-
摘要:目的
观察PD-1治疗晚期肝癌患者的近期临床疗效及总生存期。
方法回顾性分析48例PD-1(观察组)治疗及55例甲磺酸阿帕替尼(对照组)治疗晚期肝癌患者的临床资料,分析患者近期临床疗效、总生存期和不良反应。
结果观察组AFP、ALT、AST、ECOG、Child-Paugh评分、客观缓解率及疾病控制率优于对照组(P < 0.05),且观察组患者的生存期(95%CI: 7.24~8.64月)明显高于对照组(95%CI: 5.13~6.39月)(P < 0.05)。两组间皮疹、恶心呕吐及高血压不良反应差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
结论PD-1较甲磺酸阿帕替尼可改善晚期肝癌患者近期临床疗效及延长晚期肝癌患者总生存期。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo observe the short-term clinical effect and total survival of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with PD-1.
MethodsWe retrospectively analyzed the clinical data of 48 patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with PD-1 monoclonal antibody (observation group) and 55 patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with apatinib mesylate(control group). Short-term clinical effect, overall survival and adverse reactions were analyzed.
ResultsThe AFP, ALT, AST, ECOG, Child-Paugh score, objective remission rate and disease control rate in the observation group were better than those in the control group (P < 0.05), and the overall survival in the observation group (95%CI: 7.24-8.64 months) was significantly longer than that in the control group (95%CI: 5.13-6.39 months) (P < 0.05). There were significant differences in rashes, nausea, vomiting and adverse reactions of hypertension between two groups (P < 0.05).
ConclusionCompared with apatinib mesylate, PD-1 could improve the short-term clinical efficacy and prolong the overall survival of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.
-
Key words:
- Hepatocellular carcinoma /
- Immunotherapy /
- Targeted therapy /
- PD-1
-
0 引言
原发性肝癌发病率居我国恶性肿瘤第5位,死亡率居恶性肿瘤的第3位[1]。多数患者确诊时已处于中晚期,只能接受经皮肝动脉栓塞化疗、放疗、靶向、对症等治疗,然而这些方式未能显著改善近期疗效及延长生存期[2]。程序性死亡蛋白1(programmed cell death protein 1,PD-1)是一种与免疫功能有关的Ⅰ型跨膜糖蛋白,是CD28/CTLA-4家族T细胞调控器的一个成员[3]。PD-1主要在T淋巴细胞中表达,其有两个结合配体,即PD-L1及PD-L2,均为B7家族成员,在人体免疫细胞及部分组织细胞中广泛表达,同时在肿瘤细胞中也有明显表达[4-5]。目前PD-1在恶性黑色素瘤、非小细胞肺癌等临床试验中均取得了较好的疗效[6]。但是针对晚期肝癌的临床研究相对较少。本研究主要探讨PD-1治疗晚期原发性肝癌患者的疗效和安全性,为临床治疗提供指导。
1 资料与方法
1.1 病例选择
回顾性分析2016年1月—2019年1月于中国科学院合肥肿瘤医院就诊的原发性肝癌晚期患者,该研究获得了中国科学院合肥肿瘤医院伦理委员会的批准。其中48例患者接受PD-1治疗为观察组,55例患者接受甲磺酸阿帕替尼治疗为对照组。纳入标准:(1)病理确诊或临床诊断晚期肝癌;(2)年龄18岁及以上;(3)东部肿瘤协作组(ECOG)体力状况评分为0~1;(4)有符合RECIST 1.1标准的可测量病灶;(5)预期寿命 > 12周;(6)既往未行免疫治疗。排除标准:(1)具有症状的、已转移到脏器的、短期内有出现危及生命的并发症风险的患者;(2)存在任何活动性自身免疫性疾病或有自身免疫疾病病史;(3)人类免疫缺陷病毒(HIV)感染或已知有获得性免疫缺陷综合征。
1.2 PD-1来源与治疗方法
观察组患者自购PD-1单抗于中国香港及中国北京,所有患者均签署外院自购药物使用同意书。纳武利尤单抗(Nivolumab)(百时美施贵宝公司,美国)3 mg/kg,每2周给药1次;帕博利珠单抗(Pembrolizumab)(默沙东公司,爱尔兰),200毫克/次,每3周给药1次。对照组甲磺酸阿帕替尼(江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司,H20140103,0.25 g)0.5毫克/次,1天1次。观察组与对照组治疗至疾病进展或出现不可耐受的不良反应。
1.3 观察指标
1.3.1 两组患者的近期临床疗效
治疗4~8周定期复查肝脏CT或MRI,参照世界卫生组织(WHO)1979年评价标准:完全缓解(CR):所有可见病灶完全消失并维持4周以上;部分缓解(PR):肿瘤缩小50%以上,维持4周以上;稳定(SD):肿瘤病灶两径乘积缩小至原乘积的50%以下,或增大25%以下,无新病灶出现;进展(PD):肿瘤病灶两径乘积增大25%以上或出现新病灶。客观有效率(objective response rate, ORR)=(CR+PR)/总例数×100%,疾病控制率(disease control rate, DCR)=(CR+PR+SD)/总例数×100%。
1.3.2 不良反应
详细记录治疗过程中出现的不良反应,根据NCI-CTC4.0标准评价不良反应,从轻到重分为1~4级。
1.3.3 总生存率(OS)
患者出院后,从2016年1月—2019年7月每月第一天进行电话随访。所有患者均接受我院电话随访。根据随访结果记录总生存率。总生存率(OS)定义为从随机化到任何原因死亡时间。
1.4 统计学方法
所有数据应用SPSS22.0统计软件处理。患者计量资料采用t检验,计数资料采用χ2检验,用Kaplan-Meier方法绘制OS生存曲线,Log rank检验分析组间差异,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 研究人群基本特征
观察组与对照组一般临床资料(性别、年龄、诊断方式、既往治疗方式、合并HBV感染、ECOG、Child-Paugh评分)差异无统计学意义(P < 0.05),但观察组PD-1检测明显多于对照组(P < 0.01),见表 1。
表 1 治疗前两组原发性肝癌患者一般资料比较Table 1 Comparison of general clinical data before treatment between two groups
2.2 观察组与对照组临床资料比较
患者治疗中期AFP水平、ALT水平、AST水平、ECOG、Child-Paugh评分,观察组优于对照组,且差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),而两组间总胆红素(total bilirubin, TBIL)及白蛋白(albumin, ALB)无明显差别(均P < 0.05),见表 2。
表 2 治疗中期两组原发性肝癌患者临床资料比较Table 2 Comparison of clinical data during treatment between two groups
2.3 近期临床疗效比较
观察组的客观缓解率(CR+PR)高于对照组(45.8% vs. 21.76%, χ2=3.17, P=0.045);疾病控制率(CR+PR+SD)观察组高于对照组(91.67% vs. 78.18%, χ2=5.26, P=0.031),见表 3。
表 3 两组原发性肝癌患者近期临床疗效(n(%))Table 3 Comparison of short-term clinical efficacy between two groups (n(%))
2.4 不良反应
2.4.1 一般不良反应
观察组中有22例患者发生骨髓抑制,对照组有25例患者发生骨髓抑制,差异无统计学意义(P=0.520)。在皮疹、恶心、呕吐及高血压等不良反应中,观察组与对照组比较差异有统计学意义(均P < 0.05),见表 4。
表 4 两组原发性肝癌患者的一般不良反应(n(%))Table 4 Common adverse reactions in two groups (n(%))
2.4.2 免疫相关不良反应
观察组中2例患者因免疫相关性肺炎死亡,其余患者无因药物相关毒性而终止治疗,其中纳武利尤单抗与帕博利珠单抗的免疫相关不良反应差异无统计学意义(均P < 0.05),见表 5。
表 5 Nivolumab与Pembrolizumab之间免疫相关不良反应(n(%))Table 5 Immune-related adverse reactions between Nivolumab and Pembrolizumab (n(%))
2.5 总生存率
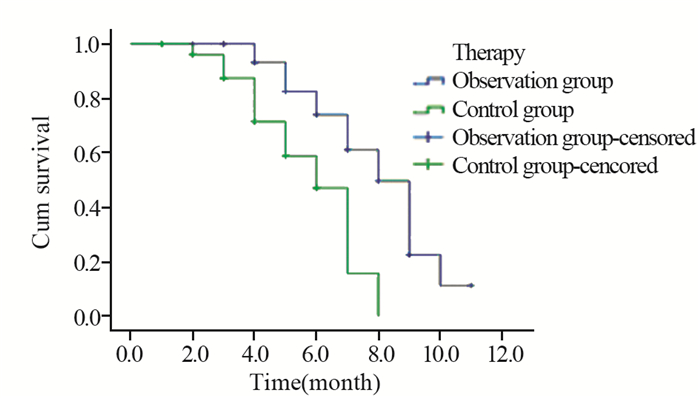
观察组患者的总生存率(95%CI: 7.24~8.64月)与对照组(95%CI: 5.13~6.39月)比较,差异均有统计学意义(χ2=11.933, P < 0.05)(t=11.188, P=0.01),见图 1。
3 讨论
肝癌的发生是一个多基因参与、多途径调控的复杂过程,免疫抑制在其发生过程中具有重要作用,且与肿瘤细胞PD-L1的表达密切相关[7-8]。PD-1与PD-L1结合可阻断T细胞活化、增殖及产生细胞因子从而发挥着负性免疫调节作用,诱导产生免疫抑制[9]。国外一项关于PD-1治疗晚期肝癌的研究中,治疗组的总生存时间为11月,明显高于对照组[10]。同时肝癌是富血管肿瘤,血管生成在肝癌发生、浸润、转移过程中也发挥了重要作用。血管内皮生长因子受体VEGFR高度表达于恶性肿瘤细胞中,促进血管生成[11]。甲磺酸阿帕替尼是一种新型口服小分子抗血管生成制剂,可高度选择性地结合并抑制VEGFR-2,抑制肿瘤血管衍生[12],阿帕替尼治疗晚期肝癌存在潜在的生存获益[13]。本文通过比较PD-1与甲磺酸阿帕替尼在治疗晚期原发性肝癌患者中的疗效与安全性,为晚期肝癌患者的临床治疗提供指导。
一项研究显示,使用纳武利尤单抗(Nivolumab)治疗的肝癌患者较索拉菲尼靶向治疗的患者其中位生存期明显延长[14]。本研究中,观察组患者总生存率较对照组延长且差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),客观缓解率及疾病控制率方面,观察组也高于对照组且差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。但观察组总生存率较对照组未有明显的延长(观察组95%CI: 7.24~8.64月;对照组95%CI: 5.13~6.39月),可能与晚期肝癌患者本身预后欠佳、易合并全身系统疾病如感染、黄疸、恶病质相关。患者一般情况及肝功能中,治疗后观察组Child-Paugh评分、甲胎蛋白(AFP)、谷丙转氨酶(ALT)、谷草转氨酶(AST)及ECOG优于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。本研究中,PD-1不仅可以提高晚期肝癌患者的总生存率、客观缓解率及疾病控制率,还可以改善患者一般情况及肝功能。
本研究中,治疗后两组患者均有不良反应发生,骨髓抑制在两组间差异无统计学意义(P < 0.05),而在皮疹、恶心呕吐及高血压等不良反应中,观察组发生率为(2.08%、6.25%、0)与对照组(16.36%、45.45%、10.9%)比较,观察组优于对照组(P < 0.05)。值得指出的是PD-1治疗产生的免疫相关不良反应。PD-1与受体结合在解除免疫抑制增强T细胞抗肿瘤效应的同时,也异常增强自身正常的免疫反应,导致免疫失衡,表现出自身免疫样的炎性反应[15],其涉及胰腺、肺部、皮肤、消化道、肝脏、胰腺、甲状腺等在内的多个器官[16]。该研究中晚期肝癌患者免疫相关不良反应主要有免疫相关性肺炎(22.91%)、肝脏毒性(12.5%)、胰腺毒性(8.33%)、心脏毒性(6.25%)、肾脏毒性(2.08%),且纳武利尤单抗与帕博利珠单抗之间差异无统计学意义(P < 0.05)。研究指出,PD-1引起的免疫相关性肺炎,主要表现为非特异性间质性肺炎[17]。国外关于肺癌患者使用PD-1治疗中发生免疫相关性肺炎约为10%,且偶有危及生命报道[18-19]。本研究中,有近1/5的患者出现免疫相关性肺炎并有2例患者因免疫相关性肺炎治疗无效死亡。在临床治疗中可定期完善肺部相关检测,避免免疫相关肺炎的发生。Hofmann等发现合并2型糖尿病的癌症患者接受PD-1治疗后会出现胰腺β细胞功能衰竭,需要胰岛素替代治疗[20]。本研究中,观察组4例既往无糖尿病病史及家族史的患者中出现胰腺功能受损,其中,3例患者表现为轻度血糖升高,1例出现需要胰岛素控制的血糖升高,建议患者定期监测血糖。因此,PD-1的免疫相关反应可作为今后临床关注的重点。
综上所述,PD-1较甲磺酸阿帕替尼可提高晚期原发性肝癌患者的近期临床疗效及总生存率,可作为晚期肝癌的一种治疗方法。
作者贡献王毅欣:整理资料、分析数据、书写文章胡宗涛:指导全文、校对文章张永康:校对文章曾平:整理资料、分析数据王宏志:指导全文 -
表 1 治疗前两组原发性肝癌患者一般资料比较
Table 1 Comparison of general clinical data before treatment between two groups

表 2 治疗中期两组原发性肝癌患者临床资料比较
Table 2 Comparison of clinical data during treatment between two groups

表 3 两组原发性肝癌患者近期临床疗效(n(%))
Table 3 Comparison of short-term clinical efficacy between two groups (n(%))

表 4 两组原发性肝癌患者的一般不良反应(n(%))
Table 4 Common adverse reactions in two groups (n(%))

表 5 Nivolumab与Pembrolizumab之间免疫相关不良反应(n(%))
Table 5 Immune-related adverse reactions between Nivolumab and Pembrolizumab (n(%))

-
[1] Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(2): 115-132.
[2] Huang ZY, Liang BY, Xiong M, et al. Long-term Outcomes of Repeat Hepatic Resection in Patients with Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Analysis of Recurrent Types and Their Prognosis: A Single-Center Experience in China[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2012, 19(8): 2515-2525.
[3] Salmaninejad A, Valilou SF, Shabgah AG, et al. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: Basic biology and role in cancer immunotherapy[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(10): 16824-16837.
[4] Liu B, Arakawa Y, Yokogawa R, et al. PD-1/PD-L1 expression in a series of intracranial germinoma and its association with Foxp3+ and CD8+ infiltrating lymphocytes[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(4): e0194594.
[5] Kline J, Gajewski TF. Clinical development of mAbs to block the PD1 pathway as an immunotherapy for cancer[J]. Curr Opin Investig Drugs, 2010, 11(12): 1354-1359.
[6] Sharma P, Allison JP. The future of immune checkpoint therapy[J]. Science, 2015, 348(6230): 56-61.
[7] Liu B, Song Y, Liu D. Recent development in clinical applicationsof PD-1 and PD-L1 antibodies for cancer immunotherapy[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2017, 10(1): 174.
[8] Chang H, Jung W, Kim A, et al. Expression and prognostic significance of programmed death protein 1 and programmed death ligand-1, and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated molecule-4 in hepatocellularcarcinoma[J]. APMIS, 2017, 125(8): 690-698.
[9] Butte MJ, Keir ME, Phamduy TB, et al. Programmed Death-1 Ligand 1 Interacts Specifically with the B7-1 Costimulatory Molecule to Inhibit T Cell Responses[J]. Immunity, 2007, 27(1): 111-122.
[10] Scheiner B, Kirstein MM, Hucke F, et al. Programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1)-targeted immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: efficacy and safety data from an international multicentre real-world cohort[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 49(10): 1323-1333.
[11] Peng S, Zhang Y, Peng H, et al. Intracellular autocrine VEGF signaling promotes EBDC cell proliferation, which can be inhibited by Apatinib[J]. Cancer Lett, 2016, 373(2): 193-202.
[12] Scott AJ, Messersmith WA, Jimeno A. Apatinib: a promising oral antiangiogenic agent in the treatment of multiple solid tumors[J]. Drugs Today (Barc), 2015, 51(4): 223-229.
[13] 秦叔逵, 白玉贤, 欧阳学农, 等.阿帕替尼一线治疗晚期肝细胞癌的前瞻性、随机、开放、全国多中心Ⅱ期临床试验[J].临床肿瘤学杂志, 2017, 22(12): 1057-1065. Qin SK, Bai YX, Ouyang XN, et al. Apatinib for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised, open-label, multicentre, phaseⅡ clinical trial[J]. Lin Chuang Zhong Liu Xue Za Zhi, 2017, 22(12): 1057-1065.
[14] Crocenzi TS, Ei-Khoueiry AB, Yau TC, et al. Nivolumab (nivo) in sorafenib(sor)-naive and -experienced pts with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC): CheckMate 040 study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2017, 35: 4013.
[15] Stucci S, Palmirotta R, Passarelli A, et al. Immune-related adverse events during anticancer immunotherapy: Pathogenesis and management (Review)[J]. Oncol Lett, 2017, 14(5): 5671-5680.
[16] Naidoo J, Page DB, Li BT, et al. Toxicities of the anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 immune checkpoint antibodies[J]. Ann Oncol, 2016, 27(7): 1362.
[17] Nishino M, Sholl LM, Hodi FS, et al. Anti-PD-1-related pneumonitis during cancer immunotherapy[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 373(3): 288-290.
[18] Garon EB, Rizvi NA, Hui R, et al. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 372(21): 2018-2028.
[19] Gettinger SN, Horn L, Gandhi L, et al. Overall survival and long term safety of nivolumab (anti-programmed death 1 antibody, bms-936558, ono-4538) in patients with previously treatedadvanced non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2015, 33(18): 2004-2012.
[20] Hofmann L, Forschner A, Loquai C, et al. Cutaneous, gastrointestinal, hepatic, endocrine, and renal side-effects of anti-PD-1 therapy[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2016, 60: 190-209.
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 梅琪,袁牧,钱景瑜,刘若宇,谭玉林. 肝动脉化疗栓塞术联合卡瑞利珠及阿帕替尼治疗中晚期肝癌的安全性及临床疗效观察. 蚌埠医学院学报. 2024(01): 51-54+58 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李丽敏,王璐,曹阳博,刘栋利,陈鹏飞. 肝癌患者经导管动脉化疗栓塞后发生栓塞综合征的影响因素分析. 癌症进展. 2024(01): 72-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 费睿成,亓民. PD-1单抗联合TACE对晚期原发性肝癌患者的治疗效果. 实用中西医结合临床. 2024(10): 16-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘小梅,钟梅,刘浩,易军,王洪云. 晚期肝癌免疫相关治疗的获益和不良反应临床研究. 基层医学论坛. 2023(19): 20-22+35 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 何晓锐,王淑红. 阿替利珠单抗联合贝伐珠单抗治疗晚期肝癌的临床效果. 临床医学研究与实践. 2023(27): 29-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 陈方红,刘娱,边界. PD-1抑制剂治疗肝癌患者的临床疗效及ECOG-PS评分联合Child-Pugh分级对肿瘤超进展的预测价值. 广西医学. 2023(15): 1800-1806 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 郭稳稳,程昌盛,吴燕,林文东,赖辉强,黄吉荣,龙高云. 安罗替尼治疗晚期肝癌的疗效及预后的影响因素. 临床与病理杂志. 2022(08): 1822-1828 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 殷云飞,鲁邱阳. 抗PD-1单抗对中晚期肝癌患者近期疗效、外周血T淋巴细胞亚群指标的影响. 中国医学创新. 2021(13): 19-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李冰妍,陈林会,郑颖娟,梁天嵩,杨道科. 程序性死亡受体1抑制剂治疗远处转移鼻咽癌疗效观察. 肿瘤基础与临床. 2021(03): 207-211 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 朱风婷,曾江正,姜靖雯,陈学武,张慧. 卡瑞利珠单抗联合射频消融术及FOLFOX方案治疗原发性肝癌疗效研究. 中国药业. 2021(15): 38-41 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 王俊旗,徐锋. 程序性死亡受体1及其配体PD-L1、细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关抗原4抑制剂在晚期肝癌治疗中的进展. 中华普通外科学文献(电子版). 2021(04): 304-308 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 鄢清元,熊巍,杨文平. 晚期肝癌患者索拉非尼分子靶向治疗的有效性及对疾病控制率的影响研究. 中国医学创新. 2021(29): 173-177 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: