Role of Autophagy in Cisplatin Resistance of Retinoblastoma Y79 Cells and Its Mechanism
-
摘要:目的
研究自噬在视网膜母细胞瘤Y79细胞顺铂耐药中的作用及其机制。
方法CCK-8法检测细胞IC50;将Y79细胞随机分为对照组(Control)、顺铂组(Cis)和顺铂联合应用自噬阻断剂3-甲基腺嘌呤组(Cis+3-MA),Western blot法、细胞自噬染色检测试剂盒(MDC法)和透射电子显微镜观察细胞自噬情况;CCK-8法检测顺铂对细胞的抑制率变化,Annexin V/PI双染流式法检测细胞凋亡变化,q-PCR检测相关耐药基因转录水平,Fluo-4 AM钙离子荧光探针染色检测细胞内钙离子变化,Western blot法检测CaMKK2、p-AMPK、mTORC1、LC3Ⅱ的表达。
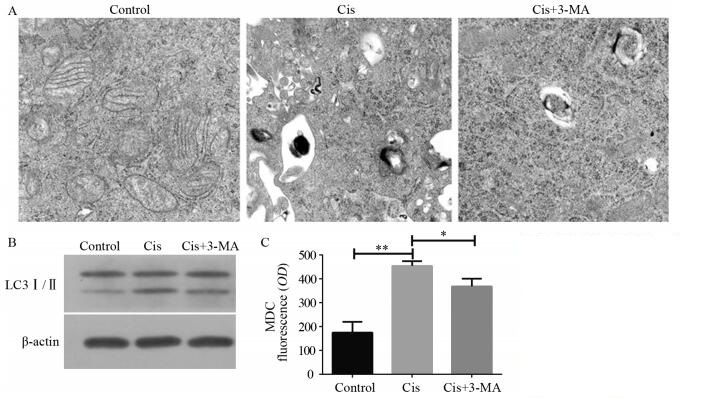
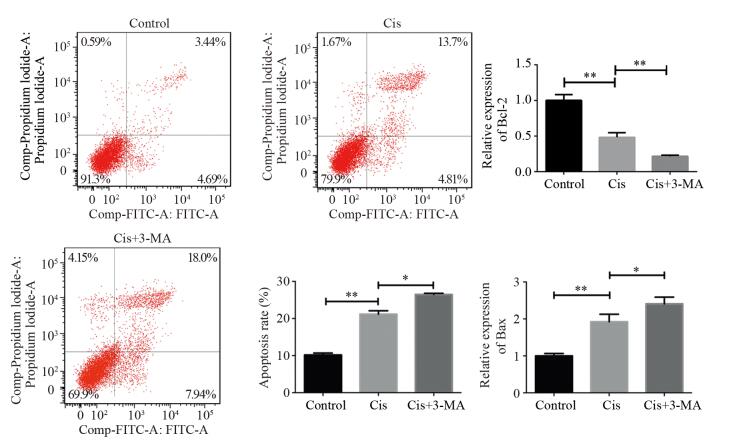
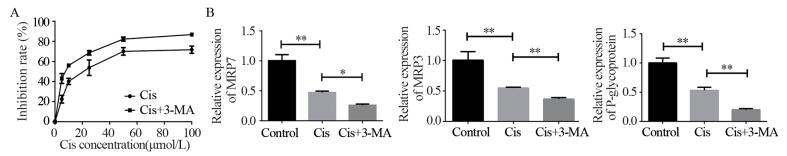
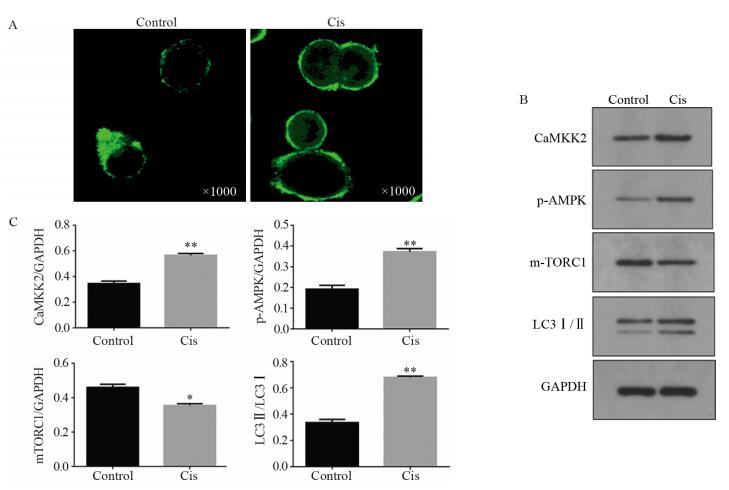
结果视网膜母细胞瘤Y79细胞在顺铂的诱导下发生自噬,加入自噬阻断剂3-MA后细胞自噬水平下调。与顺铂组相比,Cis+3-MA组顺铂抑制率增加,凋亡率增加,相关耐药基因转录水平下调。细胞加入顺铂后,细胞内钙离子水平增加,CaMKK2、p-AMPK、LC3Ⅱ表达上调,mTORC1表达下调。
结论顺铂诱导肿瘤细胞产生的自噬对视网膜母细胞瘤细胞Y79耐药起保护作用,抑制自噬可以改善肿瘤细胞对顺铂的耐药性。顺铂可能是通过Ca2+激活CaMKK2/AMPK/mTORC1通路诱导Y79细胞自噬。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the role of autophagy in cisplatin resistance of retinoblastoma Y79 cells and its mechanism.
MethodsThe IC50 of cells was detected by CCK-8 assay. Y79 cells were randomly divided into control group, Cisplatin group and cisplatin combined with autophagyroup). Western blot, cell autophagy staining kit (MDC method) and transmi inhibitor 3-methyladenine group(Cis+3-MA gssion electron microscopy were used to observe cell autophagy. CCK-8 assay was used to detect the inhibitory rate of cisplatin on Y79 cells. Annexin V/PI double staining was used to detect cells apoptosis. q-PCR was applied to detect drug-resistance-related genes transcription levels. The expression of CaMKK2, p-AMPK, mTORC1 and LC3Ⅱ were detected by Fluo-4 AM calcium ion fluorescent probe staining.
ResultsAutophagy of retinoblastoma Y79 cells was induced by cisplatin. Autophagy inhibitor 3-MA reduced the level of autophagy. Compared with cisplatin group, the cisplatin inhibition rate was increased, the apoptosis rate was increased and the drug-resistance-related gene transcription level was down-regulated in Cis+3-MA group. After adding cisplatin, the level of intracellular calcium was increased, the expressions of CaMKK2, p-AMPK and LC3Ⅱ were up-regulated and the expression of mTORC1 was down-regulated.
ConclusionCisplatin-induced autophagy is protective for the drug resistance of retinoblastoma Y79 cells and the inhibition of autophagy could improve tumor cells resistance to cisplatin. Cisplatin could induce autophagy in Y79 cells by Ca2+ activation of CAMKK2/AMPK/mTORC1 pathway.
-
Key words:
- Retinoblastoma /
- Autophagy /
- Drug resistance /
- Calcium
-
0 引言
子宫内膜癌位于我国妇女生殖道恶性肿瘤的第二位,仅次于宫颈癌,占全部女性生殖系统恶性肿瘤的20%~30%[1]。尽管子宫内膜癌的诊断治疗有了迅速发展,但仍有5%~15%的早期子宫内膜癌不仅复发且有较高的死亡率[2]。因此研究Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发相关危险因素,从而有效干预是目前关注的重点。本研究就此进行具体分析,现报告如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
采用回顾性研究方法收集南京鼓楼医院2010年1月~2017年12月期间收治的子宫内膜癌手术患者747例,随访606例,失访141例,最后归纳516例初始诊断为Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌的患者作为研究对象,住院患者均有不同程度的阴道流血、分泌物增多、腹痛等。按照国际妇产科联盟FIGO 2009规定的“子宫内膜癌手术-病理分期”标准,确定其病理类型及术后分期。患者年龄24~83岁,平均年龄(57.07±10.63)岁。排除标准:术前放化疗、心肺肝肾功能不全、急性感染、凝血异常、自身免疫性疾病、子宫内膜癌为第二原发癌等患者。
1.2 方法
回顾全部患者的基本信息及有关病史详细记载,统计有关生化及影像学检查。全部患者行全面分期手术,部分患者根据淋巴浸润、病理分级等术后辅助放化疗或激素治疗。首次手术术中标本均采用免疫组织化学法(IHC)检测雌激素受体(ER)和孕激素受体(PR),根据染色程度采用积分综合测量分类。门诊及电话随访1~8年。按照复发与否分为复发组和未复发组。复发是指在阴道残端、腹股沟区、肺部、骨、盆腔等出现肿瘤,经生化肿瘤相关指标、妇科B型超声、盆腔(增强)CT或MRI、PET-CT、病理学等检查确诊。
1.3 统计学方法
用SPSS22.0软件包进行数据处理,(x±s)表示正态分布且方差齐的计量资料,比较用t检验。计数资料用百分数表示,组间比较用χ2检验。非参数资料采用秩和检验,Logistic多因素回归进行危险因素分析。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 复发情况
在516例Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌患者中,46例复发,复发率为8.91%,平均复发时间间隔为(19.47 ±13.79)月;其中盆腔复发16例。转移30例:8例阴道下段转移、8例肺转移、3例腹股沟淋巴结转移、6例骨转移、其余5例出现其他部位转移。46例复发患者中30例入院再次治疗后复发病灶消失,其余16例死亡(3例死于其他疾病)。
2.2 影响Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发的单因素分析
对影响Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发的单因素分析显示,高龄、低体重、高血压、手术病理分期、病理类型、ER及PR低表达与Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发存在一定相关性,两组间比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);糖尿病、脉管转移、病理分化程度、淋巴结切除、腹水细胞学检查比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),见表 1。
表 1 影响Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发的单因素关系分析(x±s)Table 1 Univariate analysis of influence factors for recurrence of stage Ⅰ-Ⅱ endometrial cancer (x±s)
2.3 影响Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发的独立危险因素分析
对单因素分析中P < 0.20的因素进行多因素Cox比例风险回归模型进行分析,结果表明:年龄、体重、血压是Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发的独立危险因素,高龄、低体重、高血压使Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌的复发率增加(P < 0.05),见表 2。
表 2 影响Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发的独立危险因素分析Table 2 Analysis of independent risk factors affecting recurrence of stage Ⅰ-Ⅱendometrial carcinoma
3 讨论
国内文献报道Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌患者复发转移率在5.0%~18.0%[3],对相关因素分析未做多因素分析,本研究516例Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌患者发现复发46例,复发率为8.91%,与上述报道相符。既往研究多对Ⅰ~Ⅳ期子宫内膜癌患者整体研究,本研究主要对Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌患者进行研究,排除肿瘤患者已有远处转移因素,从而减少复发因素研究的偏畸。
在国内外已有的子宫内膜癌预后分析相关因素文献报道中,大多数认为子宫内膜癌的预后可能与年龄、生育史、内科合并症、手术-病理分期、病理类型、组织学分级、肌层浸润、宫颈受累、淋巴结转移等因素有关[4-5],但是文献报道的结果不一。本研究单因素分析中发现年龄、体重、血压、手术病理分期、病理类型、ER及PR表达与Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发存在相关性。年龄、体重、血压是Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发的风险因子,手术病理分期越高Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发的风险增大;特殊类型的子宫内膜癌的Ⅰ~Ⅱ期患者复发风险随之增高;ER、PR在病理检查中表达越低复发风险越大。相关研究显示随ER、PR表达率降低,早期子宫内膜癌术后患者复发率增高,病理分期、病理分化程度、脉管癌栓以及肌层浸润或淋巴结转移率增加,进一步支持ER、PR的缺失与细胞恶性程度上升、侵袭性增加及向非激素依赖型肿瘤转化相关这一结论[6]。ER、PR的存在提示子宫内膜癌细胞对激素刺激有一定反应能力,也是内分泌抗雌激素治疗子宫内膜癌的理论基础,两者之一或同时缺失会导致肿瘤对激素治疗的效果不明显及预后不佳。
本次研究中病理分化程度、脉管转移及腹水细胞学异常与Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发关系研究中未见明显差异,可能与以上有关高危因素患者术后已添加相关的辅助治疗,降低了复发风险,从而影响其复发结果;Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌患者术中是否行淋巴结切除并未影响患者术后复发,可能与淋巴结转移并非是内膜癌转移唯一途径有关。虽然流行病学提示糖尿病是子宫内膜癌发病因素之一[7-8],但是本次Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌合并糖尿病患者研究未见明显的术后复发差异。
单因素分析及多因素分析证实年龄、体重、血压是Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发的独立危险因素。年龄越大复发率越高;低体重及高血压Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌术后复发率增加。可能随着年龄的增加,伴随体重的减轻,子宫内膜癌患者机体本身机能下降,术后恢复能力降低。Santeufemia等研究Ⅰ~Ⅳ期子宫内膜癌复发患者中发现,年龄大于60岁是子宫内膜癌患者复发的独立危险因素[9],但其研究过程中未能有效排除Ⅲ~Ⅳ期患者自身对复发的影响。虽然肥胖是子宫内膜癌的发病因素之一[10-11],也有报道指出肥胖与子宫内膜癌的复发有关[12],然而最近Felix等对Ⅰ~Ⅲ期子宫内膜癌复发因素研究中提出低体重可能是影响因素之一,低体重子宫内膜癌患者中的复发风险增高[13],在其研究中没有排除Ⅲ期子宫内膜癌中肿瘤远处转移的可能性及未提出其作为独立危险因素,但本次研究Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌患者低体重既是相关影响因素同时也成为独立危险因素之一。流行病学调查显示高血压是子宫内膜癌发病因素之一[14];随年龄增长高血压患病率上升,60岁前男性高血压的患病率普遍高于女性,之后女性的患病率逐渐增高超过男性,这可能与女性雌激素的保护有关[15]。本研究证实高血压是Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发的相关影响因素,更是独立危险因素之一。可能高血压与Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发患者存在相关分子机制相互影响,但还有待进一步研究。
本次研究中未将肿瘤的直径大小纳入研究对象,因为患者入院治疗前大多数行诊刮术或宫腔镜检查,检查后再手术时间长短影响肿瘤的直径大小。通过回顾性研究发现年龄、体重、高血压是Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发独立危险因素,提示我们可从以上三方面进一步研究Ⅰ~Ⅱ期子宫内膜癌复发的机制。
-
表 1 q-PCR引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences for q-PCR

-
[1] Rodriguez-Galindo C, Orbach DB, Vanderveen D. Retinoblastoma[J]. Pediatric Clin North Am, 2015, 62(1): 201-23. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2014.09.014
[2] Canturk S, Qaddoumi I, Khetan V, et al. Survival of retinoblastoma in less-developed countries impact of socioeconomic and health-related indicators[J]. Br J Ophthalmol, 2010, 94(11): 1432-6. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2009.168062
[3] Ford JS, Chou JF, Sklar CA, et al. Psychosocial Outcomes in Adult Survivors of Retinoblastoma[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2015, 33(31): 3608-14. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.60.5733
[4] 陆烨, 童剑萍.视网膜母细胞瘤的发生机制及诊断和治疗进展[J].现代肿瘤医学, 2016, 24(6): 1007-14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sxzlyx201606047 Lu Y, Tong JP. The pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of retinoblastoma[J]. Xian Dai Zhong Liu Yi Xue, 2016, 24(6): 1077-14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sxzlyx201606047
[5] Honavar SG, Manjandavida FP, Reddy VAP. Orbital retinoblastoma: An update[J]. Indian J Ophthalmol, 2017, 65(6): 435-42. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_352_15
[6] Chawla B, Singh R. Recent advances and challenges in the management of retinoblastoma[J]. Indian J Ophthalmol, 2017, 65(2): 133-9. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_883_16
[7] Liu X, Sun K, Wang H, et al. Knockdown of retinoblastoma protein may sensitize glioma cells to cisplatin through inhibition of autophagy[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2016, 620: 137-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.04.001
[8] Dikic I, Johansen T, Kirkin V. Selective autophagy in cancer development and therapy[J]. Cancer Res, 2010, 70(9): 3431-4. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4027
[9] Li YJ, Lei YH, Yao N, et al. Autophagy and multidrug resistance in cancer[J]. Chin J Cancer, 2017, 36(1): 52. doi: 10.1186/s40880-017-0219-2
[10] Fu W, Li X, Lu X, et al. A novel acridine derivative, LS-1-10 inhibits autophagic degradation and triggers apoptosis in colon cancer cells[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2017, 8(10): e3086. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.498
[11] Pagotto A, Pilotto G, Mazzoldi EL, et al. Autophagy inhibition reduces chemoresistance and tumorigenic potential of human ovarian cancer stem cells[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2017, 8(7): e2943. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.327
[12] Wei F, Jiang X, Gao HY, et al. Liquiritin induces apoptosis and autophagy in cisplatin (DDP)-resistant gastric cancer cells in vitro and xenograft nude mice in vivo[J]. Int J Oncol, 2017, 51(5): 1383-94. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.4134
[13] Yang X, Bai F, Xu Y, et al. Intensified Beclin-1 Mediated by Low Expression of Mir-30a-5p Promotes Chemoresistance in Human Small Cell Lung Cancer[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2017, 43(3): 1126-39. doi: 10.1159/000481754
[14] Sun WL, Chen J, Wang YP, et al. Autophagy protects breast cancer cells from epirubicin-induced apoptosis and facilitates epirubicin-resistance development[J]. Autophagy, 2014, 7(9): 1035-44. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0225468518/
[15] Poźniak B, Pawlak A, Obmińska-Mrukowicz B. Flow cytometric assessment of P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-associated protein activity and expression in canine lymphoma[J]. In vivo, 2015, 29(1): 149-53. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2c72fb47a92089ee91426008f6b70c5f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[16] Filippi-Chiela EC, Viegas MS, Thomé MP, et al. Modulation of Autophagy by Calcium Signalosome in Human Disease[J]. Mol Pharmacol, 2016, 90(3): 371-84. doi: 10.1124/mol.116.105171
[17] Hoxhaj G, Hughes-Hallett J, Timson RC, et al. The mTORC1 Signaling Network Senses Changes in Cellular Purine Nucleotide Levels[J]. Cell Re, 2017, 21(5): 1331-46. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.029



 下载:
下载: