miR-497-5p Inhibits Proliferation of Pancreatic Cancer Cells by Targeting CCNE1 Gene
-
摘要:目的
明确miR-497-5p在胰腺癌(PaCa)中的表达及临床意义,并探究其对PaCa细胞增殖的影响及机制。
方法实时荧光定量PCR实验检测miR-497-5p的表达,卡方检验和Kaplan-Meier生存法分析miR-497-5p的表达与临床病理特征及预后的关系;CCK-8实验和流式细胞术检测过表达miR-497-5p对Capan-2和PANC-1细胞增殖和周期的影响,Spearman相关性检验分析miR-497-5p表达与G1/S特异性细胞周期蛋白E1(cyclin E1, CCNE1)mRNA表达的关系;双荧光素酶报告基因实验和蛋白质印迹法验证miR-497-5p对CCNE1表达的调控作用。
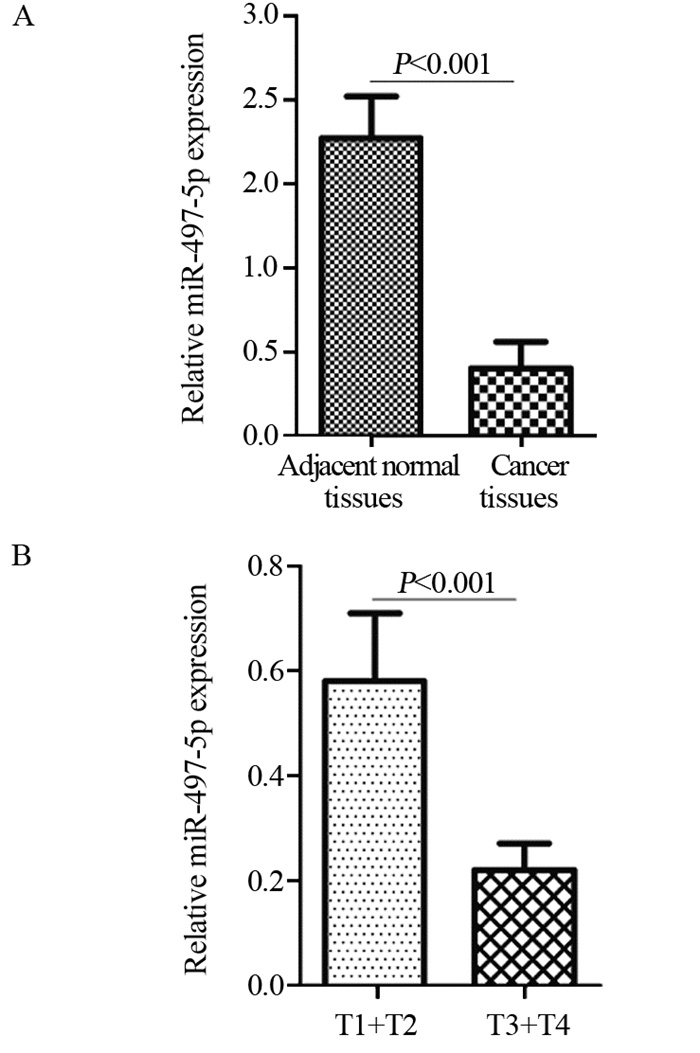
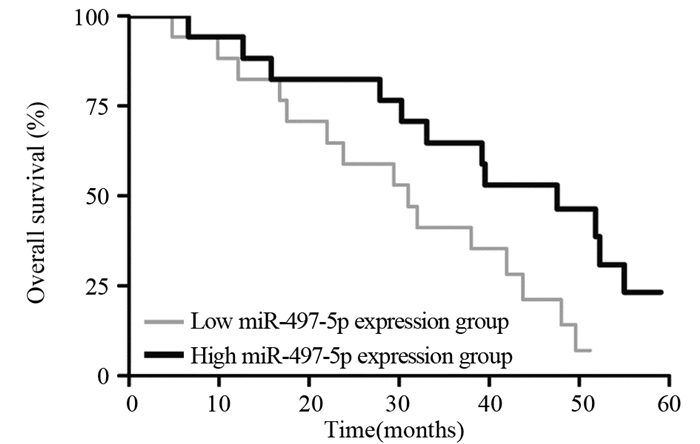
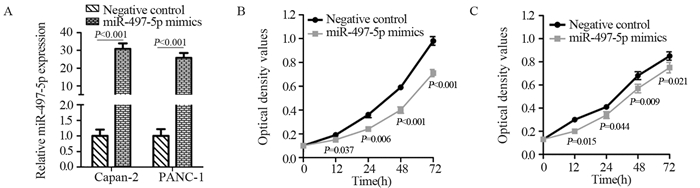
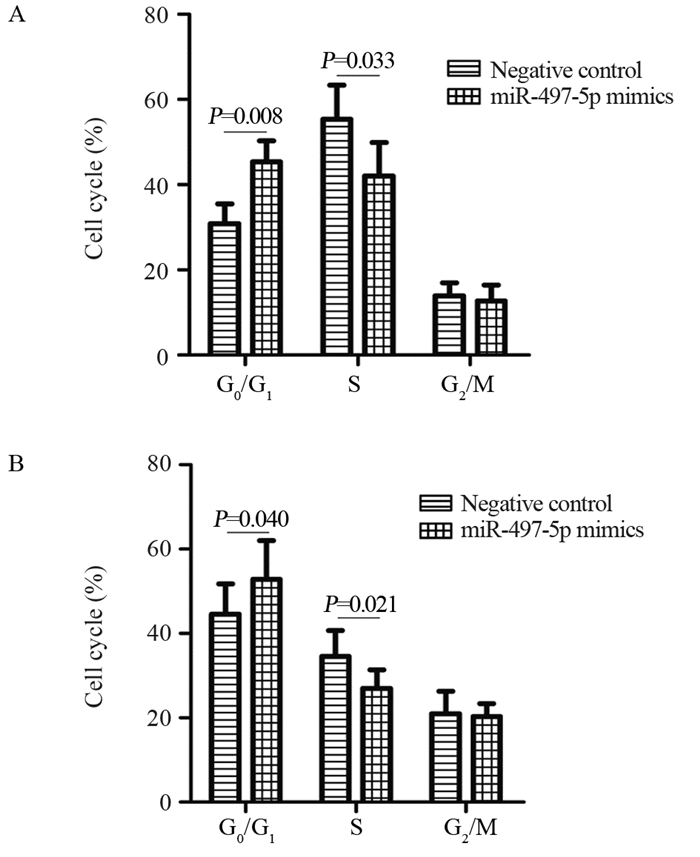
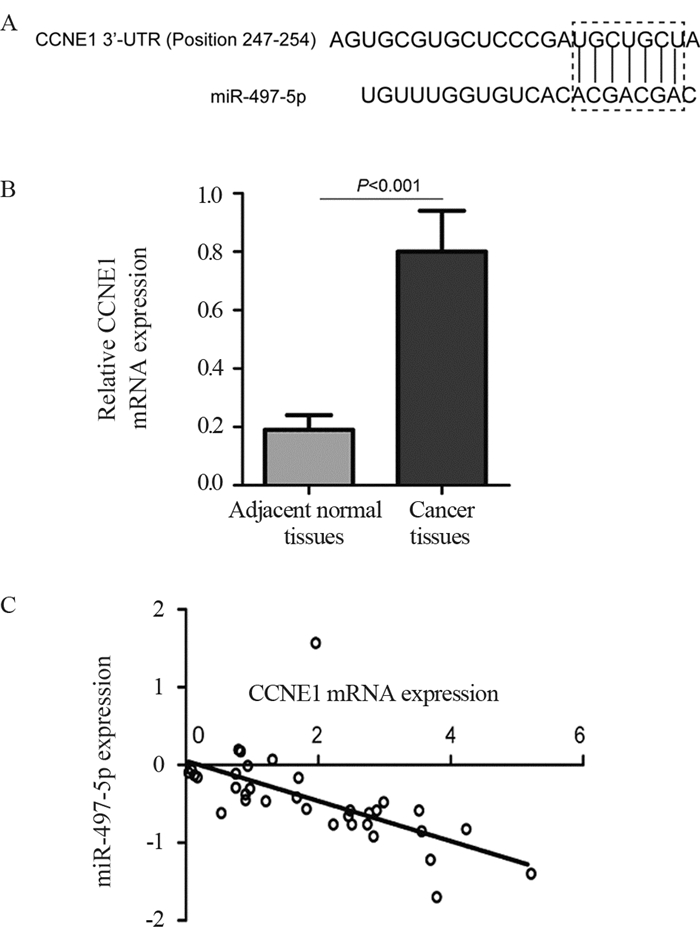
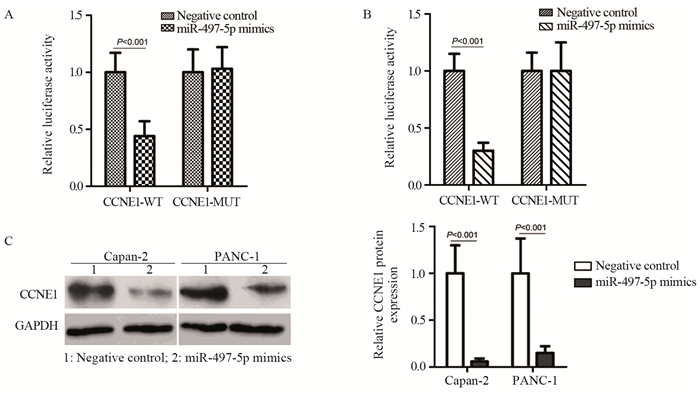
结果miR-497-5p在癌组织中的表达显著低于癌旁正常组织(P < 0.001),T3+T4期患者癌组织中miR-497-5p的表达显著低于T1+T2期癌组织(P < 0.001);低表达miR-497-5p与较高的T分期相关(P=0.003);低表达miR-497-5p的患者5年总体生存率显著低于高表达者(P=0.036)。与对照组相比,miR-497-5p过表达组细胞增殖显著降低,G0/G1期比例增加,S期比例减少。CCNE1 mRNA在癌组织的表达显著高于癌旁正常组织(P < 0.001),且与miR-497-5p表达呈负相关(P < 0.001)。miR-497-5p可直接与CCNE1 mRNA 3’-UTR互补结合从而抑制CCNE1蛋白的表达。
结论miR-497-5p在PaCa中低表达,且与较高的T分期及不良预后相关;过表达miR-497-5p通过靶向调控CCNE1基因诱导细胞周期阻滞进而抑制PaCa细胞增殖。
-
关键词:
- miR-497-5p /
- 胰腺癌 /
- 预后 /
- 增殖 /
- CCNE1
Abstract:ObjectiveTo determine miR-497-5p expression in pancreatic cancer (PaCa) and its clinical significance, and to explore its effects and mechanisms on the proliferation of PaCa cells.
MethodsThe expression levels of miR-497-5p were detected by real-time quantitative PCR experiment. The relation between miR-497-5p expression and clinicopathological features, the prognosis of PaCa patients were analyzed by Chi-square test and Kaplan-Meier method. The effects of miR-497-5p overexpression on the proliferation and cell cycle of Capan-2 and PANC-1 cells were detected by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) experiment and flow cytometry. The relation between miR-497-5p level and the cyclin E1 (CCNE1) mRNA expression was analyzed by Spearman correlation test. The regulatory effect of miR-497-5p on CCNE1 expression was confirmed by dual luciferase reporter experiment and Western blot.
ResultsmiR-497-5p expression in cancer tissues was significantly lower than that in adjacent normal tissues (P < 0.001), and its expression in T3+T4 stages cancer tissues were significantly lower than those in T1+T2 stages cancer tissues (P < 0.001); low expression of miR-497-5p was associated with advanced T stage (P=0.003); The 5-year overall survival rate of patients with low miR-497-5p expression was significantly lower than those with high miR-497-5p expression (P=0.036). Compared with the control group, miR-497-5p overexpression significantly reduced cell proliferation, increased the cell proportion in G0/G1 phase and decreased the cell proportion in S phase. The expression levels of CCNE1 mRNA in cancer tissues were significantly higher than those in adjacent normal tissues (P < 0.001), and its expression was negatively correlated with miR-497-5p expression (P < 0.001). miR-497-5p could bind directly to the 3'-UTR of CCNE1 mRNA and inhibit the expression of CCNE1 protein.
ConclusionmiR-497-5p expression is downregulated in PaCa cells and associated with relatively advanced T stage and poor prognosis; the overexpression of miR-497-5p induces the cell cycle arrest to inhibit the proliferation of PaCa cells by targeting CCNE1 gene.
-
Key words:
- miR-497-5p /
- PaCa /
- Prognosis /
- Proliferation /
- CCNE1
-
0 引言
子宫内膜癌是在北美和欧洲最常见的女性恶性肿瘤,近年来我国的发病率明显增加,发病人群年轻化[1]。子宫内膜癌的发病机制目前尚未完全明确,随着研究的深入,越来越清晰地认识到子宫内膜癌是多种因素协同交叉作用、具有不同遗传和分子特征的一类疾病[2-3]。根据肿瘤发病机制与雌激素依赖相关性,将其分为Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型,80%以上为Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌。遗传易感性是导致个体对相同致癌因素敏感度不一致的重要因素,某些雌激素代谢通路中关键酶可以改变体内雌激素或外源性雌激素及其代谢产物的水平。基因多态性与酶活性有关,雌激素代谢酶基因多态性可能导致子宫内膜癌发病易感性差异[4]。本研究利用SNP分型检测技术,探索雌激素代谢关键酶CYP1B1、CYP1A1和NQO1基因的单核苷酸多态性(single nucleotide polymorphisms, SNPs)位点分布频率与Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌易感性之间关系,以期对Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的易感人群进行筛查。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料
抽取我院2014年3月—2016年10月收治的经病理诊断为子宫内膜样腺癌的103例患者和同期子宫内膜正常的100例其他疾病患者静脉外周全血2~3 ml,作为检测标本。病例和对照组均取得患者的知情同意并详细询问病史,包括初潮年龄、生育状况、绝经年龄、孕产次数、内科并发症及肿瘤家族史。测量身高与体重,并计算体质指数(body mass index, BMI),测量血压,采集静脉血化验空腹血糖(FPG)及血脂、肿瘤标志物[5-6]。年龄31~78岁,平均(51.15±9.69)岁,子宫内膜癌组平均年龄(54.77±8.21)岁,对照组为(46.95±9.65)岁。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 确定候选基因及其SNPs位点
由于Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌为雌激素依赖性肿瘤,结合相关文献报道,在美国国家生物技术信息中心(National Center for Biotechnology Information, NCBI)人类基因组数据库中选择与雌激素代谢相关的关键酶CYP1A1、CYP1B1,具有抗癌突变的依赖还原型辅酶Ⅰ/Ⅱ醌氧化还原酶1(quinone oxido-reductase1, NQO1)3个基因,选取与代谢酶活性密切相关且杂合度大于10%的SNPs位点进行基因型分析。
1.2.2 引物设计合成
利用引物设计软件premier 5.0,在含SNPs的DNA序列上设计PCR引物,并将设计的引物进行引物的同源性比较,选出同源性最小而Tm值和G/C比值合适的引物作为PCR反应引物,所扩增片段应包含要检测的SNPs位点,其位置尽可能设计在PCR扩增片段的中部。
1.2.3 检测方法
使用DNA提取试剂盒(DP304-03)从外周血中提取DNA,进行预扩增,琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测DNA完整性。根据设计引物模板,进行延伸反应及延伸产物纯化。PCR扩增反应体系总体积为50 μl,内含5 μl 10×PCR缓冲液,3 μl 25 mmol/L MgCl2溶液,5 μl 2 mmol/L dNTP混合物,1.25 U Taq DNA聚合酶,0.5 μmol/L引物及100g的基因组DNA。反应在MJ公司PTC-100 PCR反应仪中进行。PCR循环条件为95℃预变性10 min,然后94℃变性30 s,60℃复性30 s,72℃延伸30 s,反应40个循环后,72℃再延伸10 min。扩增产物用2%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,4℃保存。PCR产物经纯化后作为测序模板,用Big-Dye末端荧光标记试剂盒进行测序反应,测序反应产物经纯化后在ABI公司3730XL测序仪上进行测序电泳,用Gene codes公司的Sequencer4.2对测序结果进行分析。
1.3 统计学方法
采用SPSS18.0软件对实验数据进行统计学分析,用χ2检验和多因素Logistic回归模型分析各基因型在两组人群中的分布差异及其与子宫内膜癌临床病理特征的相关性,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 多因素回归分析
CYP1B1基因SNPs位点rs111888224因无碱基改变未纳入统计,rs1056836、rs2551188、rs10916在研究人群中均存在多态性,但分布频率差异无统计学意义;rs1056836 C、G基因分布频率差异有统计学意义(P=0.0454)。
CYP1A1基因SNP位点rs4646421在研究人群中存在CT、CC、TT多态性。与CT型相比,CC型为保护基因型,OR=0.479(95%CI: 0.255~0.899),差异有统计学意义(P=0.0219),其C、T基因分布频率差异有统计学意义(P=0.0041),见表 1。
表 1 基因型/等位基因在Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌患者中的分布(n(%))Table 1 Genotype/alleles distributions in typeⅠendometrial carcinoma cases (n(%))
2.2 CYP1A1基因rs4646421位点多态性与Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌危险因素的分层分析
对CYP1A1基因rs4646421位点不同基因型与Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的危险因素相关性进行分层比较,发现在年龄 > 60岁、BMI≥25、绝经延迟、并发高血压的个体中,携带CT+TT突变基因型将增加罹患Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的风险(P < 0.05),见表 2。
表 2 发病危险因素与基因型分布的关系(n(%))Table 2 Association between risk factors and genotypes distributions of SNP(rs4646421) in CYP1A1 (n(%))
3 讨论
雌激素分布在细胞内外表面,通过雌激素受体的核内结合蛋白在靶细胞中保持高亲和力和特异性。涉及雌激素生物合成和代谢的基因的多态性是雌激素受体阳性恶性肿瘤的潜在危险因素,有几种细胞色素P450(CYP)酶参与雌激素的氧化代谢途径[7]。CYP1A1和CYP1B1是代谢产生2-羟基-4-羟基雌激素代谢物的基本酶[8-9],在不同人群中不仅存在多态性,并且在性激素相关组织中的表达高于细胞色素P450超家族的其他成员,其基因多态性与乳腺癌、子宫肌瘤、子宫内膜异位症、宫颈癌等疾病风险相关[10-14]。
CYP1A1基因定位于人类染色体15q22-24,编码由512个氨基酸组成的蛋白质,是细胞色素P450家族中高诱导成员。CYP1A1酶的激活参与内源性和外源性化合物的氧化作用,催化多环芳香族碳氢化合物转化为酚与环氧化合物。一些酚类和环氧化合物可与DNA结合形成加合物,最终转化为致癌物、二醇环氧化物,通过环氧化物水解酶与一些抗肿瘤药物发生耐药,并增加个体肿瘤风险[9, 15]。本研究结果显示CYP1A1基因SNP位点rs4646421在子宫内膜癌人群中存在CT、CC、TT多态性,与携带CT基因型相比,携带CC基因型的个体罹患子宫内膜癌的风险较小,携带T等位基因的个体子宫内膜癌的发病风险高于C等位基因携带者。与携带CC基因型相比,携带TC+TT基因型在年龄 > 60岁、BMI≥25、绝经延迟(超过52岁)、合并高血压的女性中Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的发病风险增加。
CYP1B1基因位于染色体2q21-22,其单核苷酸多态性SNP总数有353个,目前研究较多的是SNPrs1056836,其mRNA发生1294位碱基胞嘧啶(cytosine, C)变异为鸟嘌呤(guanine, G),使DNA两条链形成野生CC型,杂合CG型和变异GG型3种基因型,即基因多态性。这种改变导致第三外显子432密码子的碱基由CTG变异为GTG,由其编码的亮氨酸(leucine, Leu)变异为缬氨酸(valine, Val),导致CYP1B1酶蛋白功能的改变[16]。CYP1B1通过多方面影响肿瘤的易感性和预后,在胰岛素抵抗中产生作用,突变型表达的酶之蛋白质表现出更强的激活癌前物质活性,或影响睾酮的6β-羟化作用及性激素的激活代谢等[17-18]。
本研究中CYP1B1基因SNP rs2551188、rs10916两个位点在人群中存在多态性,但分布频率无统计学差异;rs1056836在正常子宫内膜组与子宫内膜癌两组间的基因型分布频率无差异,但发生更多的碱基胞嘧啶变异为鸟嘌呤,可能会使罹患子宫内膜癌的风险增加,以往文献中发现对于单个位点基因突变的表现为阴性结论时,多个位点联合的单倍体基因型研究却往往能得到阳性结论,似乎预示着CYP1B1基因在分子遗传学上有一定的倾向性[16-19],但其与肿瘤易感性及预后的机制问题还存在着诸多争议与疑惑,有待于进一步研究。
NQO1是一种重要的化学致癌物质代谢酶,具有抗癌作用,可使内源性及外源性醌类化合物通过电子还原反应变成低毒性的氢醌类物质,再转化为水溶性化合物排出体外,降低了细胞发生突变及癌变的概率。如果位点发生突变,使原位编码的氨基酸发生改变,将会导致该酶活性减弱或完全丧失,降低解毒功能且不能维护细胞稳定,增加某些易感个体细胞发生癌变[20]。报道显示NQO1蛋白高表达在卵巢癌、乳腺癌、结直肠癌等肿瘤中,与临床分期晚、分化程度差和淋巴结转移等临床特征有关[21-22],本研究选择的SNP位点rs45488899和rs1800566虽在两组间均存在基因多态性,但分布频率不具有差异性,因此认为这两个SNP位点与Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的发生无显著相关性。
本研究通过基因表达谱差异的分析,推测CYP1A1基因rs4646421位点的多态性在Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的发生发展中起着重要作用,可作为进行高危人群筛查的基因位点,还可以突变的基因型为基础,采取针对性的基因靶向治疗,或者通过修正基因突变谱来改善其预后。但是,基因多态性受复杂的遗传、环境因素、种族等的影响,并与样本量的大小有关,必须经过大样本试验来进一步明确基因多态性与子宫内膜癌易感性之间的基因环境交互作用及具体机制。
作者贡献姜达伟:标本收集,实验操作,统计分析,论文撰写与修改许浏:标本收集,统计分析王伟林:实验设计,论文撰写与修改 -
表 1 miR-497-5p的表达与胰腺癌患者临床病理特征之间的关系
Table 1 Relation between miR-497-5p expression and clinicopathological characteristics of pancreatic cancer (PaCa) patients

-
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2017, 67(1): 7-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21387
[2] Ilic M, Ilic I. Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22(44): 9694-9705. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i44.9694
[3] Yonemori K, Kurahara H, Maemura K, et al. MicroRNA in pancreatic cancer[J]. J Hum Genet, 2017, 62(1): 33-40. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27251005
[4] 何峰, 陈曦, 程方雄, 等. miR-130b调控RAB34的表达在胰腺癌发生发展中的作用[J].肿瘤防治研究, 2018, 45(3): 144-147. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2018.17.0960 He F, Chen X, Cheng FX, et al. Effect of miR-130b Targeting RAB34 Expression in Occurrence and Development of Pancreatic Cancer[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2018, 45(3): 144-147. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2018.17.0960
[5] Chen Y, Kuang D, Zhao X, et al. miR-497-5p inhibits cell proliferation and invasion by targeting KCa3.1 in angiosarcoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(36): 58148-58161. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11252
[6] Sun Z, Li A, Yu Z, et al. MicroRNA-497-5p Suppresses Tumor Cell Growth of Osteosarcoma by Targeting ADP Ribosylation Factor-Like Protein 2[J]. Cancer Biother Radiopharm, 2017, 32(10): 371-378. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2017.2268
[7] Chai L, Kang XJ, Sun ZZ, et al. MiR-497-5p, miR-195-5p and miR-455-3p function as tumor suppressors by targeting hTERT in melanoma A375 cells[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2018, 10: 989-1003. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S163335
[8] Ran X, Xiao CH, Xiang GM, et al. Regulation of Embryonic Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Differentiation by MicroRNAs[J]. Cell Reprogram, 2017, 19(3): 150-158. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=21aa027f7158bd8d4d66a6c5f000160e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[9] Quinlan S, Kenny A, Medina M, et al. MicroRNAs in Neurodegenerative Diseases[J]. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol, 2017, 334: 309-343. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2017.04.002
[10] Nemecz M, Alexandru N, Tanko G, et al. Role of MicroRNA in Endothelial Dysfunction and Hypertension[J]. Curr Hypertens Rep, 2016, 18(12): 87. doi: 10.1007/s11906-016-0696-8
[11] Agrawal S. Potential prognostic biomarkers in pancreatic juice of resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. World J Clin Oncol, 2017, 8(3): 255-260. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v8.i3.255
[12] Svoronos AA, Engelman DM, and Slack FJ. OncomiR or Tumor Suppressor? The Duplicity of MicroRNAs in Cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2016, 76(13): 3666-3670. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-0359
[13] Lv F, Zheng K, Yu J, et al. MicroRNA-661 expression is upregulated in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and promotes cell proliferation[J]. Oncol Lett, 2018, 16(5): 6293-6298. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2f71508910f067709c9e54b41c89f0e6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[14] Ta N, Huang X, Zheng K, et al. miRNA-1290 Promotes Aggressiveness in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma by Targeting IKK1[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 51(2): 711-728. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0096288dd8183f53cd14be6d89c3ae27&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[15] Zhu L, Chen Y, Nie K, et al. MiR-101 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of pancreatic cancer through targeting STMN1[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2018, 23(2): 301-309. doi: 10.3233/CBM-181675
[16] Yang Y, Tao X, Li CB, et al. MicroRNA-494 acts as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer, inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion by binding to SDC1[J]. Int J Oncol, 2018, 53(3): 1204-1214. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f1549a5f52fc6d3f041c065019a73a7a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[17] Li G, Wang K, Wang J, et al. miR-497-5p inhibits tumor cell growth and invasion by targeting SOX5 in non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(6): 10587-10595. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28345
[18] Zhao H, Wang J, Zhang Y, et al. Prognostic Values of CCNE1 Amplification and Overexpression in Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis[J]. J Cancer, 2018, 9(13): 2397-2407. doi: 10.7150/jca.24179
[19] de Maturana EL, Rava M, Anumudu C, et al. Bladder Cancer Genetic Susceptibility. A Systematic Review[J]. Bladder Cancer, 2018, 4(2): 215-226. doi: 10.3233/BLC-170159



 下载:
下载: