-
摘要:
前列腺癌(prostate cancer, PCa)转移中大约80%是发生骨转移,是造成患者死亡的主要原因。前列腺癌骨转移主要呈现成骨和破骨混合性损伤。然而,诱发肿瘤细胞转移到骨以及引起混合样病变的机制仍不十分清楚。宿主微环境与前列腺癌细胞间的相互作用是其中一个重要原因。本文主要讨论宿主微环境如何影响前列腺癌骨转移各个阶段的发生及其中的机制,探讨多种细胞因子、分泌蛋白、微环境中的免疫细胞、成骨细胞、破骨细胞等分泌的因子在前列腺癌骨转移中的重要作用。
Abstract:The majority of prostate cancer (PCa)-induced deaths is due to the development of metastatic disease, 80% of which is primarily localized in the bone. The types of bone metastasis of PCa are mainly osteoblastic or osteoclastic lesions. What triggers PCa metastasis to the bone and what causes osteoblastic and osteoclast lesions remain unanswered. A major contributor to PCa metastasis is the host microenvironment. Here, we mainly discuss how primary tumor microenvironment affects the occurrence and mechanism of bone metastasis in prostate cancer. The mechanisms and effects of secretory factors, secretory proteins, immune cells, osteoblasts, osteoclasts and other secreted factors on bone metastasis of prostate cancer will be discussed and summarized.
-
Key words:
- Prostate cancer /
- Bone metastasis /
- Tumor microenvironment /
- Secretion factor
-
0 引言
最新研究显示前列腺癌在美国是男性发病率最高的恶性肿瘤,死亡率排名第二[1]。在中国,前列腺癌发病率呈逐年增长趋势,增长率排名第一,且预后往往不好[2]。骨转移在晚期前列腺癌患者中非常常见,常引起高钙血症,病理性骨折,脊髓压迫等并发症,甚至可导致永久性瘫痪和肢体功能丧失,目前骨转移治疗主要是姑息治疗,仅能改善患者的生活质量[3-4]。因此我们需要深入研究前列腺癌骨转移发生的分子机制,开发有效的治疗方法来提高前列腺癌骨转移患者总体生存时间和生活质量。
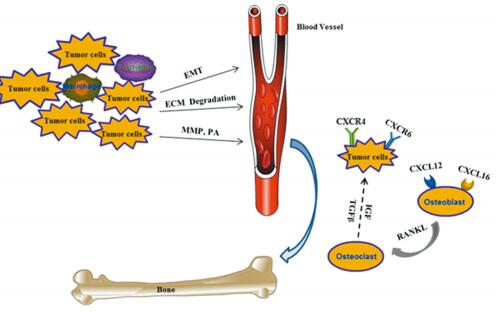
前列腺癌细胞与骨微环境中的细胞相互作用促进了肿瘤细胞的生长和骨定植[5]。Stephan Paget 1889年提出了著名的“种子和土壤”学说:肿瘤转移依赖于肿瘤细胞(作为“种子”)和宿主微环境(作为“土壤”)之间相互作用的结果[6]。尽管这是经典的理论,但它仍不能全面的解释器官特异性转移的分子机制。肿瘤细胞在骨髓中定植需要经过多个步骤,包括血管的生成、局部转移和侵袭,脱离原发灶进入血管,然后从血管溢出,在骨髓中适应、存活和定植。肿瘤细胞可通过分泌一些因子或蛋白来调节骨髓微环境或转移前微环境的形成从而有利于肿瘤的转移,见图 1。本文主要对以上各个阶段主要参与的分子及其发生的机制进行综述。
1 降低细胞的黏附和发生上皮间质转化
肿瘤转移首先需要从原发病灶中脱落,包括细胞外基质降解,肿瘤细胞发生上皮间质转化,进入血液循环或淋巴循环,在这一过程中,其中有两类分子发挥重要作用。
1.1 整合素(Integrin)
整合素是细胞表面糖蛋白的一类大家族,它能与黏附分子形成异二聚体,并绑定很多细胞外基质成分,调节细胞骨架的结构来维持细胞的形状以利于细胞的迁移。不同的整合素在前列腺癌侵袭转移中的作用不同,有些已成为抗前列腺癌转移的靶标。如Integrin α2β1是胶原蛋白的受体,研究发现其与前列腺癌的侵袭性密切相关,靶向Integrin α2β1开发的抑制剂(如G. sinensis)在体外通过失活Integrin α2β1的表达抑制了由胶原介导的PC3细胞的迁移和黏附[7]。
1.2 影响上皮细胞-间充质转化(epithelia-mesenchymal transition, EMT)的相关分子
在原发肿瘤微环境中,肿瘤上皮细胞被成纤维细胞、巨噬细胞、周皮细胞和各种细胞外基质所包围。这些肿瘤微环境产生各种细胞因子:肿瘤坏死因子α(tumor necrosis factor, TNFα)、转化生长因子-β(transforming growth factor-β, TGF-β)、Wnt和低氧诱导因子-1(hypoxia inducible factor-1, HIF-1α)等促进EMT的发生。在EMT过程中,E-Cadherin表达降低,细胞紧密连接作用减弱,离开基底层有利于细胞的转移。同时重要的间质标志物如波形蛋白(Vimentin)、转录因子Snail、Slug、Twist 1、锌指增强绑定蛋白1(zinc-finger-enhancer binding protein 1, ZEB1)和锌指增强绑定蛋白2(zinc-finger-enhancer binding protein 2, ZEB2)在EMT过程中表达增加,导致细胞的运动能力增强[8]。
2 侵袭和转移
肿瘤细胞从原发部位脱落,侵入到细胞外基质(extracellular matrix, ECM),与基底膜(basement membrane, BM)及细胞间质中一些分子结合,并激活细胞合成、分泌各种降解酶类(如基质金属蛋白酶,丝氨酸蛋白酶等),协助肿瘤细胞穿过ECM进入血管,然后在某些炎性反应细胞或细胞因子等的作用下运行并穿过血管壁外渗到继发部位,从而使肿瘤细胞获得了侵袭和转移的能力。
2.1 基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)
前列腺癌侵袭需要部分降解细胞外基质,很多研究显示高MMPs的表达与前列腺癌患者不良预后相关[9-10]。Nabha等[11]研究发现PC3细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞混合培养能够增加PC3细胞中MMP-12的含量,RNAi干扰PC3细胞MMP-12的表达,能够通过减少骨内Ⅰ型胶原的降解从而降低了PC3细胞的侵袭能力。
2.2 纤溶酶原激活物(plasminogen activator, PA)
纤溶酶原激活物是一种主要的丝氨酸蛋白酶,能降解细胞外基质。Urokinase-type plasminogen activator-Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor(uPA-uPAR)的结合能使纤溶酶原转变成纤溶酶,从而降解细胞外基质。通过对前列腺癌样本进行分析发现,上调uPA和uPAR表达与高的肿瘤分级密切相关[12]。Dong等[13]研究显示,将稳定转染uPA siRNA的PC3细胞注射入胎骨中,随后将这些骨植入免疫缺陷小鼠体内,结果发现uPA siRNA组相较于对照组显著的减少了肿瘤负荷和骨降解,表明肿瘤来源的uPA对前列腺肿瘤在骨中的生长起重要作用。
2.3 炎性反应免疫细胞
炎性反应可以通过多种途径影响前列腺的病理生理学改变:包括产生活性氧导致突变形成、产生一些促进肿瘤生长和抑制抗肿瘤免疫的因子,以及通过促进免疫细胞进入肿瘤从而促进肿瘤的转移[14-15]。
调节性T细胞(Treg)被认为是介导肿瘤进程的一类细胞。Treg是CD4+的T细胞,它能抑制效应性T细胞的活性。前列腺癌患者相较于健康人外周血中,CD4+CD25high这类Treg具有更强的免疫抑制功能[16]。除了Tregs,另外一类CD4+ T细胞—Th17细胞,也能够影响前列腺癌的进程和免疫治疗的反应。Th17细胞能够产生促炎因子IL17从而吸引和激活粒细胞和单核细胞[17]。
巨噬细胞在肿瘤的发生发展中发挥着重要作用。在前列腺癌中,增加的肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(tumor-associated macrophage, TAM)可通过激活CCL22-CCR4轴促进前列腺癌转移[18]。尽管TAM在前列腺癌中已明确是增加的,但其促进前列腺癌进程的具体分子机制仍然不清楚。
3 前列腺癌细胞的归巢、存活和定植
骨基质是由95%的Ⅰ型胶原和5%的非胶原蛋白、蛋白多糖组成[19]。骨髓中的细胞不仅包括成骨细胞、破骨细胞,还包括造血细胞、脂肪细胞和免疫细胞。骨基质和骨髓细胞分泌的大量生长因子构成了骨微环境复杂的空间结构和前列腺癌细胞生长所需的肥沃土壤。
3.1 归巢
在转移的后期,肿瘤细胞需要从血管中溢出,进入靶器官定植,肿瘤细胞首先需要黏附到内皮细胞上。研究显示前列腺癌细胞上的E选择素(E-selectin)配体与骨髓内皮细胞上的E-selectin结合,导致黏附[20]。前列腺癌细胞表达CD44与血管细胞黏附分子1(vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, VCAM-1)结合,促进了肿瘤细胞与内皮细胞的黏附,且IL-17、胰岛素和胰岛素样生长因子1(insulin-like growth factor 1, IGF-1)能增强这种黏附作用[21]。另外,播散的肿瘤细胞(disseminated tumor cells, DTCs)表达Annexin Ⅱ受体(Annexin Ⅱ receptor, Annexin ⅡR)与表达Annexin Ⅱ的成骨细胞结合,促进肿瘤细胞骨转移[22]。此外,趋化因子在前列腺癌细胞归巢过程中也发挥着重要作用。表达趋化因子配体16(CXC ligand 16, CXCL16)的前列腺癌细胞通过与骨髓间充质干细胞(bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, BMSCs)上相应受体CXCR6的结合,诱导BMSCs转变成肿瘤相关的成纤维细胞,产生更多的CXCL12,从而促进肿瘤细胞播散到骨[23]。CXCR4和它的配体CXCL12/SDF1通过归巢信号趋化肿瘤细胞到骨髓微环境中[24]。靶向CXCR4药理学的抑制剂(Plerixafor和CTE9908)能够抑制PC3细胞在骨内的定植生长[25]。这些发现说明抑制骨髓微环境的细胞与肿瘤细胞的相互作用可能成为治疗前列腺癌骨转移的有效方法。
3.2 肿瘤休眠与存活
DTCs在骨髓中存活需要适应新的环境,逃避免疫系统并长期保持休眠状态(约1~10年)。富含半胱氨酸的酸性分泌蛋白(secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine, SPARC)通过上调骨形成蛋白7(bone morphogenetic protein 7, BMP7)诱导前列腺癌细胞的休眠和复发[26]。研究发现注射BMP7的裸鼠,前列腺癌细胞在骨内的增殖变慢[27]。另外,生长停止特异性蛋白6(growth arrest specific 6, GAS6)是一种络氨酸激酶受体家族成员的配体,它在骨骼中的表达水平也影响了前列腺癌细胞的休眠[28]。
3.3 骨髓定植
肿瘤细胞在骨髓中定植必须脱离休眠状态,骨形成和骨吸收释放和激活存活和生长促进因子导致骨转移的发生。整合素除在肿瘤转移的早期外,还在前列腺癌的骨髓定植中发挥着重要的作用。如前列腺癌细胞表达Integrin α2β1,能够黏附和转移到骨基质上,从而利于肿瘤细胞定植到骨髓中[29]。Cadherin-11,也称为成骨细胞来源的cadherin,高表达在人前列腺癌骨转移组织和前列腺癌骨转移细胞系中[30]。在PC3细胞中使用shRNA干扰Cadherin-11的表达,导致了小鼠骨转移的发生率明显降低[30]。核因子κB受体活化因子配体(receptor activator for nuclear factor-κB ligand, RANKL)在骨重建中是一个重要介导分子。前列腺癌DTCs通过表达甲状旁腺激素相关蛋白(parathyroid hormone-related protein, PTHrP)增强了成骨细胞表达RANKL,从而促进破骨细胞形成,也为DTCs在骨内的转移生长创造了空间[31]。抗RANKL的人源单克隆抗体已经显示能作为一种选择性靶向破骨细胞的药物,通过阻断RANK和RANKL的相互作用来抑制破骨细胞的活性[32]。目前,靶向治疗前列腺癌骨转移主要的策略是:靶向肿瘤细胞高表达基因以降低其与肿瘤微环境细胞的相互作用或者是靶向宿主微环境中的细胞功能。表 1列举了一些调节前列腺癌骨转移重要的蛋白质。
表 1 调节前列腺癌骨转移重要的蛋白质Table 1 Key proteins for regulation of prostate cancer bone metastasis
4 结论及展望
骨转移仍然是引起前列腺癌患者死亡的主要原因。科学家一直在努力寻找有效的治疗手段,然而由于骨髓微环境的复杂性和异质性,直至今天,尚无有效的药物能从根本上治疗前列腺癌骨转移,双磷酸盐仅能在一定程度上限制骨的降解和缓减骨痛,但不能明显改善患者总生存期,总体疗效仍不尽如人意。Ra223是目前唯一一个得到FDA批准用于治疗去势抵抗型前列腺癌骨转移的放射性同位素,它通过模拟钙,在骨基质区域或成骨性骨转移病灶处与羟基磷灰石结合,然后释放高能量的α粒子诱发骨转移细胞DNA损伤和细胞死亡[39]。但其价格昂贵,也不能从根本上解决和防止前列腺癌骨转移的发生。只有我们了解和掌握前列腺癌骨转移发展的过程和分子机制,特别是肿瘤细胞和微环境是如何相互对话和发挥作用,才能更好地发现和验证靶向骨转移的药物。如针对骨转移细胞休眠的特性,我们可以通过抑制骨转移细胞再激活的过程,让肿瘤细胞一直处于休眠状态,达到控制转移的目的;另外肿瘤细胞需要与微环境中的细胞相互作用促进其骨髓定植,因此可以通过抑制剂靶向它们相互作用的蛋白,阻断它们连接的纽带,从而达到抑制骨转移的目的。未来会有更多前列腺癌骨转移潜在的治疗靶点被发现,将会进一步揭示前列腺癌的生物学特征,为前列腺癌的治疗带来更多的手段,最终使患者获益。
-
表 1 调节前列腺癌骨转移重要的蛋白质
Table 1 Key proteins for regulation of prostate cancer bone metastasis

-
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(1): 7-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.v68.1
[2] Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(2): 115-32. doi: 10.3322/caac.21338
[3] Krzeszinski JY, Wan Y. New therapeutic targets for cancer bone metastasis[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2015, 36(6): 360-73. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2015.04.006
[4] Tsuzuki S, Park SH, Eber MR, et al. Skeletal complications in cancer patients with bone metastases[J]. Int J Urol, 2016, 23(10): 825-32. doi: 10.1111/iju.13170
[5] Park SH, Keller ET, Shiozawa Y. Bone Marrow Microenvironment as a Regulator and Therapeutic Target for Prostate Cancer Bone Metastasis[J]. Calcif Tissue Int, 2018, 102(2): 152-62. doi: 10.1007/s00223-017-0350-8
[6] Roodman GD. Mechanisms of bone metastasis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2004, 350(16): 1655-64. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra030831
[7] Ryu S, Park KM, Lee SH. Gleditsia Sinensis Thorn Attenuates the Collagen-Based Migration of PC3 Prostate Cancer Cells through the Suppression of α2β1 Integrin Expression[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2016, 17(3): 328. doi: 10.3390/ijms17030328
[8] Grant CM, Kyprianou N. Epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) in prostate growth and tumor progression[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2013, 2(3): 202-11. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_2830130
[9] Wang J, Liu D, Zhou W, et al. Prognostic value of matrix metalloprotease-1/protease-activated receptor-1 axis in patients with prostate cancer[J]. Med Oncol, 2014, 31(6): 968. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0968-6
[10] Moroz A, Delella FK, Almeida R, et al. Finasteride inhibits human prostate cancer cell invasion through MMP2 and MMP9 downregulation[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(12): e84757. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084757
[11] Nabha SM, dos Santos EB, Yamamoto HA, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells enhance prostate cancer cell invasion through type Ⅰ collagen in an MMP-12 dependent manner[J]. Int J Cancer, 2008, 122(11): 2482-90. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0215
[12] Kumano M, Miyake H, Muramaki M, et al. Expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator system prostate cancer: correlation with clinicopathological outcomes in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy[J]. Urol Oncol, 2009, 27(2): 180-6. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2008.01.012
[13] Dong Z, Saliganan AD, Meng H, et al. Prostate cancer cell-derived urokinase-type plasminogen activator contributes to intraosseous tumor growth and bone turnover[J]. Neoplasia, 2008, 10(5): 439-49. doi: 10.1593/neo.08106
[14] Liou GY. Inflammatory Cytokine Signaling during Development of Pancreatic and Prostate Cancers[J]. J Immunol Res. 2017, 2017: 7979637. http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC5742898/
[15] Sfanos KS, Yegnasubramanian S, Nelson WG, et al. The inflammatory microenvironment and microbiome in prostate cancer development[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2018, 15(1):11-24. http://www.nature.com/nrurol/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nrurol.2017.167.html?error=cookies_not_supported&code=421490ab-b4df-4b99-bf05-bba5cfcf8219
[16] Yokokawa J, Cereda V, Remondo C, et al. Enhanced functionality of CD4+CD25(high)FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in the peripheral blood of patients with prostate cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2008, 14(4): 1032-40. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-2056
[17] Rakebrandt N, Littringer K, Joller N. Regulatory T cells: balancing protection versus pathology[J]. Swiss Med Wkly, 2016, 146: w14343. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0229568746/
[18] Maolake A, Izumi K, Shigehara K, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages promote prostate cancer migration through activation of the CCL22-CCR4 axis[J]. Oncotarget. 2017, 8(6): 9739-51. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2b000b55c770d3a8b96cd0acdd445e7a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[19] Bussard KM, Gay CV, Mastro AM. The bone microenvironment in metastasis; what is special about bone?[J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2008, 27(1): 41-55. doi: 10.1007/s10555-007-9109-4
[20] Barthel SR, Wiese GK, Cho J, et al. Alpha 1, 3 fucosyltransferases are master regulators of prostate cancer cell trafficking[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2009, 106(46): 19491-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906074106
[21] Chen C, Zhang Q, Liu S, et al. IL-17 and insulin/IGF1 enhance adhesion of prostate cancer cells to vascular endothelial cells through CD44-VCAM-1 interaction[J]. Prostate, 2015, 75(8): 883-95. doi: 10.1002/pros.v75.8
[22] Shiozawa Y, Havens AM, Jung Y, et al. Annexin Ⅱ/annexin Ⅱ receptor axis regulates adhesion, migration, homing, and growth of prostate cancer[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2008, 105(2): 370-80. doi: 10.1002/jcb.v105:2
[23] Jung Y, Kim JK, Shiozawa Y, et al. Recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells into prostate tumours promotes metastasis[J]. Nat Commun, 2013, 4: 1795. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2766
[24] Uygur B, Wu WS. SLUG promotes prostate cancer cell migration and invasion via CXCR4/CXCL12 axis[J]. Mol Cancer, 2011, 10: 139. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-139
[25] Gravina GL, Mancini A, Muzi P, et al. CXCR4 pharmacogical inhibition reduces bone and soft tissue metastatic burden by affecting tumor growth and tumorigenic potential in prostate cancer preclinical models[J]. Prostate, 2015, 75(12):1227-46. doi: 10.1002/pros.v75.12
[26] Sharma S, Xing F, Liu Y, et al. Secreted Protein Acidic and Rich in Cysteine (SPARC) Mediates Metastatic Dormancy of Prostate Cancer in Bone [J]. J Biol Chem, 2016, 291(37): 19351-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.737379
[27] Buijs JT, Rentsch CA, van der Horst G, et al. BMP7, a putative regulator of epithelial homeostasis in the human prostate, is a potent inhibitor of prostate cancer bone metastasis in vivo[J]. Am J Pathol, 2007, 171(3): 1047-57. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070168
[28] Jung Y, Shiozawa Y, Wang J, et al. Prevalence of prostate cancer metastases after intravenous inoculation provides clues into the molecular basis of dormancy in the bone marrow microenvironment[J]. Neoplasia, 2012, 14(5): 429-39. doi: 10.1596/neo.111740
[29] Hall CL, Dubyk CW, Riesenberger TA, et al. Type Ⅰ collagen receptor (alpha2beta1) signaling promotes prostate cancer invasion through RhoC GTPase[J]. Neoplasia, 2008, 10(8): 797-803. doi: 10.1593/neo.08380
[30] Chu K, Cheng CJ, Ye X, et al. Cadherin-11 promotes the metastasis of prostate cancer cells to bone[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2008, 6(8): 1259-67. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0077
[31] Sottnik JL, Keller ET. Understanding and targeting osteoclastic activity in prostate cancer bone metastases[J]. Curr Mol Med, 2013, 13(4): 626-39. doi: 10.2174/1566524011313040012
[32] Paller CJ, Carducci MA, Philips GK. Management of bone metastases in refractory prostate cancer-role of denosumab[J]. Clin Interv Aging, 2012, 7: 363-72. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_3459574
[33] Kolonin MG, Sergeeva A, Staquicini DI, et al. Interaction between Tumor Cell Surface Receptor RAGE and Proteinase 3 Mediates Prostate Cancer Metastasis to Bone[J]. Cancer Res, 2017, 77(12): 3144-50. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-0708
[34] Nandana S, Tripathi M, Duan P, et al. Bone Metastasis of Prostate Cancer Can Be Therapeutically Targeted at the TBX2-WNT Signaling Axis[J]. Cancer Res, 2017, 77(6): 1331-44. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-0497
[35] Thudi NK, Martin CK, Murahari S, et al. Dickkopf-1 (DKK-1) stimulated prostate cancer growth and metastasis and inhibited bone formation in osteoblastic bone metastases[J]. Prostate, 2011, 71(6): 615-25. doi: 10.1002/pros.21277
[36] Di Giacomo V, Tian TV, Mas A, et al. ΔNp63α promotes adhesion of metastatic prostate cancer cells to the bone through regulation of CD82[J]. Oncogene, 2017, 36(31): 4381-92. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.42
[37] Li Q, Yin L, Jones LW, et al. Keratin 13 expression reprograms bone and brain metastases of human prostate cancer cells[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(51): 84645-57. http://europepmc.org/articles/pmc5356688
[38] Chen PC, Tang CH, Lin LW, et al. Thrombospondin-2 promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis by the up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 through down-regulating miR-376c expression[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2017, 10(1): 33. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0390-6
[39] Harrison MR, Wong TZ, Armstrong AJ, et al. Radium-223 chloride: a potential new treatment for castration resistant prostate cancer patients with metastatic bone disease[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2013, 5: 1-14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_7774abe833bf12360faac06d384abb7d



 下载:
下载:

