Immunological Competence of Dendritic Cell Vaccine Loaded with CD133+ Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell RNA
-
摘要:目的
探讨负载人肝细胞性肝癌(HCC)组织来源的CD133+肝癌细胞RNA树突状细胞(CD133+HCC RNA-DC)疫苗的免疫活性。
方法采用酶消化法从人HCC组织中分离出肝癌细胞,利用流式细胞术分选出CD133+肝癌细胞,制备负载CD133+肝癌细胞RNA树突状细胞疫苗,最后用流式细胞术检测DC的表型,ELISA法测定DC分泌IL-12水平,采用混合淋巴细胞反应法检测DC在体外刺激自体淋巴细胞增殖的能力。
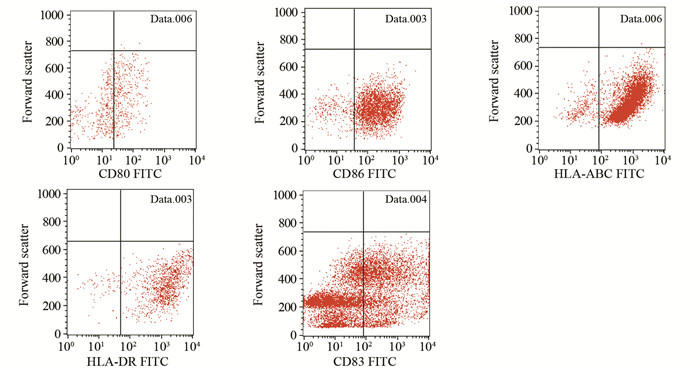
结果CD133+肝癌细胞RNA树突状细胞的HLA-ABC、HLA-DR、CD86、CD80、CD83表达水平分别是(96.52±2.02)%、(92.17±3.04)%、(94.25±3.28)%、(55.14±1.67)%、(40.53±2.31)%,与肝癌细胞RNA树突状细胞和成熟DC比较,差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。CD133+肝癌细胞RNA-DC、肝癌细胞RNA-DC、成熟DC和未成熟DC分泌IL-12的量分别为(421.50±3.12)、(418.20±1.10)、(324.20±2.19)和(102.47±4.60)pg/ml,前两者之间差异无统计学意义(P=0.14),前两者均高于后两者,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。CD133+肝癌细胞RNA-DC与肝癌细胞RNA-DC刺激自体T淋巴细胞增殖能力分别均强于成熟DC和无DC刺激的自体T淋巴细胞,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
结论CD133+肝癌细胞RNA树突状细胞疫苗具有成熟表型,能够在体外有效刺激自体T淋巴细胞增殖。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the immunological competence of dendritic cell loaded with CD133+ hepatocellular carcinoma cell RNA (CD133+ HCC RNA-DC) vaccine.
MethodsHCC cells were separated from hepatocellular carcinoma tissues through Enzyme Digestion, and then CD133+ HCC cells were sorted by flow cytometry. CD133+ HCC RNA-DC vaccine was obtained. Flow cytometry was used to detect the phenotype of DC, and ELISA was applied to determine the level of DC's secretion of IL-12. Mixed lymphocyte reaction was applied to test the ability of DC to stimulate the proliferation of autologous T lymphocytes in vitro.
ResultsThe expression levels of HLA-ABC, HLA-DR, CD86, CD80 and CD83 in CD133+ HCC RNA-DC group were (96.52±2.02)%, (92.17±3.04)%, (94.25±3.28)%, (55.14±1.67)% and (40.53±2.31)%, respectively. Phenotypes expression levels were not significantly different among CD133+ HCC RNA-DC, HCC-DC and mature DC. The secretion of IL-12 in CD133+ HCC RNA-DC group, HCC-DC group, mature DC group and immature DC group were (421.50±3.12), (418.20±1.10), (324.20±2.19) and (102.47±4.60) pg/ml, respectively; the difference of the former two had no statistical significance (P=0.14), and the amounts of the former two were higher than that of the latter two (P < 0.05). The proliferation of autologous T lymphocytes stimulated by CD133+ HCC RNA-DC and HCC-DC were stronger than those by mature DC and no DC (P < 0.05).
ConclusionThe dendritic cell vaccine loaded with CD133+ hepatocellular carcinoma cell RNA (CD133+ HCC RNA-DC) has mature phenotype and can effectively stimulate the proliferation of autologous T lymphocytes in vitro.
-
Key words:
- CD133 /
- Hepatocellular carcinoma /
- RNA /
- Dendritic cell vaccine
-
-
表 1 不同DC的抗原递呈相关分子表达情况 (x±s, %)
Table 1 Phenotypes expression of CD133+ HCC RNA-DCs, HCC-DCs and mature DCs (x±s, %)

-
[1] Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. Ca Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(2): 115-32. doi: 10.3322/caac.21338
[2] Dillman RO, Mcclay EF, Barth NM, et al. Dendritic Versus Tumor Cell Presentation of Autologous Tumor Antigens for Active Specific Immunotherapy in Metastatic Melanoma: Impact on Long-term Survival by Extent of Disease at the Time of Treatment[J]. Cancer Biother Radiopharm, 2015, 30(5): 187-94. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2015.1843
[3] Anguille S, Smits EL, Lion E, et al. Clinical use of dendritic cells for cancer therapy[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2014, 15(7): e257-67. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70585-0
[4] 肖宗宇, 陈晓娟, 杨艺, 等.肿瘤干细胞样细胞RNA致敏树突状细胞治疗大鼠9L脑肿瘤[J].北京大学学报 (医学版), 2015, 47(4): 661-6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BYDB201504025.htm Xiao ZY, Chen XJ, Yang Y, et al. Experimental study of dendritic cells transfected with cancer stem like cells RNA against 9L brain tumors[J]. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao (Yi Xue Ban), 2015, 47(4): 661-6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BYDB201504025.htm
[5] Chan AW, Tong JH, Chan SL, et al. Expression of stemness markers (CD133 and EpCAM) in prognostication of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Histopathology, 2014, 64(7): 935-50. doi: 10.1111/his.2014.64.issue-7
[6] 林家耀, 张志明, 刘剑勇, 等.肝细胞性肝癌组织CD133+细胞肿瘤干细胞特性的研究[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2016, 23(4): 223-7, 232. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QLZL201604006.htm Lin JY, Zhang ZM, Liu JY, et al. Identification and characterization of cancer stem cells from CD133+ cells separated from hepatocellular carcinoma tissue[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Za Zhi, 2016, 23(4): 223-7, 232. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QLZL201604006.htm
[7] Ma Y, Shurin GV, Peiyuan Z, et al. Dendritic Cells in the Cancer Microenvironment[J]. J Cancer, 2013, 4(1): 36-44. doi: 10.7150/jca.5046
[8] Zou W. Immunosuppressive networks in the tumour environment and their therapeutic relevance[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2005, 5(4): 263-74. doi: 10.1038/nrc1586
[9] Tada F, Abe M, Hirooka M, et al. PhaseⅠ/Ⅱ study of immunotherapy using tumor antigen-pulsed dendritic cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Oncol, 2012, 41(5): 1601-9. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/230841343_Phase_III_study_of_immunotherapy_using_tumor_antigen-pulsed_dendritic_cells_in_patients_with_hepatocellular_carcinoma
[10] Sun TY, Yan W, Yang CM, et al. Clinical research on dendritic cell vaccines to prevent postoperative recurrence and metastasis of liver cancer[J]. Genet Mol Res, 2015, 14(4): 16222-32. doi: 10.4238/2015.December.8.12
[11] 冯钟煦, 刘剑勇, 赵荫农, 等. H22细胞全细胞抗原负载的树突状细胞激活肿瘤浸润性淋巴细胞抗小鼠肝癌的实验[J].肿瘤防治研究, 2012, 39(10): 1179-82. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2012.10.005 Feng ZX, Liu JY, Zhao YN, et al. Anti-mouse Hepatoma Effect of Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocyte Stimulated by DCs Pulsed with H22 Full-cell Antigen[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2012, 39(10): 1179-82. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2012.10.005
[12] 谭德敏, 向阳, 谭千林.狼疮性肾炎患者外周血树突状细胞功能的研究[J].中国免疫学杂志, 2016, 32(4): 570-2. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZMXZ201604029.htm Tan DM, Xiang Y, Tan QL. Study on immune function of blood dendritic cells in patients with lupus nephritis[J]. Zhongguo Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2016, 32(4): 570-2. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZMXZ201604029.htm
[13] 江龙委, 蔡凯, 黄伟谦, 等. rhG-CSF与rhGM-CSF动员人外周血单核细胞后DC疫苗数量及功能变化的比较[J].肿瘤防治研究, 2015, 42(11): 1095-9. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2015.11.008 Jiang LW, Cai K, Huang WQ, et al. Comparison of rhG-CSF and rhGM-CSF Mobilization on Quantity and Function Change of Dendritic Cell-based Tumor Vaccine via Human Peripheral Blood Monocytes[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2015, 42(11): 1095-9. doi: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2015.11.008
[14] Kyte JA, Mu L, Aamdal S, et al. PhaseⅠ/Ⅱ trial of melanoma therapy with dendritic cells transfected with autologous tumor-mRNA[J]. Cancer gene ther, 2006, 13(10): 905-18. doi: 10.1038/sj.cgt.7700961
[15] Gao D, Li C, Xie X, et al. Autologous tumor lysate-pulsed dendritic cell immunotherapy with cytokine-induced killer cells improves survival in gastric and colorectal cancer patients[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(4): e93886. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093886
[16] Xi HB, Wang GX, Fu B, et al. Survivin and PSMA Loaded Dendritic Cell Vaccine for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer[J]. Biol Pharm Bull, 2015, 38(6): 827-35. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b14-00518
[17] Sun JC, Pan K, Chen MS, et al. Dendritic cells-mediated CTLs targeting hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2010, 10(4): 368-75. doi: 10.4161/cbt.10.4.12440



 下载:
下载: