Effects of Long Non-coding RNA-MALAT1 on Proliferation and Apoptosis of Prostate Cancer Cells
-
摘要:目的
探讨长链非编码RNA-MALAT1对激素依赖性前列腺癌细胞增殖与凋亡的影响及其作用机制。
方法以激素依赖性前列腺癌细胞PC3和LNCaP为研究对象,对细胞进行MALAT1过表达及干扰处理,并通过MTT、流式细胞仪、基质胶和平板克隆等方法检测MALAT1过表达或干扰对细胞生物学行为的影响。Western blot检测MALAT1对与细胞周期及凋亡相关蛋白Cyclin D1、Bcl-2、Bax及p-ERK1/2表达的影响。
结果与对照组比较,MALAT1组细胞的增殖能力明显增强(P < 0.01),克隆形成能力、血管生成能力增强,G0/G1期细胞数量增多,凋亡率降低;si-MALAT1组细胞增殖能力明显低于对照组(P < 0.01),克隆形成能力、血管生成能力减弱,G0/G1期细胞数量减少,凋亡率升高。
结论MALAT1对前列腺癌的发生发展有促进作用,抑制MALAT1表达可能对前列腺癌的治疗具有重要意义。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the effect of long non-coding RNA-MALAT1 on the proliferation and apoptosis of hormone-dependent prostate cancer cells and possible mechanisms.
MethodsMALAT1 overexpression and interference treatment were performed in the hormone-dependent prostate cancer PC3 and LNCaP cell lines. MTT assay, flow cytometry, Matrigel and clone formation were used to examine the effects of MALAT1 overexpression and interference on cell biological behavior. Western blot was used to evaluate the effects of MALAT1 on the expression of Cyclin D1, Bcl-2, Bax and p-ERK1/2.
ResultsCompared with control group, MALAT1 group cells showed enhanced abilities of proliferation (P < 0.01), clone formation and angiogenesis; the cells number in the G0/G1 phase was increased; the apoptotic rate was decreased. In contrast, the cells in si-MALAT1 group showed significantly lower proliferation ability compared with control group (P < 0.01); the abilities of clone formation and angiogenesis were reduced; the number of cells in the G0/G1 phase was decreased, while apoptotic rate was increased.
ConclusionMALAT1 promotes the occurrence and development of prostate cancer. The inhibition of MALAT1 expression may play important roles in the treatment of prostate cancer.
-
Key words:
- Long non-coding RNA /
- MALAT1 /
- Prostate cancer /
- Cell proliferation /
- Cell apoptosis
-
0 引言
前列腺癌(prostate cancer, PCa)是男性泌尿生殖系统发病率较高的恶性肿瘤之一,近年来我国前列腺癌发病率呈上升趋势[1]。因此,研究前列腺癌的致癌机制,开发新的研究方法,对挽救前列腺癌患者的生命具有重大意义。随着二代测序技术的发展,大量对长链非编码RNA(long non-coding RNA, lncRNA)的深入研究结果发现一些异常表达的lncRNA与肿瘤的发生与发展有关[2-4]。
肺腺癌转移相关转录子1(metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1, MALAT1)属于lncRNA中的一种,研究发现,MALAT1的表达与癌细胞的增殖、转移、成瘤率及血管生成密切相关[5]。本研究以激素依赖性的前列腺癌细胞株PC3、LNCaP为对象,构建MALAT1过表达及干扰模型,通过对MALAT1过表达(或干扰后)前列腺癌细胞生物学行为变化的检测,探讨MALAT1在前列腺癌增殖中的作用机制,为研究前列腺癌发生发展机制奠定一定的基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
激素依赖性前列腺癌细胞株PC3和LNCaP(武汉华联科生物技术有限公司,中国武汉);载体pCDH、pSICOR(Addgene,美国);RPMI 1640培养基(HyClone,美国);胎牛血清(Gibco,美国);TRIzol(Ambion,美国);YBR Green PCR试剂盒(KAPA Biosystems,美国);反转录试剂盒(TaKaRa,中国大连);PBS、胰蛋白酶、MTT、瑞氏-姬姆萨复合染液(Bioswamp,中国);细胞周期检测试剂盒、凋亡检测试剂盒(BD,美国);Matrigel(Corning,美国);兔抗人Cyclin D1单克隆抗体、兔抗人Bcl-2单克隆抗体、兔抗人Bax单克隆抗体及兔抗人ERK1/2单克隆抗体(Abcam,英国);兔抗人p-ERK1/2单克隆抗体(CST,美国)。
1.2 细胞复苏与培养
将冻存的PC3及LNCaP细胞从液氮罐中取出后,移至37℃水浴中,将细胞悬液吸至离心管中,1 000 r/min离心3 min,弃上清液,在含10%胎牛血清的新鲜RPMI 1640培养基中培养,并置于37℃、含体积分数为5%CO2的培养箱内。
1.3 构建MALAT1过表达及siRNA载体
为了探讨lncRNA-MALAT1对前列腺癌细胞增殖的作用机制,本研究构建了MALAT1过表达载体pCDH-MALAT1和干扰载体pSICOR-shMALAT1,以及起对照作用的过表达空载体和干扰空载体。MALAT1-siRNA序列:5’-TGTACTATCCCATCACTGAAG-3’。
1.4 荧光定量PCR检测MALAT1相对表达量
利用TRIzol提取PC3细胞的总RNA,反转录生成cDNA,进行Real-time PCR扩增。MALAT1扩增引物序列:上游引物:5’-CCGCTGCTATTAGAATGC-3’;下游引物:5’-CTTCAACAATCACTACTCCAA-3’。内参基因β-Actin上游引物:5’-ACACTGTGCCCATCTACG-3’;下游引物:5’-TGTCACGCACGATTTCC-3’。PCR反应条件:95℃ 3 min;95℃ 5 s;56℃ 10 s;72℃ 25 s,共39个循环。
1.5 MTT检测细胞增殖
取对数生长期细胞,调整浓度并分于96孔板,每种细胞设置3个复孔,37℃培养过夜。根据实验分组:(1)对照组(Control);(2)过表达空载体组(EV);(3)干扰空载体组(si-EV);(4)MALAT1过表达组(MALAT1);(5)MALAT1-siRNA干扰组(si-MALAT1),分组处理细胞,继续培养24、48和72 h。取出不同分组的细胞培养板,每孔加入20 μl MTT溶液(5 mg/ml),继续培养4 h。最后用酶联免疫检测仪测量各孔490 nm处的吸光度值。
1.6 流式细胞仪检测细胞周期及凋亡
收集胰酶消化处理后的不同细胞,PBS清洗两次以后,加入400 µl碘化丙啶(propidium iodide, PI)溶液(50 μg/ml),避光染核10 min,用流式细胞仪测定细胞含量,确定细胞在有丝分裂各个时期所占的比例。将细胞重悬于200 μl结合缓冲液中,并加入5 μl Annexin V-FITC和5 μl PI溶液,轻轻混匀,4℃避光孵育30 min。最后,加入300 μl缓冲液,随即用流式细胞仪检测各组细胞凋亡情况。
1.7 基质胶检测成管能力
在96孔板中加入50 μl Matrigel基质胶,在凝胶过程中,消化各组细胞并用PBS重悬,制备细胞悬液,加入100 μl细胞悬浮液。37℃孵育,14 h后观察细胞成管情况。
1.8 平板克隆检测细胞成瘤率
取对数生长期的细胞,胰蛋白酶消化处理后吹打成单个细胞,并培养于含10%胎牛血清的培养液中备用。将细胞梯度稀释,放置于37℃、5%CO2及饱和湿度的培养箱中培养2~3周。4%多聚甲醛固定细胞,加适量GIMSA染色液进行染色。
1.9 Western blot检测细胞周期及凋亡相关蛋白表达
本研究利用Western blot实验检测了Cyclin D1、Bcl-2、Bax及ERK1/2和p-ERK1/2蛋白的表达水平,实验过程如下:提取细胞蛋白并置于沸水浴中10 min,使蛋白变性。利用SDS-PAGE胶分离蛋白,电泳结束后湿转法将蛋白转印至PVDF膜上。5%脱脂奶粉室温封闭2 h,加入一抗室温孵育1 h,PBST洗膜3次,再加入二抗(1:10 000稀释HRP标记),室温孵育1 h。PBST洗涤三次后用ECL化学发光检测并拍照。
1.10 统计学方法
实验数据以平均值±标准差(x±s)表示,应用SPSS22.0软件对以上实验所获得的数据进行统计学分析,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,且P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
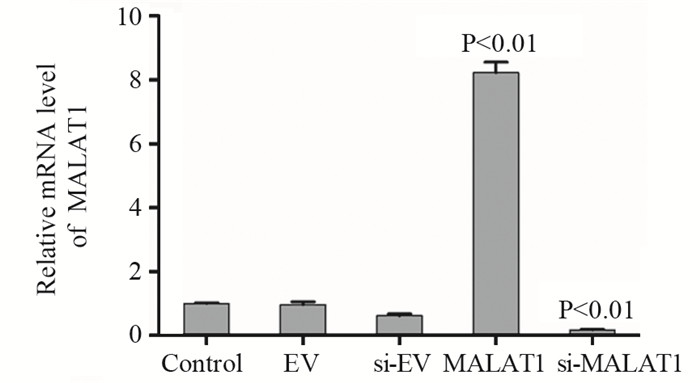
2.1 MALAT1在PC3中的相对表达量
荧光定量PCR检测前列腺癌细胞株PC3对照组、EV组、si-EV组、MALAT1组及si-MALAT1组中lncRNA-MALAT1的相对表达量。对照组与EV组、si-EV组的MALAT1相对表达量之间的差异无统计学意义;与对照组相比,MALAT1组中MALAT1表达量明显上调(P < 0.01),si-MALAT1组中MALAT1表达量明显下调(P < 0.01),说明MALAT1过表达和干扰细胞株构建成功,见图 1。
2.2 MALAT1对前列腺癌细胞体外增殖能力的影响
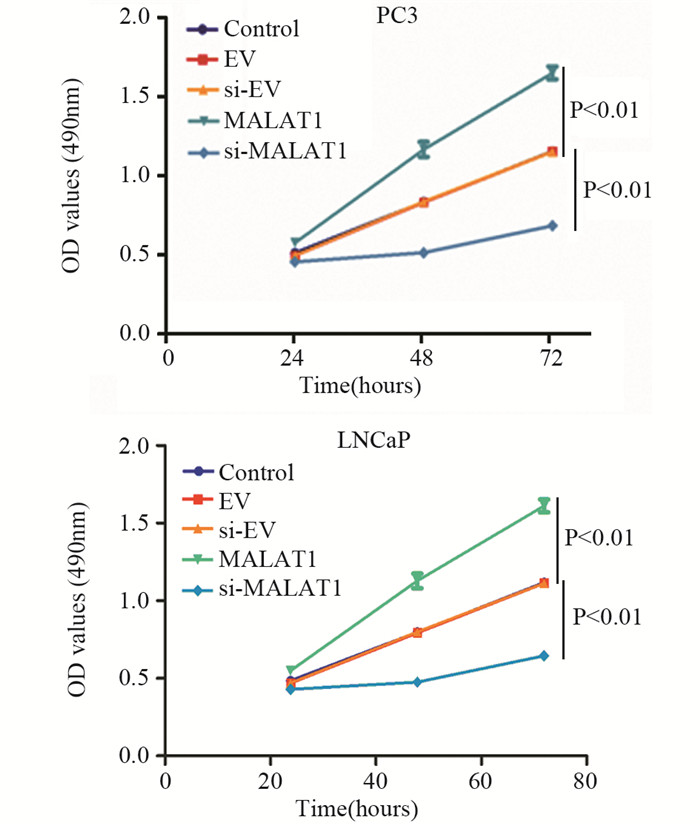
MTT检测了培养24、48及72 h的PC3和LNCaP细胞株的细胞增殖情况,描绘对照组和四组实验组细胞的生长曲线。结果显示,MALAT1组的前列腺癌细胞体外增殖能力明显高于对照组和EV组(P < 0.01);si-MALAT1组的前列腺癌细胞的增殖能力明显低于对照组和si-EV组(P < 0.01),见图 2。
2.3 MALAT1对前列腺癌细胞周期和凋亡的影响
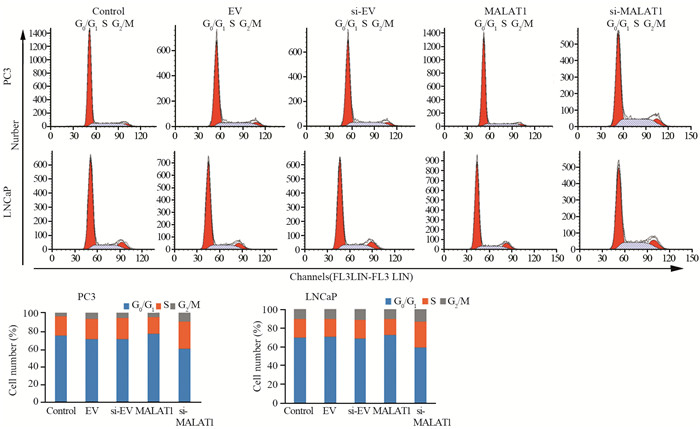
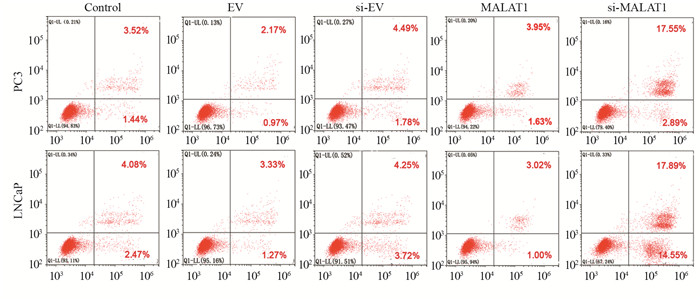
PC3和LNCaP细胞中MALAT1组处于静止期和DNA合成前期(G0/G1期)的细胞数量多于对照组,在DNA合成期(S期)的细胞少于对照组;si-MALAT1组处于G0/G1期的细胞数量少于对照组,而S期细胞多于对照组,见图 3。MALAT1组的细胞凋亡率与对照组细胞凋亡率相近;si-MALAT1组的细胞凋亡率高于对照组,见图 4。
2.4 MALAT1对前列腺癌细胞血管形成能力的影响
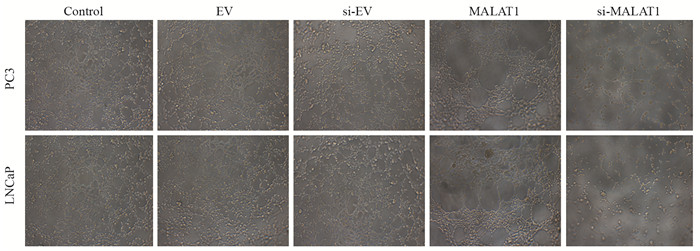
PC3、LNCaP细胞中,与对照组比较,MALAT1组细胞形成的管状结构更多,在主要的管状结构附近聚集的血管内皮层细胞也更多,更容易形成分支。而si-MALAT1组的内皮层细胞少,基本没有形成管状结构,见图 5。
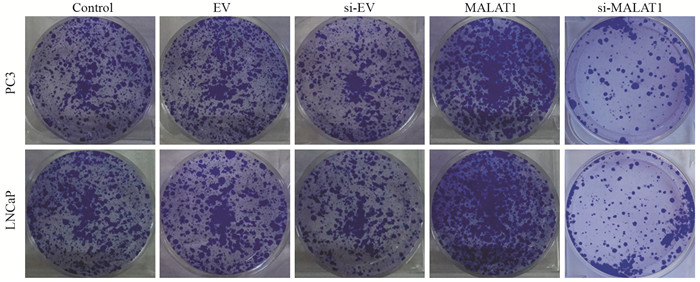
2.5 MALAT1对前列腺细胞克隆形成能力的影响
MALAT1组的PC3、LNCaP细胞的克隆数量明显多于对照组,说明MALAT1组细胞的克隆形成能力明显增强。si-MALAT1组的细胞数量明显少于对照组,克隆形成能力减弱,见图 6。
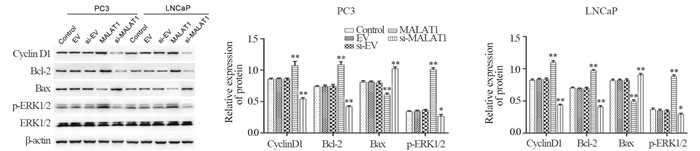
2.6 MALAT1对Cyclin D1、Bcl-2、Bax及p-ERK1/2蛋白表达的影响
与对照组相比,MALAT1组细胞中参与周期调控的Cyclin D1蛋白、抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2及磷酸化的细胞外信号调节激酶(p-ERK1/2)的表达水平显著升高(P < 0.01),而促凋亡蛋白Bax的表达水平明显降低(P < 0.01);si-MALAT1组的Cyclin D1、Bcl-2和p-ERK1/2蛋白表达水平显著降低(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),Bax表达水平升高(P < 0.01),见图 7。
3 讨论
前列腺癌的发病率随着生活质量的提高呈现上升趋势,对前列腺癌的发生和发展研究也随之增多。近些年研究发现lncRNA在前列腺癌的发生发展过程中扮演了重要的角色:Chung等研究发现PRNCR1(前列腺非编码RNA1)-siRNA会减弱前列腺癌细胞的生存、增殖能力和雄激素受体的活性,揭示PRNCR1通过影响雄激素受体活性参与前列腺癌的发生过程,为前列腺癌的发病机制提供了新的认识[6];lncRNA SOCS2-ASI可以促进前列腺癌细胞的生长、抑制凋亡,对前列腺癌的发生发展影响甚大[7];Liu等发现lncRNA-PVTI在前列腺癌发生过程中表达上调,进一步研究其影响机制,发现lncRNA-PVTI与miR-146a存在调控关系,过表达lncRNA-PVTI或沉默miR-146a,可明显提高前列腺癌细胞的活力,抑制细胞凋亡[8]。
MALAT1是一种致癌性的长链非编码RNA,参与癌细胞的增殖、转移等过程,在宫颈癌、结直肠癌、非小细胞肺癌以及食管鳞状细胞癌等癌细胞中都表达上调[9-12]。Cai等发现,MALAT1在人骨肉瘤细胞和组织中都表达上调,而敲除MALAT1显著抑制了骨肉瘤细胞的增殖和迁移,并诱导了细胞的周期阻滞和凋亡,这些结果表明MALAT1在骨肉瘤中有促癌的作用[13]。Ren等的研究表明MALAT1也参与了前列腺癌细胞的发展过程,发现MALATI-siRNA抑制了前列腺癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭,并在G0/G1期诱导周期阻滞,可作为去势抗性前列腺癌的潜在治疗靶点[14]。Cyclin D1是周期蛋白家族成员之一,细胞从G1期进入S期需要Cyclin/CDK进行调控[15]。本研究结果发现MALAT1过表达后细胞增殖能力增强,且促进了细胞从G0/G1期向S期转换,进一步检测周期蛋白Cyclin D1表达,显示MALAT1过表达组的Cyclin D1蛋白表达量显著高于对照组,而干扰组降低,该结果说明MALAT1过表达促进Cyclin D1高表达,从而促进了细胞增殖。对细胞凋亡情况进行研究,发现MALAT1过表达组凋亡率降低,干扰组升高,MALAT1过表达组的抗凋亡因子Bcl-2高表达,而促凋亡因子Bax低表达,MALAT1表达干扰后结果相反,说明MALAT1过表达会抑制癌细胞凋亡,干扰MALAT1表达则促进细胞凋亡。本研究还检测了各组细胞p-ERK1/2蛋白相对表达量,结果显示MALAT1过表达组高表达p-ERK1/2,推测MALAT1促进了ERK1/2信号通路的激活,进而影响前列腺癌细胞的生物学行为发生变化。
综上所述,MALAT1过表达促进前列腺癌细胞的增殖,抑制凋亡,在前列腺癌的发生、发展过程中发挥重要的作用。而干扰MALAT1的表达后,抑制了癌细胞的增殖,并促进其凋亡,推测抑制MALAT1表达会对前列腺癌的治疗具有非常重要的意义,但lcnRNA-MALAT1对前列腺癌的具体作用机制还需进一步深入研究。
作者贡献宋 鹏:设计研究方案、实施研究过程、撰写论文龙 彤:课题设计、撰写论文梁培育:提出研究思路、分析试验数据、审核论文欧善际:实施研究过程、资料搜集整理、修改论文 -
-
[1] Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(2): 115-32. doi: 10.3322/caac.21338
[2] Yang F, Zhang L, Huo XS, et al. Long noncoding RNA high expression in hepatocellular carcinoma facilitates tumor growth through enhancer of zeste homolog 2 in humans[J]. Hepatology, 2011, 54(5): 1679-89. doi: 10.1002/hep.24563
[3] Wan G, Hu X, Liu Y, et al. A novel non-coding RNA lncRNA-JADE connects DNA damage signalling to histone H4 acetylation[J]. EMBO J, 2013, 32(21): 2833-47. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.221
[4] Wu P, Zuo X, Deng H, et al. Roles of long noncoding RNAs in brain development, functional diversification and neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Brain Res Bull, 2013, 97: 69-80. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2013.06.001
[5] Li Y, Wu Z, Yuan J, et al. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes gastric cancer tumorigenicity and metastasis by regulating vasculogenic mimicry and angiogenesis[J]. Cancer Lett, 2017, 395: 31-44. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.02.035
[6] Chung S, Nakagawa H, Uemura M, et al. Association of a novel long non‐coding RNA in 8q24 with prostate cancer susceptibility[J]. Cancer Sci, 2011, 102(1): 245-52. doi: 10.1111/cas.2010.102.issue-1
[7] Misawa A, Takayama KI, Urano T, et al. Androgen-induced lncRNA SOCS2-AS1 Promotes Cell Growth and Inhibits Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2016, 291(34): 17861-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.718536
[8] Liu HT, Fang L, Cheng YX, et al. LncRNA PVT1 regulates prostate cancer cell growth by inducing the methylation of miR‐146a[J]. Cancer Med, 2016, 5(12): 3512-9. doi: 10.1002/cam4.900
[9] Jiang Y, Li Y, Fang S, et al. The role of MALAT1 correlates with HPV in cervical cancer[J]. Oncol Lett, 2014, 7(6): 2135-41. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.1996
[10] Zheng HT, Shi DB, Wang YW, et al. High expression of lncRNA MALAT1 suggests a biomarker of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2014, 7(6): 3174-81. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=049a3f81c0ac6a2ff9b9890053cd0c13&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[11] Ji P, Diederichs S, Wang W, et al. MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin beta4 predict metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Oncogene, 2003, 22(39): 8031-41. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206928
[12] Cao X, Zhao R, Chen Q, et al. MALAT1 might be a predictive marker of poor prognosis in patients who underwent radical resection of middle thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2015, 15(6): 717-23. doi: 10.3233/CBM-150513
[13] Cai X, Liu Y, Yang W, et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 as a potential therapeutic target in osteosarcoma[J]. J Orthop Res, 2016, 34(6): 932-41. doi: 10.1002/jor.23105
[14] Ren S, Liu Y, Xu W, et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 is a new potential therapeutic target for castration resistant prostate cancer[J]. J Urol, 2013, 190(6): 2278-87. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.07.001
[15] 钟伟枫, 刘思平, 潘斌, 等.龙葵素通过诱导细胞周期G1/S阻滞抑制裸鼠前列腺癌细胞Du145移植瘤生长[J].南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(5): 665-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2016.05.013 Zhong WF, Liu SP, Pan B, et al. Solanine inhibits prostate cancer Du145 xenograft growth in nude mice by inducing cell cycle arrest in G1/S phase[J]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao, 2016, 36(5): 665-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2016.05.013



 下载:
下载: