有可能是三阴性乳腺癌患者独立预后指标,高密度浸润患者术后pCR率高、DFS长、远期疗效更优。
-
关键词:
- 三阴性乳腺癌 /
- CD8+T淋巴细胞浸润 /
- 新辅助化疗
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the relation between the characteristics of CD8+T lymphocyte infiltration and the prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer patients.
MethodsWe retrospectively analyzed the clinicopathological data of 126 patients with triple-negative breast cancer undergoing preoperative neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Immunohistochemical staining was used to analyze the relation between CD8+T lymphocyte infiltration and clinicopathological characteristics. Kaplan-Meier method was used to draw the survival curve, and Cox risk ratio regression model was used to analyze the prognostic factors affecting disease-free survival time (DFS).
ResultsHigh-density CD8+Tils was associated with age < 60 years old, high pathological grade and high clinical stage (P < 0.05). The pCR rate of high-density CD8+Tils group was higher than that of the low-density group (66.7% vs. 19.8%, P=0.000). The median DFS of the high-density group was significantly longer than that of the low-density group (49 vs. 25 months, P < 0.05). Multivariate analysis showed that high pathological grade, tumor diameter > 2 cm, lymph node metastasis, vascular invasion and CD8+Tils low-density infiltration were factors for poor prognosis (P < 0.05), and CD8+Tils was an independent prognostic factor.
ConclusionCD8+Tils may be an independent prognostic indicator for triple-negative breast cancer. The patients with high-density infiltration have high postoperative pCR rate, long DFS and better long-term efficacy.
-
0 引言
神经纤毛蛋白1(Neuropilin-1, NRP-1)是一种多功能的跨膜糖蛋白,在生理和病理条件下都可作为多种生长因子或其他配体的共受体而发挥不同的生物学功能,在免疫、肿瘤、血管发育和神经等系统中发挥重要作用[1],前期研究表明NRP-1在乳腺癌、淋巴瘤、卵巢癌、黑色素瘤、胃肠道肿瘤等多种人类肿瘤组织及癌细胞株中均过表达,但在相应的正常组织中表达较低,并与肿瘤的预后相关,因此NRP-1在肿瘤的发生和发展中起重要作用[2-5]。
Treg细胞(CD4+CD25+CD127-Treg)是一群具有低反应性及免疫抑制功能的调节性T细胞,能阻断机体抗肿瘤免疫,达到肿瘤免疫逃逸,促进肿瘤发生、发展的作用[6]。树突状细胞(dendritic cell, DC)是一种抗原呈递细胞,目前人类外周血DC细胞主要分为髓样树突状细胞(myeloid dendritic cell, MDC)和浆细胞样树突状细胞(plasmacytdid dendritic cell, PDC)(CD123+CD303+CD304+)2个亚型,其中PDC在诱导抗原特异性抗肿瘤免疫反应上发挥重要作用[7]。但有关NRP-1与Treg、PDC在非小细胞肺癌方面的研究却鲜见报道,本研究检测了非小细胞肺癌患者和健康体检者外周血中NRP-1在Treg、PDC的表达,旨在探讨其在非小细胞肺癌发生中免疫调节的可能机制,并分析其与临床参数的相关性,为NSCLC病情监测、治疗策略、疗效判断及预后评估提供新的相关指标。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
收集2018年6月—2019年9月就诊于徐州医科大学附属医院的49例均经手术、纤维支气管镜或经皮肺穿刺活检确诊为非小细胞肺癌患者的外周血,具有完整的临床、影像学、病理及随访资料。前期均未接受针对癌症的治疗(化疗、放疗以及生物免疫治疗等),近3月内未使用过免疫增强剂。全部符合世界卫生组织(WHO)的诊断标准。49例非小细胞肺癌患者年龄30~74岁,中位年龄61岁。其中男32例、女17例。按2018年国际抗癌联盟TNM肺癌病理分期分为:Ⅰ期18例、Ⅱ12例、Ⅲ期11例、Ⅳ期8例。同时收集徐州医科大学附属医院33例健康体检者外周血作为对照组,年龄22~70岁,中位年龄55岁。其中男17例、女16例。本研究获得徐州医科大学伦理委员会批准。
1.2 实验材料
FITC/Alexa Fluor 488-A标记的抗人CD4单克隆抗体试剂、APC标记的抗人CD25单克隆抗体试剂、Alexa Fluor 700标记的抗人CD3单克隆抗体试剂及PE.Cy5标记的抗人CDl27单克隆抗体试剂均购自美国Biolegend公司;Brilliant Violet 421标记的抗人CD304(NRP-1)单克隆抗体试剂、PEcy7标记的抗人CD123单克隆抗体试剂、APC-Fire750标记的抗人CD303单克隆抗体试剂、libIlr流式细胞仪及percp-cy5.5标记的抗人CD45单克隆抗体试剂均购自美国BD公司。
1.3 实验方法
清晨空腹抽取外周静脉血2 ml(肝素抗凝),于2 h内检测。取200 μl静脉血于流式管中,加抗体2 μl混匀,暗处孵育20 min;加红细胞裂解液2 ml,混匀,充分裂解红细胞;加2 ml PBS混匀,2 000 r/min离心,洗涤3次,加200 μl PBS混匀,置暗处4℃待上机,流式细胞仪检测NRP-1的表达。
1.4 统计学方法
用SPSS21.0软件对数据进行统计分析。计量资料经正态性检验,符合正态分布的数据均采用均数±标准差(

2 结果
2.1 NRP-l在肺癌患者和健康体检者外周血Treg(CD4+CD25+CD127-Treg)细胞中的表达
结果显示,肺癌患者外周血CD4+T表达为(34.19±7.61)%,Treg表达为(8.24±1.12)%,Treg上中NRP-1的表达为17.44±5.04;健康体检者外周血CD4+T表达为(38.91±4.85)%,Treg表达为(5.25±0.82)%,Treg中NRP-1的表达为12.69±3.29,见图 1。
2.2 对照组和非小细胞肺癌组临床指标比较
对照组外周血CD4+T、PDC的表达均明显高于非小细胞肺癌组,对照组外周血Treg/CD4+T表达与NRP-1的表达均明显低于非小细胞肺癌组(均P < 0.05),见表 1。
表 1 对照组和肺癌组临床指标比较(( Table 1 Comparison of clinical indicators between control group and NSCLC group (
Table 1 Comparison of clinical indicators between control group and NSCLC group (

2.3 Treg/CD4+T、NRP-1、PDC与NSCLC患者临床病理参数的关系
2.3.1 Treg/CD4+T
49例NSCLC外周血中Treg/CD4+T表达情况与肿瘤最大径、有无淋巴结转移、TNM分期、分化程度有关,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。随着TNM分期的升高和分化程度的降低,TregCD4+T的表达呈增高趋势,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),见表 2。
表 2 Treg/CD4+T、NRP-1与NSCLC患者临床病理参数之间的关系( Table 2 Correlation of Treg/CD4+T, NRP-1 with clinicopathological parameters of NSCLC patients ((
Table 2 Correlation of Treg/CD4+T, NRP-1 with clinicopathological parameters of NSCLC patients ((

2.3.2 Treg中NRP-1的表达
49例NSCLC外周血Treg中NRP-1的表达情况与肿瘤最大径、有无淋巴结转移、TNM分期、分化程度有关,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),随着TNM分期的升高和分化程度的降低,NRP-1的表达呈增高趋势,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),见表 2。
2.3.3 PDC中NRP-1的表达
49例NSCLC外周血PDC中NRP-1的表达情况与肿瘤最大径、有无淋巴结转移、TNM分期有关,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。随着TNM分期的升高,NRP-1在PDC中的表达呈递减趋势,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),见表 3。
表 3 NRP-1在PDC中的表达与NSCLC患者临床病理参数之间的关系( Table 3 Relation between NRP-1 expression on PDC and clinicopathological parameters of NSCLC patients ((
Table 3 Relation between NRP-1 expression on PDC and clinicopathological parameters of NSCLC patients ((

2.4 Treg/CD4+T与CD4+T、NRP-1(Treg)、PDC的相关性分析
NSCLC患者Treg/CD4+T与NRP-1存在明显的正相关关系(r > 0, P < 0.05);Treg/CD4+T与PDC存在明显的负相关关系(r < 0, P < 0.05),见表 4。
表 4 Treg/CD4+T与CD4+T、NRP-1(Treg)、PDC的相关性分析Table 4 Correlation of Treg/CD4+T with CD4+T, NRP-1 (Treg) and PDC
3 讨论
肺癌是全球癌症死亡的主要原因之一,死亡率在中国癌症相关死亡率中排名第一。最常见的病理类型是非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer, NSCLC),主要包含鳞状细胞癌(SCC)、腺癌(LAC)和大细胞癌(LCC)[8]。随着精准医学的发展,化学治疗、放射治疗、靶向治疗以及免疫治疗虽然延长了一部分中晚期肺癌患者的生存期,然而5年生存率仍小于21%[9]。因此,寻找简便易操作的预后评估指标具有重要的临床意义。近年来,关于肺癌患者的免疫功能引起重视,研究表明恶性肿瘤的发生、发展、转移和复发与机体的免疫功能缺陷有关,肺癌患者存在一定程度的免疫功能异常。随着对肺癌免疫耐受机制的深入研究,CD4+T、NRP-1、Treg以及PDC在肺癌发生、发展中的相互作用日益引起国内外学者的关注。
T淋巴细胞亚群的主要作用是调节机体免疫系统,在正常机体内各T细胞亚群保持动态平衡,维持机体正常细胞免疫应答。当T淋巴细胞亚群比例出现异常时,杀伤肿瘤细胞、控制肿瘤生长的作用明显减低[10]。CD3+代表总T细胞,主要分为CD4+、CD8+T细胞两大亚群,本研究检测CD4+T(CD3+CD4+T)在非小细胞肺癌患者和健康体检者的细胞比率,结果显示非小细胞肺癌患者CD4+T细胞比率明显低于健康体检者,可能原因是肿瘤细胞诱导抑制性免疫微环境的形成。临床上可通过检测肿瘤患者外周血中T淋巴细胞亚群的变化来进一步评估患者免疫功能状态和病情变化,可指导临床使用免疫调节剂及其他药物。
目前国内外大多数学者认为NRP-1是VEGF165高亲和力受体,NRP-1通过NRP-1b1/b2结构域与络氨酸激酶受体VEGFR2结合,促进肿瘤血管的生成,在肿瘤细胞增殖、黏附、迁移、侵袭中都发挥重要作用,并且与肿瘤的发生、发展、转移、复发有关[1]。Treg是一群具有独特免疫负性调节功能的细胞,不但可抑制自身免疫性疾病的发生,而且还参与肿瘤的免疫调节[11]。近年来癌症患者肿瘤组织及外周血中Treg的积累已被广泛研究,并且与癌症进展、肿瘤免疫逃逸、预后差和对治疗缺乏反应有关。但迄今为止国内外研究中鲜见NRP-1和Treg两者在非小细胞肺癌中表达的相关研究。本研究同时检测了NRP-1和Treg两者在非小细胞肺癌中表达的情况。结果发现,两者在非小细胞肺癌表达明显高于健康体检者,随着肺癌TNM分期的升高和分化程度的降低,NRP-l、Treg的表达呈明显递增趋势。而且,相关性分析发现外周血中NRP-1表达与Treg细胞比率呈正相关(r > 0, P < 0.05)。NRP-1在癌症患者外周血Treg中的表达上调。动物实验已经证明,NRP-1与Treg介导的肿瘤免疫逃逸机制有关,NRP-1充当VEGF的共受体,并已被证明在肿瘤的Treg浸润中起重要作用,通过在Treg中表达的NRP-1起作用,肿瘤衍生的VEGF吸引NRP-1+Treg进入肿瘤组织[12],增强肿瘤的免疫逃逸,从而促进肿瘤的发生和发展。
在人外周血中,NRP-1在PDC细胞上高表达,当前有许多标记用于识别PDC,包括CD123、BDCA-2(CD303)和NRP1(CD304)。研究表明NRP-1可通过与肿瘤细胞衍生出的VEGF的相互作用而参与PDC的肿瘤浸润,而Treg则可通过与NRP-1的相互作用,弱化DC活化效应性T细胞的功能,最终使效应性淋巴细胞活化不足,抗肿瘤抗原效应减弱[1]。本实验数据提示非小细胞肺癌外周血Treg与PDC呈明显负相关(r < 0, P < 0.05)。近年来,程序性死亡受体1(programmed death 1, PD-1)/程序性死亡配体1(programmed death ligand 1, PD-L1)免疫检查点抑制剂成为肺癌免疫治疗研究热点,PD-1在活化后的CD8+T、CD4+T、B、DC及单核细胞等诸多免疫细胞上表达[13-14]。胸腺来源的Treg细胞(tTreg)可表达PD-1。PD-1/PD-L1相互作用有助于使CD4+T细胞转化成Treg细胞,Treg细胞上表达的PD-1还可以与T细胞上表达的PD-L1相互作用,以介导免疫抑制,在抗原识别过程中,NRP-1表达促进Treg与DC的相互作用,从而抑制T细胞活化[15]。但非小细胞肺癌患者外周血中NRP-1与Treg、PDC、PD-1相互作用的具体机制,相关文献报道较少,因此明确其相互作用的关系可能有利于对非小细胞肺癌免疫治疗。
NRP-1在人外周血Treg、PDC细胞表达的研究结果有显著差异,提示NRP-1通过与Treg、PDC的广泛相互作用在免疫调节和功能中起着重要作用。但NRP-1与Treg、PDC之间的作用机制有待进一步研究,从而使抗NRP-1治疗成为肿瘤治疗的新靶点和途径,为临床寻找新的治疗方法提供理论依据。
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.作者贡献:孔天东:论文撰写陈露:文献搜集及试验数据整理统计段方方、王留晏、周寒丽:病例资料筛选及随访登记赵晓丽:部分随访登记刘萌萌:实验实施刘丹娜:数据统计分析及论文审校 -
表 1 CD8+淋巴细胞高密度浸润与入组患者临床病理资料关系(n(%))
Table 1 Relation between high-density infiltration of CD8+ lymphocytes and clinicopathological data of involved patients(n(%))

表 2 不同临床病理特征生存风险的单因素及多因素分析
Table 2 Univariate and multivariate analyses of survival hazards for different clinicopathological features

-
[1] Thorat MA, Balasubramanian R. Breast cancer prevention in high-risk women[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol, 2020, 65: 18-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2019.11.006
[2] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(1): 7-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21590
[3] Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492
[4] Blows FM, Driver KE, Schmidt MK, et al. Subtyping of Breast Cancer by Immunohistochemistry to Investigate a Relationship between Subtype and Short and Long Term Survival: A Collaborative Analysis of Data for 10, 159 Cases from 12 Studies[J]. PLoS Med, 2010, 7(5): e1000279. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000279
[5] Jitariu AA, Cîmpean AM, Ribatti D, et al. Triple negative breast cancer: the kiss of death[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(28): 46652-46662. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16938
[6] Camorani S, Fedele M, Zannetti A, et al. TNBC Challenge: Oligonucleotide Aptamers for New Imaging and Therapy Modalities[J]. Pharmaceuticals (Basel), 2018, 11(4): 123. doi: 10.3390/ph11040123
[7] Park JH, Ahn JH, Kim SB. How shall we treat early triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC): from the current standard to upcoming immuno-molecular strategies[J]. ESMO Open, 2018, 3(Suppl 1): e000357.
[8] Ikeda Y, Kiyotani K, Yew PY, et al. Clinical significance of T cell clonality and expression levels of immune-related genes in endometrial cancer[J]. Oncol Rep, 2017, 37(5): 2603-2610. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5536
[9] Al-Saleh K, Abd El-Aziz N, Ali A, et al. Predictive and prognostic significance of CD8(+) tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with luminal B/HER 2 negative breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy[J]. Oncol Lett, 2017, 14(1): 337-344. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6144
[10] Ahn SG, Kim SJ, Kim C, et al. Molecular Classification of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer[J]. J Breast Cancer, 2016, 19(3): 223-230. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2016.19.3.223
[11] Le Du F, Eckhardt BL, Lim B, et al. Is the future of personalized therapy in triple-negative breast cancer based on molecular subtype?[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(15): 12890-12908. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3849
[12] Liu YR, Jiang YZ, Xu XE, et al. Comprehensive transcriptome analysis identifies novel molecular subtypes and subtype-specific RNAs of triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2016, 18(1): 33. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0690-8
[13] Gooden MJM, de Bock GH, Leffers N, et al. The prognostic influence of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis[J]. Br J Cancer, 2011, 105(1): 93-103. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.189
[14] Webb JR, Milne K, Nelson BH. Location, location, location: CD103 demarcates intraepithelial, prognostically favorable CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in ovarian cancer[J]. Oncoimmunology, 2014, 3: e27668. doi: 10.4161/onci.27668
[15] Sarrabayrouse G, Corvaisier M, Ouisse LH, et al. Tumor-reactive CD4+ CD8αβ+ CD103+ αβT cells: a prevalent tumor-reactive T-cell subset in metastatic colorectal cancers[J]. Int J Cancer, 2011, 128(12): 2923-2932. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25640
[16] Liu S, Lachapelle J, Leung S, et al. CD8+ lymphocyte infiltration is an independent favorable prognostic indicator in basal-like breast cancer[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2012, 14(2): R48. doi: 10.1186/bcr3148
[17] 林晶, 陈誉, 陈刚, 等. CD8+T细胞浸润与STATs家族活化在胃癌组织中表达及临床意义[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志, 2019, 24(6): 548-553. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2019.06.013 Lin J, Chen Y, Chen G, et al. Expression and clinical significance of CD8+T cell infiltration and STATs family activation in gastric cancer[J]. Lin Chuang Zhong Liu Xue Za Zhi, 2019, 24(6): 548-553. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2019.06.013
[18] 卢慧敏, 王琰, 陈陆俊, 等. CD103+CD8+T细胞在结直肠癌组织中的浸润分布及其临床意义[J]. 中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志, 2019, 26(1): 50-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLSW201901009.htm Lu HM, Wang Y, Chen LJ, et al. Distribution of CD103+ CD8+T cell infiltration in colorectal cancer tissues and its clinical significance[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Liu Sheng Wu Zhi Liao Za Zhi, 2019, 26(1): 50-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLSW201901009.htm
[19] de Groot AF, Blok EJ, Charehbili A, et al. Strong CD8+ lymphocyte infiltration in combination with expression of HLA class I is associated with better tumor control in breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2019, 175(3): 605-615. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05195-y




 下载:
下载: