Circ_0001946 Expression and Its Correlation with Prognosis of Pancreatic Cancer Patients
-
摘要:目的
探讨Circ_0001946在胰腺癌患者中的表达及其与患者预后的相关性。
方法qRT-PCR法检测Circ_0001946在胰腺癌患者组织及血清标本中的表达, Chi-Square检验分析Circ_0001946与各临床病理参数之间的关系; Kaplan-Meier法分析Circ_0001946的表达与生存时间及预后的关系, 单因素及多因素Cox分析影响胰腺癌患者预后的因素, ROC曲线分析其作为胰腺癌早期诊断生物标志物的效能。
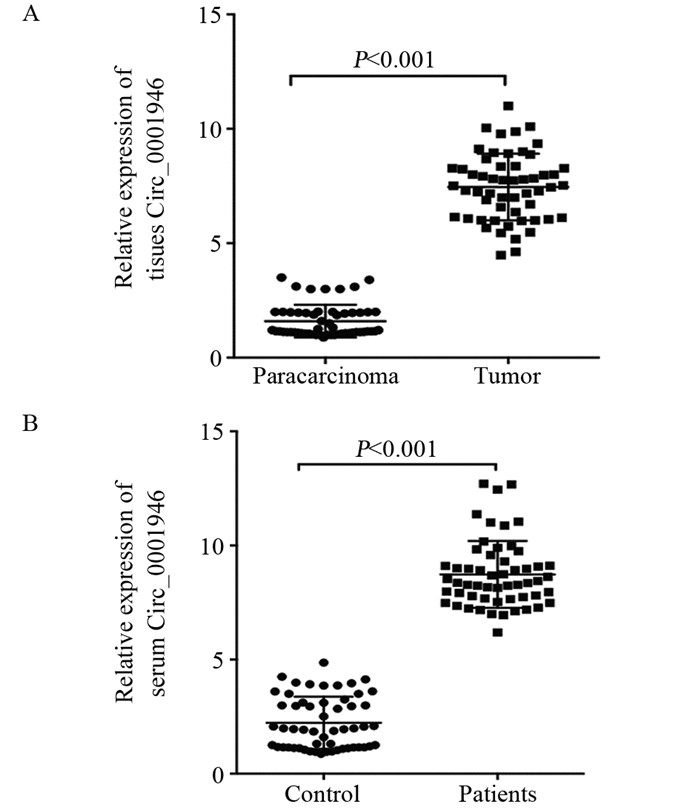
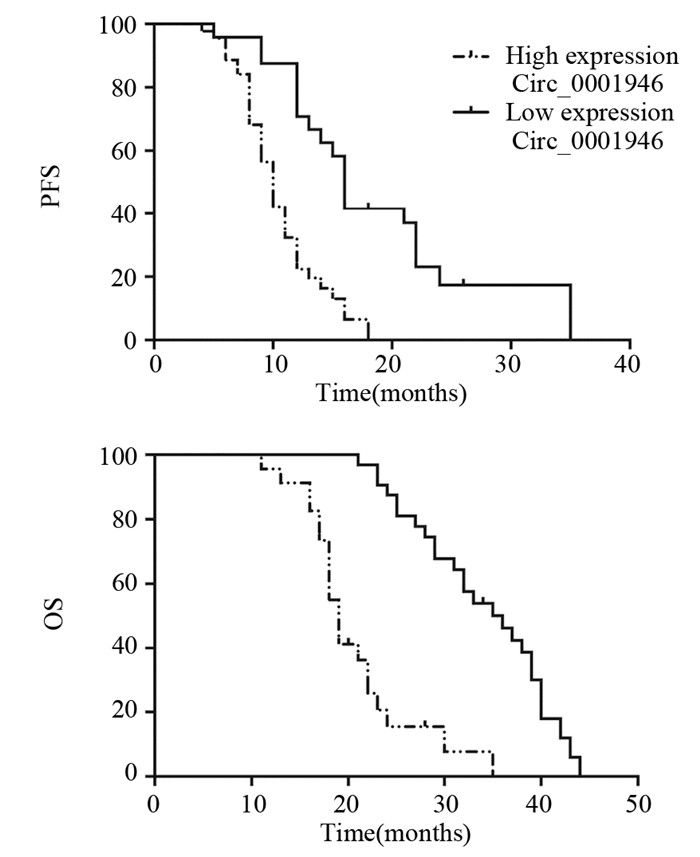
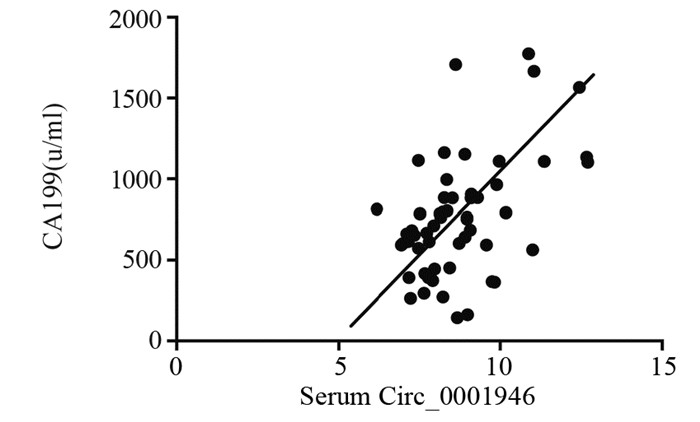
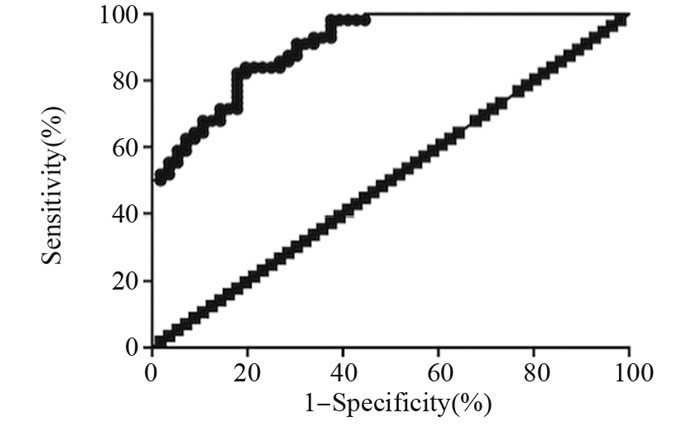
结果Circ_0001946在胰腺癌患者组织和血清中高表达, 差异有统计学意义(均P < 0.001)。Circ_0001946与脉管癌栓、淋巴结转移、CA199的表达及疾病分期显著相关(均P < 0.05)。血清Circ_0001946表达与AFP的量呈正相关关系(r=0.765, P=0.000)。血清Circ_0001946作为诊断胰腺癌血清标志物的ROC曲线下面积为0.805(95% CI:0.754~0.927, P=0.000)。高表达Circ_0001946的患者总生存时间及无进展生存时间均较低表达者明显缩短(均P=0.000)。单因素及多因素Cox分析结果显示, 疾病分期、Circ_0001946表达及脉管癌栓是胰腺癌患者预后的独立影响因素。
结论Circ_0001946在胰腺癌患者中高表达, 与患者的预后相关。
-
关键词:
- Circ_0001946 /
- 胰腺癌 /
- 预后
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the prognostic significance of Circ_0001946 expression in pancreatic cancer patients.
MethodsThe expression of Circ_0001946 in pancreatic cancer tissues and serum samples were detected by qRT-PCR, and the relation between Circ_0001946 and various clinicopathological parameters was analyzed by Chi-Square test. Kaplan-Meier method was used to analyze the relation between Circ_0001946 expression and survival time and prognosis. Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional risk models were used to analyze the factors affecting the prognosis of pancreatic cancer patients, and ROC curve was used to analyze its effect as a biomarker for early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.
ResultsCirc_0001946 was highly expressed in pancreatic cancer tissues and serum (all P < 0.0001). Circ_0001946 was significantly associated with vascular thrombosis, lymphatic metastasis, CA199 expression and disease stage (all P < 0.05). Serum Circ_0001946 expression was positively correlated with AFP (r=0.765, P=0.000). The area under the ROC curve of Circ_0001946 as a serum marker for the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer was 0.805(95% CI:0.754-0.927, P=0.000). The overall survival and progressive-free survival of patients with high Circ_0001946 expression were significantly shorter than those with low Circ_0001946 expression (all P=0.000). Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses showed that disease stage, Circ_0001946 expression and vascular thrombus were independent prognostic factors for pancreatic cancer patients.
ConclusionCirc_0001946 is highly expressed in pancreatic cancer tissues and related to the prognosis of patients.
-
Key words:
- Circ_0001946 /
- Pancreatic cancer /
- Prognosis
-
0 引言
胰腺癌是一种消化系统常见恶性肿瘤,预后较差,其发病率和死亡率占全球常见癌症的第11位和第4位,5年生存率为5%~15%[1],是我国第十大常见癌症和第六大常见癌症相关死亡原因。我国胰腺癌患者的5年生存率仅为7.2%[2]。最新癌症统计数据显示,预计在2022年我国胰腺癌的发生率和死亡率将达到13.4万和13.1万[3],这主要是由于胰腺癌本身的强侵袭力、富血管包绕、浸润性生长、早期症状隐匿等特点,使得80%~90%的患者无法行手术治疗[4]。美国NCCN基于影像学检查结果提示肿瘤与其周围重要血管的关系及远处转移情况,根据肿瘤的可切除性,将其分为可切除、交界可切除和不可切除三种类型,其中不可切除胰腺癌包括局部进展期胰腺癌(locally advanced pancreatic cancer, LAPC)和合并远处转移[5]。NCCN指南将LAPC定义为胰腺癌侵犯肠系膜上动脉(SMA)或腹腔轴(CA)超过180°或累及肠系膜上静脉(SMV)或门静脉(PV)致使不可修复重建。虽然化疗或者化疗联合放疗是该类患者的一种选择性治疗方案,但反应率低,生存效益有限。近年来,热消融和非热消融技术已广泛应用,如射频消融、微波消融、高强度聚焦超声、冷冻消融、不可逆电穿孔和图像引导经皮消融[6],但由于大多数消融方式具有热损伤等不良反应,使其在临床应用受限。不可逆电穿孔(irreversible electroporation, IRE),又名为“纳米刀”,作为一种新兴的肿瘤局部消融技术,其原理主要是通过对肿瘤细胞实施瞬时、高频、反复的高电压脉冲引起肿瘤细胞膜不可逆性穿孔从而导致细胞凋亡,达到消融肿瘤的目的。其非热效应基础的特点使得IRE热损伤风险明显降低,相比于其他物理消融方法,IRE更适用于靠近或侵犯重要器官或管道结构的肿瘤治疗,如胰腺肿瘤,从而为局部进展期肿瘤的治疗提供新的思路[7]。IRE凭借其独特的优势成为临床上可以辅助或巩固肿瘤局部治疗的选择性手段,以提高LAPC患者的总生存期。更重要的是,IRE允许肿瘤周围的大血管保持完整,活化的抗原提呈细胞可以浸润病变,并将浸润的肿瘤碎片传递到淋巴结,从而激活适应性免疫系统[8]。本研究通过Meta分析对IRE联合新辅助化疗与单纯新辅助化疗治疗LAPC患者疗效比较的相关文献进行综合评价,分析联合治疗方案的安全性和有效性,为临床选择提供一定参考价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1 文献检索策略
检索PubMed、Embase、Cochrane Library、Web of Science、中国生物医学文献服务系统、知网、万方和维普等数据库从建库至2022年3月发表的关于IRE和新辅助化疗治疗LAPC患者的相关文献。采用自由词和主题词结合的方法检索。英文检索词有“pancreatic neoplasm*、pancreatic cancer*、pancreas neoplasm*、pancreas cancer*、Irreversible electroporation、Nano knife、Neoadjuvant chemotherapy*、Neoadjuvant Therapy*”。中文检索词“胰腺癌、胰腺肿瘤、胰腺恶性肿瘤、不可逆电穿孔、纳米刀、新辅助化疗”,并对纳入的参考文献进行补充检索。
1.2 选择标准
纳入标准:(1)研究对象:不可切除的局部进展期的胰腺癌患者,语种、种族、年龄及性别等不限;(2)干预措施:不可逆电穿孔或纳米刀消融术联合新辅助化疗;(3)对照组:单纯使用新辅助化疗药物治疗;(4)评估指标:总生存期(overall survival, OS)、疾病控制率(disease control rate, DCR)、疾病进展(progression disease, PD)、不良反应发生率等结局指标。
排除标准:(1)综述、会议摘要、信件、基础实验、案例报道(少于10例)、专家共识和指南以及其他不相关的文献;(2)干预措施不是以单纯新辅助化疗对比联合不可逆电穿孔的研究;(3)对于同一研究人群样本的多篇重复报道,只选择样本量最大、最新发表或报告数据最全面的研究;(4)研究指标与本研究评估指标不一致;(5)原文不规范或数据不全;(6)已发生远处转移的胰腺癌患者。
1.3 文献筛选、数据提取和质量评价
由两名评价者根据检索策略中纳入与排除标准独立筛选文献,确定最终纳入研究的文献。若出现意见不一致,则通过双方协商决定,或由第三名评价者与前两名评价者共同分析,得出最终结论。提取资料内容:(1)纳入研究的基本信息:研究作者及研究的类型,发表的年份和国家等;(2)研究对象的基本特征:研究的样本量,患者年龄、性别、肿瘤大小、肿瘤分期等;(3)干预措施:化疗方案及随访时间等;(4)结局指标:安全性结局指标和疗效性结局指标;(5)偏倚风险评价的关键要素。最终纳入的文献采用Cochrane偏倚风险评价工具[9],包括随机方法(选择偏倚)、分配隐藏(选择偏倚)、对研究者和受试者施盲(实施偏倚)、研究结果盲法评价(测量偏倚)、结局数据完整性(随访偏倚)、选择性报告研究结果(报告偏倚)和其他偏倚。
1.4 统计学方法
采用Review Manager 5.4软件进行数据分析。生存资料统计分析方法为倒方差法,使用OR和95%CI作为效应指标;DCR、PD及不良反应的发生率等数据类型皆为二分类变量,使用OR和95%CI作为效应指标。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。异质性检验方法采用Q检验和I2检验,设定值为P=0和I2=50%。若P > 0.1且I2≤50%,认为各研究间统计学异质性较小,采用固定效应模型进行分析;若P≤0.1或I2 > 50%,则认为各研究间存在统计学异质性较大,采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析。
2 结果
2.1 文献选择与基本特征
根据制定的检索策略,共检索到了427篇文献,剔除重复的115篇文献。通过浏览题目及摘要,剔除综述、病例报道、信件、会议摘要及其他无关文献258篇。对剩余的54篇文献进行全文阅读后,最终有8篇文献纳入Meta分析,见图 1。8项研究共计3 970例患者,其中联合组344例,单纯化疗组3 626例。纳入分析的文献基本特征及治疗策略见表 1。
表 1 纳入Meta分析的8篇文献基本特征Table 1 Basic characteristics of the eight articles included in the meta-analysis
2.2 偏倚风险评估
最终纳入的8项研究中,随机对照试验1项、回顾性研究4项和前瞻性研究3项。通过Revman5.4软件进行质量评估,见图 2。
2.3 Meta分析结果
2.3.1 疗效评价
所纳入的8篇文献均有对患者总生存期、疾病控制情况和疾病进展状况的研究,异质性检验提示各研究间存在异质性(P=0.009, I2=62%、P < 0.00001, I2=98%和P=0.003, I2=74%),故均采用随机效应模型进行荟萃分析。结果表明联合治疗组患者的总生存期明显高于单纯化疗组(OR=4.52, 95%CI: 2.63~7.77, P < 0.00001),见图 3A;但两组患者的疾病控制率(OR=0.58, 95%CI: 0.02~18.74, P=0.76)和疾病进展率(OR=0.49, 95%CI: 0.23~1.02, P=0.06)比较差异无统计学意义,见图 3B~C。
2.3.2 安全性评价
纳入的8篇文献中,6篇文献共511例患者是关于治疗期间发生相关不良反应的研究。其中发生胃肠道不良反应患者248例,发生骨髓抑制患者159例。异质性检验提示胃肠道不良反应和骨髓抑制在各研究间存在异质性,分别为(P=0.0001, I2=81%)和(P=0.04, I2=61%),故采用随机效应模型进行荟萃分析,结果表明两组患者胃肠道不良反应发生率(OR=0.37, 95%CI: 0.10~1.34, P=0.13)和骨髓抑制的发生率(OR=0.61, 95%CI: 0.26~1.40, P=0.24)差异均无统计学意义,见图 4。
![]() 图 4 不可逆电穿孔术联合新辅助化疗组对比单纯新辅助化疗组患者发生胃肠道反应和骨髓抑制等不良反应的Meta分析Figure 4 Meta-analysis results of adverse reactions, such as gastrointestinal reactions and bone marrow suppression, in patients who received irreversible electroporation combined with neoadjuvant chemotherapy compared with patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy alone
图 4 不可逆电穿孔术联合新辅助化疗组对比单纯新辅助化疗组患者发生胃肠道反应和骨髓抑制等不良反应的Meta分析Figure 4 Meta-analysis results of adverse reactions, such as gastrointestinal reactions and bone marrow suppression, in patients who received irreversible electroporation combined with neoadjuvant chemotherapy compared with patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy alone3 讨论
LAPC作为不可切除胰腺癌的一种,与合并远处转移的胰腺癌统称为晚期胰腺癌。如果缺乏有效的治疗,LAPC中位生存时间仅为4.6月,合并远处转移时总的中位生存时间为2.8~5.7月[18]。目前对于LAPC最主要的治疗方式仍然是转化治疗,尽管其临床疗效和潜在风险并未得到充分的证实。研究发现有20%~60%的LAPC患者在化疗后辅助局部治疗可获得更好的生存效益[19]。一项单中心、回顾性研究发现,对于边缘性可切除胰腺癌(borderline resectable pancreatic cancer, BRPC)和LAPC患者在新辅助化疗(neoadjuvant chemotherapy, NACT)后转换局部手术治疗,发现患者的中位OS(17.1月vs. 7.1月)和DFS(15.5~18.7 vs. 6.4~7.8月)明显优于单纯手术组。术后并发症发生率也有所下降(38% vs. 27%)。这表明对于BRPC和LAPC患者,NACT后的转化手术是一种可行而有效的治疗策略[20]。目前尚无最佳的转化治疗方案,而且,化疗药物的临床应用也受到患者健康状况的影响。对于体能状态差的患者,一般首选吉西他滨,次之氟尿嘧啶。而对于具有良好体能的患者,可选择AG方案(吉西他滨+白蛋白紫杉醇)、GS方案(吉西他滨+替吉奥)、FOLFIRINOX方案(氟尿嘧啶+奥沙利铂+亚叶酸钙+伊力替康)及其改良方案,如果伴有BRCA1/2或PALB2的突变,也可以考虑吉西他滨联合顺铂治疗[21]。
近年来,随着靶向治疗和免疫治疗的不断涌现,已被广泛应用于许多癌症中。但对于胰腺癌,有Meta分析显示,化疗联合免疫治疗组患者的DCR和PFS均高于单独化疗组(RR=1.17, 95%CI: 1.06~1.31; HR=0.87, 95%CI: 0.77~0.98),但由于样本量少,结果单一,其临床疗效仍不肯定[22]。因此,转化治疗仍是LAPC患者的首选治疗方案,通过化疗后的LAPC患者需要合适的局部治疗手段,以试图改善疾病的控制率及患者的总生存期。标准分级放疗、立体定向体部放疗、高强度聚焦超声和IRE是正在被研究的应用于临床的新型局部治疗手段[23-24]。其中IRE凭借其无热沉淀效应在众多消融术中脱颖而出,成为肿瘤患者的一种替代治疗手段,可与化疗、放化疗及免疫治疗联合应用,提高肿瘤患者的生存率[25]。针对转化治疗后手术时机的选择仍无定论,多建议在新辅助治疗后4~8周进行。Oikonomou等[26]的研究对40例Ⅲ期LAPC患者进行IRE联合新辅助治疗,结果发现LAPC患者的中位OS达到24.2个月,中位PFS达到10.3个月。同时He等[27]通过比较新辅助化疗联合IRE和转化切除治疗与单纯新辅助化疗治疗LAPC患者的疗效,发现切除组和IRE组患者的中位OS时间相似(25.3 vs. 26.0月,P < 0.05),明显长于化疗组(8.7月,P < 0.001)。此外,切除组和IRE组患者的中位PFS分别为10.6和12.0个月,且明显长于化疗组。尽管已有研究证实IRE在LAPC患者中的有效性,但其实用价值仍饱受争议。
本项Meta分析中的主要结局指标是OS,次要结局指标是DCR和PD,同时还分析了两种治疗方案所致的胃肠道反应和骨髓抑制等不良反应的发生。He等[10]研究发现联合治疗组LAPC患者的OS最长(24月vs. 7.1月),远高于程宇等[11]报道的结果(7.6月vs. 3.4月),其他的研究[12-17]也均报道了LAPC患者的总生存期。这与本研究结果一致,我们发现联合治疗组患者的总生存期明显高于单纯化疗组(OR=4.52, 95%CI: 2.63~7.77,P < 0.00001),但联合治疗组和单纯化疗组患者的疾病控制率和疾病进展差异无统计学意义。针对联合方案治疗后患者的不良反应情况,目前仍存在一定争议[11-12],本研究中的胃肠道反应主要包括恶心、呕吐、腹泻、乏力等,骨髓抑制主要是指白细胞减少。结果表明治疗后两组患者的胃肠道反应和骨髓抑制相比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),这与黄德良等[12]研究结果相似。
虽然对于错过最佳手术时机且对化疗方案不敏感的LAPC患者而言,采用IRE消融联合治疗已成为控制疾病进展的关键,但消融后残留的肿瘤会加重病变区域的局部复发,使肿瘤的生长速度更快、侵袭性更高,并有耐药的可能性。因此,完全破坏病变区域和消除残余是确保消融疗效的关键[28]。
本研究也存在一定的局限性:(1)本荟萃分析是基于8项研究和一个相对较少的样本量,所纳入的文献也并不都是高质量的随机对照试验研究;(2)同时由于纳入的文献篇数小于10篇,没有进行Egger偏倚检验,这可能导致一些潜在的发表偏倚;(3)由于纳入本研究的外科医生手术熟练度不同,手术结果可能存在差异,对Meta分析的结果造成一定的影响。未来需要进一步验证IRE联合治疗在LAPC患者中的安全性及有效性。
综上所述,IRE联合新辅助化疗在LAPC患者中的治疗和预后安全有效。与单纯化疗相比,该方案显著提高患者的总生存时间。特别是,IRE对特定解剖部位的LAPC具有独特的优势。我们希望随着内镜技术的发展和手术经验的积累,该技术适用于更多的患者。
作者贡献邓颖、白义凤:文章构思、撰写及数据统计杨兰、周晓刚:临床标本收集及部分分子生物学实验王林:大部分分子生物学实验 -
表 1 胰腺癌患者血清Circ_0001946的表达与临床病理特征的关系
Table 1 Correlation between Circ_0001946 expression and clinicopathological features of pancreatic cancer patients

表 2 Cox比例风险模型分析影响胰腺癌患者OS的临床病理因素
Table 2 Univariate and multivariate analyses of clinicopathological features for OS of pancreatic carcinoma patients

-
[1] Guo S, Xu X, Ouyang Y, et al. Microarray expression profile analysis of circular RNAs in pancreatic cancer[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 17(6):7661-7671. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2a4311dda7daf09d0ba5d91bd62c597b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[2] Zhu P, Ge N, Liu D, et al. Preliminary investigation of the function of hsa_circ_0006215 in pancreatic cancer[J]. Oncol Lett, 2018, 16(1):603-611. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29930719
[3] Zhang HD, Jiang LH, Sun DW, et al. CircRNA:a novel type of biomarker for cancer[J]. Breast Cancer, 2018, 25(1):1-7. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dyjydxxb201911009
[4] Wang Y, Liu J, Ma J, et al. Exosomal circRNAs:biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1041-z
[5] Li J, Yang J, Zhou P, et al. Circular RNAs in cancer:novel insights into origins, properties, functions and implications[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2015, 5(2):472-480. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=de06ab4039f96f0435f127f82873fd04&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[6] Wang X, Hamann MT. Marine natural products in the discovery and development of potential pancreatic cancer therapeutics[J]. Adv Cancer Res, 2019, 114:299-314. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_e8b5542da19dc11556c9257c0c811c3e
[7] Masoudi S, Hassanzadeh Nemati A, Fazli HR, et al. An increased level of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in patients with pancreatic cancer[J]. Middle East J Dig Dis, 2019, 11(1):38-44. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31049181
[8] Chen Y, Li C, Tan C, et al. Circular RNAs:a new frontier in the study of human diseases[J]. J Med Genet, 2016, 53(6):359-365. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2016-103758
[9] Liu L, Liu FB, Huang M, et al. Circular RNA ciRS-7 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of pancreatic cancer by regulating miR-7-mediated EGFR/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2019, pii:S1499-3872(19)30039-6. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gjgdybzz-z201906014
[10] Xu Y, Yao Y, Gao P, et al. Upregulated circular RNA circ_0030235 predicts unfavorable prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and facilitates cell progression by sponging miR-1253 and miR-1294[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2019, 509(1):138-142. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.088
[11] An Y, Cai H, Zhang Y, et al. circZMYM2 competed endogenously with miR-335-5p to regulate JMJD2C in pancreatic cancer[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 51(5):2224-2236. doi: 10.1159/000495868
[12] Qu S, Hao X, Song W, et al. Circular RNA circRHOT1 is upregulated and promotes cell proliferation and invasion in pancreatic cancer[J]. Epigenomics, 2019, 11(1):53-63. doi: 10.2217/epi-2018-0051
[13] Hao L, Rong W, Bai L, et al. Upregulated circular RNA circ_0007534 indicates an unfavorable prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion by sponging miR-625 and miR-892b[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(3):3780-3789. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30382592
[14] Li Z, Yanfang W, Li J, et al. Tumor-released exosomal circular RNA PDE8A promotes invasive growth via the miR-338/MACC1/MET pathway in pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Lett, 2018, 432:237-250. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.04.035
[15] Huang WJ, Wang Y, Liu S, et al. Retraction notice to "Silencing circular RNA hsa_circ_0000977 suppresses pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression by stimulating miR-874-3p and inhibiting PLK1 expression"[Cancer Letters 422C (2018) 70-80] [J]. Cancer Lett, 2018, 438:232. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.09.027




 下载:
下载: