Correlation Between Stromal Microenvironment and TLR3 Expression, Prognosis Respectively in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
摘要:目的
分析肝细胞肝癌(hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC)间质微环境与Toll样受体3(Toll-like receptor 3, TLR3)表达的相关性及其对预后的影响。
方法利用已有专利技术制备人体HCC组织芯片,通过免疫组织化学检测HCC间质中各项指标及HCC细胞中TLR3表达,各因素相关分析和Kaplan-meier生存分析上述指标与TLR3的关系,及其与HCC预后的关系。
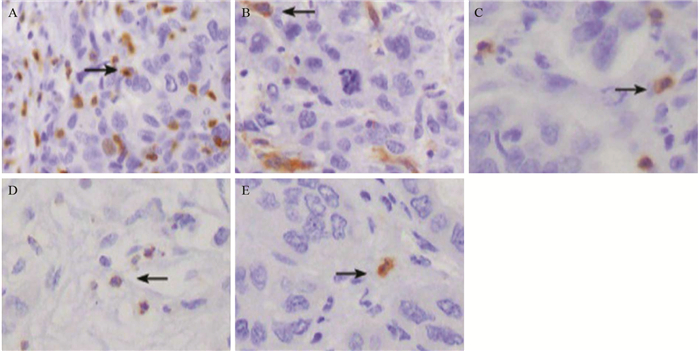
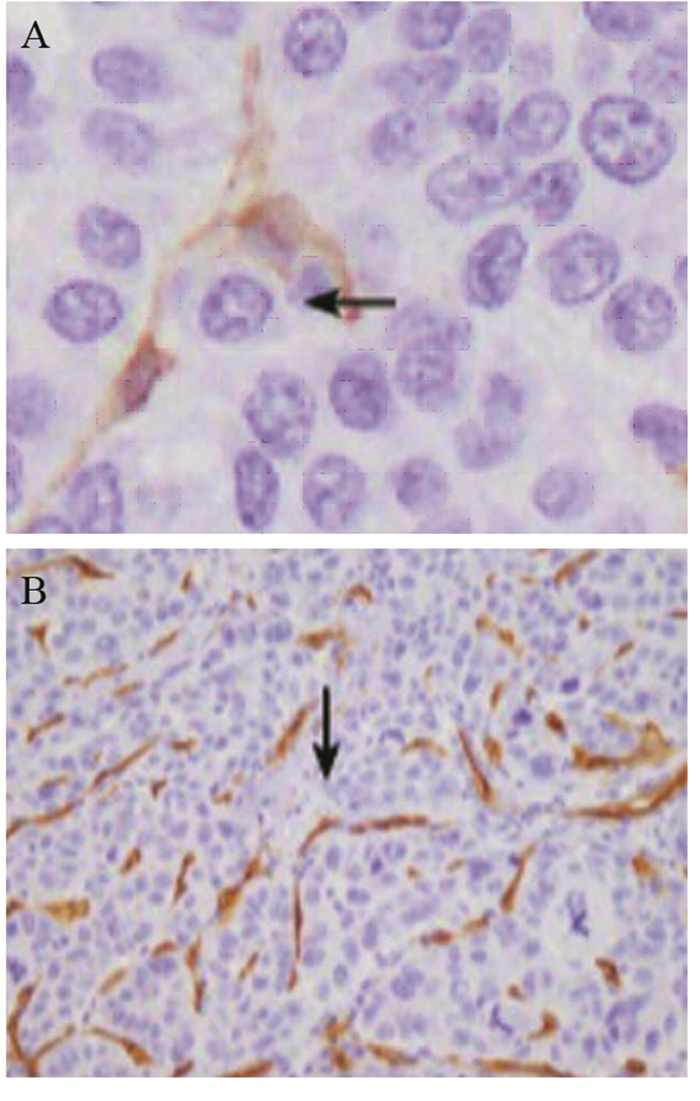
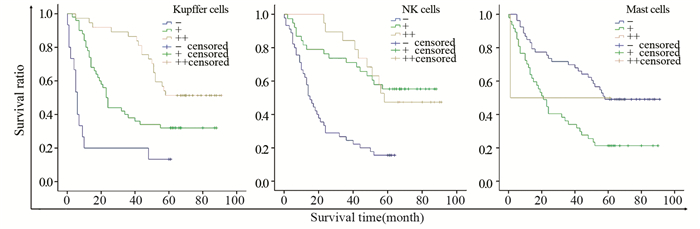
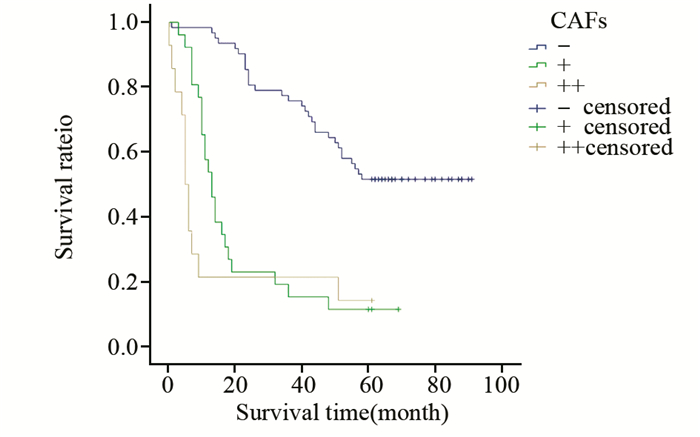
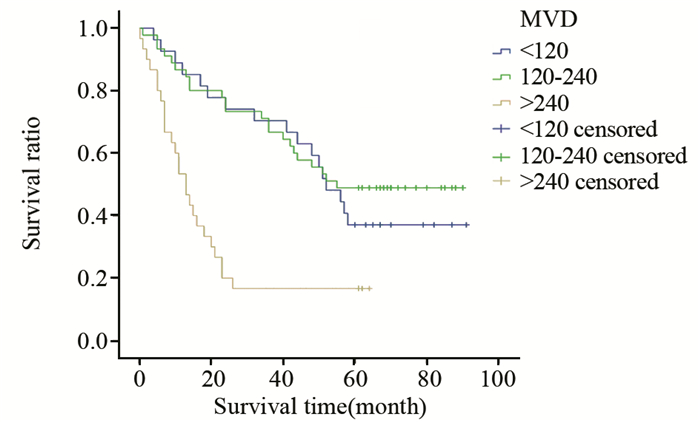
结果HCC间质微环境中浸润的T细胞(P=0.002)、Kupffer细胞(P=0.049)、自然杀伤(natural killer, NK)细胞(P=0.000)和树突状细胞(dendritic cells, DCs)(P=0.027)与TLR3表达呈正相关,而肥大细胞(P=0.000)、癌相关肌纤维母细胞(carcinoma-associated fibroblasts, CAFs)(P=0.000)和微血管密度(microvessel density, MVD)(P=0.000)与TLR3表达呈负相关;Kupffer细胞(P=0.013)和NK细胞(P=0.001)与预后呈正相关,而肥大细胞(P=0.008)、CAFs(P=0.000)和MVD(P=0.089)与预后呈负相关。
结论间质微环境在HCC的演进过程中起着重要作用。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo analyse the correlation between the stromal microenvironment and the Toll-like receptor 3(TLR3) expression, the prognosis respectively in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
MethodsThe tissue microarrays of human HCC were prepared with self-owned patent technology. The expression of various indexes in HCC stroma and TLR3 in HCC cells were examined with immunohistochemistry. The correlation between the indexes with TLR3 and theirs relationship with the prognosis of HCC were analyzed by multi-factor correlation analysis as well as survival analysis of Kaplan-Meier.
ResultsT cells, Kupffer cells, natural killer (NK) cells and dendritic cells (DCs) had positive correlation with the TLR3 expression in HCC. Mast cells, carcinoma-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and microvessel density (MVD) had negative correlation with the TLR3 expression in HCC. Kupffer cells and NK cells were positively related with the prognosis of HCC. Mast cells, CAFs and MVD were negatively related with the prognosis of HCC.
ConclusionThe stromal microenvironment of HCC plays an important role in HCC evolution.
-
Key words:
- Hepatocellular carcinoma /
- Microenvironment /
- Toll-like receptor 3(TLR3) /
- Correlation
-
-
表 1 HCC组织中癌间质免疫活性细胞反应与TLR3表达的相关性
Table 1 Correlation between stromal immunocompetent cell reaction and TLR3 expression in HCC

表 2 HCC组织中癌间质CAFs反应及微血管密度与TLR3表达的相关性
Table 2 Correlation between stromal CAFs, MVD and TLR3 expression in HCC

表 3 HCC间质免疫活性细胞反应与预后的相关性
Table 3 Correlation between stromal immunocom petent cell reaction and prognosis in HCC

表 4 HCC间质CAFs反应及MVD与预后的相关性
Table 4 Correlation between stromal CAFs reaction, MVD and prognosis in HCC

-
[1] Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012[J]. Int J Cancer, 2015, 136(5): E359-86. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29210
[2] Leonardi GC, Candido S, Cervello M, et al. The tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma (review)[J]. Int J Oncol, 2012, 40(6): 1733-47. https://www.spandidos-publications.com/ijo/40/6/1733
[3] Li K, Chen Z, Kato N, et al. Distinct poly (I-C) and virus-activated signaling pathways leading to interferon-beta production in hepatocytes[J]. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280(17): 16739-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M414139200
[4] Salaun B, Coste I, Rissoan MC, et al. TLR3 can directly trigger apoptosis in human cancer cells[J]. J Immunol, 2006, 176(8): 4894-901. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.8.4894
[5] 鄂群, 陈莉, 金国华. 石蜡组织芯片制备方法: 中国, CN101319971B[P]. 2010-12-01. E Q, Chen L, Jin GH. A method for preparing paraffin tissue chip: China, CN101319971B[P]. 2010-12-01.
[6] 王秀玲, 益莉娜, 徐杭佩, 等. Hercept test试剂在乳腺癌中的表达及判断标准[J].临床与实验病理学杂志, 2004, 20(2): 251-2. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LSBL200402039.htm Wang XL, Yi LN, Xu HP, et al. Expression and judgment standard of Hercept test regent in breast cancer[J]. Lin Chuang Yu Shi Yan Bing Li Xue Za Zhi, 2004, 20(2): 251-2. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LSBL200402039.htm
[7] Weidner N. Intratumor microvessel density as a prognostic factor in cancer[J]. Am J Pathol, 1995, 147(1): 9-l9. http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC1869874
[8] Lee SO, Brown RA, Razonable RR, et al. Association between a functional polymorphism in Toll-like receptor 3 and chronic hepatitis C in liver transplant recipients[J]. Transpl Infect Dis, 2013, 15(2): 111-9. doi: 10.1111/tid.2013.15.issue-2
[9] CHEN L, Xu YY, Zhou JM, et al. TLR3 dsRNA agonist inhibits growth and invasion of HepG2.2.15 HCC cells[J]. Oncol Rep, 2012, 28(1): 200-6. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224888347_TLR3_dsRNA_agonist_inhibits_growth_and_invasion_of_HepG2215_HCC_cells
[10] Falco A, Miest JJ, Pionnier N, et al. β-Glucan-supplemented diets increase poly (I:C)-induced gene expression of Mx, possibly via Tlr3-mediated recognition mechanism in common carp (Cyprinus carpio)[J]. Fish Shellfish Immunol, 2014, 36(2): 494-502. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2013.12.005
[11] Yuan MM, Xu YY, Chen L, et al. TLR3 expression correlates with apoptosis, proliferation and angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma and predicts prognosis[J]. BMC Cancer, 2015, 15(1): 245. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1262-5
[12] Faraji Farhoud, Pang Yanli, Walker Renard C, et al. Cadm1 Is a Metastasis Susceptibility Gene That Suppresses Metastasis by Modifying Tumor Interaction with the Cell-Mediated Immunity[J]. PLoS Genet, 2012, 8(9): e1002926. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002926
[13] Bidwell BN, Slaney CY, Withana NP, et al. Silencing of Irf7 pathways in breast cancer cells promotes bone metastasis through immune escape[J]. Nat Med, 2012, 18(8): 1224-31. doi: 10.1038/nm.2830
[14] Waidmann O, Koberle V, Bettinger D, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of cell death and macrophage activation markers in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2013, 59(4): 769-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.06.008
[15] Capece D, Fischietti M, Verzella D, et al. The inflammatory microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma: a pivotal role for tumor-associated macrophages[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2013, 2013: 187204. http://www.pubfacts.com/detail/23533994/The-inflammatory-microenvironment-in-hepatocellular-carcinoma-a-pivotal-role-for-tumor-associated-ma
[16] Zhuang PY, Shen J, Zhu XD, et al. Direct transformation of lung microenvironment by interferon-alpha treatment counteracts growth of lung metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(3): e58913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058913
[17] Pulko V, Liu X, Krco CJ, et al. TLR3-stimulated dendritic cells up-regulate B7-H1 expression and influence the magnitude of CD8 T cell responses to tumorvaccination[J]. J Immunol, 2009, 183(6): 3634-41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900974
[18] Conti P, Castellani ML, Kempuraj D, et al. Role of mast cells in tumor growth[J]. Ann Clin Lab Sci, 2007, 37(4): 315-21. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18000287
[19] Ö stman A. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: recent developments and emerging challenges[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2014, 25: 1-2. https://www.deepdyve.com/lp/elsevier/cancer-associated-fibroblasts-recent-developments-and-emerging-epIQShLKE7 [20] Augsten M. Cancer-associated fibroblasts as another polarized cell type of the tumor microenvironment[J]. Front Oncol, 2014, 4: 62. http://www.oalib.com/paper/3121066
[21] Chu TY, Yang JT, Huang TH, et al. Crosstalk with cancer-associated fibroblasts increases the growth and radiation survival of cervical cancer cells[J]. Radiat Res, 2014, 181(5): 540-7. doi: 10.1667/RR13583.1
[22] 程树群, 李楠, 吴孟超.门静脉癌栓分型与治疗选择[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2012, 19(3): 240-2. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYX200401001.htm Cheng SQ, Li N, Wu MC. Treatment Choice on Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Different Types of Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus[J]. Zhongguo Pu Wai Ji Chu Yu Lin Chuang Za Zhi, 2012, 19(3): 240-2. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYX200401001.htm
[23] Guo ZY, Chen L, Zhu YY, et al. Double-stranded RNA-induced TLR3 activation inhibits angiogenesis and triggers apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Oncol Rep, 2012, 27(2): 396-402. https://www.spandidos-publications.com/or/27/2/396/abstract




 下载:
下载: