Risk or Protective Factors of Prostate Cancer Progressing to Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer After Androgen Deprivation Therapy
-
摘要:目的
从前列腺癌的若干临床指标中,筛查早期(2年内)进展为去势抵抗性前列腺癌(CRPC)的可能危险及保护因素。
方法确诊前列腺癌后的2年内发生去势抵抗的患者作为病例组(n=71),2年内未发生去势抵抗的患者作对照组(n=71),应用Logistic回归模型及生存分析筛选出可能的危险或保护因素。
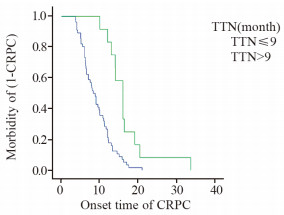
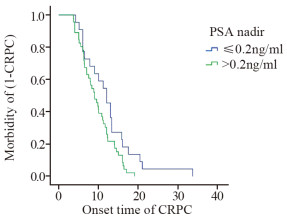
结果多因素Logistic分析:两组PSA最低值(PSA nadir)和到达最低值时间(TTN)差异具有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。TTN≤9月和 > 9月时,发生CRPC中位时间是8.29和16月;PSA nadir≤0.2 ng/ml和 > 0.2 ng/ml时,发生CRPC中位时间是12和9月。
结论TTN可能是早期进展为CRPC的保护因素,PSA nadir可能是早期进展为CRPC的独立危险因素,其中TTN≤9月和PSA nadir > 0.2 ng/ml是CRPC的危险因素。
-
关键词:
- 去势抵抗性前列腺癌 /
- 危险因素 /
- 保护因素 /
- 生存分析 /
- Logistic回归分析
Abstract:ObjectiveTo screen the possible risk factors and protective factors for prostate cancer early (in 2 years)progressing to castration resistant prostate cancer (CRPC).
MethodsA total of 71 patients who had progressed to CRPC in 2 years were classified as case group and 71 patients without progressing to CRPC in 2 years were classified as control group. Logistic regression analysis and survival analysis were applied to screen the risk or protective factors.
ResultsPSA nadir and Time to PSA nadir (TTN) were statistically significant between case group and control group in logistic regression analysis (P < 0.05). Median CRPC occurrence time was 8.29 and 16 months in TTN≤9 months group and TTN > 9 months group, respectively. Median CRPC occurrence time was 12 and 9 months in PSA nadir≤0.2 ng/ml group and PSA nadir > 0.2 ng/ml group, respectively.
ConclusionTTN may be a protective factor and PSA nadir may be an independent risk factor for prostate cancer early progressing to CRPC. TTN≤9 months and PSA nadir > 0.2 ng/ml are the risk factors of CRPC.
-
0 引言
双表达大B细胞淋巴瘤(double-expression large B-cell lymphoma, DEL)临床上以MYC/BCL2双表达最为常见, 占弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤(diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, DLBCL)的19%~34%[1-2], 已有较多研究证实DEL患者临床预后和治疗效果相对较差, 且易发展为复发/难治性大B细胞淋巴瘤[3-6]。染色体9p24.2上CD274基因编码的PD-L1是程序性细胞死亡蛋白-1(programmed cell death 1, PD-1)的配体, 其相互结合可以介导肿瘤细胞获得免疫逃逸能力[7-8]。研究[9]发现MYC可以结合PD-L1的启动子, 促进其表达, 从而促进肿瘤的发生发展; 具有协同作用的原癌基因MYC、BCL2可能是影响PD-L1蛋白表达的上游基因, 三者在淋巴瘤的发病机制中发挥了重要作用[9-11]。本研究收集了一组大B细胞淋巴瘤病例, 通过qPCR技术、免疫组织化学双标记和普通免疫组织化学染色法、临床病理资料收集和随访, 分析PD-L1表达与DEL的关系及其与患者预后的关系, 并探讨PD-L1表达在DEL临床预后评估中的价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1 病例收集
收集贵州医科大学附属医院病理科2010年1月1日至2017年12月31日期间确诊的DLBCL病例, 将临床病理资料相对完整、肿瘤组织充足的90例病例纳入实验研究。
1.2 主要试剂
PD-L1单抗购于美国Abcam公司, 单克隆一抗Pax5、MYC、BCL2和二抗试剂盒(PV-9001、SAP-9102)、EDTA修复液、AP-Red及DAB试剂盒均购自北京中杉公司; RNA提取试剂盒(FFPE RNA)购自厦门艾德公司; SYBR Green荧光染料(TaKaRa RR820A)、反转录试剂盒(TaKaRa RR47A)、内参均购于美国TaKaRa公司; PD-L1引物购于上海生工公司。
1.3 免疫组织化学染色及分组
采用PV二步法检测MYC、BCL2蛋白表达:MYC、BCL2以扁桃体组织为阳性对照; 以PBS(pH7.35)代替一抗作阴性对照; 以pH(8.0)的EDTA溶液修复抗原; MYC、BCL2稀释比均为1:200;步骤按PV-9001说明进行。
判读标准:MYC阳性信号位于细胞核, BCL2阳性信号位于细胞质。根据文献[12-14]略作修改, 随机选择10个不重复的400倍视野, 每个视野随机计数400个肿瘤细胞中阳性细胞所占比例, 取10个视野的平均值作为该病例表达率。据文献[1-4, 12-14]定义MYC ≥ 40%为高表达, BCL2 ≥ 70%为高表达。若MYC、BCL2均高表达定义为MYC/BCL2双表达大B细胞淋巴瘤组(简称DEL组), 余下归为non-DEL组。
1.4 免疫组织化学双标记染色检测PD-L1表达
根据试剂盒说明Pax5、PD-L1设置阳性对照为扁桃体组织, 阴性对照以TBS(pH7.35)替代一抗, 并以TBS作为缓冲液及冲洗液; 用间接法进行双标记染色, 染色步骤简述如下:4 μm厚石蜡切片, 脱蜡、水洗、EDTA(pH9.0)进行修复抗原, 消除内源性过氧化物酶后血清封闭, 先进行Pax5鼠抗人单克隆抗体染色(1:300稀释), 按(SAP-9102)试剂盒说明进行Pax5标记(AP-Red显色), 再次EDTA(pH8.0)修复后, 按Pax5染色的相同步骤进行PD-L1兔抗人单克隆抗体(1:250稀释)标记, DAB显色, 透明封片后进行观察和图像分析。
判读方法:Pax5以细胞核出现红色或浅红色颗粒为阳性表达; PD-L1以细胞质或细胞膜形成黄色或棕黄色颗粒为阳性表达。参照文献[15-16]分析:同MYC、BCL2一样统计肿瘤细胞PD-L1表达率(10个高倍视野平均值), 定义肿瘤细胞双标记阳性细胞≥ 30%(细胞质或膜着黄色、核着红色)为肿瘤细胞PD-L1阳性(PD-L1+); 在PD-L1阴性的病例中, 若肿瘤微环境细胞(主要为肿瘤组织浸润T细胞tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, TILs)PD-L1表达率≥ 20%, 定义为微环境PD-L1阳性[15], 即mPD-L1+。
1.5 RNA提取、反转录、qPCR方法
RNA的提取、检测及反转录:取8 μm组织进行脱蜡、去除二甲苯、蛋白酶消化至清亮后, 按RNA提取试剂盒说明进行RNA提取, 最后以50 μl的DEPC水溶解RNA, 核酸定量仪检测RNA浓度及纯度, 取OD值(A260/A280)在1.8到2.0的RNA样本进行实验, 按TaKaRa RR47A试剂说明于冰上进行去除基因组DNA(42℃ 2 min), 于冰上配置反转录体系后进行反转录(37℃ 30 min, 再加热至85℃ 5 s), 缓慢冷却后于-80℃冰箱保存。
qPCR:使用两步法检测DEL组与non-DEL组PD-L1的mRNA, 据TaKaRa RR820A试剂盒说明, 取cDNA样本于冰上配置SYBR Green RT-qPCR反应体系, PD-L1引物:上游:5'-CTATGGTGGTGCCGACTACA-3', 下游:5'-TGCTTGTCCAGATGACTTCG-3', 每个样本设置3个复孔, 先配置总反应体系, 再分装3个复孔; 用β-actin(上游:5'-TAGTTGCGTTACA CCCTTTCTTG-3', 下游:5'-TCACCCTTCACCGTTCCAAGTTT-3')作为内参, 于Bio-Rad CFX connect荧光定量PCR仪上进行反应(反应条件:预变性95℃ 30 s, 变性95℃ 5 s, 退火/延伸为60℃ 30 s, 50个循环), 以2-ΔΔCt值为mRNA相对表达量, ΔCt=Ct目的基因-Ct内参基因, ΔΔCt=ΔCt样本-ΔCt组内最低值。
1.6 随访方法
采取电话或走访方式, 以首次确诊时间为开始时间, 随访患者首次确诊以后的治疗、健康、复发及生存等情况; 每隔3月随访1次(出现死亡或失访时结束该例患者随访), 长期存活患者随访截至2018年12月31日。
1.7 统计学方法
用SPSS 17.0软件对数据整理分析; mRNA相对表达量在各组间比较采用t检验, 正态分布用(


2 结果
2.1 一般资料
DLBCL90例, HE染色见图 1。男47例, 女43例; 年龄17~82岁(中位年龄58.5);根据免疫组织化学染色结果分组, 28例为DEL, 62例为non-DEL, 见图 2。据1993年NHL国际预后指数IPI评分:0~2分49例, 3~5分41例; 临床分期:Ⅰ+Ⅱ期54例, Ⅲ+Ⅳ期36例。
2.2 DEL组与non-DEL组PD-L1蛋白表达情况比较
90例DLBCL肿瘤细胞和微环境中PD-L1阳性分别为22例(24.44%)和26例(28.89%), 见图 3。DEL组肿瘤细胞和微环境中PD-L1阳性表达率分别为50.00%和32.14%, non-DEL组分别为12.90%和27.42%。肿瘤细胞和微环境PD-L1蛋白表达在DEL组与non-DEL组间比较, 差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05), 见表 1。
表 1 DEL组与non-DEL组PD-L1蛋白表达的比较Table 1 Comparison of PD-L1 protein expression between DEL and non-DEL groups
2.3 DEL组与non-DEL组间PD-L1 mRNA相对表达量比较
qPCR检测结果显示DEL组(0.9862±0.49853)与non-DEL组(0.7175±0.29265)PD-L1 mRNA相对表达量比较, 差异有统计学意义(95% CI:0.06325~0.47419, t=2.653, P=0.012)。
2.4 DEL组中PD-L1表达与临床病理特征的关系
DEL组中, 25例检查血清乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)其中13例PD-L1+, 8例mPD-L1+, 4例mPD-L1-; 24例检查β2微球蛋白(β2-MG), 其中14例PD-L1+, 7例mPD-L1+, 3例mPD-L1-, IPI评分0~2分组、3~5分组均为14例, Ⅰ+Ⅱ期、Ⅲ+Ⅳ期分别为15例、13例; PD-L1+与性别、年龄、Ann Arbor分期、LDH、β2-MG无相关性, 但与IPI评分和B症状的出现显著相关(P值分别为0.007、0.021);mPD-L1+与上述临床病理特征均无相关性(均P>0.05), 见表 2。
表 2 DEL组肿瘤细胞和微环境中PD-L1表达与临床病理特征的关系Table 2 Relation between PD-L1+, mPD-L1+ and clinicopathological characteristics of DEL patients
2.5 DEL患者预后及PD-L1蛋白表达生存分析
DEL组中, 生存8例, 死亡14例, 失访6例, 其中复发9例; 中位生存时间29月。20例接受R-CHOP治疗, 其余不详; Kaplan-Meier生存分析显示PD-L1+组患者总体生存时间(OS)明显短于PD-L1-组(P=0.005), 见图 4; mPD-L1+组患者OS明显短于mPD-L1-组(P=0.001), 见图 5。
3 讨论
尽管淋巴瘤的WHO分类还未将DEL单独列出, 但这类淋巴瘤和"双打击淋巴瘤"相类似, 在临床上具有独特的临床特点。多项研究[1-4, 12-14]表明这类共表达淋巴瘤的IPI评分和肿瘤细胞增殖指数高, 常有多个结外部位累及, 患者在接受标准的R-CHOP免疫化疗方案治疗后复发率高, 且5年生存率也较低。因此, 发现这类DEL的理想预后评估因素和有效的治疗靶点有着重要意义。
PD-L1表达与T淋巴细胞的凋亡及活化有关, 其上调表达通过与浸润T细胞表面受体PD1的结合诱导效应T细胞凋亡、抑制T细胞活化, 从而产生肿瘤生长的微环境, 介导肿瘤细胞的免疫逃逸[6-7]。PD-L1表达对大B细胞淋巴瘤影响的研究多集中在部位特点和细胞来源特点等方面。Kiyasu研究小组[15]统计1 235例临床样本, 发现肿瘤细胞表达PD-L1在DLBCL中阳性率为11%, 微环境细胞PD-L1阳性表达率为15.3%, PD-L1及mPD-L1的表达与GCB样DLBCL和EB病毒阳性的大B细胞淋巴瘤病例显著相关, 且PD-L1+的患者总生存期(OS)低于PD-L1-的DLBCL患者。Liu等[16]检测92例原发肠道的弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤样本中PD-L1的表达, 结果与Kiyasu研究小组的结果相似, 但微环境中PD-L1的阳性率相对较高。本研究发现PD-L1、mPD-L1在90例大B细胞淋巴瘤中的阳性表达率分别为24.44%和28.89%, 与Liu等的研究报道相近。
有研究报道[17]DLBCL患者如果伴有PD-L1的DNA扩增、mRNA上调及蛋白高表达, 其生存预后均不理想, 且PD-L1蛋白表达并不完全由基因调控, 可能还受肿瘤环境中的其他因素影响。Casey团队[9]发现MYC可以与PD-L1启动子结合, 直接调控PD-L1表达, 沉默MYC后PD-L1蛋白表达明显下降; Rossille研究结果[18]表明, 在BCL2阳性侵袭性弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤患者中, 血清PD-L1高表达水平患者的总体生存期(OS)明显短于血清PD-L1低表达水平患者。本研究发现在MYC/BCL2共表达淋巴瘤中PD-L1、mPD-L1的阳性表达率明显高于非共表达大B细胞淋巴瘤, 且在该类淋巴瘤中PD-L1 mRNA相对表达量明显上调。既往报道和我们的结果都提示PD-L1与MYC/BCL2蛋白表达可能存在某种关联, 它们之间可能存在一些信号转导通路的"串话"。具体机制有待于进一步深入的分子、基因等方面研究探讨。
本研究统计DEL患者临床相关数据提示在DEL中PD-L1蛋白表达与高IPI评分和B症状的出现有关; 此外, 通过对28例DEL患者生存随访资料统计分析发现, DEL患者中PD-L1无论在肿瘤细胞表达还是在肿瘤微环境细胞中的表达, 患者OS均显著低于阴性组; 这些结果都提示, PD-L1蛋白的上调表达与DEL患者不良预后相关。
作为一项回顾性的研究, 本实验存在一定的缺陷:首先因受到总样本量收集的限制, 纳入研究样本量相对较小, 统计结果可能与大样本的研究结果会存在一定误差; 其次, 本实验部分RNA提取使用的组织为年份较长的石蜡组织, 可能提取RNA存在降解, 对实验也有一定的影响。因此, 还需扩大样本量、使用新鲜离体组织或提高各项检测技术等来验证我们的结果。
综上所述, MYC/BCL2共表达大B细胞淋巴瘤中PD-L1蛋白和mRNA均上调表达, 这可能与这类淋巴瘤不良预后有关, 它在这类淋巴瘤预后评估中的价值还有待于进一步研究证实。
作者贡献陈炽炜:录入及核对数据、统计分析质量控制及文章撰写林曼迪、刘昊、朱陆军、曾海平、王志刚:病例资料收集陈铭:录入及核对数据、统计分析质量控制王峻:思路指导及学术支持 -
表 1 模型预测去势抵抗性前列腺癌的准确性
Table 1 Accuracy of prediction model of CRPC

表 2 去势抵抗性前列腺癌二元Logistic回归分析
Table 2 Logistic regression analysis results of risk factors of CRPC

-
[1] 唐志柳, 白洁, 顾丽娜, 等. 2000~2010年我国前列腺癌和乳腺癌流行状况的系统性综述[J].中国肿瘤, 2013, 22(4): 260-265. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgzl201304005 Tang ZL, Bai J, Gu LN, et al. Systematic review the epidemic condition of prostate and breast cancer[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Liu, 2013, 22(4): 260-265. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgzl201304005
[2] 韩苏军, 张思维, 陈万青, 等.中国前列腺癌发病现状和流行趋势分析[J].临床肿瘤学, 2013, 18(4): 330-334. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2013.04.009 Han SJ, Zhang SW, Chen WQ, et al. Trend analysis of morbidity of Chinese prostate cancer[J]. Lin Chuang Zhong Liu Xue, 2013, 18(4): 330-334. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2013.04.009
[3] 那彦群, 叶章群, 孙颖浩, 等.中国泌尿外科疾病诊断治疗指南[M].人民卫生出版社, 2014: 61-84. Na YQ, Ye ZQ, Sun YH, et al. China diagnosis and treatment guidelines of urology disease [M]. People's Medical Publishing House, 2014: 61-84.
[4] 纪光杰, 黄聪, 宋刚, 等.去势抵抗性前列腺癌进展时间的预测因素分析[J].北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(4): 657-662. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-167X.2017.04.020 Ji GJ, Huang C, Song G, et al. Predictive factor analysis of time to progression of castration-resistant prostate cancer after androgen deprivation therapy[J]. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao (Yi Xue Ban), 2017, 49(4): 657-662. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-167X.2017.04.020
[5] 徐凡, 董柏君, 潘家骅, 等.转移性前列腺癌早期去势抵抗的预测因素分析[J].现代泌尿外科杂志, 2015, 20(2): 80-84. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xdmnwkzz201502003 Xu F, Dong BJ, Pan JH, et al. Early castration prostate cancer:analysis of prognostic factors[J]. Xian Dai Mi Niao Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2015, 20(2): 80-84. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xdmnwkzz201502003
[6] 孙涛.维、汉前列腺癌患者内分泌治疗敏感时间相关因素分析[D].新疆医科大学, 2016. Sun T. Analysis of correlation factors on the sensitive time of hormonal therapy for Uygur and Han patients with prostate cancer[D]. Xinjiang Medical University, 2016.
[7] 王镇伟.雄激素阻断治疗后进展到去势抵抗性前列腺癌时间预测因素分析[D].大连医科大学, 2017. Wang ZW. Time to Castration resistant prostate cancer after maximal androgen blockade: analysis of prognostic factors[D]. Dalian Medical University, 2017.
[8] Teoh JY, Tsu JH, Yuen SK, et al. Association of time to prostate-specific antigen nadir logarithm of prostate-specific antigen velocity after progression in metastatic prostate cancer with priorprimary androgen deprivation therapy[J]. Asian J Androl, 2017, 19(1): 98-102. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26585698
[9] Thomas BM, Smith C, Evans J, et al. Time to prostate specific antigen(PSA) nadir may predict rapid relapse in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate ancer(CRPC) receiving docetaxel chemotherapy[J]. Med Oncol, 2013, 30(4): 719. http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/24026658
[10] Wenisch JM, Mayr FB, Spiel AO, et al. Androgen deprivation decrease prostate specific antigen in the absence of tumor:implications for interpretation of PSA results[J]. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2014, 52(3): 431-436. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24423580
[11] Benaim EA, Pace CM, ROehrborn CG, et al. Gleason score predicts androgen independent progression after androgen deprivation therapy[J]. Eur Urolo, 2002, 42: 12-17. doi: 10.1016/S0302-2838(02)00238-5
[12] 郑路.前列腺癌骨转移的相关因素分析[D].新疆医科大学, 2016. Zheng L. Analysis of related factors of bone metastasis of prostate cancer[D]. Xinjiang Medical University, 2016.
[13] 欧汝彪, 陈晖, 钟红, 等.前列腺体积和年龄因素对前列腺特异性抗原等指标在前列腺癌筛选中的影响[J].新医学, 2009, 40(2): 83-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9802.2009.02.004 Ou RB, Chen H, Zhong H, et al. Effect of prostate volume and patients age on PSA and other indexs in screening prostate cancer[J]. Xin Yi Xue, 2009, 40(2): 83-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9802.2009.02.004
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李晓荟,王秋爽,马京华,郝子兰,田晗,刘云肖. 癌症疼痛患者疼痛灾难化水平及影响因素分析. 护理实践与研究. 2025(01): 61-68 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: