Expression of Infiltrating NK Cell Surface Receptors in Peripheral Blood and Cancer Tissues of Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-
摘要:目的
分析食管鳞癌患者外周血及组织中NK细胞的比例及其表面受体的表达。
方法流式细胞仪检测食管鳞癌患者外周血及组织中NK细胞的比例及其表面受体的表达。
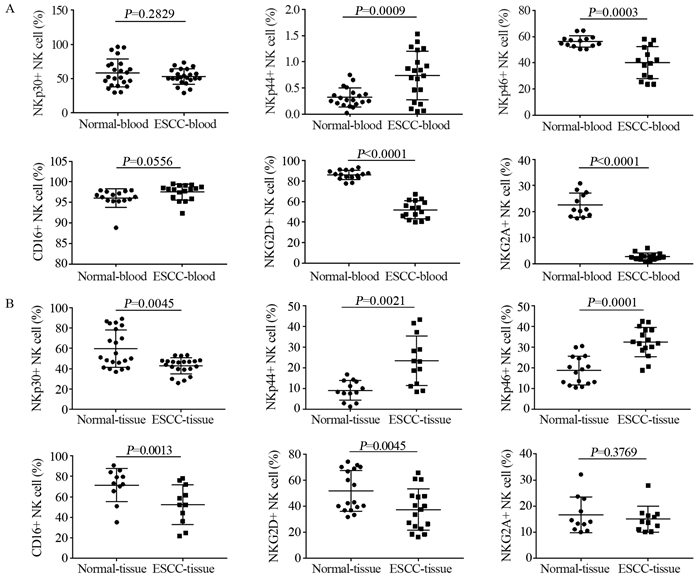
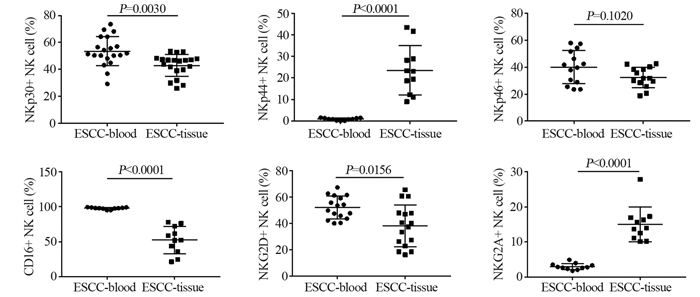
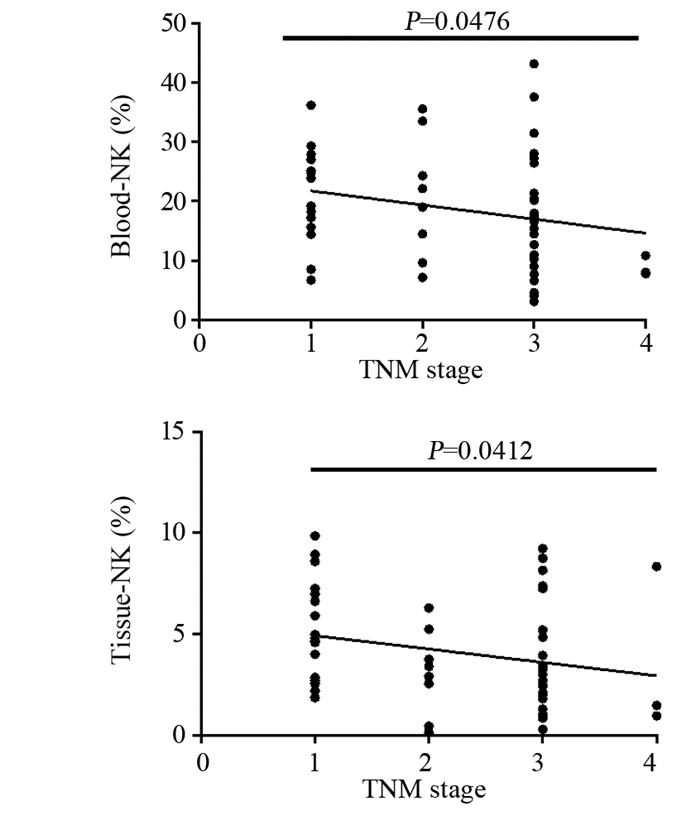
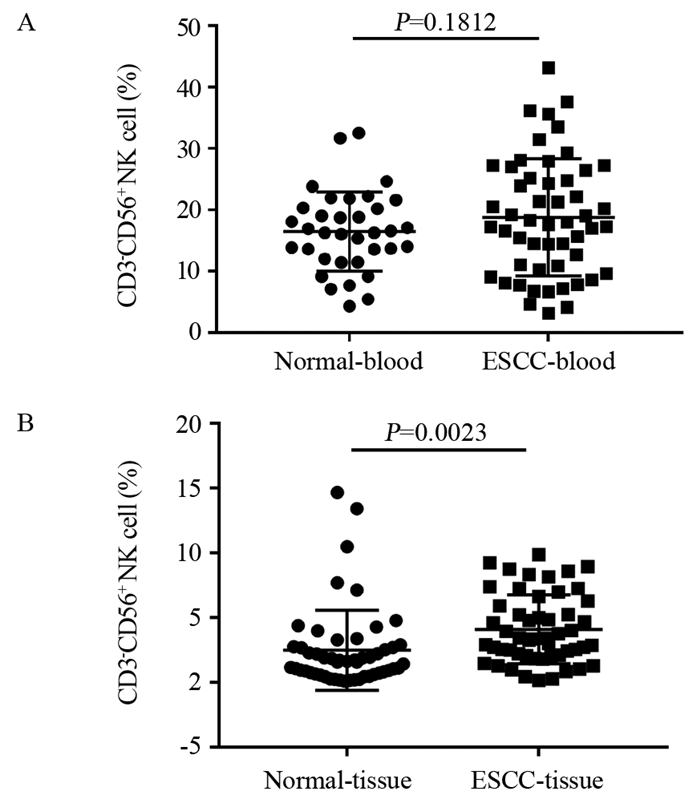
结果食管鳞癌组织中NK细胞比例明显高于癌旁5 cm以远的非肿瘤正常组织。CD16在食管鳞癌患者外周血中的表达与健康者外周血并无明显差异,但在鳞癌组织中的表达则明显低于正常组织;癌组织中NKp30、NKG2D的表达均明显低于正常组织;NKp44的表达明显高于正常组织。在同一患者体内,与外周血相比,癌组织中的CD16、NKp30、NKG2D的表达更低;而NKp44、NKG2A的表达更高。外周血与癌组织中浸润的NK细胞数量与肿瘤进展呈负相关。
结论食管鳞癌组织中NK细胞表面受体表达失衡可介导食管鳞癌细胞发生免疫逃逸。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo analyze the ratio and the surface receptor expression of natural killer (NK) cells in peripheral blood and cancer tissues of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients.
MethodsNK cell ratio and its surface receptor expression were detected by flow cytometry.
ResultsThe ratio of NK cells in ESCC tissues was significantly higher than that in normal tissues. The expression of CD16 in peripheral blood of ESCC patients was not significantly different from that of healthy controls, however, that in cancer tissues was significantly lower than that in normal tissues. The expression of NKp30 and NKG2D in cancer tissues were significantly lower than those in normal tissues. The expression of NKp44 was significantly higher than that in normal tissues. In the same patient, the expression of CD16, NKp30 and NKG2D in cancer tissues were significantly lower while the expression of NKp44 and NKG2A were higher than those in peripheral blood. The number of infiltrating NK cells both in peripheral blood and cancer tissues were negatively correlated with the progression of tumor.
ConclusionThe imbalance of NK cell surface receptor expression in ESCC tissues may mediate the immune escape of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
-
Key words:
- Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma /
- NK cells /
- Tumor immunity
-
0 引言
骨与软组织肉瘤是指发生在间叶系统的肿瘤,包括原发恶性骨肿瘤和软组织肉瘤两大类。原发恶性骨肿瘤和软组织肉瘤大约占成人恶性肿瘤的1%,占儿童恶性肿瘤的15%。骨肉瘤(35%)、软骨肉瘤(30%)和尤文肉瘤(16%)是最常见的三种原发恶性骨肿瘤。而软组织肉瘤则病理类型复杂,亚型有50余种,其中最常见的是未分化多型性肉瘤、脂肪肉瘤及平滑肌肉瘤等。
当今中国的肿瘤防治领域,普遍倡导以循证医学证据为基础,参考发达国家临床实践指南(如美国NCCN指南),制订适合我国国情和患者特点的临床诊疗指南,以实现肿瘤诊疗的规范化、科学化和可持续化。本文旨在对国际和国内骨与软组织肉瘤研究进展进行更新和述评,以推动肉瘤的学科建设,更好的服务于临床。
1 国际、国内骨与软组织肉瘤研究现状与进展
1.1 骨肉瘤
骨肉瘤的MAP(甲氨蝶呤+多柔比星+顺铂)化疗仍然是治疗的基石,通常在手术后3周内开始,研究表明延迟时间超过3周会增加复发风险,特别是对于新辅助化疗后未达到高水平坏死率的患者。标准化疗方案应包括29周内多个MAP周期,以达到标准化疗的总累积剂量[1]:甲氨蝶呤144 g/m2,多柔比星450 mg/m2,顺铂480 mg/m2。为避免甲氨蝶呤的长期肾毒性作用,有研究显示使用大剂量异环磷酰胺代替甲氨蝶呤得到了类似的预后[2-3],也有研究通过将右雷佐生作为心脏保护剂纳入多种方案,以最大限度地减少阿霉素对骨肉瘤患者长期的心脏毒性作用[4]。
一项欧洲和美国合作组联合进行的Euramos-1研究结果证明[5],对于新辅助化疗后组织学反应差的患者,强化化疗方案并不能改善其预后,并进一步强调了骨肉瘤转化研究的迫切需要,包括对所有肿瘤样本进行广泛测序和免疫表型分析,以确定新的治疗靶点。
有学者发现就诊时症状持续时间与年龄之间存在着显著的关系,年龄每增加1岁对应的症状持续时间增加1.3周,而症状持续时间与肿瘤大小并无显著关联性。尽管症状持续时间存在回忆偏差,但该研究提出了一个观点,即生物学等其他因素似乎比症状持续时间对预后的影响更为显著[6]。
1.2 尤文肉瘤
在388例非转移性尤文肉瘤患者的治疗分析中,Albergo等[7]发现辅助放疗显著降低了边缘切除肿瘤的局部复发风险(5年局部无复发生存率放疗组为96%,未放疗组为81%),四肢发病组较中轴骨发病组差异更显著。放射治疗并未显著影响广泛切除患者的局部复发率。这项研究强调了广泛切除的价值,同时也肯定了未实现广泛切缘时辅助放疗的价值。
Thévenin-Lemoine等[8]比较化疗前后20例长骨尤文肉瘤的磁共振成像扫描结果和病理标本,以判断其在描述肿瘤范围方面的准确性。化疗后MRI最准确,与病理标本的中位数差异为5.0 mm(2.0~13.0 mm)。化疗前MRI与病理标本的中位数差异为19.0 mm(4.3~38.2 mm)。T1加权是最准确的磁共振序列,加强序列并未提高准确性。笔者得出结论,根据化疗后的T1 MRI序列,给予20 mm的切除边界能获得大概率的阴性切缘。
1.3 软组织肉瘤
分析来自两个前瞻性试验的数据,Ferrari等[9]分析了60例年龄小于21岁的低危滑膜肉瘤患者,其中FNCLCC 3级滑膜肉瘤≤5 cm(8例),2级滑膜肉瘤为任意大小(52例); 其中仅8%的患者术前接受活检,68%的患者在初次病理回报后接受了再次切除,54%的再切除标本中残存有肿瘤,所有患者的最终手术切缘为阴性,中位随访5.2年,患者生存率100%。8例患者有局部复发,接受了再次手术治疗及辅助治疗。在此低风险人群组中没有发现转移病例。
在软组织肉瘤的检查中,淋巴结转移并不常见。Jacobs等[10]在美国国家癌症研究所监测、流行病学和SEER数据库中对15 525例软组织肉瘤患者进行了回顾,结果显示5.3%的患者诊断为淋巴结转移。横纹肌肉瘤、透明细胞肉瘤、上皮样肉瘤和圆形细胞脂肪肉瘤最常发生淋巴结转移。以往滑膜肉瘤通常被认为属于淋巴结转移的高风险组。然而在这项分析中,滑膜肉瘤(885例患者)的淋巴结受累风险不高于整个软组织肉瘤组。
1.4 肉瘤随访
对500例非转移性四肢肉瘤进行随机对照试验,每隔3月或6月对肺部进行CT或胸片随访,随访时间为60~118月。结果显示,在辐射强度较低和随访间隔较长的情况下,生存率并无显著降低。CT扫描发现转移性疾病明显早于胸片,但提前发现微小病灶并未能显著改善患者的生存率,这也是当前转移性肉瘤治疗面临的挑战[11]。
1.5 靶向治疗
意大利肉瘤协作组报道了一项关于索拉非尼联合依维莫司治疗无法切除的骨肉瘤的Ⅱ期研究。在该研究中,38名患者每天一次接受800 mg索拉非尼加5 mg依维莫司,直至疾病进展或不可接受的毒性作用。该研究显示,38名患者中有17名(45%)在6月时无进展[12]。Gounder等[13]应用索拉非尼治疗硬纤维瘤的Ⅲ期研究中,索拉非尼治疗患者的无进展生存期显著改善。
瑞戈非尼(Regorafenib)是一种针对肿瘤细胞、血管系统、血管生成和肿瘤微环境的多激酶抑制剂,通过阻断几种蛋白激酶的活性,包括参与血管生成调节(VEGFR-1、VEGFR-2、VEGFR-3和TIE2)、肿瘤发生(KIT,RET,RAF-1,BRAF和BRAFV600E)和肿瘤微环境(PDGFR和FGFR)发挥作用[14]。在一项对转移性骨肉瘤患者的Ⅱ期研究中,26名接受瑞戈非尼治疗的患者中,有17名在8周时无进展,而安慰剂组则均出现进展[15]。
Cabozantinib是多种酪氨酸激酶的小分子抑制剂,包括MET、VEGF2、RET和AXL等。Cabozantinib于2012年被FDA批准用于转移性甲状腺癌和晚期肾细胞癌患者。一项包含有41例难治性或复发性实体瘤的Cabozantinib的Ⅰ期研究中,4例患者包括2例甲状腺髓样癌、1例Wilms肿瘤和1例透明细胞肉瘤达到部分缓解,7例患者包括2例甲状腺髓样癌、1例尤文氏肉瘤、1例滑膜肉瘤、1例ASPS、1例副神经节瘤和1个室管膜瘤显示疾病稳定[16]。
TRC105(Carotuximab)是内皮素的单克隆抗体,内皮素是血管肉瘤中增殖内皮细胞和肿瘤细胞高度表达的重要血管生成靶点。TRC105在临床前模型中能够抑制血管生成、肿瘤生长和转移,并补充多激酶VEGFRI的活性[17-18]。目前,TRC105联合帕唑帕尼的疗效和安全性已在晚期血管肉瘤患者的Ⅲ期研究中得到评估[19]。
神经营养素原肌球蛋白受体激酶TRKs由神经营养受体酪氨酸激酶(NTRK)基因编码。TRK在神经生物学中起着不同的作用,但也与一组涉及TRK基因融合的肿瘤发病机制有关。TRK融合在多种恶性肿瘤中都有报道[20]。Larotrectinib是TRK的选择性抑制剂,在TRK融合恶性肿瘤中具有显著活性[21]。在TRK融合肉瘤患者Larotroctinib的Ⅰ/Ⅱ期研究中,5名患者都有部分缓解[22]。此外,3名患者达到完全(2名患者)或接近完全(1名患者)的病理缓解。这些结果表明,Larotroctinib可能是目前针对TRK融合肉瘤患者的一种治疗方法,其疗效和安全性需要进一步的临床研究来评估。
艾日布林(Eribulin)是一种软海藻素B的合成类似物,它通过β-微管蛋白上的特异性结合位点抑制微管聚合,具有基于微管蛋白的抗有丝分裂作用,并通过阻止细胞在G2期和M期的生长而破坏有丝分裂纺锤体的形成[23-24]。EORTC/STBSG对患有复发或转移性软组织肉瘤的患者进行了一项关于艾日布林的Ⅱ期研究[25],该研究中,平滑肌肉瘤患者12周时无进展生存率为32%,脂肪肉瘤患者为47%,滑膜肉瘤患者为21%,其他肉瘤患者为19%。Kawai等也报道了一项关于艾日布林治疗晚期软组织肉瘤患者的Ⅱ期研究[26]。在这项研究中,51名患者在第1天和第8天接受了甲磺酸艾日布林(1.4 mg/m2)静脉注射治疗,每21天为1周期。脂肪肉瘤/平滑肌肉瘤患者无进展生存期为5.5月,其他肉瘤患者为2.0月。与帕唑帕尼和曲贝替定相比,只有艾日布林能显著提高晚期肉瘤患者的总生存率。这些研究表明,艾日布林是晚期肉瘤患者的治疗选择之一,尤其是脂肪肉瘤和平滑肌肉瘤患者。然而,需要进一步研究分析艾日布林在肉瘤各亚型中的作用[24]。
1.6 免疫治疗
最近的基础和临床研究已经证实了免疫检查点与恶性肿瘤进展的关系,以及免疫检查点抑制剂对各种恶性肿瘤的疗效[27-29]。但免疫检查点抑制剂在肉瘤治疗中的应用仍需要基础和临床研究来证实。然而,由于免疫检查点阻断激活免疫系统,很可能发生免疫相关的不良事件[28]。免疫相关不良事件,包括免疫检查点抑制剂的炎性反应等不良反应,可影响胃肠道、内分泌腺、皮肤、肝脏和中枢神经、心血管、肺、肌肉骨骼和血液系统。尽管大多数免疫相关的不良事件是可逆的,但其中一部分事件可能是永久性的,并可能导致死亡。
程序性细胞死亡1(PD-1)受体与程序性死亡配体1(PD-L1)的结合是免疫系统介导恶性肿瘤逃逸的关键机制。在一项荟萃分析研究中,PD-L1的表达与骨肉瘤(骨肉瘤和软骨肉瘤)患者的总生存率和骨软组织肉瘤患者的无事件生存率显著相关[30]。在另一项荟萃分析研究中,PD-L1/PD-1的过度表达与骨肉瘤患者的转移显著相关,但PD-1/PD-L1的表达与总生存率没有显著相关性[31]。同样,对于尤文肉瘤的一项研究表明,转移性肿瘤的PD-L1表达较高,但PD-L1表达与无进展生存率或总生存率之间也没有显著相关性[32]。这些研究表明,免疫检查点可以作为肉瘤的治疗靶点。
最近的一些临床研究报道了免疫检查点抑制剂用于肉瘤治疗的结果[33-37]。2017年,Tawbi等报道了抗PD-1抗体Pembrolizumab的单臂Ⅱ期研究[36]。在这项研究中,Pembrolizumab的活性和安全性在80名晚期骨和软组织肉瘤患者中进行了评估:在40例软组织肉瘤患者中,7名患者(18%)表现出客观缓解,分别为4例未分化多形性肉瘤、2例脂肪肉瘤和1例滑膜肉瘤; 在40例骨恶性肿瘤患者中,1例骨肉瘤及1例软骨肉瘤表现出客观缓解。80例患者中有9例(11%)治疗后出现严重不良事件(SAE),其中观测到的免疫相关性SAE包括肾上腺皮质功能不全(2%)、肺炎(2%)和肾炎(1%)。2018年,Toulmonde等报道了一项针对晚期软组织肉瘤患者的PembrolizumabⅡ期研究[37]。在这项研究中,平滑肌肉瘤和未分化多形性肉瘤患者的6月无进展率为0,其他肉瘤患者为14.3%。
尽管使用免疫检查点抑制剂的单药治疗在之前的报告中显示效果有限,但联合治疗(如CTLA-4抑制剂和PD-1抑制剂)的研究表明联合治疗在黑色素瘤小鼠模型中具有协同作用[38]。D'Angelo等报告了一项关于转移性肉瘤患者使用Nivolumab、联合或不联合Ipilumab的Ⅱ期研究[39]。在该研究中,85例转移性肉瘤患者接受了Nivolumab单药疗法(3 mg/kg)或Nivolumab和Ipilimumab(1 mg/kg)的联合治疗。Nivolumab单药治疗的患者有效率为5%(2/38),而Nivolumab和Ipilimumab联合治疗的患者有效率为16%(6/38)。该研究提示联合免疫检测点抑制是治疗肉瘤的一种有前途的方法,需要进一步的临床研究来评估其疗效和不良事件。此外,迫切需要寻找可以预测免疫治疗疗效的分子标志物[40]。
2 存在的问题
近年来,我国骨与软组织肉瘤的整体治疗水平已有了明显提升,多项治疗技术已达到国际先进水平,我国学者也在逐步奠定我国在国际骨与软组织肉瘤治疗领域的学术地位。但是,与国际一流的骨与软组织肿瘤中心相比,仍然存在明显不足,在病因研究、系统诊疗、规范治疗和多学科合作诊治等方面还存在差距。
骨与软组织肉瘤的发病原因和发病机制至今尚未被完全阐明,细胞遗传学的相关研究表明,骨与软组织肉瘤细胞的染色体多发生突变,但是其突变模式以及部位多不固定。针对骨与软组织肉瘤预后不佳的问题,有研究者开始关注其基因分子水平的变化,尝试通过基因测序、化疗药物筛选等个体化诊疗手段来提高高危肉瘤患者治疗效果,但上述研究在国内尚属起步阶段,目前还没有充分的证据说明患者是获益的。
近30年来,骨肉瘤患者的生存率一直未能得到明显提升。目前,我国主要的骨肿瘤中心虽然在一线化疗药物的选择上趋于一致,但其用法用量以及所使用的疗程都存在较大的差异,没有形成统一的标准,这种单中心的经验化临床治疗干扰了化疗效果的整体评价。
此外,还有一些治疗方法正处于研究阶段,比如基因治疗、免疫治疗、干细胞治疗和光动力治疗等。然而,在国内,上述辅助治疗方法多以单中心临床试验为主,主要针对的是常规治疗效果不理想、已有复发或转移以及特殊部位难以手术切除的患者。这种患者治疗上的特殊性及辅助方法的多样化严重影响了不同辅助治疗效果的评价。
3 解决方案与建议
在骨与软组织肿瘤领域,目前积极倡导MDT(多学科联合诊疗模式),发挥各学科优势、取长补短; 积极鼓励和支持各学组开展学术交流,在适度控制数量、保证质量的前提下统筹管理、整合资源,鼓励和支持各学组自主或联合开展学术活动,切实使学术交流成为“百花齐放、百家争鸣”的学术平台; 积极培养青年医师、复合型人才,为全国肉瘤事业补充新鲜血液,注入新的活力,不断推动肉瘤学科的持续发展; 积极加强继续教育工作,发挥专委会资源优势,加强继续医学教育工作,以点带面推进骨与软组织肉瘤治疗临床路径或共识在全国医疗机构开展,使其更加规范化、合理化和制度化,制订适合我国国情和患者特点的临床诊疗指南。
此外,亟须探寻适合我国的骨与软组织肉瘤诊断与治疗的新途径,积极开展创新技术和方法的临床转化研究,但不能生搬硬套国外的经验和其他病种治疗经验,要针对骨与软组织肉瘤的特点认真组织讨论研究方案,确定新技术准入标准,力争开展多中心随机对照研究,在确保安全的前提下,提高治疗的有效性,同时不可随意增加患者的治疗成本。
随着骨与软组织肉瘤诊疗技术的提高,借助基因组学等方法对骨与软组织肉瘤发病机制的深入研究,今后我国在骨与软组织肉瘤治疗上必将呈现精细化和个体化治疗的特点。对化疗、放疗、手术、靶向和免疫治疗等各种治疗的精细化选择,必将使骨与软组织肉瘤患者获益。
作者贡献王超:标本收集、单细胞悬液研磨与采集、数据收集、整理、分析及论文书写杨晓燕、高凤霞:标本收集与单细胞悬液研磨与采集吴剑、戴天阳:指导课题、实验设计、论文书写指导 -
表 1 NK细胞表面受体的表达结果
Table 1 Expression of NK cells surface receptors

表 2 同一食管鳞癌患者外周血和癌组织NK细胞表面受体的表达
Table 2 Comparison of NK cells surface receptor expression in peripheral blood and cancer tissues of the same patient

-
[1] Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics, 2012[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2015, 65(2): 87-108. doi: 10.3322/caac.21262
[2] Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(2): 115-132. doi: 10.3322/caac.21338
[3] Pasquali S, Yim G, Vohra RS, et al. Survival after neoadjuvant and adjuvant treatments compared to surgery alone for resectable esophageal carcinoma: a network meta-analysis[J]. Ann Surg, 2017, 265(3): 481-491. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001905
[4] Artis D, Spits H. The biology of innate lymphoid cells[J]. Nature, 2015, 517(7534): 293-301. doi: 10.1038/nature14189
[5] Lee HH, Kang H, Cho H. Natural killer cells and tumor metastasis[J]. Arch Pharm Res, 2017, 40(9): 1037-1049. doi: 10.1007/s12272-017-0951-9
[6] 刘方方, 谢军平.肿瘤微环境中免疫细胞与肿瘤逃逸[J].医学分子生物学杂志, 2015(1): 21-25. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1672-8009.2015.01.005 Liu FF, Xie JP. Immune cells in tumor microenvironment and tumor immune escape[J]. Yi Xue Fen Zi Sheng Wu Xue Za Zhi, 2015(1): 21-25. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1672-8009.2015.01.005
[7] 吴姗姗.小细胞和非小细胞肺癌晚期患者NK细胞表达的差异[J].中国免疫学杂志, 2015, 31(2): 250-252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2015.02.025 Wu SS. Different expression of NK cells in patients with advanced small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Zhongguo Main Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2015, 31(2): 250-252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2015.02.025
[8] 汪茜茜, 毛朝明, 陈德玉.食管鳞癌患者外周血NK细胞、γδ T细胞变化的临床意义[J].山东医药, 2011, 51(45): 39-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2011.45.022 Wang QQ, Mao CM, Chen DY. Clinical significance of NK cells and γ δ T cells changes in peripheral blood of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Shandong Yi Yao, 2011, 51(45): 39-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2011.45.022
[9] 刘启胜, 杨志花, 卢学兵, 等.食管癌患者NK细胞和T淋巴细胞免疫功能的检测及临床意义[J].现代消化及介入诊疗, 2016, 21(1): 1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2159.2016.01.001 Liu QS, Yang ZH, Lu XB, et al. Detection and clinical significance of NK cells and T lymphocytes immune function in the patients with esophageal cancer[J]. Xian Dai Xiao Hua Ji Jie Ru Zhen Liao, 2016, 21(1): 1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2159.2016.01.001
[10] Cassetta L, Pollard JW. Cancer immunosurveillance: role of patrolling monocytes[J]. Cell Res, 2016, 26(1): 3-4. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26634605
[11] 徐斌, 陈陆俊, 邓海峰, 等. CD57+自然杀伤细胞及CD68+巨噬细胞浸润密度对食管癌患者预后的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2016, 33(4): 1117-1121. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9030.2016.04.076 Xu B, Chen LJ, Deng HF, et al. Different density of CD57+ tumor-infiltrating natural killer cells and CD68+ tumor-infiltrating macrophages associated with the prognosis in patients with esophagus cancer[J]. Zhonghua Shi Yan Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2016, 33(4): 1117-1121. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9030.2016.04.076
[12] Izawa S, Kono K, Mimura K, et al. H2O2 production within tumor microenvironment inversely correlated with infiltration of CD56dim NK cells in gastric and esophageal cancer: possible mechanisms of NK cell dysfunction[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2011, 60(12): 1801-1810. doi: 10.1007/s00262-011-1082-7
[13] Muntasell A, Ochoa MC, Cordeiro L, et al. Targeting NK-cell checkpoints for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Curr Opin Immunol, 2017, 45: 73-81. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2017.01.003
[14] Pazina T, Shemesh A, Brusilovsky M, et al. Regulation of the functions of natural cytotoxicity receptors by interactions with diverse ligands and alterations in splice variant expression[J]. Front Immunol, 2017, 8: 369. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5371597/
[15] Schmohl JU, Felices M, Taras E, et al. Enhanced ADCC and NK Cell Activation of an Anticarcinoma Bispecific Antibody by Genetic Insertion of a Modified IL-15 Cross-linker[J]. Mol Ther, 2016, 24(7): 1312-1322. doi: 10.1038/mt.2016.88
[16] Lanier LL. NKG2D receptor and its ligands in host defense[J]. Cancer Immunol Res, 2015, 3(6): 575-582. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0098
[17] Kaur G, Trowsdale J, Fugger L. Natural killer cells and their receptors in multiple sclerosis[J]. Brain, 2013, 136(9): 2657-2676. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws159
[18] Melsen JE, Lugthart G, Lankester AC, et al. Human circulating and tissue-resident CD56(bright) natural killer cell populations[J]. Front Immunol, 2016, (7): 262. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4927633/
[19] Carrega P, Bonaccorsi I, Di Carlo E, et al. CD56(bright)perforin(low) noncytotoxic human NK cells are abundant in both healthy and neoplastic solid tissues and recirculate to secondary lymphoid organs via afferent lymph[J]. J Immunol, 2014, 192(8): 3805-3815. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301889
[20] Béziat V, Descours B, Parizot C, et al. NK cell terminal differentiation: correlated stepwise decrease of NKG2A and acquisition of KIRs[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(8): e11966. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011966
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 候博,陈挺,商冠宁. 负压封闭引流技术在骨与软组织肿瘤高危切口中的应用. 中国医师进修杂志. 2023(04): 301-305 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 单静,吕苏梅,李海红,刘伟. 思维导图联合回授法健康教育模式在骨与软组织肿瘤病人胸壁输液港护理中的应用. 循证护理. 2023(13): 2381-2385 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 冯颖颖,赵思,宗园. 超声造影与MRI-DWI对良恶性软组织肿瘤的诊断效能比较. 中国医药导报. 2023(25): 160-163 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 赵玲玲,张晓娟,郭倩,陈平,贾莉. 恶性骨肿瘤患者疾病感知现状及其影响因素分析. 护理实践与研究. 2023(24): 3657-3663 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王默然,王峻,李星晨,刘浩,葛艳玲. 原发性恶性骨肉瘤术中输血影响因素的回顾性研究. 中国输血杂志. 2022(01): 35-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. Yi-Ting Zhou,Ruo-Yu Wang,Yao Zhang,Dong-Yi Li,Jian Yu. Local hyperthermia combined with chemotherapy for the treatment of multiple recurrences of undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma: A case report. World Journal of Clinical Cases. 2022(09): 2916-2922 .  必应学术
必应学术
7. 方菲,原浩,韦燕. 调强放射治疗联合安罗替尼治疗转移性四肢软组织肉瘤的临床观察. 中国现代医药杂志. 2022(06): 57-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 李善武,叶永杰,王志强,银毅,孙官军. 高强度聚焦超声治疗恶性骨肿瘤的研究进展. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版). 2021(02): 231-234 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 徐婉琳,李柳宁. 李柳宁教授从虚痰瘀论治软组织肉瘤思想探析. 四川中医. 2021(10): 1-4 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 孙全球,夏国仁,詹守山,姜世峰,付宇,储彬,段瑾. 3D可视化技术在骨与软组织肿瘤个体化精准治疗中的临床应用及探索. 中国基层医药. 2021(12): 1861-1865 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 吴昕,刘家明,宋宏海,杨起坤,应辉,刘志礼. 抑制Aurora激酶B的表达可促进骨肉瘤143B细胞凋亡. 南方医科大学学报. 2020(09): 1273-1279 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 祝开忠,王挺锐,陈焕雄,陈涛,钟贞浩. 骨肉瘤中O-GlcNAc糖基转移酶的表达及其对增殖和顺铂敏感性的影响. 中国癌症杂志. 2020(09): 682-688 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)



 下载:
下载: