Effect of Whole-course Nutrition Support on Nutritional Status of Patients with Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
-
摘要:目的
探讨全程营养支持治疗对局部晚期鼻咽癌患者营养状况的影响。
方法选取90例初治局部晚期鼻咽癌患者,随机分为实验组(全程营养支持治疗+同步放化疗)45例和对照组(同步放化疗)45例。运用PG-SGA评分、体格测量、血液学指标和急性放射反应,观察两组患者营养状况的变化,分析全程营养支持对营养状况的影响。
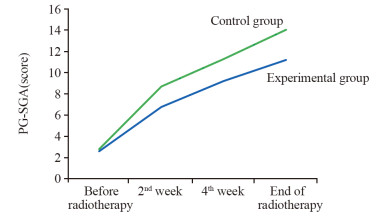
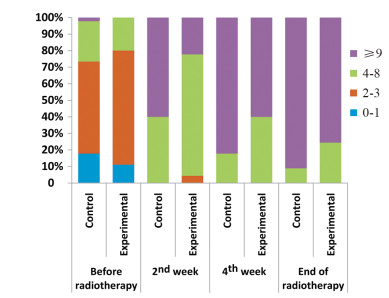
结果放疗第2周后,对照组PA、Hb已明显下降,且Hb明显低于实验组;放疗第4周后,对照组体重明显低于放疗前,实验组体重和BMI明显优于对照组。放疗第4周后,对照组TP、ALB和PA显著低于实验组。放疗结束后,对照组PG-SGA评分及重度营养不良发生率均显著高于实验组。对照组骨髓抑制、口腔黏膜炎、吞咽困难或疼痛的分级程度明显高于实验组。
结论全程营养支持治疗可显著减缓患者体重下降,减缓营养相关血液学指标的持续降低,减轻急性放射反应,能有效改善局部晚期鼻咽癌患者的营养状况,降低营养不良发生率。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the effect of whole-course nutrition support on nutritional status of patients with locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC).
MethodsWe randomly divided 96 locally advanced NPC patients into the experimental group (whole-course nutrition support combined concurrent chemoradiotherapy, n=45) and the control group (only concurrent chemoradiotherapy, n=45). PG-SGA questionnaire, the anthropometry measurements, hematological indexes and acute radiology reactions were used to observe the nutritional status of NPC patients and analyzed the effect of whole-course nutrition support on nutritional status.
ResultsPA and Hb of control group were significantly declined and Hb was significantly lower than that of the experimental group at the 2nd week of radiotherapy. At the 4th week of radiotherapy, the weight of control group were significantly lower than that before radiotherapy, and the weight, BMI, TP, ALB and PA of the experimental group were higher than those in control group. PG-SGA score and the incidence of severe malnutrition of control group were significantly higher than those of the experimental group at the end of radiotherapy. The grading of myelosuppression, oral mucositis and dysphagia of control group were significantly higher than those of the experimental group during radiotherapy.
ConclusionWhole-course nutrition support can significantly retard the weight loss and the sustained decline in hematological indexes, reduce the acute radiation reactions, and then effectively improve the nutritional status and reduce the incidence of severe malnutrition of locally advanced NPC patients.
-
0 引言
子宫内膜癌是在北美和欧洲最常见的女性恶性肿瘤,近年来我国的发病率明显增加,发病人群年轻化[1]。子宫内膜癌的发病机制目前尚未完全明确,随着研究的深入,越来越清晰地认识到子宫内膜癌是多种因素协同交叉作用、具有不同遗传和分子特征的一类疾病[2-3]。根据肿瘤发病机制与雌激素依赖相关性,将其分为Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型,80%以上为Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌。遗传易感性是导致个体对相同致癌因素敏感度不一致的重要因素,某些雌激素代谢通路中关键酶可以改变体内雌激素或外源性雌激素及其代谢产物的水平。基因多态性与酶活性有关,雌激素代谢酶基因多态性可能导致子宫内膜癌发病易感性差异[4]。本研究利用SNP分型检测技术,探索雌激素代谢关键酶CYP1B1、CYP1A1和NQO1基因的单核苷酸多态性(single nucleotide polymorphisms, SNPs)位点分布频率与Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌易感性之间关系,以期对Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的易感人群进行筛查。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料
抽取我院2014年3月—2016年10月收治的经病理诊断为子宫内膜样腺癌的103例患者和同期子宫内膜正常的100例其他疾病患者静脉外周全血2~3 ml,作为检测标本。病例和对照组均取得患者的知情同意并详细询问病史,包括初潮年龄、生育状况、绝经年龄、孕产次数、内科并发症及肿瘤家族史。测量身高与体重,并计算体质指数(body mass index, BMI),测量血压,采集静脉血化验空腹血糖(FPG)及血脂、肿瘤标志物[5-6]。年龄31~78岁,平均(51.15±9.69)岁,子宫内膜癌组平均年龄(54.77±8.21)岁,对照组为(46.95±9.65)岁。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 确定候选基因及其SNPs位点
由于Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌为雌激素依赖性肿瘤,结合相关文献报道,在美国国家生物技术信息中心(National Center for Biotechnology Information, NCBI)人类基因组数据库中选择与雌激素代谢相关的关键酶CYP1A1、CYP1B1,具有抗癌突变的依赖还原型辅酶Ⅰ/Ⅱ醌氧化还原酶1(quinone oxido-reductase1, NQO1)3个基因,选取与代谢酶活性密切相关且杂合度大于10%的SNPs位点进行基因型分析。
1.2.2 引物设计合成
利用引物设计软件premier 5.0,在含SNPs的DNA序列上设计PCR引物,并将设计的引物进行引物的同源性比较,选出同源性最小而Tm值和G/C比值合适的引物作为PCR反应引物,所扩增片段应包含要检测的SNPs位点,其位置尽可能设计在PCR扩增片段的中部。
1.2.3 检测方法
使用DNA提取试剂盒(DP304-03)从外周血中提取DNA,进行预扩增,琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测DNA完整性。根据设计引物模板,进行延伸反应及延伸产物纯化。PCR扩增反应体系总体积为50 μl,内含5 μl 10×PCR缓冲液,3 μl 25 mmol/L MgCl2溶液,5 μl 2 mmol/L dNTP混合物,1.25 U Taq DNA聚合酶,0.5 μmol/L引物及100g的基因组DNA。反应在MJ公司PTC-100 PCR反应仪中进行。PCR循环条件为95℃预变性10 min,然后94℃变性30 s,60℃复性30 s,72℃延伸30 s,反应40个循环后,72℃再延伸10 min。扩增产物用2%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,4℃保存。PCR产物经纯化后作为测序模板,用Big-Dye末端荧光标记试剂盒进行测序反应,测序反应产物经纯化后在ABI公司3730XL测序仪上进行测序电泳,用Gene codes公司的Sequencer4.2对测序结果进行分析。
1.3 统计学方法
采用SPSS18.0软件对实验数据进行统计学分析,用χ2检验和多因素Logistic回归模型分析各基因型在两组人群中的分布差异及其与子宫内膜癌临床病理特征的相关性,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 多因素回归分析
CYP1B1基因SNPs位点rs111888224因无碱基改变未纳入统计,rs1056836、rs2551188、rs10916在研究人群中均存在多态性,但分布频率差异无统计学意义;rs1056836 C、G基因分布频率差异有统计学意义(P=0.0454)。
CYP1A1基因SNP位点rs4646421在研究人群中存在CT、CC、TT多态性。与CT型相比,CC型为保护基因型,OR=0.479(95%CI: 0.255~0.899),差异有统计学意义(P=0.0219),其C、T基因分布频率差异有统计学意义(P=0.0041),见表 1。
表 1 基因型/等位基因在Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌患者中的分布(n(%))Table 1 Genotype/alleles distributions in typeⅠendometrial carcinoma cases (n(%))
2.2 CYP1A1基因rs4646421位点多态性与Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌危险因素的分层分析
对CYP1A1基因rs4646421位点不同基因型与Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的危险因素相关性进行分层比较,发现在年龄 > 60岁、BMI≥25、绝经延迟、并发高血压的个体中,携带CT+TT突变基因型将增加罹患Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的风险(P < 0.05),见表 2。
表 2 发病危险因素与基因型分布的关系(n(%))Table 2 Association between risk factors and genotypes distributions of SNP(rs4646421) in CYP1A1 (n(%))
3 讨论
雌激素分布在细胞内外表面,通过雌激素受体的核内结合蛋白在靶细胞中保持高亲和力和特异性。涉及雌激素生物合成和代谢的基因的多态性是雌激素受体阳性恶性肿瘤的潜在危险因素,有几种细胞色素P450(CYP)酶参与雌激素的氧化代谢途径[7]。CYP1A1和CYP1B1是代谢产生2-羟基-4-羟基雌激素代谢物的基本酶[8-9],在不同人群中不仅存在多态性,并且在性激素相关组织中的表达高于细胞色素P450超家族的其他成员,其基因多态性与乳腺癌、子宫肌瘤、子宫内膜异位症、宫颈癌等疾病风险相关[10-14]。
CYP1A1基因定位于人类染色体15q22-24,编码由512个氨基酸组成的蛋白质,是细胞色素P450家族中高诱导成员。CYP1A1酶的激活参与内源性和外源性化合物的氧化作用,催化多环芳香族碳氢化合物转化为酚与环氧化合物。一些酚类和环氧化合物可与DNA结合形成加合物,最终转化为致癌物、二醇环氧化物,通过环氧化物水解酶与一些抗肿瘤药物发生耐药,并增加个体肿瘤风险[9, 15]。本研究结果显示CYP1A1基因SNP位点rs4646421在子宫内膜癌人群中存在CT、CC、TT多态性,与携带CT基因型相比,携带CC基因型的个体罹患子宫内膜癌的风险较小,携带T等位基因的个体子宫内膜癌的发病风险高于C等位基因携带者。与携带CC基因型相比,携带TC+TT基因型在年龄 > 60岁、BMI≥25、绝经延迟(超过52岁)、合并高血压的女性中Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的发病风险增加。
CYP1B1基因位于染色体2q21-22,其单核苷酸多态性SNP总数有353个,目前研究较多的是SNPrs1056836,其mRNA发生1294位碱基胞嘧啶(cytosine, C)变异为鸟嘌呤(guanine, G),使DNA两条链形成野生CC型,杂合CG型和变异GG型3种基因型,即基因多态性。这种改变导致第三外显子432密码子的碱基由CTG变异为GTG,由其编码的亮氨酸(leucine, Leu)变异为缬氨酸(valine, Val),导致CYP1B1酶蛋白功能的改变[16]。CYP1B1通过多方面影响肿瘤的易感性和预后,在胰岛素抵抗中产生作用,突变型表达的酶之蛋白质表现出更强的激活癌前物质活性,或影响睾酮的6β-羟化作用及性激素的激活代谢等[17-18]。
本研究中CYP1B1基因SNP rs2551188、rs10916两个位点在人群中存在多态性,但分布频率无统计学差异;rs1056836在正常子宫内膜组与子宫内膜癌两组间的基因型分布频率无差异,但发生更多的碱基胞嘧啶变异为鸟嘌呤,可能会使罹患子宫内膜癌的风险增加,以往文献中发现对于单个位点基因突变的表现为阴性结论时,多个位点联合的单倍体基因型研究却往往能得到阳性结论,似乎预示着CYP1B1基因在分子遗传学上有一定的倾向性[16-19],但其与肿瘤易感性及预后的机制问题还存在着诸多争议与疑惑,有待于进一步研究。
NQO1是一种重要的化学致癌物质代谢酶,具有抗癌作用,可使内源性及外源性醌类化合物通过电子还原反应变成低毒性的氢醌类物质,再转化为水溶性化合物排出体外,降低了细胞发生突变及癌变的概率。如果位点发生突变,使原位编码的氨基酸发生改变,将会导致该酶活性减弱或完全丧失,降低解毒功能且不能维护细胞稳定,增加某些易感个体细胞发生癌变[20]。报道显示NQO1蛋白高表达在卵巢癌、乳腺癌、结直肠癌等肿瘤中,与临床分期晚、分化程度差和淋巴结转移等临床特征有关[21-22],本研究选择的SNP位点rs45488899和rs1800566虽在两组间均存在基因多态性,但分布频率不具有差异性,因此认为这两个SNP位点与Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的发生无显著相关性。
本研究通过基因表达谱差异的分析,推测CYP1A1基因rs4646421位点的多态性在Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的发生发展中起着重要作用,可作为进行高危人群筛查的基因位点,还可以突变的基因型为基础,采取针对性的基因靶向治疗,或者通过修正基因突变谱来改善其预后。但是,基因多态性受复杂的遗传、环境因素、种族等的影响,并与样本量的大小有关,必须经过大样本试验来进一步明确基因多态性与子宫内膜癌易感性之间的基因环境交互作用及具体机制。
作者贡献魏学燕:数据整理、论文设计与撰写韩光:参与选题及设计李莹:病例收治、提出写作建议并参与修改胡德胜:参与选题及设计、对论文提出建议并修改 -
表 1 两组患者基本临床资料比较(n(%))
Table 1 Comparison of clinical characteristics of NPC patients between two groups (n(%))

表 2 两组患者的体重下降比较(n(%))
Table 2 Comparison of weight loss between two groups (n(%))

表 3 两组患者的BMI变化比较(n(%))
Table 3 Comparison of BMI between two groups (n(%))

表 4 两组患者营养相关指标的变化比较(x±s)
Table 4 Comparison of nutritional indexes between two groups (x±s)

表 5 两组患者急性放射反应(n(%))
Table 5 Comparison of acute radiation reaction between two groups (n(%))

-
[1] Lin YH, Huang TL, Chien CY, et al. Pretreatment prognostic factors of survival and late toxicities for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated by simultaneous integrated boost intensity-modulated radiotherapy[J]. Radiat Oncol, 2018, 13(1): 45. doi: 10.1186/s13014-018-0990-5
[2] 张力.鼻咽癌的综合治疗进展[J].肿瘤防治研究, 2019, 46(8): 667-671. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2019.19.0636 Zhang L. Progress on Comprehensive Treatment of Nasopharyngeal Cancer[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2019, 46(8): 667-671. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2019.19.0636
[3] 沈梅竹, 龙国贤, 孙伟, 等.鼻咽癌患者营养状态变化调查[J].内科急危重症杂志, 2015, 21(5): 348-351. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nkjwzzzz201505010 Shen MZ, Long GX, Sun W, et al. Investigation on the nutritional status of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Nei Ke Ji Wei Zhong Zheng Za Zhi, 2015, 21(5): 348-351. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nkjwzzzz201505010
[4] Xiao W, Chan CWH, Fan YY, et al. Symptom clusters in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma duringradiotherapy[J]. Eur J Oncol Nurs, 2017, 28: 7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ejon.2017.02.004
[5] 陈梦微, 林少俊.鼻咽癌的营养治疗[J].中国癌症防治杂志, 2017, 9(4): 255-259. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgyxwz-zlxfc201704003 Chen MW, Lin SJ. Nutritional therapy for patients with nasopharyngeal carcer[J]. Zhongguo Ai Zheng Fang Zhi Za Zhi, 2017, 9(4): 255-259. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgyxwz-zlxfc201704003
[6] 中国抗癌协会, 中国抗癌协会肿瘤营养与支持治疗专业委员会, 中国抗癌协会肿瘤康复与姑息治疗专业委员会, 等.鼻咽癌营养治疗专家共识[J].肿瘤代谢与营养电子杂志, 2018, 5(1): 30-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0120181103724815 Chinese Anti-Cancer Association, ChineseSociety for Oncological Nutrition and Supportive Care, The Committee of Rehabilitation and Palliative Care, et al. Expert consensus on nutritional therapy for patients with nasopharyngeal carcer[J]. Zhong Liu Dai Xie Yu Ying Yang Dian Zi Za Zhi, 2018, 5(1): 30-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0120181103724815
[7] 曹远东, 孙新臣, 唐心宇, 等.全程营养支持治疗对鼻咽癌急性放疗反应及治疗依从性的影响[J].临床肿瘤学杂志, 2016, 21(4): 349-352. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lczlxzz201604013 Cao YD, Sun XC, Tang XY, et al. Effect of whole course nutrition support on the acute radiation response and treatment compliance of naso-pharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Lin Chuang Zhong Liu Xue Za Zhi, 2016, 21(4): 349-352. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lczlxzz201604013
[8] 李厨荣, 李涛, 李昉, 等.营养治疗对头颈部肿瘤放化疗营养状况影响的前瞻性研究[J].肿瘤代谢与营养电子杂志, 2017, 6(4): 168-173. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zldxyyy201702008 Li CR, Li T, Li F, et al. A prospective study on the effect of nutritional intervention on nutritional status in head and neck cancer during chemoradiotherapy[J]. Zhong Liu Dai Xie Yu Ying Yang Dian Zi Za Zhi, 2017, 6(4): 168-173. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zldxyyy201702008
[9] 丁慧萍, 窦圣金, 汪琼, 等.口服营养补充对鼻咽癌同期放化疗患者的影响[J].中国癌症杂志, 2018, 28(1): 62-68. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgazzz201801009 Ding HP, Dou SJ, Wang Q, et al. Effect of oral nutritional supplements on nutritional status and quality of life in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma receiving chemoradiotherapy[J]. Zhongguo Ai Zheng Za Zhi, 2018, 28(1): 62-68. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgazzz201801009
[10] Arends J, Bachmann P, Baracos V, et al. ESPEN guidelines on nutrition in cancer patients[J]. Clin Nutr, 2017, 36(1): 11-48. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2016.07.015
[11] 中国抗癌协会肿瘤营养与支持治疗专业委员会.中国肿瘤营养治疗指南[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2015. China Society for Oncological Nutrition and Supportive Care. Guidelines for Chinese Oncology nutrition therapy[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2015.
[12] 于娇, 喻凤, 曹席明.全程营养支持治疗对宫颈癌患者急性放射反应、耐受性和疗效影响的临床观察[J].临床肿瘤学杂志, 2018, 23(7): 635-639. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lczlxzz201807012 Yu J, Yu F, Cao XM. Clinical observation on the effect of whole course nutritional support on acute radiation response, tolerance and curative effect of cervical cancer patients[J]. Lin Chuang Zhong Liu Xue Za Zhi, 2018, 23(7): 635-639. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lczlxzz201807012
[13] 李涛, 吕家华, 郎锦义, 等.恶性肿瘤放疗患者营养治疗专家共识[J].肿瘤代谢与营养电子杂志, 2018, 5(4): 358-365. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zldxyyy201804009 Li T, Lv JH, Lang JY, et al. Expert consensus on nutrition therapy in cancer patients receiving radiotherapy[J]. Zhong Liu Dai Xie Yu Ying Yang Dian Zi Za Zhi, 2018, 5(4): 358-365. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zldxyyy201804009
[14] Li G, Gao J, Liu ZG, et al. Influence of pretreatment ideal body weight percentile and albumin on prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Long-term outcomes of 512 patients from a single institution[J]. Head Neck, 2014, 36(5): 660-666. doi: 10.1002/hed.23357
[15] 王剑锋, 方芳, 于雷.营养干预对头颈部肿瘤急性放射性口腔粘膜反应的影响[J].肠外与肠内营养, 2018, 25(1): 28-31. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cwycnyy201801009 Wang JF, Fang F, Yu L. Effect of nutritional intervention on acute radiation oral mucositis in patients with head and neck cancer[J]. Chang Wai Yu Chang Nei Ying Yang, 2018, 25(1): 28-31. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cwycnyy201801009
[16] 郭尔钢, 吴成, 胡国清.鼻咽癌患者病程中的营养状况[J].中国肿瘤临床, 2018, 45(10): 492-496. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgzllc201810002 Guo EG, Wu C, Hu GQ. Nutritional status in patients with nasopharyngeal cancer[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Liu Lin Chuang, 2018, 45(10): 492-496. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgzllc201810002
[17] 石汉平, 许红霞, 李苏宜, 等.营养不良的五阶梯治疗[J].肿瘤代谢与营养电子杂志, 2015, 2(1): 29-33. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zldxyyy201501010 Shi HP, Xu HX, Li SY, et al. Five steps treatment of malnutrition[J]. Zhong Liu Dai Xie Yu Ying Yang Dian Zi Za Zhi, 2015, 2(1): 29-33. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zldxyyy201501010
[18] 李涛, 吕家华, 郎锦义, 等.恶性肿瘤放射治疗患者肠内营养专家共识[J].肿瘤代谢与营养电子杂志, 2017, 4(3): 272-279. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zldxyyy201703006 Li T, Lv JH, Lang JY, et al. The enteral nutrition in radiotherapeutic cancer patients[J]. Zhong Liu Dai Xie Yu Ying Yang Dian Zi Za Zhi, 2017, 4(3): 272-279. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zldxyyy201703006
[19] 崔巍, 韩磊.鼻咽癌患者同步放化疗期间营养状况变化及其营养支持治疗的影响[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2011, 18(18): 1466-1469. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qlzlzz201118012 Cui W, Han L. Nutritional status assessment and effect of nutritional intervention during concurrent radiochemotherapy for locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Za Zhi, 2011, 18(18): 1466-1469. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qlzlzz201118012
[20] Qiu C, Yang N, Tian G, et al. Weight loss during radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a prospective study from northern China[J]. Nutr Cancer, 2011, 63(6): 873-879. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2011.582223
[21] 苏端玉, 侯如蓉.口服营养支持在鼻咽癌放疗患者中的临床研究[J].中国现代医生, 2016, 54(26): 73-77. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zwkjzlml-yyws201626023 Su DY, Hou RR. Clinical study of oral nutrition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with radiotherapy[J]. Zhongguo Xian Dai Yi Sheng, 2016, 54(26): 73-77. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zwkjzlml-yyws201626023
[22] 潘海卿, 王笑微, 丁进, 等.早期营养干预对头颈部肿瘤同期放化疗患者营养状况及耐受性的影响[J].中国现代医生, 2014, 52(22): 154-157. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zwkjzlml-yyws201422050 Pan HQ, Wang XW, Ding J, et al. The impact of early nutritional intervention on nutritional status and treatment tolerance in head and neck cancer patients undergoing concurrent chemoradiotherapy[J]. Zhongguo Xian Dai Yi Sheng, 2014, 52(22): 154-157. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zwkjzlml-yyws201422050
[23] Pan P, Tao G, Sun X. Subjective global assessment and prealbumin levels of esophageal cancer patieents undergoing concurrent chemoradiotherapy[J]. Nutr Hosp, 2015, 31(5): 2167-2173. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25929389
[24] 韩东景, 杨峥, 赵楠, 等.鼻咽癌放疗患者营养状况及营养干预的临床观察[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2013, 20(10): 786-789. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qlzlzz201310018 Han DJ, Yang Z, Zhao N, et al. Nutritional status and interventions nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with radiotherapy[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Za Zhi, 2013, 20(10): 786-789. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qlzlzz201310018
[25] 丁可, 韩菲菲, 张瑞, 等.全程营养支持在降低鼻咽癌急性放射反应和提高治疗依从性中的作用[J].实用中西医结合临床, 2018, 18(6): 106-107. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syzxyjhlc201806054 Ding K, Han FF, Zhang R, et al. Effect of whole course nutrition support on the acute radiation response and the treatment compliance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Shi Yong Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Lin Chuang, 2018, 18(6): 106-107. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syzxyjhlc201806054
[26] 韦燕, 张芸, 宁春玉, 等.营养管理对鼻咽癌患者营养状态及急性放疗反应的影响[J].系统医学, 2017, 2(9): 106-109. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xtyx201709033 Wei Y, Zhang Y, Ning CY, et al. Effect of Nutrition Management on the Nutrition State and Emergency Radiotherapy Reactions of Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma[J]. Xi Tong Yi Xue, 2017, 2(9): 106-109. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xtyx201709033



 下载:
下载: