Experiment of Different Administration Sequences of Apatinib and Paclitaxel on Lung Cancer
-
摘要:目的
观察阿帕替尼联合紫杉醇不同时序给药对肺癌的抗肿瘤效应。
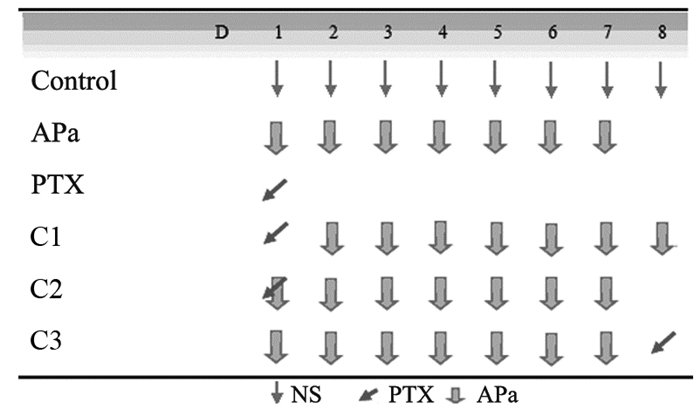
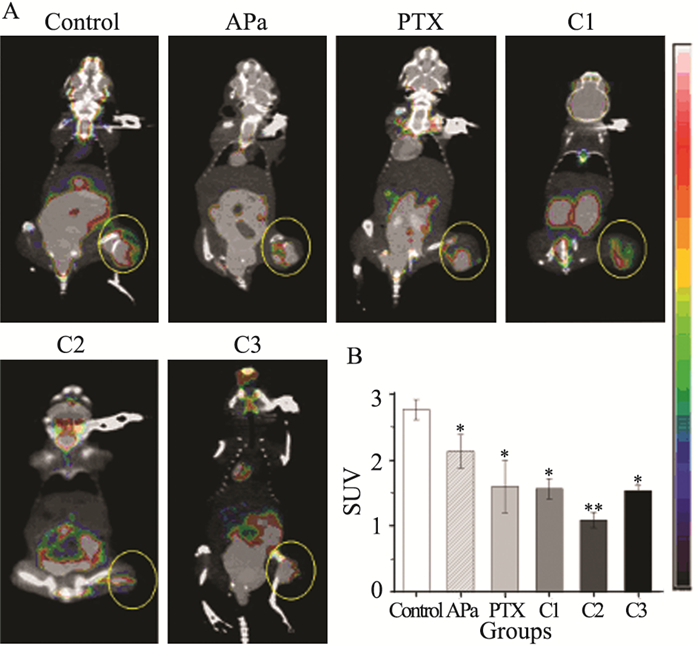
方法建立裸鼠A549肺癌模型,随机分成6组。A:0.9%氯化钠溶液组(0.9%NS, d1~8)。B:单用阿帕替尼组(APa, d1~7)。C:单用紫杉醇组(PTX, d1)。D:联合用药组1(C1组:PTX, d1;APa, d2~8)。E:联合用药组2(同时用药组,C2组:PTX, d1;APa, d1~7)。F:联合用药组3(C3组:APa,D1~7;PTX, d8),治疗结束次日行PET/CT扫描测肿瘤组织SUV值、ELISA检测血中VEGFR-2浓度、免疫组织化学检测肿瘤组织微血管计数、TUNEL法检测肿瘤组织细胞凋亡,绘制肿瘤生长曲线,计算肿瘤抑制率。
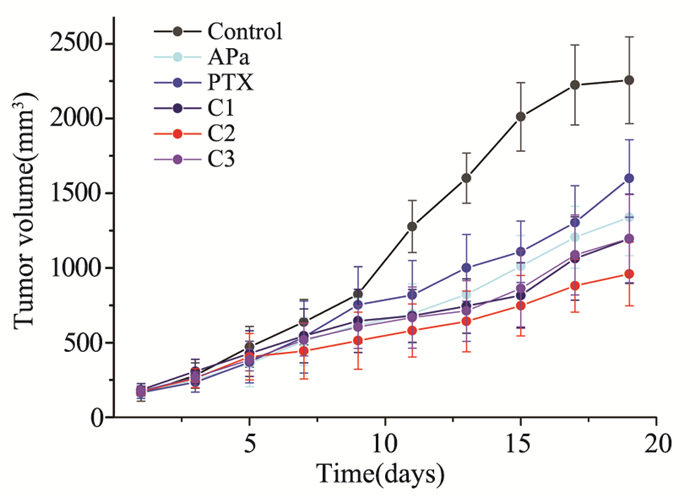
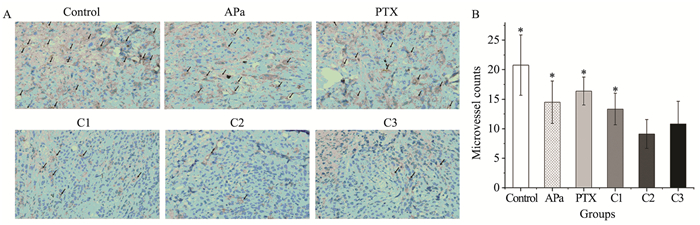
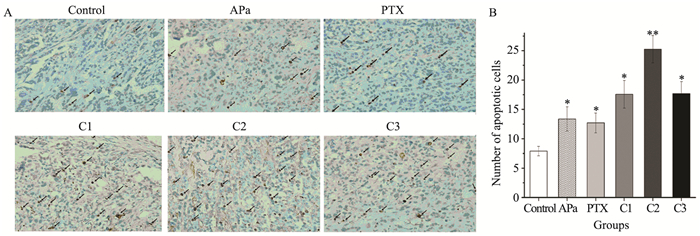
结果治疗组移植瘤生长速率较0.9%氯化钠溶液组均有所减慢(P < 0.05),联合用药组间抑瘤率差异无统计学意义,联合用药组2凋亡细胞数最多,VEGFR-2浓度、SUV值最低(P < 0.05),联合用药组2 MVD-CD31表达最低,与除联合用药组3外的其余各组比较,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
结论阿帕替尼联合紫杉醇同时用药对肺癌治疗效果最好。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo observe the anti-tumor effect of apatinib(APa) combined with paclitaxel(PTX) at different sequential dosing on lung cancer.
MethodsA549 lung cancer nude mice model was established and randomly divided into six groups: A: Control group (0.9% NS, D1-8); B: Apatinib alone group (APa, D1-7); C: Paclitaxel alone group (PTX, D1); D: Combined group 1 (PTX, D1; APa, D2-8); E: Combined group 2 (PTX, D1; APa, D1-7); F: Combinaed group 3 (APa, D1-7; PTX, D8). The day after the end of treatment, we used ELISA to detect the VEGFR2 concentration of blood, immunohistochemistry was used to measure the microvessel number, TUNEL assay was employed to detect the apoptosis cells of tumor, and PET/CT was used to probe SUV value. We observed and drew the tumor growth curve, and then calculated the tumor inhibition rate.
ResultsThe tumor growth rate of treatment groups were all significantly slowed, compared with the physiological saline group (P < 0.05), and the tumor inhibition rate of all combined groups had no statistically significance compared with each other, respectively. The Combined group 2 showed most apoptotic cells, lowest VEGFR-2 levels and SUV value (P < 0.05), while the lowest MVD-CD31 expression in Combined group 2 had statistically significance compared with the physiological saline group, except the Combined group 3 (P < 0.05).
ConclusionApatinib combined with paclitaxel shows the best effect on treating lung cancer.
-
Key words:
- Apatinib /
- Paclitaxel /
- Sequential dosing /
- Anti-angiogenesis therapy /
- Lung cancer
-
0 引言
化疗所致的恶心呕吐(chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, CINV)是肿瘤治疗过程中最常见的不良反应之一,如不进行预防干预,约有70%~80%的患者会出现恶心呕吐,影响患者的依存性和降低其生活质量[1-2]。严重的恶心呕吐不仅导致营养缺乏、脱水和电解质失衡,还会使患者被迫中止有效的治疗[3]。积极有效控制顺铂诱导的恶心呕吐可以提高患者的生活质量,对生存期有着莫大的影响。联合NK-1受体抑制剂三联止吐方案与传统两联方案比较的052、054随机对照临床研究奠定了阿瑞匹坦联合5-羟色胺-3受体抑制剂(5-HT3)和皮质类固醇的三联方案成为指南中预防中重度催吐药物诱导恶心呕吐的Ⅰ类推荐方案[4-5]。阿瑞匹坦在中国人群中第一个Ⅲ期随机对照临床研究2014年发表[6],但临床研究中顺铂等高催吐性药物都是一次给入[4],我们对三联方案与传统两联方案在预防高催吐类药物分次给药诱导恶心呕吐的疗效进行前瞻性对照研究,现对中期结果报告如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料
2014年6月至2015年12月收集内蒙古自治区鄂尔多斯市中心医院、包头市中心医院和达拉特旗人民医院肿瘤内科经病理确诊的恶性肿瘤患者。将102例接受顺铂或蒽环类分次给药的根据接受的止吐方案分为两组。其中53例接受阿瑞匹坦联合5-羟色胺-3受体抑制剂和托烷司琼三联止吐方案,49例接受5-羟色胺-3受体抑制剂和托烷司琼两联止吐方案。两组的人群基线特征具有可比性,见表 1。
表 1 患者基线特征 (n(%))Table 1 Patients' baseline characteristics (n(%))
1.2 纳入和排除标准
纳入标准:(1)年龄≥18岁;(2)KPS≥70分;(3)入组前3周内未接受过全身化疗;(4)中重度催吐性化疗方案中顺铂或蒽环类药物采用多日给药方式;(5)接受高剂量顺铂患者1周内未接受过腹盆腔放射治疗;(6)顺铂40 mg/m2联合同期放疗的患者;(7)血液检验必须满足白细胞 > 3.5×109/L,中性粒细胞 > 1.5×109/L,血小板 > 85×109/L,碱性磷酸酶 < 正常值上限2.5倍,谷丙转氨酶 < 正常值上限2.5倍,胆红素 < 正常值上限1.5倍,肌酐 < 正常值上限1.5倍。排除标准:(1)中枢神经系统肿瘤或中枢神经系统转移肿瘤;(2)使用违禁药品或酒精中毒的患者;(3)入组前3周内接受过中重度化疗方案,1周内接受过腹盆腔放射治疗;(4)活动性感染或其他不可控制疾病;(5)并发疾病需同时口服地塞米松类药物。
1.3 治疗方法
中高度催吐性化疗方案包括:接受顺铂≥70 mg/m2强度方案的患者,顺铂d1~3给入,接受顺铂40 mg/m2同期放化疗的患者,顺铂一次性给入;接受蒽环类方案的患者,蒽环类d1、2给入。两联组止吐方案为:5-羟色胺-3受体抑制剂(5-HT3)托烷司琼10 mg/d,顺铂或蒽环类药物当日给,地塞米松10.5 mg d1,7.5 mg d2、3;三联组止吐方案为:阿瑞匹坦125 mg d1,80 mg d2、3,5-羟色胺-3受体抑制剂(5-HT3)托烷司琼10 mg/d,顺铂或蒽环类药物当日给,前期研究[7]证实阿瑞匹坦会干扰地塞米松药代动力学,升高地塞米松血药浓度,故将地塞米松调整为6 mg d1,3.75 mg d2、3。
1.4 评价目标
化疗开始后0~120 h每日早晨按时查房以保证患者的依存性,主要评价指标为总时期(overall phase, OP)(急性期+延迟期)(0~120 h)完全缓解率(CR),完全缓解定义为化疗后没有呕吐或需解救措施的严重干呕;次要指标为化疗后急性期(acute phase, AP)(0~24 h)和延迟期(delay phase, DP)(25~120 h)的完全缓解率(CR);阿瑞匹坦治疗组和对照组间第一呕吐发生时间比较采用Kaplan-Meier曲线,采用FLIE量表评估恶心呕吐对生活质量的影响[8]。
恶心呕吐生活量表(functional living index-emesis, FLIE)评估在化疗开始后第6天进行,填表前医务人员要进行FLIE规范化使用培训,一定要强调患者对恶心呕吐自己的主观感觉,医务人员及患者家属不可以影响患者自己的判断,并对量表质量进行审核,不符合相关要求的量表不纳入评估[9-10]。所有患者在治疗后均接受相关化疗后定期检测随访,并进入下一周期治疗。同时进行不良反应评估。
1.5 统计学方法
使用SPSS13.0统计软件进行数据分析,数据近似符合正态分布时,以均数±标准差(x±s)表示,计量资料比较采用两独立样本t检验,配对样本多参数比较用Hotelling’s Trace检验;计数资料采用卡方检验,呕吐发生时间比较采用Kaplan-Meier法,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 研究完成情况
102例患者都完成了主要研究指标的随访,4例患者FLIE不符合要求,98份生活质量量表纳入分析。传统组中1例女性患者单身,未纳入怀孕期间恶心呕吐分析。
2.2 治疗效果
2.2.1 各终点指标比较
阿瑞匹坦三联方案组化疗给药后OP、AP和DP期间的CR率分别为83.0%、94.3%和84.9%,传统治疗组OP、AP和DP期间的CR率分别为53.1%、75.5%和49.0%,三个时期疗效比较,两组差异均有统计学意义(P=0.001、P=0.011、P=0.019),见图 1。进一步分析不同性别采用阿瑞匹坦三联方案治疗获益情况,其中女性患者从阿瑞匹坦治疗中的获益率(50.0%)明显大于男性患者(7.3%)(P=0.000)。
2.2.2 FLIE指数比较
OP期间,阿瑞匹坦三联方案组的无呕吐发生率为75.5%(40/53)高于对照组无呕吐发生率46.9%(23/49)(P=0.004)。阿瑞匹坦三联方案组补救治疗率[7.5%(4/53)]较对照组[10.2% (5/49)]低(P=0.636)。采用FLIE量表评价恶心呕吐对生活质量的影响,大于108分对生活质量无影响,阿瑞匹坦三联方案组和传统组FLIE量表中大于108分的分别为48.0%(24/50)和20.8%(10/48),两组比较差异有统计学意义(P=0.006),见表 2。
表 2 FLIE指数比较Table 2 Comparison of FLIE Index
2.2.3 呕吐时间比较
从治疗开始,阿瑞匹坦三联方案组第一次呕吐发生时间较传统组延迟(P=0.044),见图 2。
2.2.4 耐受性比较
阿瑞匹坦三联方案组上腹胀痛(upper abdominal pain)的发生率为20.8%(11/53),传统组上腹胀痛发生率为8.2%(4/49),两组比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.095);阿瑞匹坦三联方案组便秘(constipation)的发生率为15.1%(8/53),与传统组的14.3%(7/49)相比,差异无统计学意义(P=1.000)。
3 讨论
本研究采用的主要研究终点和次要研究终点指标与国际大型临床研究相同。在托烷司琼,昂丹司琼、道拉司琼总体疗效相当情况下[11],结合医院药物准入情况我们选择托烷司琼5 mg联合阿瑞匹坦、地塞米松作为三联止吐方案。已有前期研究证实阿瑞匹坦会干扰地塞米松药代动力学,升高地塞米松血药浓度,故将地塞米松剂量调整为6 mg第1天,3.75 mg第2~4天[7]。
阿瑞匹坦三联方案与传统两联方案在内蒙古地区预防高催吐类化疗药物分次给药诱导恶心呕吐疗效比较,与国际两项Ⅲ期随机对照临床研究结论相似,无论在总的时相、急性期、延迟期三联方案CR率较传统两联方案均明显改善(P < 0.05)。研究主要终点指标与张力教授在中国注册临床研究在OP和DR期间CR的明显改善的报道一致[6],但中国注册临床研究中AP期间没有体现出统计学意义上的获益,本研究高催吐化疗药物分次给药后三联方案却体现出在AP期比传统两联方案有明显的获益(94.3% vs. 75.5%),而传统组53.1%的CR明显低于中国人群或日本人群中急性期对照组79.3%和83.3%的CR[12]。我们总的获益程度达到30%,明显高于中国人群研究中的水平(10%),也高于054或052国际临床研究总体获益度(20%)的水平。差异来源的主要原因可能是采用了分次给药的模式,总的剂量强度没有改变,但在AP或DP期间不同时间窗剂量强度是不同的,分次给药后延迟性恶心呕吐的时间窗也不同于一次性给药,其机制还需要进一步对高催吐化疗药物分次给药后尿5-羟色胺代谢物变化趋势测定来解释[13]。本研究是前瞻性非随机对照研究,样本例数只有102例,试验设计不同于以上提到的三个大型临床研究,也会影响结果的不同。此外,目前的结论是中期研究报告,包含了顺铂或蒽环类两类药物,由于两类高催吐药物的发生恶心呕吐时间窗并不相同,之间会存在交互影响[14-15]。将来需增加样本量,分药物分病种对中重度催吐药物分次给予的止吐疗效进行比较分析。
与Ⅲ期临床研究用药方式不同,高催吐药物分次给予,5-HT3托烷司琼10 mg在每日分次给予高催吐化疗药物前都预防性用药,研究中获得较高CR率可能与这种使用模式有关,客观上起到了阿瑞匹坦联合长效5-HT3的作用。采用FILE量表评价生活质量影响,大于108分对生活质量无影响,阿瑞匹坦组中有48.0%(24/50)、对照组中有20.8%(10/48)FLIE量表大于108分,两组比较差异有统计学意义(P=0.006),接受了三联止吐方案后生活质量明显改善,这点不同于阿瑞匹坦在中国人群Ⅲ期随机临床研究中FLIE量表生活质量影响的报道(70.5% vs. 68.3%)(P > 0.05)[6]。本研究中FILE量表评分对生活质量影响的结果明显低于国际大型临床研究60%~70%的水平,可能是由于内蒙古地区地广人稀,患者就诊较为分散,研究入组患者不只是接受第一个周期化疗的患者,还包括后续化疗周期的患者,尽管两组接受不同周期化疗间基线具有可比性,但随着化疗周期的延长,患者相应生活质量可能会伴随降低[16]。
采用Kaplan-Meier曲线对阿瑞匹坦治疗组和对照组间第一次呕吐发生时间比较,可以看到从治疗伊始阿瑞匹坦治疗组呕吐发生时间较对照组延迟,体现出三联药物预防分次给予高催吐化疗药物不仅较传统方案降低呕吐发生率,还可以推迟呕吐发生时间。药物相关不良反应上腹胀痛在国际054研究或中国注册研究中发生比率基本未见;便秘的发生率与中国注册研究或054国际研究相近,但高于052研究8%的比率[4-6]。
总之,三联止吐方案在预防中高度催吐性化疗方案分次用药诱导恶心呕吐方面疗效较好,值得临床推广应用。需进一步分别对不同瘤种,不同的诱导恶心呕吐药物,与不同5-HT3联合效果深入研究。
-
表 1 各组肿瘤体积大小及肿瘤体积抑制率
Table 1 Tumor volume and tumor volume inhibition rate of each group

表 2 ELISA法检测各组VEGFR-2水平的比较
Table 2 Statistical table of VEGFR-2 levels in each group detected by ELISA

-
[1] Torre LA, Brav F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2015, 65(2): 87-108. doi: 10.3322/caac.21262
[1] Torre LA, Brav F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 20 12[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2015, 65(2): 87-108. [2] Park do J, Thomas NJ, Yoon C, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor a inhibition in gastric cancer[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2015, 18 (1): 33-42. [2] Park do J, Thomas NJ, Yoon C, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor a inhibition in gastric cancer[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2015, 18(1): 33-42. doi: 10.1007/s10120-014-0397-4
[3] Fan J, Du J, Wu J, et al. Antitumor effects of different administration sequences of cisplatin and Endostar on Lewis lung carcinoma[J]. Oncol Lett, 2015, 9(2): 822-8. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2111397538&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[3] Fan J, Du J, Wu J, et al. Antitumor effects of different administration sequences of cisplatin and Endostar on Lewis lung carcinoma[J]. Oncol Lett, 2015, 9(2): 822-8. [4] Bertolini F. Chemotherapy and the tumor microenvironment: the contribution of circulating endothelial cells[J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2008, 27(1): 95-101. doi: 10.1007/s10555-007-9110-y
[4] Bertolini F. Chemotherapy and the tumor microenvironment: the contribution of circulating endothelial cells[J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2008, 27(1): 95-101. [5] Tian S, Quan H, Xie C, et al. YN968D1 is a novel and selective inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinase with potent activity in vitro and in vivo[J]. Cancer Sci, 2011, 102(7): 1374-80. doi: 10.1111/cas.2011.102.issue-7
[5] Tian S, Quan H, Xie C, et al. YN968D1 is a novel and selective inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinase with potent activity in vitro and in vivo[J]. Cancer Sci, 20 11, 102(7): 1374-80. [6] Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, et al. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis--correlation in invasive breast carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 1991, 324(1): 1-8. [6] Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, et al. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis--correlation in invasive breast carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 1991, 324(1): 1-8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101033240101
[7] 刘文静, 曾宪涛, 刘晓晴, 等.恩度联合化疗治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌疗效和安全性的系统评价[J].中国循证医学杂志, 2011, 11(11): 1268-79. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZXZ201111012.htm Liu WJ, Zeng XT, Liu XQ, et al. Effectiveness of endostar combined with chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review[J]. Zhongguo Xun Zheng Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2011, 11(11): 1268-79. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZXZ201111012.htm
[7] Liu WJ, Zeng XT, Liu XQ, et al. Effectiveness of endostar combined with chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review[J]. Zhongguo Xun Zheng Yi Xue ZaZhi, 2011, 11(11): 1268-79. [刘文静,曾宪涛,刘晓晴,等. 恩 度联合化疗治疗晚期非小细胞肺癌疗效和安全性的系统评价 [J] 中国循证医学杂志, 2011, 11(11): 1268-79.] [8] Zhao X, Mei K, Cai X, et al. A randomized phase Ⅱ study of recombinant human endostatin plus gemcitabine/cisplatin compared with gemcitabine/cisplatin alone as first-line therapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Invest New Drugs, 2012, 30 (3): 1144-9. [8] Zhao X, Mei K, Cai X, et al. A randomized phaseⅡstudy of recombinant human endostatin plus gemcitabine/cisplatin compared with gemcitabine/cisplatin alone as first-line therapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Invest New Drugs, 2012, 30(3): 1144-9. doi: 10.1007/s10637-011-9631-7
[9] Peng XC, Qiu M, Wei M, et al. Different combination schedules of gemcitabine with endostar affect antitumor efficacy[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2012, 69(1): 239-46. [9] Peng XC, Qiu M, Wei M, et al. Different combination schedules of gemcitabine with endostar affect antitumor efficacy[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2012, 69(1): 239-46. doi: 10.1007/s00280-011-1695-8
[10] Zhang D, Hedlund EM, Lim S, et al. Antiangiogenic agents significantly improve survival in tumor-bearing mice by increasing tolerance to chemotherapy-induced toxicity[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2011, 108(10): 4117-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1016220108
[10] Zhang D, Hedlund EM, Lim S, et al. Antiangiogenic agents significantly improve survival in tumor-bearing mice by increasing tolerance to chemotherapy-induced toxicity[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2011, 108(10): 4117-22. [11] Peng F, Xu Z, Wang J, et al. Recombinant human endostatin normalizes tumor vasculature and enhances radiation response in xenografted human nasopharyngeal carcinoma models[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(4): e34646. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034646
[11] Peng F, Xu Z, Wang J, et al. Recombinant human endostatin normalizes tumor vasculature and enhances radiation response in xenografted human nasopharyngeal carcinoma models[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(4): e34646. [12] Li N, Zheng D, Wei X, et al. Effects of recombinant human endostatin and its synergy with cisplatin on circulating endothelial cells and tumor vascular normalization in A549 xenograft murine model[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2012, 138(7): 1131-44. [12] Li N, Zheng D, Wei X, et al. Effects of recombinant human endostatin and its synergy with cisplatin on circulating endothelial cells and tumor vascular normalization in A549 xenograft murine model[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2012, 138(7): 1131-44. doi: 10.1007/s00432-012-1189-z
[13] 边劲, 王琳, 寻琛, 等.培美曲塞和吉非替尼不同时序应用对人肺腺癌细胞的作用和机制[J].肿瘤防治研究, 2014, 41(12): 1266-70. http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/abstract/abstract8161.shtml Bian J, Wang L, Xun C, et al. Sequence-dependent Effects and Mechanism of Pemetrexed and Gefitinib on Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2014, 41(12): 1266-70. http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/abstract/abstract8161.shtml
[13] Bian J, Wang L, Xun C, et al. Sequence-dependent Effects and Mechanism of Pemetrexed and Gefitinib on Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2014, 41 (12): 1266-70. [边劲, 王琳, 寻琛, 等. 培美曲塞和吉非替尼不 同时序应用对人肺腺癌细胞的作用和机制[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 20 14, 41(12): 1266-70.] [14] Roskoski R Jr. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling in tumor progression[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2007, 62 (3): 179-213. [14] Roskoski R Jr. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling in tumor progression[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2007, 62(3): 179-213. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2007.01.006
[15] Z h a n g L . R a n d o m i z e d , d o u b l e - b l i n d , p l a c e b o - c o n t r o l l e d , m u l t i - c e n t e r P h a s e Ⅱ c l i n i c a l s t u d y o f i m a t i n i b m e s y l a t e t r e a t m e n t o n n o n - s q u a m o u s n o n - small cell lung cancer[C]. //The essays of the 5th National conference of clinical oncology and the CSCO academic annual meeting in 2012: 24. [张力. 甲磺酸阿帕替尼治疗晚期非鳞非小 细胞肺癌随机、双盲、安慰剂对照、多中心Ⅱ期临床研究[C]. //第十五届全国临床肿瘤学大会暨2012年CSCO学术年会论文 集, 2012: 24.] [15] 张力.甲磺酸阿帕替尼治疗晚期非鳞非小细胞肺癌随机、双盲、安慰剂对照、多中心Ⅱ期临床研究[C]. //第十五届全国临床肿瘤学大会暨2012年CSCO学术年会论文集, 2012: 24. http://d.g.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference_7981277.aspx Zhang L. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center PhaseⅡclinical study of imatinib mesylate treatment on non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer[C]. //The essays of the 5th National conference of clinical oncology and the CSCO academic annual meeting in 2012: 24. http://d.g.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference_7981277.aspx
[16] Liang S, Tong XZ, Fu LW. Inhibitory effect of apatinib on HL-60 cell proliferation and its mechanism[J]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao, 2011, 31(5): 871-4. [粱树, 童秀珍, 符立悟. 小分子酪 氨酸激酶抑制剂Apatinib对白血病HL-60细胞株抑制增殖作用 及机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2011, 31(5): 871-4.] [16] 粱树, 童秀珍, 符立悟.小分子酪氨酸激酶抑制剂Apatinib对白血病HL-60细胞株抑制增殖作用及机制[J].南方医科大学学报, 2011, 31(5): 871-4. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dyjydxxb201105031 Liang S, Tong XZ, Fu LW. Inhibitory effect of apatinib on HL-60 cell proliferation and its mechanism[J]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao, 2011, 31(5): 871-4. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dyjydxxb201105031
[17] Tong XZ, Wang F, Liang S, et al. Apatinib (YN968D1) enhances the efficacy of conventional chemotherapeutical drugs in side population cells and ABCB1-overexpressing leukemia cells[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2012, 83(5): 586-97. [17] Tong XZ, Wang F, Liang S, et al. Apatinib (YN968D1) enhances the efficacy of conventional chemotherapeutical drugs in side population cells and ABCB1-overexpressing leukemia cells[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2012, 83(5): 586-97. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.12.007
[18] Schiff PB, Fant J, Horwitz SB. Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol[J]. Nature, 1979, 277(5698): 665-7. [18] Schiff PB, Fant J, Horwitz SB. Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol[J]. Nature, 1979, 277(5698): 665-7. doi: 10.1038/277665a0
[19] Yang ZX. The study of anti-liver cancer cell growth effects and its mechanism of VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor apatinib[C]. //The essays of the 5th National conferrence of clinnical oncology and the CSCO academic annual meeting in 2012: 101-2. [杨朝旭. 小分子VEGFR-2酪氨酸激酶抑制剂阿帕替尼对肝癌细胞的抑 制作用及其机制的研究[C]. //第十五届全国临床肿瘤学大会暨 20 12年CSCO学术年会论文集, 2012: 101-2.] [19] 杨朝旭.小分子VEGFR-2酪氨酸激酶抑制剂阿帕替尼对肝癌细胞的抑制作用及其机制的研究[C]. //第十五届全国临床肿瘤学大会暨2012年CSCO学术年会论文集, 2012: 101-2. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7981174 Yang ZX. The study of anti-liver cancer cell growth effects and its mechanism of VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor apatinib[C]. //The essays of the 5th National conferrence of clinnical oncology and the CSCO academic annual meeting in 2012: 101-2. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7981174
[20] Peng XC, Qiu M, Wei M, et al. Different combination schedules of gemcitabine with endostar affect antitumor efficacy[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2012, 69(1): 239-46. [20] Peng XC, Qiu M, Wei M, et al. Different combination schedules of gemcitabine with endostar affect antitumor efficacy[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2012, 69(1): 239-46. doi: 10.1007/s00280-011-1695-8
[21] de Mello RA, Costa BM, Reis RM, et al. Insights into angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: molecular mechanisms, polymorphic genes, and targeted therapies[J]. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov, 2012, 7(1): 118-13. [21] de Mello RA, Costa BM, Reis RM, et al. Insights into angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: molecular mechanisms, polymorphic genes, and targeted therapies[J]. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov, 2012, 7(1): 118-13. doi: 10.2174/157489212798357994
[22] Yoshikawa A, Saura R, Matsubara T, et al. A mechanism of cisplatin action: antineoplastic effect through inhibition of neovascularization[J]. Kobe J Med Sci, 1997, 43(3-4): 109-20. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=122354300&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[22] Yoshikawa A, Saura R, Matsubara T, et al. A mechanism of cisplatin action: antineoplastic effect through inhibition of neovascularization[J]. Kobe J Med Sci, 1997, 43(3-4): 109-20. [23] Miyahara Y, Yoshida S, Motoyama S, et al. Effect of cis-diammine dichloroplatinum on vascular endothelial growth factor expression in uterine cervical carcinoma[J]. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol, 2004, 25(1):33-9. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2414219273&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[23] Miyahara Y, Yoshida S, Motoyama S, et al. Effect of cis-diammine dichloroplatinum on vascular endothelial growth factor expression in uterine cervical carcinoma[J]. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol, 2004, 25 (1):33-9.



 下载:
下载: