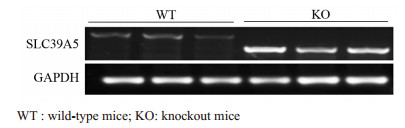
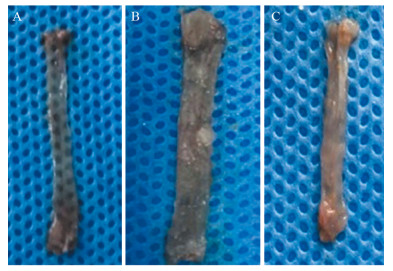
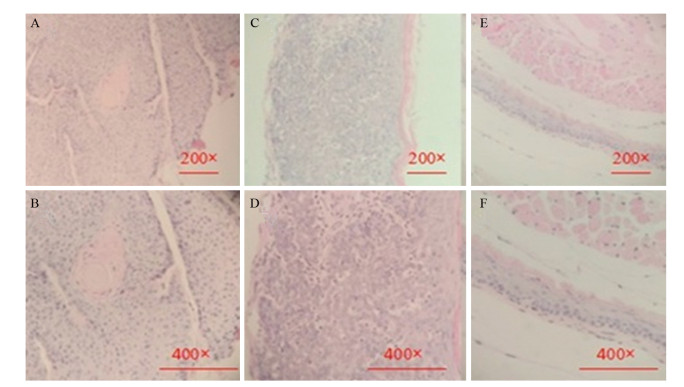
Impact of SLC39A5 Knockout on Establishment of Esophageal Cancer Model Induced by 4-NQO in C57BL/6 Mice
-
摘要:目的
探索敲除SLC39A5基因对4-NQO诱导的C57BL/6小鼠食管癌模型的影响。
方法选取10只C57BL/6野生型小鼠作为阴性对照组,饮用浓度为100 μg/ml的丙二醇空白溶液;选取140只野生型小鼠与80只SLC39A5基因敲除小鼠,采用饮水法摄入诱癌剂,即浓度为100 μg/ml的4-NQO(4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide),实验时间为28周,实验结束后处死三组小鼠。
结果阴性对照组小鼠、野生型小鼠和SLC39A5基因敲除小鼠在实验结束时其存活率分别为100%、92.96%、91.25%;三组小鼠食管癌诱癌成功率分别为0、61.36%、28.77%,两实验组小鼠诱癌成功率差异有统计学意义(χ2=19.98, P < 0.001)。
结论成功建立了C57BL/6小鼠及SLC39A5基因敲除小鼠的食管癌模型,同时验证了SLC39A5基因在食管癌发生发展中的促进作用。
-
关键词:
- 4-硝基喹啉-N-氧化物(4-NQO) /
- 食管癌 /
- SLC39A5基因敲除小鼠 /
- C57BL/6野生型小鼠
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the influences of SLC39A5 knockout on the establishment of esophageal cancer model induced by 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide (4-NQO) in C57BL/6 mice.
MethodsTen wild-type mice were treated as negative control group and drank the 1, 2-propylene glycol at 100 μg/ml; 140 wild-type mice and 80 knockout genotype mice were treated as experimental groups and drank the carcinogen 4-NQO stock solution dissolved in 1, 2-propylene glycol at 100μg/ml, the experimental time was 28 weeks and all three groups' mice were sacrificed.
ResultsThe survival rates were 100%, 92.96% and 91.25% in negative group, wild-type experimental group and SLC39A5 knockout genotype experimental group, respectively; the rates of tumor formation were 0, 61.36% and 28.77%, and there was a statistical difference between the two experimental groups(χ2=19.98, P < 0.001).
ConclusionThe esophageal cancer model in C57BL/6 mice and SLC39A5 knockout mice are established successfully and the facilitated role of SLC39A5 in the occurrence and development of esophageal cancer is verified.
-
0 引言
铁死亡是一种铁离子依赖的脂质过氧化物累积而导致的非凋亡形式的新型细胞死亡方式,2012年由Brent R. Stockwell提出[1],研究人员发现,小分子化合物Erastin可以特异性诱导Ras突变细胞发生铁离子依赖的、非凋亡性的细胞死亡,将这一过程称为铁死亡[2]。铁死亡的形态特征包括线粒体体积缩小、膜密度增高、线粒嵴减少或消失[3];其生化特点表现为细胞内铁和活性氧(reactive oxygen species, ROS) 的大量积累,产生过度的氧化应激以及脂质过氧化[4]。研究发现铁死亡与肿瘤放射治疗增敏、免疫治疗及耐药性方面密切相关[5-6]。TCGA数据分析发现高表达铁死亡相关转运体-SLC7A11的神经胶质瘤的患者,在接受放射治疗后肿瘤复发时间和总体生存期更短,提示铁死亡与神经胶质瘤患者放疗预后不良有关[7]。对传统疗法有抵抗力或具有高转移倾向的癌细胞可能特别容易发生铁死亡敏感,铁死亡诱导剂还可以与更传统的药物(如顺铂)协同作用,抑制肿瘤生长[8]。
前期研究中,我们构建与分析了肺腺癌(lung adenocarcinoma, LUAD)中与铁死亡有关的四个基因,其中肝型谷氨酰胺酶(GLS2)是LUAD预后的保护性因素,促进铁死亡。GLS2是谷氨酰胺酶的成员,它的活性在一些癌细胞中明显失调,GLS2是抑癌基因或癌基因取决于肿瘤的类型[9-10]。在乳腺癌中,GLS2与增强的体外细胞迁移和侵袭、间充质标志物和体内肺转移有关[11]。在胶质母细胞瘤中,GLS2可以抑制胶质母细胞瘤的生长[12]。GLS2介导的治疗在大规模临床环境中的应用仍处于初级阶段,其作为人类癌症的治疗及疾病进展标志仍存在争议。
本研究运用多个在线生物信息学平台和工具,评估了铁死亡相关基因GLS2在不同癌组织中的表达及其与癌症的可能联系,全面研究了GLS2在泛癌中的表达情况、预后和功能,分析GLS2是否可能成为癌症治疗及疾病进展的潜在靶点。
1 材料与方法
1.1 数据收集和处理
收集癌症基因组图谱(TCGA)数据库和广泛研究所癌症细胞系百科全书(CCLE)数据库的泛癌测序数据(Illumina平台),以及国际癌症基因组联盟(ICGC)数据库中的数据,所有数据均通过其门户网站进行分析。使用R包中的RMA功能(R studio版本:1.2.1335,R版本:3.6.1),过滤整个数据集,删除缺失和重复的结果,并通过log2(TPM+1)转换。通过门户网站提取相应的临床信息,包括患者的年龄、性别、肿瘤分期和临床分期。此外,仅从TCGA数据库下载肿瘤突变负荷(tumor mutational burden, TMB)和微卫星不稳定性(microsatellite instability, MSI)等信息。TMB计算为每百万碱基对的总突变发生率,MSI计算为基因重复序列中发生的插入或缺失事件数。
1.2 Cox回归分析和生存分析
Cox回归分析用于从R环境中的ICGC和TCGA数据库中检测GLS2的表达与每种癌症类型患者的总体生存率(overall survival, OS)、疾病特异性生存率(disease–specific survival, DSS)和无进展间隔期(progression–free interval, PFI)之间的相关性。根据最佳分离方法将患者分为高和低GLS2表达组后,采用Kaplan–Meier方法构建每种癌症类型患者的生存曲线。通过在R软件包(rdocumentation.org/packages/survival)中的survival ROC和survival分析,探究了生存的特异性和时间依赖性敏感性。使用对数秩检验检验曲线之间的差异,P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
1.3 免疫细胞浸润富集
肿瘤免疫评估资源数据库(TIMER)是一个用于免疫细胞浸润计算的数据库,可用于分析包括B细胞、CD4+T细胞、CD8+T细胞、巨噬细胞、中性粒细胞和树突状细胞的六种常见类型免疫细胞的浸润分数。TCGA数据库中泛癌数据的免疫细胞浸润分数用于分析其与GSL2表达的相关性。
1.4 统计学方法
Spearman相关检验用于评估GLS2表达与相关目标之间的相关性,包括免疫细胞浸润分数、TMB、MSI、错配修复(mismatch repair, MMR)基因和甲基化转移酶基因。根据样本是否配对,采用配对测试或T检验对各组之间或肿瘤与正常组织之间的GLS2表达水平进行比较。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。所有图通过ggplot2和forestplot的R包生成。
2 结果
2.1 GLS2基因在正常组织和癌组织中的表达
利用GTEx数据库分析GLS2基因在各个正常组织中的表达水平,结果显示:GLS2在31个正常组织中的表达水平均相似,见图1A。从CCLE数据库下载各个肿瘤细胞系的数据,发现不仅GLS2表达水平相较于正常组织普遍升高,而且与正常组织中的表达范围相比,GLS2的表达范围更窄,见图1B。进一步从TCGA数据库获取GLS2在各个肿瘤样本中癌与癌旁的差异,发现GLS2在大多数癌与癌旁组织中表达差异具有统计学意义(均P<0.05),见图1C,结合TCGA及GTEx的数据,发现27种癌症中,GLS2在25种癌组织和癌旁组织的表达差异存在统计学意义(均P<0.05),见图1D。
![]() 图 1 不同组织和肿瘤中GLS2的mRNA表达水平Figure 1 mRNA expression levels of GLS2 in different tissue and tumorsA: normal mRNA expression levels of GLS2 in different tissues from GTEx database; B: mRNA expression levels of GLS2 in various tumor cell lines from CCLE database; C: mRNA expression difference of GLS2 between tumor and peri-tumor samples from TCGA database; D: mRNA expression difference of GLS2 between normal, peri-tumor and tumor samples, combining data from TCGA and GTEx databases; *: P<0.05, **: P<0.01, ***: P <0.001.
图 1 不同组织和肿瘤中GLS2的mRNA表达水平Figure 1 mRNA expression levels of GLS2 in different tissue and tumorsA: normal mRNA expression levels of GLS2 in different tissues from GTEx database; B: mRNA expression levels of GLS2 in various tumor cell lines from CCLE database; C: mRNA expression difference of GLS2 between tumor and peri-tumor samples from TCGA database; D: mRNA expression difference of GLS2 between normal, peri-tumor and tumor samples, combining data from TCGA and GTEx databases; *: P<0.05, **: P<0.01, ***: P <0.001.2.2 GLS2基因表达水平与泛癌患者预后的相关性分析
我们利用TCGA数据库的数据评估了GLS2在不同癌症类型中与OS的相关性,其中GLS2在肾上腺皮质癌(ACC)中的风险效应最高(HR=4.37,P=0.0052),见图2。使用患者数据对每种癌症类型的中位表达值采用二分类进行生存率分析,结果显示高表达的GLS2不利于ACC患者预后(P<0.05),而在肾透明细胞癌(KIRC)、肺腺癌(LUAD)及胰腺癌(PAAD)中,高表达的GLS2与较好的预后相关(P<0.05),见图3。因此,GLS2可能作为ACC、KIRC、LUAD及PAAD患者预后的候选标志物。
考虑到随访期间,OS可能会受到非癌症相关死亡的影响,我们采用单变量Cox回归重新分析不同癌种中DSS和GLS2表达水平之间的相关性,分析结果与OS相关的结果相似,GLS2在ACC中的风险效应最高(HR=4.75,P=0.0013),见图4。在生存分析中,GLS2高表达在ACC中再次表现出更差的预后,见图5。最后,通过Cox回归分析GLS2表达和PFI之间的相关性(图略,请扫描OSID码),结果与上述OS及DSS分析结果相同。上述数据表明,GLS2的表达高低与不同肿瘤预后之间存在相关性。
2.3 GLS2基因可能通过影响不同癌种中的免疫细胞浸润来调节肿瘤微环境
为了研究GLS2基因表达与肿瘤微环境(TME)之间的关系,我们利用来自TCGA的TIMER数据库中6种免疫细胞类型(B细胞、CD4+T细胞、CD8+T细胞、中性粒细胞、巨噬细胞和树突状细胞)的浸润分数进行分析,结果发现在多种肿瘤中该基因表达与免疫细胞浸润水平存在显著相关性,其中排名前三位的肿瘤队列是低级别胶质瘤(LGG)、前列腺癌(PRAD)和肉瘤(SARC)。在LGG中,GLS2表达水平与CD8+T细胞浸润分数呈正相关,与B细胞、CD4+T细胞、中性粒细胞、巨噬细胞和树突状细胞浸润分数呈负相关。在PRAD中,GLS2表达水平与B细胞、CD4+T细胞、CD8+T细胞、中性粒细胞、巨噬细胞和树突状细胞浸润水平呈正相关,而在SARC中,GLS2表达水平与上述免疫细胞浸润水平呈负相关。上述结果表明,GLS2表达与LGG、PARP及SARC中免疫细胞的浸润水平有关,见图6。
2.4 GLS2表达与不同癌种的免疫检查点基因表达的相关性
通过mRNA序列数据库,我们评估了GLS2的表达与免疫检查点基因的表达关系。研究表明,在大部分肿瘤中,GLS2与多种免疫检查点相关基因高度相关(P<0.05),见图7。
![]() 图 7 来自TCGA数据库的多个肿瘤中GLS2 mRNA表达水平与免疫检查点mRNA表达之间的相关性Figure 7 Correlation between GLS2 mRNA expression levels and immune checkpoints’ mRNA expression in multiple tumors from the TCGA databaseThe lower triangle in each tile indicates coefficients calculated by Pearson’s correlation test, and the upper triangle indicates log10 transformed P value. *: P<0.05,**: P<0.01,***: P<0.001.
图 7 来自TCGA数据库的多个肿瘤中GLS2 mRNA表达水平与免疫检查点mRNA表达之间的相关性Figure 7 Correlation between GLS2 mRNA expression levels and immune checkpoints’ mRNA expression in multiple tumors from the TCGA databaseThe lower triangle in each tile indicates coefficients calculated by Pearson’s correlation test, and the upper triangle indicates log10 transformed P value. *: P<0.05,**: P<0.01,***: P<0.001.2.5 GLS2的表达与某些癌症TMB和MSI相关
在32种癌症类型中,GLS2的表达与TMB之间的相关性在12种中具有显著性(P<0.05),见图8A,6种中监测到GLS2的表达与MSI具有相关性(P<0.05),见图8B。
2.6 GLS2表达与不同癌症中的MMR缺陷密切相关,并可能干扰转录后的甲基化
我们分析了GLS2表达与一些成熟的MMR基因(MLH1、MSH2、MSH6、PMS2和EPCAM)之间的关系。结果表明,在泛癌中,GLS2的表达与MMR基因的表达显著且高度相关,见图9。关于GLS2的表达与四种甲基化转移酶(DNMT1、DNMT2、DNMT3A、DNMT3B)表达的相关性,结果与上述结果一致,在特定癌症类型中存在共表达(图略,请扫描OSID码)。
3 讨论
GLS2是谷氨酰胺酶家族成员,研究发现,谷氨酰胺酶家族有助于各种人类癌症的生长。此外,许多研究表明谷氨酰胺酶家族介导的靶向治疗是有希望抑制癌症发展的分子药物[13]。我们之前的研究中,GLS2被证实为与肺腺癌生存有关的铁死亡基因。然而,GLS2对多种癌症进展的影响仍不清楚。为了系统地了解GLS2在其他癌症进展中的作用,我们对基因表达数据集进行了比较数据挖掘。
基于肿瘤的表达分析,发现GLS2在不同组织中广泛表达,在癌症组织与正常组织中的表达存在差异,其表达程度也因组织类型而异,并且该表达与这些癌症类型中的生存相关,其中ACC的OS、DSS、PFI的HR值最高,生存曲线也显示高GLS2表达患者具有较差预后。GLS2在不同类型的肿瘤中表现出不同的表达模式和功能,并根据特定的肿瘤类型抑制或促进肿瘤的发展[14]。这与我们的研究结果相似,这里发现的GLS2表达与各种组织中的癌症之间的相关性,包括与癌症生存和预后的联系,使其成为癌症监测和进一步研究的潜在生物标志物。
TME在肿瘤生长、迁徙过程中起着多方面的作用,它可以产生免疫激活或抑制效应[15-16]。为了探究GLS2与TMB的相关性,我们测试了GLS2的表达与每种癌症类型的免疫细胞浸润水平之间的相关性,发现GLS2在多种癌症(如BLCA、BRCA等)中与免疫检查点mRNA表达之间具有相关性。在Qian之前的研究中,GLS2与LUAD的预后和免疫治疗相关[17]。Zou的研究发现,谷氨酰胺酶家族在多种癌症中与肿瘤的发展和TME有关[18]。本研究与上述研究结果一致。
TMB和MSI是多种肿瘤有效的预后生物标志物和免疫治疗反应指标[19-21]。MMR为细胞内的错配修复机制,该机制的关键基因功能丧失会导致DNA复制错误无法被修复,进而导致较高的体细胞突变的产生,MMR缺陷的肿瘤对免疫治疗有较好的反应[22]。甲基化为DNA化学修饰的一种形式,能够在不改变DNA序列的前提下,改变遗传表现,控制基因表达[23]。我们研究证明了GLS2的表达与某些癌症类型的TMB和MSI之间存在联系,并且某些肿瘤也表现出GLS2与主要MMR基因和甲基化转移酶的共同表达。先前的研究将TMB和MSI与患者的药物反应相关联,尤其是针对免疫检查点抑制剂的药物,如TGF-β拮抗剂和PD-1抑制剂[24-25]。提示GLS2可以用于癌症患者给药后免疫治疗评估,可能是潜在的药物反应良好指标。
本研究中,我们使用不同的在线生物信息学平台和工具,系统分析了GLS2在各种癌症中的表达水平及其与免疫细胞浸润、TMB、MSI、MMR基因和甲基化转移酶的关系。我们的分析显示GLS2在癌症发展中发挥着不同的作用,并对癌症的临床结果进行了不同的调节。GLS2可作为肾上腺皮质癌、肾透明细胞癌和胰腺癌患者的癌症治疗靶点及预后标志物。总之,本研究结果为不同类型癌症的分子和临床特征提供了一些见解,因此可以用来帮助将基因组知识转化为癌症治疗。
然而,完全依赖于开放存取数据库中可用的信息,没有经过实验的确认,可能出现过度拟合和欠拟合,此外,GLS2在不同癌症中的具体作用分子机制和信号通路尚不清晰,因此,这项研究需要更多的理论、实验和临床研究来验证和进一步挖掘。
-
表 1 野生型与SLC39A5基因敲除小鼠诱癌成功率的比较
Table 1 Comparison of tumor formation rates between two experimental groups

-
[1] Allemani C, Weir HK, Carreira H, et al. Global surveillance of cancer survival 1995-2009: analysis of individual data for 25, 676, 887 patients from 279 population-based registries in 67 countries (CONCORD-2)[J]. Lancet, 2015, 385(9972): 977-1010. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)62038-9
[2] Torre LA, Siegel RL, Ward EM, et al. Global Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates and Trends-An Update[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2016, 25(1): 16-27. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-15-0578
[3] 李玉林. 肿瘤[M]//李玉林. 病理学. 6版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2004: 213-4. Li YL. Tumor[M]//Li YL. Pathology. 6th. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2004: 213-4.
[4] Chen W, Zheng R, Zeng H, et al. The incidence and mortality of major cancers in China, 2012[J]. Chin J Cancer, 2016, 35(1): 73. doi: 10.1186/s40880-016-0137-8
[5] He YT, Hou J, Chen ZF, et al. Trends in incidence of esophageal and gastric cardia cancer in high-risk areas in China[J]. Eur J Cancer Prev, 2008, 17(2): 71-6. doi: 10.1097/CEJ.0b013e3282b6fd97
[6] Li M, Li ZS, Chen ZF, et al. Mortality report of malignant tumors in SheXian, Hebei Province, China, from the 1970's to the present[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2004, 5(4): 414-8. https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i1/17.htm
[7] 宋国慧, 李东方, 孟凡书, 等.磁县2003—2012年上消化道癌发病率分析[J].肿瘤防治研究, 2016, 43(10): 887-93. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2016.10.012 Song GH, Li DF, Meng FS, et al. Upper gastrointestinal carcinomas incidence from 2003 to 2012 in cixian, hebei province[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2016, 43(10): 887-93. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2016.10.012
[8] He Y, Liang D, Li D, et al. Estimated cancer incidence and mortality in Hebei province, 2012[J]. Chin J Cancer Res, 2016, 28(3): 286-300. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2016.03.03
[9] 钟钏.食管癌流行病学病因学研究进展[J].河南预防医学杂志, 2011, 22(1): 1-10, 17. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_hnyfyxzz201101001.aspx Zhang C. The research progress of esophageal cancer epidemiology and etiology[J]. HenanYu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2011, 22(1): 1-10, 17. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_hnyfyxzz201101001.aspx
[10] Rasool S, A Ganai B, Syed Sameer A, et al. Esophageal cancer: associated factors with special reference to the Kashmir Valley[J]. Tumori, 2012, 98(2): 191-203. doi: 10.1177/030089161209800203
[11] Wu M, Liu AM, Kampman E, et al. Green tea drinking, high tea temperature and esophageal cancer in high-and low-risk areas of Jiangsu Province, China: a population-based case-control study[J]. Int J Cancer, 2009, 124(8): 1907-13. doi: 10.1002/ijc.v124:8
[12] He Y, Jin J, Wang L, et al. Evaluation of miR-21 and miR-375 as prognostic biomarkers in oesophageal cancer in high-risk areas in China[J]. Clin Exp Metastasis, 2017, 34(1): 73-84. doi: 10.1007/s10585-016-9828-4
[13] Yong F, Xudong N, Lijie T. Human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 in esophagus squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis[J]. Ann Epidemiol, 2013, 23(11): 726-34. doi: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2013.07.002
[14] Zheng H, Wang Y, Tang C, et al. TP53, PIK3CA, FBXW7 and KRAS Mutations in Esophageal Cancer Identified by Targeted Sequencing[J]. Cancer Genomics Proteomics, 2016, 13(3): 231-8. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27107065
[15] Ping FM, Liu GJ, Liu ZJ, et al. Expression of RKIP, E-cadherin and NF-kB p65 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and their correlations[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2015, 8(9): 10164-70. http://www.ijcep.com/files/ijcep0013203.pdf
[16] Jin J, Li Z, Liu J, et al. Knockdown of zinc transporter ZIP5(SLC39A5) expression significantly inhibits human esophageal cancer progression[J]. Oncol Rep, 2015, 34(3): 1431-9. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4097
[17] Li Q, Jin J, Liu J, et al. Knockdown of Zinc Transporter ZIP5 by RNA Interference Inhibits Esophageal Cancer Growth in vivo[J]. Oncol Res, 2016, 24(3): 205-14. doi: 10.3727/096504016X14648701447896
[18] Fong LY, Ishii H, Nguyen VT, et al. p53 deficiency accelerates induction and progression of esophageal and forestomach tumors in zinc-deficient mice[J]. Cancer Res, 2003, 63(1): 186-95. https://sapienza.pure.elsevier.com/it/publications/p53-deficiency-accelerates-induction-and-progression-of-esophagea-4
[19] Feith DJ, Pegg AE, Fong LY. Targeted expression of ornithine decarboxylase antizyme prevents upper aerodigestive tract carcinogenesis in p53-deficient mice[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2013, 34(3): 570-6. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs377
[20] Di Pardo BJ, Bronson NW, Diggs BS, et al. The Global Burden of Esophageal Cancer: A Disability-Adjusted Life-Year Approach[J]. World J Surg, 2016, 40(2): 395-401. doi: 10.1007/s00268-015-3356-2
[21] 张林西, 齐凤英, 左连富.食管癌动物模型的研究和应用进展[J].临床与实验病理学杂志, 2002, 18(4): 421-3. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=lsbl200204028&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ Zhang LX, Qi FY, Zuo LF. Advances in Research and Application of Animal Models of Esophageal Carcinoma[J]. Lin Chuang Yu Shi Yan Bing Li Xue Za Zhi, 2002, 18(4): 421-3. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=lsbl200204028&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[22] Booth DR. A relationship found between intra-oral sites of 4NQO reductase activity and chemical carcinogenesis[J]. Cell Tissue Kinet, 1990, 23(4): 331-40. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/21038029_A_relationship_found_between_intra-oral_site_of_4NQO_reductase_activity_and_chemical_carcinogenesis
[23] Tang XH, Knudsen B, Bemis D, et al. Oral cavity and esophageal carcinogenesis modeled in carcinogen-treated mice[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2004, 10(1 Pt 1): 301-13. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/8911397_Oral_Cavity_and_Esophageal_Carcinogenesis_Modeled_in_Carcinogen-Treated_Mice
[24] 谢仰民, 谢良喜, 李德锐, 等.食管癌SCID小鼠异位移植模型建立的初步探讨[J].实验动物与比较医学, 2007, 27(1): 41-4. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1243408 Xie YM, Xie LX, Li DR, et al. Preliminary Study on Establishment of Ectopic Transplantation Model of Esophageal Carcinoma in SCID Mice[J]. Shi Yan Dong Wu Yu Bi Jiao Yi Xue, 2007, 27(1): 41-4. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1243408
[25] 郭凯, 孟志宏, 胡哲一, 等.食管癌原位模型的建立[J].肿瘤基础与临床, 2014, 27(5): 380-2. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLZL201405005.htm Guo K, Meng ZH, Hu ZY, et al. Establishment of a Mouse Model with Orthotopic Esophageal Cancer[J]. Journal of Basic and Clinical Oncology, 2014, 27(5): 380-2. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLZL201405005.htm
[26] 陈金东.肾癌敲基因小鼠模型建立及应用的研究进展[J].遵义医学院学报, 2017, 40(4): 347-57. http://www.doc88.com/p-9252886809574.html Chen JD. Advances in development and application of knockout mouse models of kidney cancer[J]. Zunyi Yi Xue Yuan Xue Bao, 2017, 40(4): 347-57. http://www.doc88.com/p-9252886809574.html
[27] 马伟, 王凯, 程玉峰.食管癌小鼠模型研究进展[J].国际肿瘤学杂志, 2013, 40(12): 915-8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-422X.2013.12.011 Ma W, Wang W, Cheng YF. Research progress of esophageal cancer mouse models[J]. Guo Ji Zhong Liu Xue Za Zhi, 2013, 40(12): 915-8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-422X.2013.12.011
[28] 刘雪静, 王欢, 严放, 等.大中型动物基因敲除技术的研究进展[J].生理科学进展, 2015, 46(1): 11-6. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/5dc80176f121dd36a22d82b3.html Liu XJ, Wang H, Yan F, et al. The Development of Gene Knockout Technologies in Large and Medium Animal Models[J]. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan, 2015, 46(1): 11-6. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/5dc80176f121dd36a22d82b3.html
[29] Ali A, Bhatti MZ, Shah AS, et al. Tumor-suppressive p53 Signaling Empowers Metastatic Inhibitor KLF17-dependent Transcription to Overcome Tumorigenesis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer[J]. J Biol Chem, 2015, 290(35): 21336-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.635730
[30] Fong LY, Jiang Y, Farber JL. Zinc deficiency potentiates induction and progression of lingual and esophageal tumors in p53-deficient mice[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2006, 27(7): 1489-96. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgl012
[31] Zhang Z, Wang Y, Yao R, et al. p53 Transgenic mice are highly susceptible to 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide-induced oral cancer[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2006, 4(6): 401-10. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-06-0028
[32] 崔智, 李瑞生, 李晓娟, 等. DEN诱发PLCε基因敲除小鼠肝癌模型的建立[J].中国比较医学杂志, 2013, 23(3): 17-20. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/86049e2c31b765ce0508146f.html Cui Z, Li RS, Li XJ, et al. Establishment of DEN induced PLCε knock-out mouse liver cancer model[J]. Zhongguo Bi Jiao Yi Xue, 2013, 23(3): 17-20. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/86049e2c31b765ce0508146f.html
[33] Nishikawa T, Salim EI, Morimura K, et al. High susceptibility of p53 knockout mice to esophageal and urinary bladder carcinogenesis induced by N, N-dibutylnitrosamine[J]. Cancer Lett, 2003, 194(1): 45-54. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3835(03)00057-0
[34] Wu X, Tang J, Xie M. Serum and hair zinc levels in breast cancer: a meta-analysis[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 12249. doi: 10.1038/srep12249
[35] Pan Z, Choi S, Ouadid-Ahidouch H, et al. Zinc transporters and dysregulated channels in cancers[J]. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 2017, 22: 623-43. doi: 10.2741/4507
[36] Guerinot ML. The ZIP family of metal transporters[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2000, 1465(1-2): 190-8. doi: 10.1016/S0005-2736(00)00138-3
[37] Chen QG, Zhang Z, Yang Q, et al. The role of zinc transporter ZIP4 in prostate carcinoma[J]. Urol Oncol, 2012, 30(6): 906-11. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2010.11.010
[38] Wu L, Chaffee KG, Parker AS, et al. Zinc transporter genes and urological cancers: integrated analysis suggests a role for ZIP11 in bladder cancer[J]. Tumour Biol, 2015, 36(10): 7431-7. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3459-2
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 吴晓昀,荆林林,齐夏丽. 2型糖尿病合并乳腺癌患者预后高危因素分析. 实用癌症杂志. 2024(08): 1356-1358 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: