yeloid-derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Proliferation and Killing Activity of Neuroblastoma Antigen-specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte in vitro
-
摘要:目的
探讨髓系抑制性细胞(myeloid-derived suppressor cell, MDSC)对神经母细胞瘤抗原特异性细胞毒性T淋巴细胞(cytotoxic T lymphocyte, CTL)体外增殖和杀伤活性的影响。
方法体外培养神经母细胞瘤SK-N-SH细胞、自BALB/c小鼠分离培养树突状细胞(dendritic cell, DC)和CD3+T细胞,制备DC诱导的神经母细胞瘤抗原特异性CTL。分离纯化小鼠MDSC,将CTL与MDSC混合培养,采用CFSE荧光染色和流式细胞学方法,检测MDSC对CTL增殖抑制情况。将CTL与SK-N-SH、MDSC混合培养,ELISA法检测不同组CTL对SK-N-SH杀伤率及上清液中IL-2和IFN-γ分泌情况。
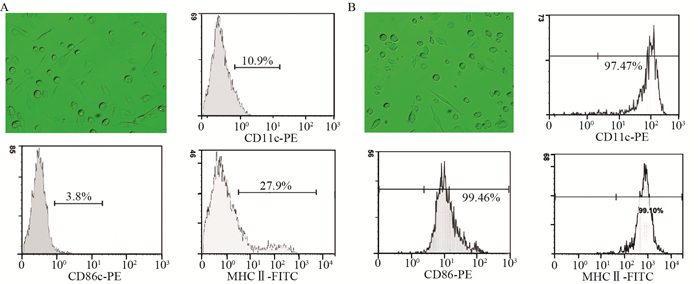
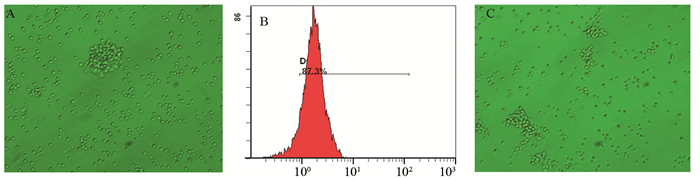
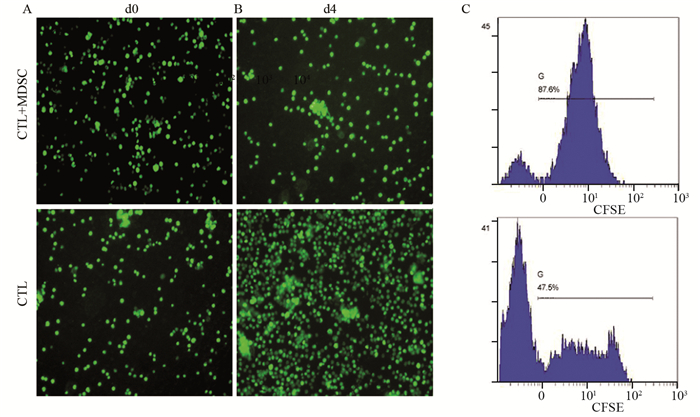
结果磁珠分选纯化后Gr-1+CD11b+MDSC细胞比例为84.6%。负载抗原的CTL细胞上清液中IL-2和IFN-γ含量较单纯培养T细胞上清液中IL-2和IFN-γ含量明显增高(P < 0.05)。与MDSC共培养的CTL细胞增殖明显受抑;而单独培养CTL随时间延长细胞增殖明显。MDSC+CTL+SK-N-SH组杀伤率较CTL+SK-N-SH组明显降低(t=6.506, P < 0.001);两组上清液中IL-2和IFN-γ分泌量差异亦有统计学意义(均P < 0.01)。
结论MDSC可抑制神经母细胞瘤抗原特异性CTL的体外增殖和活性而产生免疫耐受,抑制CTL对神经母细胞瘤细胞的杀伤作用。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the inhibitory role of myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC) in the proliferation and killing activity of neuroblastoma antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) in vitro.
MethodsThe neuroblastoma antigen specific CTLs were successfully prepared on the basis of cultivation of neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells and separation of BALB/c mice myeloid-derived dendritic cell (DC) and CD3+T cells in vitro. MDSCs were purified and cultivated with CTLs, then the inhibitory role of MDSC in the proliferation of CTL was detected by fluorescence staining of 5, 6-carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester (CFSE) and flow cytometry. Furthermore, CTL, SK-N-SH and MDSC were mixed and cultivated, the killing rate of CTL on SK-N-SH and the secretion of IL-2, IFN-γ in supernatant of the different groups were detected by ELISA.
ResultsAfter magnetic cell sorting, the rate of Gr-1+CD11b+MDSC reached to 84.6% by flow cytometry test. The levels of IL-2 and IFN-γ in supernatant of antigen-loaded CTLs were significantly higher than those in supernatant of T cells (P < 0.05). The proliferation of CTLs cultivated with MDSC was significantly inhibited, with strong fluorescence in view: however, CTLs cultivated alone proliferated obviously, with weak fluorescence intensity. The killing rate of CTLs to SK-N-SH in MDSC+CTL+SK-N-SH group was significant lower than that in CTL+SK-N-SH group (t=6.506, P < 0.001). Significant difference existed in the secretion levels of IL-2 and IFN-γ in the supernatant between the two groups (all P < 0.01).
ConclusionMDSC inhibite the proliferation and activity of neuroblastoma antigen-specific CTLs in vitro result in immune tolerance and reduced the killing effect of CTL on neuroblastoma cells.
-
0 引言
Yes相关蛋白(Yes-associated protein, YAP)参与调控细胞的生长、器官的发育,与肿瘤的发生有关[1]。研究显示,YAP在乳腺癌、卵巢癌等肿瘤中表达异常,并且其表达水平的高低与肿瘤患者分期及预后等有关[2-3]。在胃癌中发现YAP过度表达,并且与胃癌患者的病理特征等有关[4]。YAP敲低可以抑制多种肿瘤细胞的增殖,如胰腺癌、乳腺癌等,对于肿瘤细胞的凋亡也具有调控作用[5-6]。Wnt/β-catenin在真核生物体细胞内广泛存在,在正常的成熟细胞中激活水平极低,而在肿瘤细胞中过度激活,与肿瘤细胞的增殖、凋亡等有关[7]。研究表明,YAP可以通过作用于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响细胞的生长,提示两者之间存在潜在联系[8]。本实验以BGC823细胞为体外研究对象,通过小RNA干扰技术降低细胞中YAP的表达,明确YAP对胃癌BGC823细胞凋亡的影响及对Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的调控作用。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
BGC823细胞购自中国医学科学院基础医学研究所基础医学细胞中心;含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶3(cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 3, Caspase-3)活性测定试剂盒和含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶9(cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 9, Caspase-9)活性测定试剂盒为武汉艾美捷公司产品;Lipofectamine2000为美国Invitrogen公司产品;MMLV反转录试剂盒为美国Promega公司产品;qRT-PCR为大连宝生物公司产品;β-连环蛋白(β-catenin)抗体、c-myc抗体、细胞周期蛋白D1(CyclinD1)抗体、辣根过氧化物标记的二抗均为美国Abcam公司产品;YAP、β-actin引物由上海生工公司合成;YAP siRNA1、YAP siRNA2、siRNA control为美国Santa Cruz Biotech公司产品。YAP siRNA1:5’-GCAUCUUCGACAGUCUUCUTT-3’,5’-AGAAGACUGUCGAAGAUGCTT-3’。YAP siRNA2:5’-GGUGAUACUAUCAACCAAATT-3’,5’-UUUGGUUGAUAGUAUCACCTT-3’。
1.2 细胞分组
BGC823细胞中转染YAP siRNA1和YAP siRNA2,同时转染siRNA control,依次命名为si-YAP1、si-YAP2和si-NC,以不作任何处理的BGC823细胞记为Control。细胞转染用Lipofectamine2000,具体步骤参照转染试剂说明书。BGC823细胞培养参数为:饱和湿度、37℃、5%CO2培养箱。细胞为90%时,用0.25%的胰蛋白酶消化传代细胞。细胞培养于含有10%胎牛血清的RPMI1640中。
1.3 qRT-PCR测定转染后细胞YAP mRNA水平
Control、si-NC、si-YAP1、si-YAP2细胞培养48 h以后,提取总RNA。用MMLV反转录试剂盒进行反转录,程序为42℃ 65 min;70℃ 5 min;合成的cDNA保存于-80℃。以cDNA为模板,用qRT-PCR扩增。引物序列如下:β-actin F5’-CGTCTTCCCCTCCATCGT-3’,β-actin R5’-GAAGGTGTGGTGCCAGATTT-3’。YAP F5’-ACCCACAGCTCAGCATCTTCG-3’,YAP R5’-TGGCTTGTTCCCATCCATCAG-3’。结果以2-ΔΔCt法计算。
1.4 蛋白质印迹法测定转染后细胞YAP蛋白水平
Control、si-NC、si-YAP1、si-YAP2细胞培养48 h以后,提取细胞中的总蛋白,蛋白保存在-80℃。取蛋白样品,用BCA法对蛋白进行定量。以每个泳道添加40 μg蛋白进行电泳,电泳前将蛋白样品和上样缓冲液以等体积混合煮沸5 min。在浓缩胶中以90 V的低压进行电泳,在分离胶中以120 V的电压电泳,观察染料进入到分离胶的底部之后关闭电源。把蛋白凝胶上的蛋白转移到PVDF膜上,以100 mA电流进行转膜,转膜在4℃进行。转膜结束后把膜放在用TBST稀释的牛血清白蛋白中封闭2 h。取出膜,放入含有YAP一抗(1:200稀释)的平皿中,4℃反应过夜后,再把膜放入含有HRP标记的二抗(1:3 000稀释)中,室温孵育2 h。取出膜,用ECL显色试剂盒显色,凝胶成像仪拍照,分析灰度值,以β-actin为内参。
1.5 MTT法测定细胞增殖
Control、si-NC、si-YAP1细胞种植到96孔板中,分别培养24、48、72、96 h以后,用MTT法测定各组胃癌细胞增殖情况。步骤如下:在每孔中添加20 μl的MTT,把细胞放在37℃培养箱内继续培养约4 h,取出培养板,在每个孔中依次添加150 μl的DMSO溶液,置于振荡仪上10 min,放在酶标仪上测定每孔492 nm的A值。每个组设置5个重复孔,测定前以空白孔调零,空白孔中不加细胞。
1.6 平板克隆检测细胞克隆形成能力
Control、si-NC、si-YAP1细胞以每个培养皿200个细胞接种到细胞培养皿中,每个培养皿中含有10 ml的培养液。放在37℃、5%CO2培养箱中孵育14 d后,肉眼可以观察到形成的细胞克隆。把培养液吸弃后,用PBS洗涤2次,加入4%的多聚甲醛固定各组细胞15 min。用吉姆萨染色液染约20 min后,用水把染液冲洗掉,放在空气中干燥。计数细胞克隆数目,用(细胞克隆数目÷细胞总数)×100%表示细胞克隆形成率。
1.7 流式细胞术测定细胞凋亡
Control、si-NC、si-YAP1细胞分别培养48 h后,用胰蛋白酶消化,收集细胞,用PBS把细胞沉淀洗涤2次。在细胞中添加195 μl的结合缓冲液、5 μl的Annexin V-FITC,混合后再加入10 μl的PI,充分混合,流式细胞仪测定细胞凋亡。
1.8 分光光度法检测Caspase-3、Caspase-9活性
Control、si-NC、si-YAP1细胞分别培养48 h后,收集各组细胞,分别用Caspase-3、Caspase-9活性检测试剂盒测定细胞中Caspase-3、Caspase-9活性。用酶标仪测定各组样品在405 nm的A值,用实验组A值÷对照组A值表示Caspase-3、Caspase-9活性。同时用蛋白质印迹法测定细胞中β-catenin、c-myc、cyclinD1、Cleaved Caspase-3、Cleaved Caspase-9蛋白表达,步骤同上,β-catenin、c-myc、cyclinD1、Cleaved Caspase-3、Cleaved Caspase-9一抗分别以1:600稀释。
1.9 Wnt/β-catenin激活剂对敲低YAP后的胃癌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响
以20 mmol/L的Wnt/β-catenin激活剂LiCl处理在0 h加入转染YAP siRNA1后的细胞,记为si-YAP1+LiCl。用MTT实验测定si-YAP1+LiCl、si-YAP1细胞48 h的增殖情况,步骤同1.5。平板克隆实验测定克隆形成能力,步骤同1.6。流式细胞术测定48 h细胞凋亡,步骤同1.7。分光光度法检测48 h细胞中Caspase-3、Caspase-9活性,步骤同1.8。蛋白质印迹法测定48 h细胞中β-catenin、c-myc、cyclinD1、Cleaved Caspase-3、Cleaved Caspase-9蛋白水平,步骤同1.4。
1.10 统计学方法
实验数据用SPSS21.0软件统计分析,计量资料以(x±s)表示,多组差异比较用单因素方差,组间比较用LSD-t检验,以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 转染后胃癌细胞中YAP的表达
Control、si-NC、si-YAP1、si-YAP2细胞中YAP mRNA水平分别为1.00、(1.01±0.12)、(0.36±0.05)、(0.47±0.03),蛋白水平分别为(0.38±0.04)、(0.39±0.06)、(0.14±0.02)、(0.21±0.04)。si-NC胃癌细胞中的YAP mRNA和蛋白水平与Control比较没有变化。si-YAP1、si-YAP2胃癌细胞中的YAP mRNA和蛋白水平明显低于Control,差异有统计学意义(t1=22.170, P=0.000; t2=30.599, P=0.000; t3=9.295, P=0.000; t4=5.205, P=0.000)。si-YAP1胃癌细胞中的YAP mRNA和蛋白水平明显低于si-YAP2,差异有统计学意义(t1=3.268, P=0.001; t2=2.711, P=0.007),见图 1。YAP siRNA1对胃癌细胞中YAP的转录和表达抑制作用更强,后续选用si-YAP1继续研究。
2.2 YAP下调抑制胃癌细胞增殖和克隆形成能力
Control、si-NC、si-YAP1细胞24 h的A值分别为0.35±0.04、0.36±0.03、0.24±0.01;48 h的A值分别为0.56±0.06、0.54±0.05、0.28±0.03;72 h的A值分别为0.86±0.09、0.87±0.09、0.31±0.02;96 h的A值分别为0.98±0.07、0.99±0.12、0.35±0.04。克隆形成率分别为(39.62±3.24)%、(38.49±4.51)%、(25.14±2.36)%。si-NC胃癌细胞A值和克隆形成率与Control比较没有变化。si-YAP1胃癌细胞A值和克隆形成率明显低于Control,差异有统计学意义(t1=4.621, P=0.000; t2=7.230, P=0.000; t3=10.333, P=0.000; t4=13.535, P=0.000; t5=6.257, P=0.000)。YAP敲低可以降低胃癌细胞增殖和克隆形成能力,见图 2。
2.3 YAP下调诱导胃癌细胞凋亡和Caspase-3、Caspase-9活化
Control、si-NC、si-YAP1细胞Caspase-3活性分别为1.00、1.03±0.14、2.61±0.22,Caspase-9活性分别为1.00、0.99±0.11、3.25±0.30,凋亡率分别为(6.32±0.58)%、(6.53±0.71)%、(32.71±2.64)%,Cleaved Caspase-3蛋白水平依次为0.15±0.06、0.16±0.03、0.62±0.05,Cleaved Caspase-9蛋白水平依次为0.52±0.07、0.54±0.09、0.97±0.12。si-NC胃癌细胞凋亡率和Caspase-3、Caspase-9活性与Control比较没有变化。si-YAP1胃癌细胞凋亡率、Caspase-3活性、Caspase-9活性和Cleaved Caspase-3、Cleaved Caspase-9蛋白水平明显高于Control,差异有统计学意义(t1=12.676, P=0.000; t2=12.990, P=0.000; t3=16.911, P=0.000; t4=10.423, P=0.000; t5=5.610, P=0.000),见图 3。YAP敲低可以诱导胃癌细胞凋亡,增加Caspase-3、Caspase-9活性。
2.4 YAP下调抑制胃癌细胞中β-catenin、c-myc、cyclinD1蛋白表达
Control、si-NC、si-YAP1细胞β-catenin水平分别为(0.32±0.03)、(0.33±0.02)、(0.10±0.01),c-myc水平分别为(0.48±0.05)、(0.49±0.08)、(0.05±0.02),cyclinD1水平分别为(0.66±0.06)、(0.67±0.05)、(0.14±0.06)。si-NC胃癌细胞中β-catenin、c-myc、cyclinD1蛋白水平与Control比较没有变化。si-YAP1胃癌细胞中β-catenin、c-myc、cyclinD1蛋白水平明显低于Control,差异有统计学意义(t1=12.050, P=0.000; t2=13.830, P=0.000; t3=10.615, P=0.000)。YAP敲低可以抑制胃癌细胞中β-catenin、c-myc、cyclinD1蛋白表达,抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激活,见图 4。
2.5 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激活剂对敲低YAP的胃癌细胞中β-catenin、c-myc、cyclinD1蛋白表达影响
si-YAP1、si-YAP1+LiCl细胞中β-catenin水平分别为(0.12±0.03)、(0.29±0.05),c-myc水平分别为(0.16±0.03)、(0.54±0.06),cyclinD1水平分别为(0.15±0.04)、(0.71±0.07)。si-YAP1+LiCl胃癌细胞中β-catenin、c-myc、cyclinD1蛋白水平明显高于si-YAP1,差异有统计学意义(t1=5.450; P=0.000, t2=9.812, P=0.000; t3=12.031, P=0.000)。Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激活剂可以促进YAP敲低后的胃癌细胞中β-catenin、c-myc、cyclinD1蛋白表达,激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,见图 5。
2.6 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激活剂对敲低YAP的胃癌细胞增殖凋亡的影响
si-YAP1、si-YAP1+LiCl细胞A值分别为0.26±0.04、0.34±0.03;克隆形成率分别为(23.51±2.30)%、(31.14±2.69)%;凋亡率分别为(34.26±3.28)%、(15.69±1.27)%;Caspase-3活性分别为1.00、(0.62±0.06),Caspase-9活性分别为1.00、(0.76±0.05),Cleaved Caspase-3水平为(0.53±0.04)、(0.32±0.06);Cleaved Caspase-9水平为(0.94±0.11)、(0.43±0.05)。si-YAP1+LiCl胃癌细胞A值和克隆形成率明显高于si-YAP1,而细胞凋亡率和Caspase-3、Caspase-9活性、Cleaved Caspase-3水平、Cleaved Caspase-9水平明显低于si-YAP1,差异有统计学意义(t1=2.771, P=0.006, t2=3.734, P=0.000, t3=9.145, P=0.000, t4=10.970, P=0.000, t5=8.314, P=0.000, t6=5.044, P=0.000, t7=7.311, P=0.000),见图 6。Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激活剂可以降低YAP敲低诱导的胃癌细胞凋亡和增殖抑制作用。
![]() 图 6 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激活剂对敲低YAP的胃癌细胞凋亡影响Figure 6 Effect of Wnt/ β-catenin signaling pathway activator on apoptosis of gastric cancer cells with YAP knockdownA: the apoptosis of si-YAP1 and si-YAP1+LiCl; B: the protein expression of cleaved Caspase-3 and cleaved Caspase-9 in si-YAP1 and si-YAP1+LiCl groups
图 6 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激活剂对敲低YAP的胃癌细胞凋亡影响Figure 6 Effect of Wnt/ β-catenin signaling pathway activator on apoptosis of gastric cancer cells with YAP knockdownA: the apoptosis of si-YAP1 and si-YAP1+LiCl; B: the protein expression of cleaved Caspase-3 and cleaved Caspase-9 in si-YAP1 and si-YAP1+LiCl groups3 讨论
人YAP基因定位在11q13染色体上,其编码的蛋白质与转录激活有关,其本身并不能同DNA特异性结合,可以通过与存在于细胞核内的相关因子结合从而影响基因的表达[9]。YAP是Hippo的下游效应分子,其参与调控细胞的生长过程,是一个潜在的癌因子[10]。多西环素可以调控YAP的表达影响小鼠肺癌的发生和发展,而抑制YAP以后,肺癌小鼠肿瘤恶性程度降低[11]。在乳腺癌、胰腺癌、肺癌等患者的癌组织中均检测到YAP的过度表达,并且与患者的预后有关[12-14]。YAP可以调控肿瘤细胞的生长,在视网膜母细胞瘤、卵巢癌等肿瘤细胞中均得到验证[15-16]。YAP在胃癌组织中高表达,并且与胃癌裸鼠成瘤能力有关[17]。本实验结果显示,YAP敲低后的胃癌细胞增殖能力下降,并且克隆形成能力也降低,说明YAP下调后可以发挥抑制胃癌的作用,这与上述研究报道相符合。
本实验结果还显示,YAP下调后的胃癌细胞凋亡增多,并且细胞中Caspase-3、Caspase-9活化水平也升高,YAP敲低诱导Caspase-3、Caspase-9介导的胃癌细胞凋亡。很多研究报道称,YAP不仅参与肿瘤细胞的生长,还与肿瘤细胞凋亡有关[18]。研究显示,在肝癌细胞SMMC-7721中转染YAP shRNA后,细胞的生长速度明显减慢,并且细胞凋亡增多[19]。Caspase级联反应参与肿瘤细胞的凋亡,Caspase-3是该级联反应的执行因子,以酶原的形式存在于正常细胞中,其氮端含有一个前区,可以与Caspase-9等起始因子结合,在受到激活后可以诱导细胞凋亡的发生,细胞凋亡主要分为线粒体途径、死亡受体途径,其中Caspase-9参与线粒体凋亡途径,受到线粒体内相关信号刺激以后,可以活化形成Cleaved Caspase-9,从而激活Caspase级联反应,诱导凋亡发生[20]。
Wnt/β-catenin是经典的Wnt信号通路的分支,在正常情况下,β-catenin可以由多个蛋白酶形成的泛素化蛋白酶体介导而处于降解状态,使得细胞内维持低水平的β-catenin,当细胞受到相关信号刺激以后,导致细胞内的β-catenin降解受阻,β-catenin大量聚集以后转移至细胞核内,影响下游基因的转录,调控细胞的生长[21-22]。Wnt/β-catenin与多种疾病的发生有关,在糖尿病心肌病、缺血再灌注、哮喘、肺炎等疾病中均有重要作用[23-24]。研究显示,Wnt/β-catenin在肿瘤中过度激活,其下游靶基因c-myc、cyclinD1转录和表达水平升高,是肿瘤细胞过度增殖和凋亡减少的重要原因[25]。YAP与Wnt/β-catenin共同作用影响胚胎的发育,组织器官的形成,在胶质瘤中发现,YAP可以影响胶质瘤细胞中Wnt/β-catenin的激活影响肿瘤细胞的生长[26-27]。本研究表明,YAP下调可以降低Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的激活水平,减少下游靶基因c-myc、cyclinD1的表达,而用Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激活剂处理后,YAP下调对胃癌细胞增殖凋亡的影响减弱,说明YAP可以通过抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的激活再通过线粒体途径调控胃癌细胞的凋亡。
综上,YAP下调后可以诱导胃癌细胞的生长并促进胃癌细胞凋亡,并且其作用机制与抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路有关。YAP是潜在的治疗胃癌的基因靶点,沉默其表达后可以发挥抗肿瘤的作用,这为以后靶向YAP治疗胃癌提供了有力依据。本实验只在一株胃癌细胞系中进行了初步探讨,以后会在多株胃癌细胞和动物实验中进行验证,为明确YAP在胃癌中的作用提供可靠依据。
-
表 1 两组CTL上清液中IL-2和IFN-γ分泌量比较
Table 1 Comparison of secretion levels of IL-2 and IFN-γ in supernatant between the two groups

-
[1] 侯渊涛, 刘璐, 王常林.神经母细胞瘤的免疫学治疗进展[J].临床小儿外科杂志, 2011, 10(4): 290-3. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lcxewkzz201104020 Hou YT, Liu L, Wang CL. Advances in immunotherapy of neuroblastoma[J]. Lin Chuang Xiao Er Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2011, 10(4): 290-3. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lcxewkzz201104020
[2] Seeger RC. Immunology and immunotherapy of neuroblastoma[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2011, 21(4): 229-37. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2011.09.012
[3] Pistoia V, Morandi F, Bianchi G, et al. Immunosuppressive microenvironment in neuroblastoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2013, 3: 167. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_1dc1030e2ffd9722fda191e0f1a982b4
[4] Long AH, Highfill SL, Cui Y, et al. Reduction of MDSCs with All-trans Retinoic Acid Improves CAR Therapy Efficacy for Sarcomas[J]. Cancer Immunol Res, 2016, 4(10): 869-80. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0230
[5] Komohara Y, Takeya M. CAFs and TAMs: maestros of the tumourmicroenvironment[J]. J Pathol, 2017, 241(3): 313-5. doi: 10.1002/path.4824
[6] Jales A, Falahati R, Mari E, et al. Ganglioside-exposed dendritic cells inhibit T-cell effector function by promoting regulatory cell activity[J]. Immunology, 2011, 132(1): 134-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03348.x
[7] Xu W, Cai J, Li S, et al. Improving the in vivo persistence, distribution and function of cytotoxic T lymphocytes by inhibiting the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment[J]. Scand J Immunol, 2013, 78(1): 50-60. doi: 10.1111/sji.2013.78.issue-1
[8] Cheung NK, Dyer MA. Neuroblastoma: developmental biology, cancer genomics and immunotherapy[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2013, 13(6): 397-411. doi: 10.1038/nrc3526
[9] Gabrilovich DI. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells[J]. Cancer Immunol Res, 2017, 5(1): 3-8. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0297
[10] Chen J, Ye Y, Liu P, et al. Suppression of T cells by myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer[J]. Hum Immunol, 2017, 78(2): 113-9. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2016.12.001
[11] Jordan KR, Kapoor P, Spongberg E, et al. Immunosupp-ressive myeloid-derived suppressor cells are increased in splenocytes from cancer patients[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2017, 66(4): 503-13. doi: 10.1007/s00262-016-1953-z
[12] Hassin D, Garber OG, Meiraz A, et al. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte perforin and Fas ligand working in concert even when Fas ligand lytic action is still not detectable[J]. Immunology, 2011, 133(2): 190-6. doi: 10.1111/imm.2011.133.issue-2
[13] Martínez-Lostao L, Anel A, Pardo J. How Do Cytotoxic Lymphocytes Kill Cancer Cells?[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2015, 21(22): 5047-56. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0685
[14] Voskoboinik I, Whisstock JC, Trapani JA. Perforin and granzymes: function, dysfunction and human pathology[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2015, 15(6): 388-400. doi: 10.1038/nri3839
[15] Kumar R, Avagyan S, Snoeck HW. A quantitative trait locus on chr.4 regulates thymic involution[J]. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2010, 65(6): 620-5. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_2904592
[16] Lustig A, Carter A, Bertak D, et al. Transcriptome analysis of murine thymocytes reveals age-associated changes in thymic gene expression[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2009, 6(1): 51-64. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_2640475




 下载:
下载: