-
摘要:目的
通过分析肺肉瘤样癌(pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma, PSC)的临床资料,探讨其临床特征及预后因素。
方法回顾性分析79例PSC患者的临床资料,采用SPSS19.0统计软件对患者的性别、年龄、是否有吸烟史、肿瘤的原发部位、位置类型、肿瘤大小、T分期、有无淋巴结转移、有无远处转移、TNM分期、组织学亚型、治疗方法及是否手术等因素进行预后分析。采用Kaplan-Meier法进行生存分析,采用Log rank法进行单因素分析,采用Cox比例风险回归模型进行多因素分析。
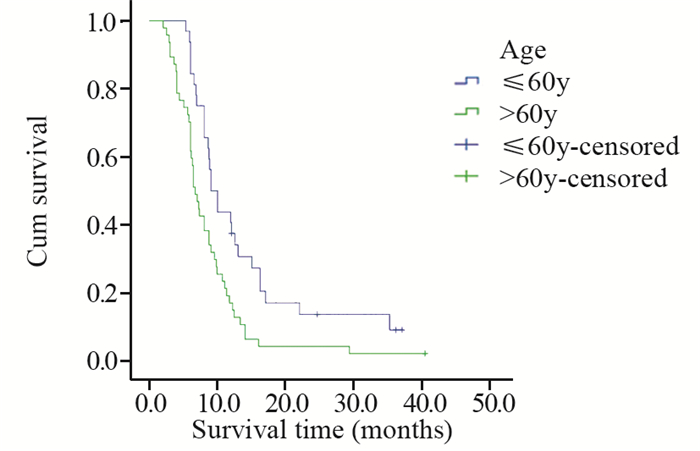
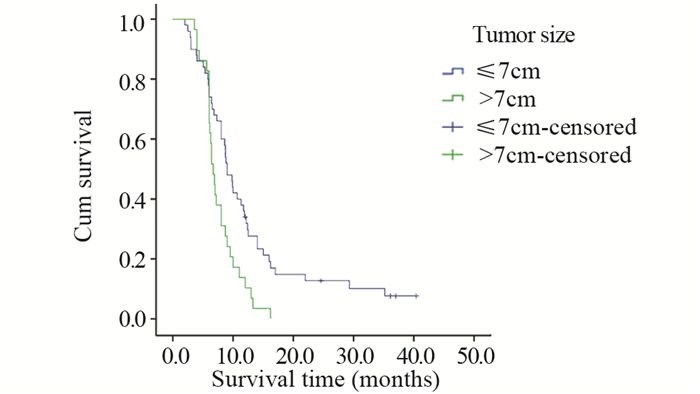
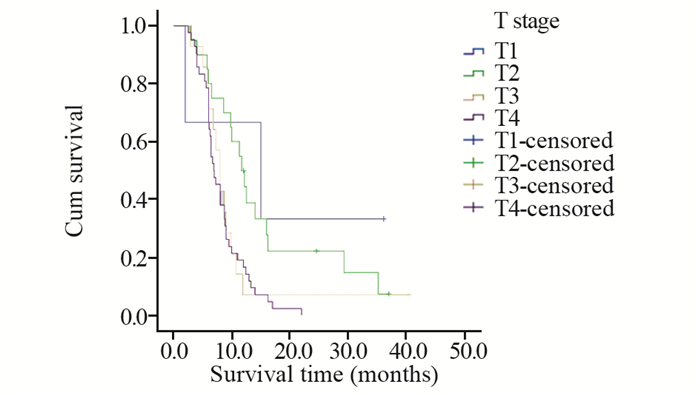
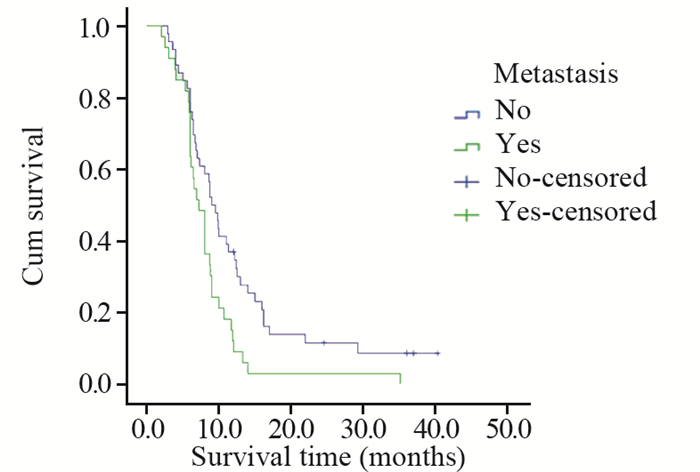
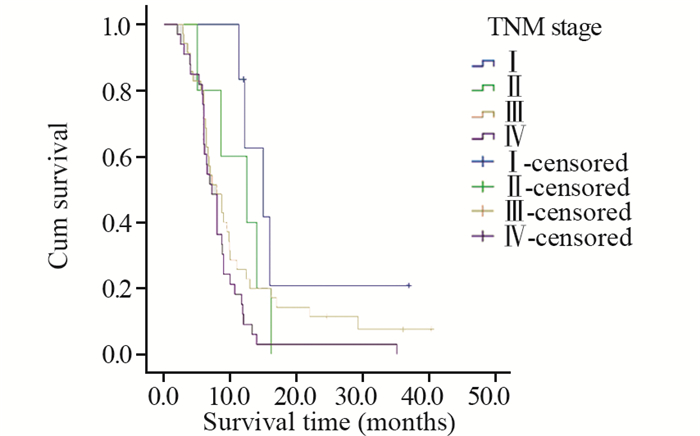
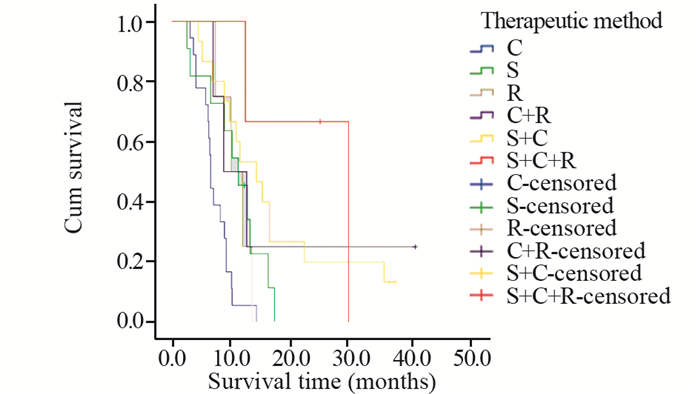
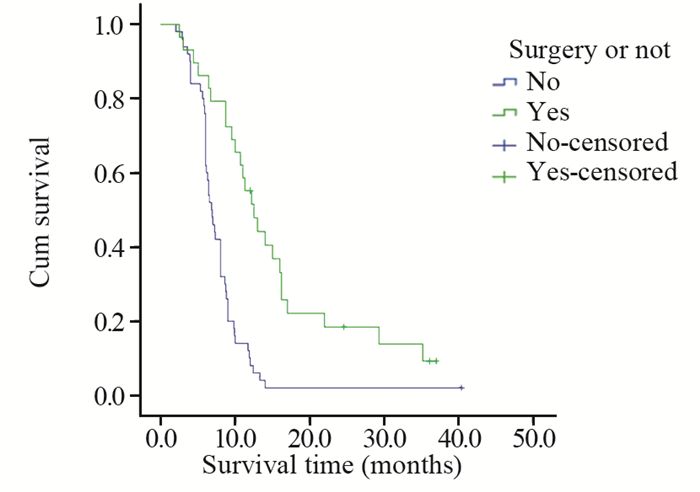
结果与腺癌、鳞癌、小细胞癌等肺癌亚型相似,PSC患者多以咳嗽、胸闷、发热、痰中带血、咯血、胸痛等为初诊症状。本研究中患者的1、2、3年总生存率分别为25.3%、8.0%、4.8%,中位生存时间为8.0月。单因素分析显示,年龄、肿瘤大小、T分期、有无远处转移、TNM分期、治疗方法及是否手术是影响预后的因素。
结论PSC是一类少见的、侵袭性较高的非小细胞肺癌,预后差。与其他肺部肿瘤相比,PSC缺乏典型的临床表现,诊断主要依靠病理学和免疫组织化学方法。本研究中患者的年龄、肿瘤大小和治疗方法是影响预后的独立因素,手术联合放化疗是首选治疗方法。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo analyse the clinical data of pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma(PSC) and investigate the clinical features and prognostic factors.
MethodsThe clinical data of 79 cases of pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma were analyzed retrospectively. The correlation between prognosis and gender, age, smoking history, primary tumor site, tumor size, location type, T staging, lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, TNM staging, histological subtype, therapeutic method, surgery or not were analyzed by statistical software SPSS 19.0. Kaplan-Meier method was used for survival analysis. Log-rank test was used for univariate analysis, and Cox proportional hazard regression model was used to carry out multivariate analysis.
ResultsPSC patients mainly presented with the symptoms of cough, chest tightness, fever, bloody sputum, hemoptysis, chest pain, which were similar to other types of lung cancer, such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and small cell carcinoma. The overall 1-, 2-, 3-year survival rates were 25.3%, 8.0%, 4.8%, respectively. The median survival time was 8.0 months. Univariate analysis showed that age, tumor size, T stage, distant metastasis, TNM staging, treatment and surgery or not were prognostic factors.
ConclusionPSC is a rare, aggressive, poorly-differentiated non-small cell lung cancer, with poor prognosis. Compared with other lung tumors, PSC lacks typical clinical manifestations. The diagnosis mainly depends on pathology and immunohistochemistry. Age, tumor size and therapeutic method are independent prognostic factors. Surgical resection combined with postoperative chemoradiotherapy is the preferred therapeutic method.
-
0 引言
子宫内膜癌是在北美和欧洲最常见的女性恶性肿瘤,近年来我国的发病率明显增加,发病人群年轻化[1]。子宫内膜癌的发病机制目前尚未完全明确,随着研究的深入,越来越清晰地认识到子宫内膜癌是多种因素协同交叉作用、具有不同遗传和分子特征的一类疾病[2-3]。根据肿瘤发病机制与雌激素依赖相关性,将其分为Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型,80%以上为Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌。遗传易感性是导致个体对相同致癌因素敏感度不一致的重要因素,某些雌激素代谢通路中关键酶可以改变体内雌激素或外源性雌激素及其代谢产物的水平。基因多态性与酶活性有关,雌激素代谢酶基因多态性可能导致子宫内膜癌发病易感性差异[4]。本研究利用SNP分型检测技术,探索雌激素代谢关键酶CYP1B1、CYP1A1和NQO1基因的单核苷酸多态性(single nucleotide polymorphisms, SNPs)位点分布频率与Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌易感性之间关系,以期对Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的易感人群进行筛查。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料
抽取我院2014年3月—2016年10月收治的经病理诊断为子宫内膜样腺癌的103例患者和同期子宫内膜正常的100例其他疾病患者静脉外周全血2~3 ml,作为检测标本。病例和对照组均取得患者的知情同意并详细询问病史,包括初潮年龄、生育状况、绝经年龄、孕产次数、内科并发症及肿瘤家族史。测量身高与体重,并计算体质指数(body mass index, BMI),测量血压,采集静脉血化验空腹血糖(FPG)及血脂、肿瘤标志物[5-6]。年龄31~78岁,平均(51.15±9.69)岁,子宫内膜癌组平均年龄(54.77±8.21)岁,对照组为(46.95±9.65)岁。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 确定候选基因及其SNPs位点
由于Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌为雌激素依赖性肿瘤,结合相关文献报道,在美国国家生物技术信息中心(National Center for Biotechnology Information, NCBI)人类基因组数据库中选择与雌激素代谢相关的关键酶CYP1A1、CYP1B1,具有抗癌突变的依赖还原型辅酶Ⅰ/Ⅱ醌氧化还原酶1(quinone oxido-reductase1, NQO1)3个基因,选取与代谢酶活性密切相关且杂合度大于10%的SNPs位点进行基因型分析。
1.2.2 引物设计合成
利用引物设计软件premier 5.0,在含SNPs的DNA序列上设计PCR引物,并将设计的引物进行引物的同源性比较,选出同源性最小而Tm值和G/C比值合适的引物作为PCR反应引物,所扩增片段应包含要检测的SNPs位点,其位置尽可能设计在PCR扩增片段的中部。
1.2.3 检测方法
使用DNA提取试剂盒(DP304-03)从外周血中提取DNA,进行预扩增,琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测DNA完整性。根据设计引物模板,进行延伸反应及延伸产物纯化。PCR扩增反应体系总体积为50 μl,内含5 μl 10×PCR缓冲液,3 μl 25 mmol/L MgCl2溶液,5 μl 2 mmol/L dNTP混合物,1.25 U Taq DNA聚合酶,0.5 μmol/L引物及100g的基因组DNA。反应在MJ公司PTC-100 PCR反应仪中进行。PCR循环条件为95℃预变性10 min,然后94℃变性30 s,60℃复性30 s,72℃延伸30 s,反应40个循环后,72℃再延伸10 min。扩增产物用2%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,4℃保存。PCR产物经纯化后作为测序模板,用Big-Dye末端荧光标记试剂盒进行测序反应,测序反应产物经纯化后在ABI公司3730XL测序仪上进行测序电泳,用Gene codes公司的Sequencer4.2对测序结果进行分析。
1.3 统计学方法
采用SPSS18.0软件对实验数据进行统计学分析,用χ2检验和多因素Logistic回归模型分析各基因型在两组人群中的分布差异及其与子宫内膜癌临床病理特征的相关性,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 多因素回归分析
CYP1B1基因SNPs位点rs111888224因无碱基改变未纳入统计,rs1056836、rs2551188、rs10916在研究人群中均存在多态性,但分布频率差异无统计学意义;rs1056836 C、G基因分布频率差异有统计学意义(P=0.0454)。
CYP1A1基因SNP位点rs4646421在研究人群中存在CT、CC、TT多态性。与CT型相比,CC型为保护基因型,OR=0.479(95%CI: 0.255~0.899),差异有统计学意义(P=0.0219),其C、T基因分布频率差异有统计学意义(P=0.0041),见表 1。
表 1 基因型/等位基因在Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌患者中的分布(n(%))Table 1 Genotype/alleles distributions in typeⅠendometrial carcinoma cases (n(%))
2.2 CYP1A1基因rs4646421位点多态性与Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌危险因素的分层分析
对CYP1A1基因rs4646421位点不同基因型与Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的危险因素相关性进行分层比较,发现在年龄 > 60岁、BMI≥25、绝经延迟、并发高血压的个体中,携带CT+TT突变基因型将增加罹患Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的风险(P < 0.05),见表 2。
表 2 发病危险因素与基因型分布的关系(n(%))Table 2 Association between risk factors and genotypes distributions of SNP(rs4646421) in CYP1A1 (n(%))
3 讨论
雌激素分布在细胞内外表面,通过雌激素受体的核内结合蛋白在靶细胞中保持高亲和力和特异性。涉及雌激素生物合成和代谢的基因的多态性是雌激素受体阳性恶性肿瘤的潜在危险因素,有几种细胞色素P450(CYP)酶参与雌激素的氧化代谢途径[7]。CYP1A1和CYP1B1是代谢产生2-羟基-4-羟基雌激素代谢物的基本酶[8-9],在不同人群中不仅存在多态性,并且在性激素相关组织中的表达高于细胞色素P450超家族的其他成员,其基因多态性与乳腺癌、子宫肌瘤、子宫内膜异位症、宫颈癌等疾病风险相关[10-14]。
CYP1A1基因定位于人类染色体15q22-24,编码由512个氨基酸组成的蛋白质,是细胞色素P450家族中高诱导成员。CYP1A1酶的激活参与内源性和外源性化合物的氧化作用,催化多环芳香族碳氢化合物转化为酚与环氧化合物。一些酚类和环氧化合物可与DNA结合形成加合物,最终转化为致癌物、二醇环氧化物,通过环氧化物水解酶与一些抗肿瘤药物发生耐药,并增加个体肿瘤风险[9, 15]。本研究结果显示CYP1A1基因SNP位点rs4646421在子宫内膜癌人群中存在CT、CC、TT多态性,与携带CT基因型相比,携带CC基因型的个体罹患子宫内膜癌的风险较小,携带T等位基因的个体子宫内膜癌的发病风险高于C等位基因携带者。与携带CC基因型相比,携带TC+TT基因型在年龄 > 60岁、BMI≥25、绝经延迟(超过52岁)、合并高血压的女性中Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的发病风险增加。
CYP1B1基因位于染色体2q21-22,其单核苷酸多态性SNP总数有353个,目前研究较多的是SNPrs1056836,其mRNA发生1294位碱基胞嘧啶(cytosine, C)变异为鸟嘌呤(guanine, G),使DNA两条链形成野生CC型,杂合CG型和变异GG型3种基因型,即基因多态性。这种改变导致第三外显子432密码子的碱基由CTG变异为GTG,由其编码的亮氨酸(leucine, Leu)变异为缬氨酸(valine, Val),导致CYP1B1酶蛋白功能的改变[16]。CYP1B1通过多方面影响肿瘤的易感性和预后,在胰岛素抵抗中产生作用,突变型表达的酶之蛋白质表现出更强的激活癌前物质活性,或影响睾酮的6β-羟化作用及性激素的激活代谢等[17-18]。
本研究中CYP1B1基因SNP rs2551188、rs10916两个位点在人群中存在多态性,但分布频率无统计学差异;rs1056836在正常子宫内膜组与子宫内膜癌两组间的基因型分布频率无差异,但发生更多的碱基胞嘧啶变异为鸟嘌呤,可能会使罹患子宫内膜癌的风险增加,以往文献中发现对于单个位点基因突变的表现为阴性结论时,多个位点联合的单倍体基因型研究却往往能得到阳性结论,似乎预示着CYP1B1基因在分子遗传学上有一定的倾向性[16-19],但其与肿瘤易感性及预后的机制问题还存在着诸多争议与疑惑,有待于进一步研究。
NQO1是一种重要的化学致癌物质代谢酶,具有抗癌作用,可使内源性及外源性醌类化合物通过电子还原反应变成低毒性的氢醌类物质,再转化为水溶性化合物排出体外,降低了细胞发生突变及癌变的概率。如果位点发生突变,使原位编码的氨基酸发生改变,将会导致该酶活性减弱或完全丧失,降低解毒功能且不能维护细胞稳定,增加某些易感个体细胞发生癌变[20]。报道显示NQO1蛋白高表达在卵巢癌、乳腺癌、结直肠癌等肿瘤中,与临床分期晚、分化程度差和淋巴结转移等临床特征有关[21-22],本研究选择的SNP位点rs45488899和rs1800566虽在两组间均存在基因多态性,但分布频率不具有差异性,因此认为这两个SNP位点与Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的发生无显著相关性。
本研究通过基因表达谱差异的分析,推测CYP1A1基因rs4646421位点的多态性在Ⅰ型子宫内膜癌的发生发展中起着重要作用,可作为进行高危人群筛查的基因位点,还可以突变的基因型为基础,采取针对性的基因靶向治疗,或者通过修正基因突变谱来改善其预后。但是,基因多态性受复杂的遗传、环境因素、种族等的影响,并与样本量的大小有关,必须经过大样本试验来进一步明确基因多态性与子宫内膜癌易感性之间的基因环境交互作用及具体机制。
-
表 1 79例肺肉瘤样癌患者的临床特征及与生存率的关系
Table 1 Clinical features and survival analysis of 79 cases with pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma

表 2 79例肺肉瘤样癌患者预后的多因素分析
Table 2 Multivariate Cox model analysis of prognosis of 79 pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma patients

-
[1] Avila Martínez RJ, Marrón Fernández C, Hermoso Alarza F, et al. Primary pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinomas[J]. Arch Bronconeumol, 2013, 49(9): 405-7. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2012.12.002
[2] Elaine Shum, Matthew Stuart, Alain Borczuk, et al. Recent advance in management of pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma[J]. Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine, 2016, 10(4): 407-16. doi: 10.1586/17476348.2016.1157475
[3] Yendamuri S, Caty L, Pine M, et al. Outcomes of sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung:a Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Database analysis[J]. Surgery, 2012, 152(3): 397-402. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2012.05.007
[4] Huang SY, Shen SJ, Li XY. Pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma: a clinicopathologic study and prognostic analysis of 51 cases[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2013, 11: 252. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-11-252
[5] Zehani A, Ayadi-Kaddour A, Marghli A, et al. Sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung: retrospective study of 28 cases[J]. Ann Pathol, 2014, 34(2): 124-9. doi: 10.1016/j.annpat.2013.12.001
[6] Lee C, Usenko D, Frampton GM, et al. MET 14 Deletion in Sarcomatoid Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Detected by Next-Generation Sequencing and Successfully Treated with a MET Inhibitor[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2015, 10(12): e113-4. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/26709483
[7] Ouziane I, Boutayeb S, Mrabti H, et al. Sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung: a model of resistance of chemotherapy[J]. N Am J Med Sci, 2014, 6(7): 342-5. doi: 10.4103/1947-2714.136920
[8] 罗扬, 冯奉仪. 22例肺肉瘤样癌临床分析[J].肿瘤防治研究, 2009, 36(3): 247-50. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2009.03.023 Luo Y, Feng FY. Clinical analysis of pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma-22 cases report[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2009, 36(3): 247-50. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2009.03.023
[9] Vieira T, Girard N, Ung M, et al. Efficacy of first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced lung sarcomatoid carcinoma[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2013, 8(12): 1574-7. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24389441
[10] Shen XY, Lin ZF, Lin Q, et al. Pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma: a case report[J]. Contemp Oncol (Pozn), 2013, 17(2): 210-3. http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC3685364/
[11] Terra SB, Aubry MC, Yi ES, et al. Immunohistochemical study of 36 cases of pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma--sensitivity of TTF-1 is superior to napsin[J]. Hum Pathol, 2014, 45(2): 294-302. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2013.09.005
[12] Cadioli A, Rossi G, Costantini M, et al. Cancer histologic and immunohistochemical heterogeneity in the era of molecular therapies: analysis of 172 consecutive surgically resected, entirely sampled pulmonary carcinomas[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2014, 38(4): 502-9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24441660
[13] Petrov DB, Vlassov VI, Kalaydjiev GT, et al. Primary pulmonary sarcomas and carcinosarcomas-postoperative results and comparative survival analysis[J]. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg, 2003, 23(4): 461-6. doi: 10.1016/S1010-7940(03)00024-1
[14] 熊伟杰, 张新星, 黄媚媚, 等. 32例晚期及术后复发肺肉瘤样癌患者的治疗及生存分析[J].四川大学学报(医学版), 2014, 45(2): 320-3. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hxykdxxb201402031 Xiong WJ, Zhang XX, Huang MJ, et al. Outcomes of treatment of 32 cases of advanced or relapsed post-surgery pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma[J]. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao(Yi Xue Ban), 2014, 45(2): 320-3. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hxykdxxb201402031
[15] Giroux Leprieur E, Antoine M, Vieira T, et al. Clinical and molecular features in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung carcinoma refractory to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy[J]. Lung Cancer, 2013, 79(2): 167-72. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2012.10.010
[16] Liu X, Jia Y, Stoopler MB, et al. Next-generation sequencing of pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma reveals high frequency of actionable MET gene mutations[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2016, 34(8): 794-802. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.62.0674
[17] Vieira T, Antoine M, Hamard C, et al. Sarcomatoid lung carcinomas show high levels of programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) and strong immune-cell infiltration by TCD3 cells and macrophages[J]. Lung Cancer, 2016, 98: 51-8. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.05.013
[18] Terra SB, Jang JS, Bi L, et al. Molecular characterization of pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma: analysis of 33 cases[J]. Mod Pathol, 2016, 29(8): 824-31. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2016.89
[19] Lococo F, Gandolfi G, Rossi G. Deep-sequencing analysis reveals that KRAS mutation is a marker of poor prognosis in pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma patients[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2016, 11(8): 1282-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.04.020



 下载:
下载: