Expression of PD-L1 and Its Clinical Significance in MYC/BCL2 Double-expression Large B Cell Lymphoma
-
摘要:目的
探讨MYC/BCL2双表达大B细胞淋巴瘤(DEL)与程序性细胞死亡受体-配体1 (PD-L1) mRNA、蛋白表达的相关性及其临床意义。
方法收集90例弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)病例, 采用免疫组织化学染色检测MYC、BCL2蛋白并分组, 双标记染色法检测各组病例的肿瘤细胞或微环境细胞中PD-L1表达; 实时荧光PCR技术(Real-time PCR, qPCR)检测DEL组与non-DEL组PD-L1 mRNA相对表达量; 收集临床病理资料并随访, 对实验数据进行统计学分析。
结果90例样本中28例为DEL, 肿瘤细胞和微环境中PD-L1+分别为22例和26例。DEL组肿瘤细胞和微环境中PD-L1+分别为14例和9例; 肿瘤细胞和微环境细胞PD-L1蛋白表达与DEL存在相关性(P < 0.05); PD-L1 mRNA相对表达量在DEL与non-DEL组间存在显著差异(P=0.012); DEL组中PD-L1+与IPI评分和B症状的出现有关(P=0.007、0.021); Kaplan-Meier显示DEL中PD-L1+、肿瘤微环境PD-L1阳性(mPD-L1+)与患者预后相关(P=0.005、0.001)。
结论DEL患者PD-L1 mRNA及蛋白表达都明显上调且与患者不良预后相关, PD-L1可作为DEL患者不良预后评估的危险因素。
-
关键词:
- MYC /
- BCL2 /
- 双表达大B细胞淋巴瘤 /
- PD-L1 /
- 预后
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the correlation between MYC/BCL2 double-expression large B cell lymphoma (DEL) and programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) mRNA or protein expressions and analyze the clinical significance of PD-L1 protein expression in DEL.
MethodsWe collected 90 cases of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma(DLBCL) and detected MYC and BCL2 protein by immunohistochemical staining, and then grouped them into DEL and non-DEL groups. The expressions of PD-L1 in tumor cells or microenvironment were detected by immunohistochemical double labeling staining. qPCR was used to detect the relative expression of PD-L1 mRNA. The clinicopathological data were collected and followed up.
ResultsAmong 90 cases of DLBCL, there were 28 cases of DEL, 22 cases of PD-L1 expression in tumor cells (PD-L1+) and 26 cases in microenvironment (mPD-L1+); while, 14 cases of PD-L1 expression in tumor cells and 9 cases in microenvironment in DEL group. PD-L1 protein expression in tumor cells or microenvironment was correlated with DEL (P < 0.05). The relative expression of PD-L1 mRNA was significantly different between two groups (P=0.012). PD-L1+ was related to IPI score and B symptom in DEL group (P=0.007, 0.021). PD-L1+ and mPD-L1+ were correlated with the prognosis of patients in DEL group (P=0.005, 0.001).
ConclusionThe mRNA and protein expression of PD-L1 are significantly up-regulated in DEL patients and correlated with the prognosis. PD-L1 could be used as an independent risk factor for the evaluation of poor prognosis of DEL patients.
-
Key words:
- MYC /
- BCL2 /
- Double-expression large B cell lymphoma /
- PD-L1 /
- Prognosis
-
0 引言
双表达大B细胞淋巴瘤(double-expression large B-cell lymphoma, DEL)临床上以MYC/BCL2双表达最为常见, 占弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤(diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, DLBCL)的19%~34%[1-2], 已有较多研究证实DEL患者临床预后和治疗效果相对较差, 且易发展为复发/难治性大B细胞淋巴瘤[3-6]。染色体9p24.2上CD274基因编码的PD-L1是程序性细胞死亡蛋白-1(programmed cell death 1, PD-1)的配体, 其相互结合可以介导肿瘤细胞获得免疫逃逸能力[7-8]。研究[9]发现MYC可以结合PD-L1的启动子, 促进其表达, 从而促进肿瘤的发生发展; 具有协同作用的原癌基因MYC、BCL2可能是影响PD-L1蛋白表达的上游基因, 三者在淋巴瘤的发病机制中发挥了重要作用[9-11]。本研究收集了一组大B细胞淋巴瘤病例, 通过qPCR技术、免疫组织化学双标记和普通免疫组织化学染色法、临床病理资料收集和随访, 分析PD-L1表达与DEL的关系及其与患者预后的关系, 并探讨PD-L1表达在DEL临床预后评估中的价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1 病例收集
收集贵州医科大学附属医院病理科2010年1月1日至2017年12月31日期间确诊的DLBCL病例, 将临床病理资料相对完整、肿瘤组织充足的90例病例纳入实验研究。
1.2 主要试剂
PD-L1单抗购于美国Abcam公司, 单克隆一抗Pax5、MYC、BCL2和二抗试剂盒(PV-9001、SAP-9102)、EDTA修复液、AP-Red及DAB试剂盒均购自北京中杉公司; RNA提取试剂盒(FFPE RNA)购自厦门艾德公司; SYBR Green荧光染料(TaKaRa RR820A)、反转录试剂盒(TaKaRa RR47A)、内参均购于美国TaKaRa公司; PD-L1引物购于上海生工公司。
1.3 免疫组织化学染色及分组
采用PV二步法检测MYC、BCL2蛋白表达:MYC、BCL2以扁桃体组织为阳性对照; 以PBS(pH7.35)代替一抗作阴性对照; 以pH(8.0)的EDTA溶液修复抗原; MYC、BCL2稀释比均为1:200;步骤按PV-9001说明进行。
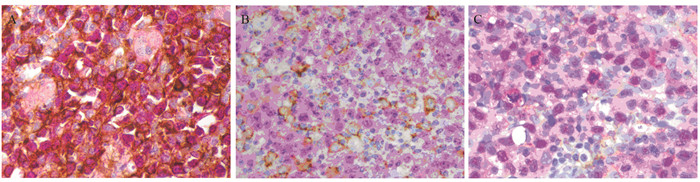
判读标准:MYC阳性信号位于细胞核, BCL2阳性信号位于细胞质。根据文献[12-14]略作修改, 随机选择10个不重复的400倍视野, 每个视野随机计数400个肿瘤细胞中阳性细胞所占比例, 取10个视野的平均值作为该病例表达率。据文献[1-4, 12-14]定义MYC ≥ 40%为高表达, BCL2 ≥ 70%为高表达。若MYC、BCL2均高表达定义为MYC/BCL2双表达大B细胞淋巴瘤组(简称DEL组), 余下归为non-DEL组。
1.4 免疫组织化学双标记染色检测PD-L1表达
根据试剂盒说明Pax5、PD-L1设置阳性对照为扁桃体组织, 阴性对照以TBS(pH7.35)替代一抗, 并以TBS作为缓冲液及冲洗液; 用间接法进行双标记染色, 染色步骤简述如下:4 μm厚石蜡切片, 脱蜡、水洗、EDTA(pH9.0)进行修复抗原, 消除内源性过氧化物酶后血清封闭, 先进行Pax5鼠抗人单克隆抗体染色(1:300稀释), 按(SAP-9102)试剂盒说明进行Pax5标记(AP-Red显色), 再次EDTA(pH8.0)修复后, 按Pax5染色的相同步骤进行PD-L1兔抗人单克隆抗体(1:250稀释)标记, DAB显色, 透明封片后进行观察和图像分析。
判读方法:Pax5以细胞核出现红色或浅红色颗粒为阳性表达; PD-L1以细胞质或细胞膜形成黄色或棕黄色颗粒为阳性表达。参照文献[15-16]分析:同MYC、BCL2一样统计肿瘤细胞PD-L1表达率(10个高倍视野平均值), 定义肿瘤细胞双标记阳性细胞≥ 30%(细胞质或膜着黄色、核着红色)为肿瘤细胞PD-L1阳性(PD-L1+); 在PD-L1阴性的病例中, 若肿瘤微环境细胞(主要为肿瘤组织浸润T细胞tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, TILs)PD-L1表达率≥ 20%, 定义为微环境PD-L1阳性[15], 即mPD-L1+。
1.5 RNA提取、反转录、qPCR方法
RNA的提取、检测及反转录:取8 μm组织进行脱蜡、去除二甲苯、蛋白酶消化至清亮后, 按RNA提取试剂盒说明进行RNA提取, 最后以50 μl的DEPC水溶解RNA, 核酸定量仪检测RNA浓度及纯度, 取OD值(A260/A280)在1.8到2.0的RNA样本进行实验, 按TaKaRa RR47A试剂说明于冰上进行去除基因组DNA(42℃ 2 min), 于冰上配置反转录体系后进行反转录(37℃ 30 min, 再加热至85℃ 5 s), 缓慢冷却后于-80℃冰箱保存。
qPCR:使用两步法检测DEL组与non-DEL组PD-L1的mRNA, 据TaKaRa RR820A试剂盒说明, 取cDNA样本于冰上配置SYBR Green RT-qPCR反应体系, PD-L1引物:上游:5'-CTATGGTGGTGCCGACTACA-3', 下游:5'-TGCTTGTCCAGATGACTTCG-3', 每个样本设置3个复孔, 先配置总反应体系, 再分装3个复孔; 用β-actin(上游:5'-TAGTTGCGTTACA CCCTTTCTTG-3', 下游:5'-TCACCCTTCACCGTTCCAAGTTT-3')作为内参, 于Bio-Rad CFX connect荧光定量PCR仪上进行反应(反应条件:预变性95℃ 30 s, 变性95℃ 5 s, 退火/延伸为60℃ 30 s, 50个循环), 以2-ΔΔCt值为mRNA相对表达量, ΔCt=Ct目的基因-Ct内参基因, ΔΔCt=ΔCt样本-ΔCt组内最低值。
1.6 随访方法
采取电话或走访方式, 以首次确诊时间为开始时间, 随访患者首次确诊以后的治疗、健康、复发及生存等情况; 每隔3月随访1次(出现死亡或失访时结束该例患者随访), 长期存活患者随访截至2018年12月31日。
1.7 统计学方法
用SPSS 17.0软件对数据整理分析; mRNA相对表达量在各组间比较采用t检验, 正态分布用(


2 结果
2.1 一般资料
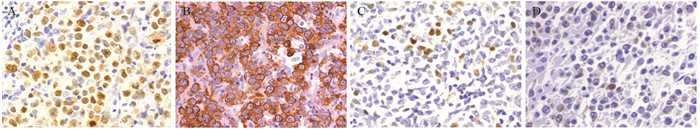
DLBCL90例, HE染色见图 1。男47例, 女43例; 年龄17~82岁(中位年龄58.5);根据免疫组织化学染色结果分组, 28例为DEL, 62例为non-DEL, 见图 2。据1993年NHL国际预后指数IPI评分:0~2分49例, 3~5分41例; 临床分期:Ⅰ+Ⅱ期54例, Ⅲ+Ⅳ期36例。
2.2 DEL组与non-DEL组PD-L1蛋白表达情况比较
90例DLBCL肿瘤细胞和微环境中PD-L1阳性分别为22例(24.44%)和26例(28.89%), 见图 3。DEL组肿瘤细胞和微环境中PD-L1阳性表达率分别为50.00%和32.14%, non-DEL组分别为12.90%和27.42%。肿瘤细胞和微环境PD-L1蛋白表达在DEL组与non-DEL组间比较, 差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05), 见表 1。
表 1 DEL组与non-DEL组PD-L1蛋白表达的比较Table 1 Comparison of PD-L1 protein expression between DEL and non-DEL groups
2.3 DEL组与non-DEL组间PD-L1 mRNA相对表达量比较
qPCR检测结果显示DEL组(0.9862±0.49853)与non-DEL组(0.7175±0.29265)PD-L1 mRNA相对表达量比较, 差异有统计学意义(95% CI:0.06325~0.47419, t=2.653, P=0.012)。
2.4 DEL组中PD-L1表达与临床病理特征的关系
DEL组中, 25例检查血清乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)其中13例PD-L1+, 8例mPD-L1+, 4例mPD-L1-; 24例检查β2微球蛋白(β2-MG), 其中14例PD-L1+, 7例mPD-L1+, 3例mPD-L1-, IPI评分0~2分组、3~5分组均为14例, Ⅰ+Ⅱ期、Ⅲ+Ⅳ期分别为15例、13例; PD-L1+与性别、年龄、Ann Arbor分期、LDH、β2-MG无相关性, 但与IPI评分和B症状的出现显著相关(P值分别为0.007、0.021);mPD-L1+与上述临床病理特征均无相关性(均P>0.05), 见表 2。
表 2 DEL组肿瘤细胞和微环境中PD-L1表达与临床病理特征的关系Table 2 Relation between PD-L1+, mPD-L1+ and clinicopathological characteristics of DEL patients
2.5 DEL患者预后及PD-L1蛋白表达生存分析
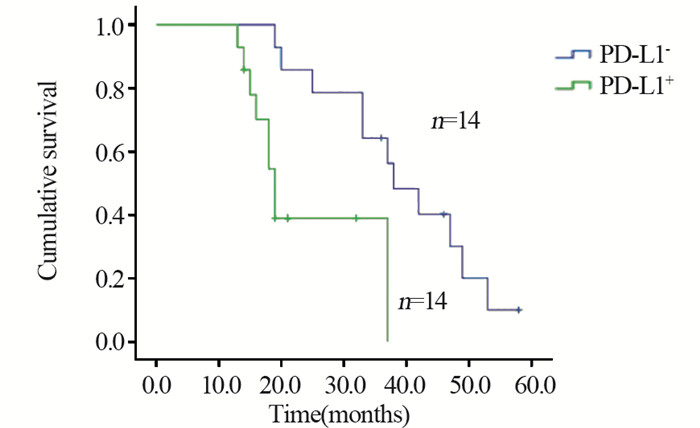
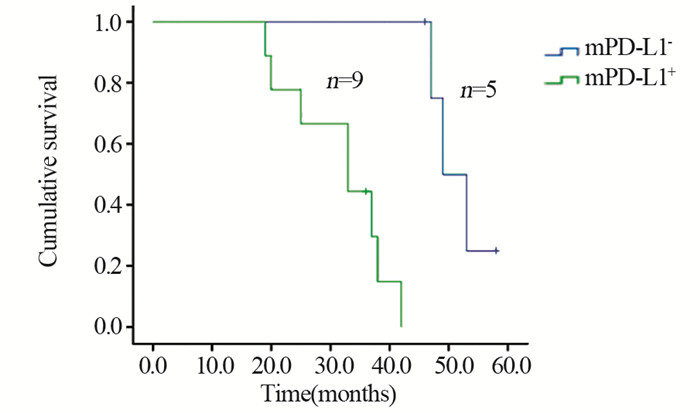
DEL组中, 生存8例, 死亡14例, 失访6例, 其中复发9例; 中位生存时间29月。20例接受R-CHOP治疗, 其余不详; Kaplan-Meier生存分析显示PD-L1+组患者总体生存时间(OS)明显短于PD-L1-组(P=0.005), 见图 4; mPD-L1+组患者OS明显短于mPD-L1-组(P=0.001), 见图 5。
3 讨论
尽管淋巴瘤的WHO分类还未将DEL单独列出, 但这类淋巴瘤和"双打击淋巴瘤"相类似, 在临床上具有独特的临床特点。多项研究[1-4, 12-14]表明这类共表达淋巴瘤的IPI评分和肿瘤细胞增殖指数高, 常有多个结外部位累及, 患者在接受标准的R-CHOP免疫化疗方案治疗后复发率高, 且5年生存率也较低。因此, 发现这类DEL的理想预后评估因素和有效的治疗靶点有着重要意义。
PD-L1表达与T淋巴细胞的凋亡及活化有关, 其上调表达通过与浸润T细胞表面受体PD1的结合诱导效应T细胞凋亡、抑制T细胞活化, 从而产生肿瘤生长的微环境, 介导肿瘤细胞的免疫逃逸[6-7]。PD-L1表达对大B细胞淋巴瘤影响的研究多集中在部位特点和细胞来源特点等方面。Kiyasu研究小组[15]统计1 235例临床样本, 发现肿瘤细胞表达PD-L1在DLBCL中阳性率为11%, 微环境细胞PD-L1阳性表达率为15.3%, PD-L1及mPD-L1的表达与GCB样DLBCL和EB病毒阳性的大B细胞淋巴瘤病例显著相关, 且PD-L1+的患者总生存期(OS)低于PD-L1-的DLBCL患者。Liu等[16]检测92例原发肠道的弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤样本中PD-L1的表达, 结果与Kiyasu研究小组的结果相似, 但微环境中PD-L1的阳性率相对较高。本研究发现PD-L1、mPD-L1在90例大B细胞淋巴瘤中的阳性表达率分别为24.44%和28.89%, 与Liu等的研究报道相近。
有研究报道[17]DLBCL患者如果伴有PD-L1的DNA扩增、mRNA上调及蛋白高表达, 其生存预后均不理想, 且PD-L1蛋白表达并不完全由基因调控, 可能还受肿瘤环境中的其他因素影响。Casey团队[9]发现MYC可以与PD-L1启动子结合, 直接调控PD-L1表达, 沉默MYC后PD-L1蛋白表达明显下降; Rossille研究结果[18]表明, 在BCL2阳性侵袭性弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤患者中, 血清PD-L1高表达水平患者的总体生存期(OS)明显短于血清PD-L1低表达水平患者。本研究发现在MYC/BCL2共表达淋巴瘤中PD-L1、mPD-L1的阳性表达率明显高于非共表达大B细胞淋巴瘤, 且在该类淋巴瘤中PD-L1 mRNA相对表达量明显上调。既往报道和我们的结果都提示PD-L1与MYC/BCL2蛋白表达可能存在某种关联, 它们之间可能存在一些信号转导通路的"串话"。具体机制有待于进一步深入的分子、基因等方面研究探讨。
本研究统计DEL患者临床相关数据提示在DEL中PD-L1蛋白表达与高IPI评分和B症状的出现有关; 此外, 通过对28例DEL患者生存随访资料统计分析发现, DEL患者中PD-L1无论在肿瘤细胞表达还是在肿瘤微环境细胞中的表达, 患者OS均显著低于阴性组; 这些结果都提示, PD-L1蛋白的上调表达与DEL患者不良预后相关。
作为一项回顾性的研究, 本实验存在一定的缺陷:首先因受到总样本量收集的限制, 纳入研究样本量相对较小, 统计结果可能与大样本的研究结果会存在一定误差; 其次, 本实验部分RNA提取使用的组织为年份较长的石蜡组织, 可能提取RNA存在降解, 对实验也有一定的影响。因此, 还需扩大样本量、使用新鲜离体组织或提高各项检测技术等来验证我们的结果。
综上所述, MYC/BCL2共表达大B细胞淋巴瘤中PD-L1蛋白和mRNA均上调表达, 这可能与这类淋巴瘤不良预后有关, 它在这类淋巴瘤预后评估中的价值还有待于进一步研究证实。
作者贡献王平:参与实验、统计分析及论文撰写杨文秀:指导试验设计、审核数据及统计分析结果、论文修改周杰:病理蜡块收集及部分免疫组织化学实验冯江龙:技术指导林超群:患者临床资料随访 -
表 1 DEL组与non-DEL组PD-L1蛋白表达的比较
Table 1 Comparison of PD-L1 protein expression between DEL and non-DEL groups

表 2 DEL组肿瘤细胞和微环境中PD-L1表达与临床病理特征的关系
Table 2 Relation between PD-L1+, mPD-L1+ and clinicopathological characteristics of DEL patients

-
[1] Friedberg JW. How I treat double-hit lymphoma[J]. Blood, 2017, 130(5):590-596. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-04-737320
[2] Kawashima I, Inamoto Y, Maeshima AM, et al. Double expressor lymphoma is associated with poor outcomes after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation[J]. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant, 2018, 24(2):294-300. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.10.013
[3] Reagan PM, Davies A. Current treatment of double hit and double expressor lymphoma[J]. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program, 2017, 2017(1):295-297. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2017.1.295
[4] Riedell PA, Smith SM. Double hit and double expressors in lymphoma:Definition and treatment[J]. Cancer, 2018, 124(3):4622-4632.
[5] Herrera AF, Mei M, Low L, et al. Relapsed or refractory doubleexpressor and double-hit lymphomas have inferior progressionfree survival after autologous stem-cell transplantation[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2017, 35(1):24-31. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.68.2740
[6] 吴辉菁, 于丁, 杨业勤, 等. ABVD成功解救难治性弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤1例报道[J].肿瘤防治研究, 2016, 43(11):1008-1010. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2016.11.018 Wu HJ, Yu D, Yang YQ, et al. Sucessful salvage therapy with ABVD on refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma:A case report[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2016, 43(11):1008-1010. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2016.11.018
[7] Francisco LM, Salinas VH, Brown KE, et al. PD-L1 regulates the development, maintenance, and function of induced regulatory T cells[J]. J Exp Med, 2009, 206(13):3015-3029. doi: 10.1084/jem.20090847
[8] Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, et a1. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer[J]. New Engl J Med, 2012, 366(26):2443-2454. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1200690
[9] Casey SC, Tong L, Li Y, et al. MYC regulates the anti-tumor immune response through CD47 and PD-L1[J]. Science, 2016, 352(6282):227-231. doi: 10.1126/science.aac9935
[10] Schmitt CA, Lowe SW. Bcl-2 mediates chemoresistance in matched pairs of primary E(mu)-myc lymphomas in vivo[J].Blood Cells Mol Dis, 2001, 27(1):206-216. doi: 10.1006-bcmd.2000.0372/
[11] Delbridge AR, Grabow S, Strasser A, et al. Thirty years of BCL-2:translating cell death discoveries into novel cancer therapies[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2016, 16(2):99-109. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2015.17
[12] Green TM, Nielsen O, De Stricker K, et al. High Levels of Nuclear MYC protein predict the presence of MYC rearrangement in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2012, 36(4):612-619. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318244e2ba
[13] Bogusz AM, Kovach AE, Le LP, et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with concurrent high MYC and BCL2 expression shows evidence of active B-cell receptor signaling byquantitative immunofluorescence[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(2):1-14. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28212447
[14] 尹文娟, 朱秀, 杨海燕, 等.原发中枢神经系统弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤中bcl-2、C-MYC基因异常、蛋白表达及治疗方案选择对患者预后的影响[J].中华病理学杂志, 2018, 47(1):32-38. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5807.2018.01.007 Yin WJ, Zhu X, Yang HY, et al. Effects of bcl-2 and c-myc gene abnormalities, protein expression and treatment protocol selection on prognosis of patients with primary diffuse large B cell lymphoma of central nervous system[J]. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi, 2018, 47(1):32-38. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5807.2018.01.007
[15] Kiyasu J, Miyoshi H, Hirata A, et al. Expression of programmed cell death ligand 1 is associated with poor overall survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Blood, 2015, 126(19):2193-2201. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-02-629600
[16] Liu Y, Ma J, Yu K, et al. Expression of programmed cell death 1/programmed cell death ligand 1 in the tumor microenvironments of primary gastrointestinal diffuse large B cell lymphomas[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2018, 214(4):507-512. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2018.03.001
[17] Sun C, Jia Y, Wang W, et al. Integrative analysis of PD-L1 DNA status, mRNA status and protein status, and their clinicopathological correlation, in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Histopathology, 2019, 74(4):618-628. doi: 10.1111/his.13765
[18] Rossille D, Gressier M, Damotte D, et al. High level of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 in blood impacts overall sur vival in aggressive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma:results from a French multicenter clinical trial[J]. Leukemia, 2014, 28(12):2367-2375. doi: 10.1038/leu.2014.137
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李晓荟,王秋爽,马京华,郝子兰,田晗,刘云肖. 癌症疼痛患者疼痛灾难化水平及影响因素分析. 护理实践与研究. 2025(01): 61-68 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: